Professional Documents
Culture Documents
30 Solution 23-10-2021 Paper
30 Solution 23-10-2021 Paper
Uploaded by
ArchanaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
30 Solution 23-10-2021 Paper
30 Solution 23-10-2021 Paper
Uploaded by
ArchanaCopyright:
Available Formats
The Leader In Chemistry NEET-2021-22 [XIIth Batch]
.....
Test-30 : Solutions
RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * *
Target Marks : 92 Date : 23/10/2021
Time : 30 min Sub. : Chemistry
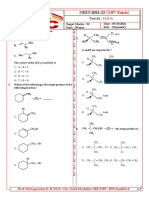
1. Match the column I with column II and mark 6. What will be the degree of dissociation of 0.1
the appropriate choice M Mg(NO3)2 solution if van’t Hoff factor is
2.74?
1) 75% 2) 87%
3) 100% 4) 92%
7. The freezing point depression constant (Kf) of
benzene is 5.12 K kg mol–1. The freezing point
depression for the solution of molality
0.078 m containing a non-electrolyte solute in
benzene is (rounded off upto two decimal places)
1) 0.20 K 2) 0.80 K
3) 0.40 K 4) 0.60 K
1) A-i, B-iii, C-ii, D-iv
8. 200 mL of an aqueous solution of a protein
2) A-iii, B-i, C-iv, D-ii contains its 1.26 g. The osmotic pressure of this
3) A-ii, B-iii, C-iv, D-i soution at 300 K is found to be 2.57 × 10–3 bar.
4) A-iii, B-ii, C-i, D-iv The molar mass of protein will be (R = 0.083 L
2. Match the column I with column II and mark bar mol–1 K–1)
the appropriate choice 1) 51022 g mol–1 2) 122044 g mol–1
3) 31011 g mol–1 4) 61038 g mol–1
9. A solution of sucrose (molar mass=342 g mol–1)
has been prepared by dissolving 68.5 g of
sucrose in 1000 g of water. The freezing point
of the solution obtained will be
(Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol–1)
1) – 0.372°C 2) – 0.520°C
1) A-i, B-ii, C-iii, D-iv 2) A-i, B-iii, C-ii, D-iv 3) + 0.372°C 4) – 0.570°C
3) A-iv, B-iii, C-ii, D-i 4) A-iii, B-ii, C-i, D-iv 10. 18 g glucose (C6H12O6) is added to 178.2 g water.
The vapour pressure of water (in torr) for this
3. What weight of glycerol should be added to
aqueous solution is :
600 g of water in order to lower its freezing
1) 7.6 2) 76.0
point by 10°C? (Kf = 1.86°C m–1)
1) 496 g 2) 297 g 3) 752.4 4) 759.0
3) 310 g 4) 426 g 11. The relative lowering of the vapoure pressure
is equal to the ratio between the number of
4. 10% solution of urea is isotopic with 6%
solution of a non-volatile solute X. What is 1) solute molecules to the solvent molecules
the molecular mass of solute X? 2) solute molecules to the total molecules in the
solution
1) 6 g mol–1 2) 60 g mol–1
3) 36 g mol–1 4) 32 g mol–1 3) solvent molecules to the total molecules in the
solution
5. Which of the following will have same value
of vant’ Hoff factor as that of K4[Fe(CN)6]? 4) solvent molecules to the total number of ions of
the solute
1) Al2 (SO4)3 2) AlCl3
3) Al(NO3)3 4) Al(OH)3
Prof. Motegaonkar S. R. M.Sc. Che. Gold Medalist, SET/NET--JRF Qualified 1
12. If 0.1 M solutions of each electrolyte are taken 18. One litre each of three solutions contain 20 g.
and if all electrolytes are completely dissociated, of fructose, 10 g. of urea and 34.2 g. of cane
then whose boiling point will be highest ? sugar. Their vapour pressure are P1, P2 and P3
RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * *
1) Glucose 2) KCl respectively. Then,
3) BaCl2 4) K4[Fe(CN)6] 1) P2 > P1 > P3 2) P2 > P3 > P1
13. True statement about non-ideal solutions is 3) P1 > P2 > P3 4) P3 > P1 > P2
1) do not obey Raoult’s law over the entire range 19. Assuming complete ionization, the depression
of concentration of freezing point of equimolar solutions of HCl,
CuSO4 and Na2SO4 are in the ratio of
2) A – A or B–B type interactions > A–B type
interactions 1) 1:2:3 2) 2:5:3
3) A –A or B–B type interactions < A–B type 3) 2:2:3 4) 1:1:1
interactions 20. The boiling point of C6H6, CH3OH, C6H5NH2
4) All of the above and C6H5NO2 are 80°C, 65°C, 184°C and 212°C
respectively. Which will show highest vapour
14. Which of the following solutions will have the
pressure at room temperature?
lowest vapour pressure ?
1) C6 H6 2) CH3 OH
1) 0.1 M Na3PO4 2) 0.1 M Na2SO4
3) C6H5NH2 4) C6 H5NO2
3) 0.1 M BaCl2 4) 0.1 M Urea
21. X3Y2 (i = 5) when reacted with A2B3(i = 5) in
15. Colligative properties depend on
aqueous solution gives brown colour. These
1) the nature of the solute particles dissolved in
are separated by a semipermeable membrane
solution
AB as shown. Due to osmosis there is
2) the number of solute particles in solution
3) the physical properties of the solute particles
dissolved in solution
4) the nature of solvent particles
16. Which of the following statements is/are true for the
diagram?
1) brown colour formation in side X
2) brown colour formation in side Y
3) formation in both of the sides X and Y
4) no brown colour formation
22. The vapour pressure at a given temperature
of an ideal solution containing 0.2 mol of a non-
vaolatile solute and 0.8 mol of solvent is 60 mm
1) The escaping tendency of molecule decreases for of Hg. The vapour pressure of the pure solvent
each component at the same temperatue is
2) Vapour pressure of the solution decreases 1) 150 mm of Hg 2) 60 mm of Hg
3) Solution shows negative deviation from Raoult’s 3) 75 mm of Hg 4) 120 mmm of Hg
law 23. Which one of the following pairs of the solution will
4) All of the above be same RLVP at the same temperature ?
17. A solution of 6 g. of a solute in 100 g. of water 1) 1.5 M AlCl3 and 2 M Na2SO4
boils at 100.52°C. The molar mass of the solute 2) 1 M NaCl and 2 M MgCl2
is (Given, Kb for water = 0.52 K kg mol–1) 3) 2.5 M KCl and 1.5 M Al2(SO4)3
–1
1) 600 g. mol 2) 6 4) 1.5 M KCl and 2.5 M urea
–1
3) 60 g. mol 4) 0.6
Prof. Motegaonkar S. R. M.Sc. Che. Gold Medalist, SET/NET--JRF Qualified 2
You might also like
- Problems in Exploration Seismology and Their SolutionsDocument525 pagesProblems in Exploration Seismology and Their Solutionschristophe100% (2)
- Statistical and Thermal Physics: With Computer Applications, Second EditionFrom EverandStatistical and Thermal Physics: With Computer Applications, Second EditionNo ratings yet
- String Theory Solution Manual PDFDocument67 pagesString Theory Solution Manual PDFkalodijfNo ratings yet
- Preparation Materials Ipho: Dinesh KandelDocument32 pagesPreparation Materials Ipho: Dinesh KandelRahul Gupta100% (1)
- Eat339 - Engineering Dynamics and Thermofluids SESSIONAL EXAMINATION 2015 - 2016 (Paper 2)Document7 pagesEat339 - Engineering Dynamics and Thermofluids SESSIONAL EXAMINATION 2015 - 2016 (Paper 2)أحمد صلاح الدين0% (1)
- 2E-PH: Belmonte, Manalo, Sarto, YanDocument5 pages2E-PH: Belmonte, Manalo, Sarto, YananonymousNo ratings yet
- 2 1 2 2 6 3 Area:: Chem 130B, Spring 2017 1Document4 pages2 1 2 2 6 3 Area:: Chem 130B, Spring 2017 1Ata-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- 05 Solution 16-05-2021Document4 pages05 Solution 16-05-2021ArchanaNo ratings yet
- AKTU - QP20E290QP: Time: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100Document2 pagesAKTU - QP20E290QP: Time: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100Sagar ShriNo ratings yet
- Determination of Molecular Weight of Polymers by Viscometry: Presented By: Udhay Kiron 13305017Document29 pagesDetermination of Molecular Weight of Polymers by Viscometry: Presented By: Udhay Kiron 13305017Dr. Soni Yadav100% (1)
- DPP-1 - PC Copy (Equivalent Concept, Mole Concept)Document3 pagesDPP-1 - PC Copy (Equivalent Concept, Mole Concept)prashantyadavpky07No ratings yet
- Chemistry - Paper - 2 - TZ1 - HL - Markscheme 4Document16 pagesChemistry - Paper - 2 - TZ1 - HL - Markscheme 4zicheng wangNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Hybrid Analytical Approach, To Film Pore Diffusion Model Using WaveletsDocument12 pagesAn Efficient Hybrid Analytical Approach, To Film Pore Diffusion Model Using WaveletsTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Microstructure in A Cosserat Continuum Using Relaxed EnergiesDocument2 pagesPrediction of Microstructure in A Cosserat Continuum Using Relaxed EnergiesMuhammad Sabeel KhanNo ratings yet
- MainDocument124 pagesMainhhhybpmdqzNo ratings yet
- Impo1 13Document20 pagesImpo1 13mouhcine maouhoubNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced P Chemistry-XIDocument99 pagesJEE Advanced P Chemistry-XIHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Mechanical Engineering Mechatronics Kme 101T 1Document2 pagesFundamentals of Mechanical Engineering Mechatronics Kme 101T 1YashNo ratings yet
- Estadistica, Articulo, Replication.Document2 pagesEstadistica, Articulo, Replication.marcoarmandoeaNo ratings yet
- AcousticsAstralia 2010Document11 pagesAcousticsAstralia 2010E Vachan RaoNo ratings yet
- Heat Kernel Gradient Estimates For The Vicsek Set: Fabrice Baudoin, Li ChenDocument32 pagesHeat Kernel Gradient Estimates For The Vicsek Set: Fabrice Baudoin, Li Chenhitesh902320No ratings yet
- Distribution CoefficientDocument5 pagesDistribution CoefficientPrem Mohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Interactive White Board LessonDocument2 pagesInteractive White Board Lessonapi-345951170No ratings yet
- Preview Ahmet AKİ, Sinan KOŞAK, Salim GÜR Physics Mechanics Zambak PDFDocument20 pagesPreview Ahmet AKİ, Sinan KOŞAK, Salim GÜR Physics Mechanics Zambak PDFdsy ftrniNo ratings yet
- NET-JRF - Classical Mechanics Solution-Feb.-2022Document8 pagesNET-JRF - Classical Mechanics Solution-Feb.-2022anshubiswas0000No ratings yet
- FD v2 BookDocument102 pagesFD v2 BookXander LaiingtonNo ratings yet
- PDE Rumbos Math182Spring2014NotesDocument125 pagesPDE Rumbos Math182Spring2014NotesThumper KatesNo ratings yet
- TextureDocument4 pagesTexturemorhaf aboNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 03855Document23 pagesMathematics 10 03855davideNo ratings yet
- DLL Dec.12-Dec.16, 2022Document7 pagesDLL Dec.12-Dec.16, 2022ALJON EMPERADONo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Fiber Optics and Waveguides SolutionsDocument6 pagesWeek 3 - Fiber Optics and Waveguides SolutionsAli hassanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: What Factors Affect The Rate of A Reaction?Document10 pagesChemical Kinetics: What Factors Affect The Rate of A Reaction?sb7204jNo ratings yet
- 26 H.D.A. 07-10-2021 PaperDocument4 pages26 H.D.A. 07-10-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- c2Document31 pagesc2AssyakurNo ratings yet
- Chap. 2. Molecular Weight and Polymer SolutionsDocument66 pagesChap. 2. Molecular Weight and Polymer SolutionsPembe HanimNo ratings yet
- Bpharm 1 Sem Pharmaceutical Analysis 1 Theory bp102t 2022Document1 pageBpharm 1 Sem Pharmaceutical Analysis 1 Theory bp102t 2022ShivamNo ratings yet
- Week2 Assignment SolutionDocument5 pagesWeek2 Assignment SolutionIsolated MelodyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Part 5 PDFDocument10 pagesChemical Kinetics Part 5 PDFShaikh FarooqNo ratings yet
- NLO NotesDocument75 pagesNLO NotesVanessa RomeroNo ratings yet
- Kawahara 1976Document13 pagesKawahara 1976prabowoNo ratings yet
- Nr. Items Score: SolutionDocument6 pagesNr. Items Score: SolutionCristina TirnovetchiNo ratings yet
- Kinetic ExptDocument3 pagesKinetic ExptJouliesNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Evaluation: Question No Answers/points To Be Covered MarksDocument2 pagesScheme of Evaluation: Question No Answers/points To Be Covered MarksParamita SahaNo ratings yet
- Electrodynamics - DAMTP Cambridge UniversityDocument39 pagesElectrodynamics - DAMTP Cambridge Universitygkinasih29No ratings yet
- JEE Main - GOC Isomerism SETDocument6 pagesJEE Main - GOC Isomerism SETVishnu VaradarajanNo ratings yet
- Solution of Harmonic Oscillator of Nonlinear Master SchrödingerDocument4 pagesSolution of Harmonic Oscillator of Nonlinear Master SchrödingerAhmad FadillahNo ratings yet
- Gce A Level - New CHEMISTRY - A Level Component 3Document16 pagesGce A Level - New CHEMISTRY - A Level Component 3NonuNo ratings yet
- Catalysts 07 00059Document28 pagesCatalysts 07 00059Sankar SasmalNo ratings yet
- m2 New SyllabusDocument2 pagesm2 New SyllabusTripathi 70No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Riemann Waves With Sharp Measure-Controlled DampingDocument32 pagesDynamics of Riemann Waves With Sharp Measure-Controlled DampingGaston GBNo ratings yet
- La - Frutera-Sax TenorDocument1 pageLa - Frutera-Sax TenorGregorio PechNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution of Partial Differential EquationsDocument108 pagesNumerical Solution of Partial Differential EquationsabdulqaderNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution of Partial Differential EquationsDocument108 pagesNumerical Solution of Partial Differential EquationsabdulqaderNo ratings yet
- Dean G Duffy Advanced Engineering Mathematics A Second Course WithDocument466 pagesDean G Duffy Advanced Engineering Mathematics A Second Course WithAsh LdhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FuntionalAnalysisDocument111 pagesIntroduction To FuntionalAnalysisOu LongNo ratings yet
- End SemesterDocument8 pagesEnd SemesterManavee Singh na20b034No ratings yet
- Quantum ConfinementDocument21 pagesQuantum Confinementnirmalya prasun nayakNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets As 002 (Mass Spectroscopy)Document2 pagesChemsheets As 002 (Mass Spectroscopy)justinpro7644No ratings yet
- 2016 Fall ME501 02 ODE Part2 PDFDocument51 pages2016 Fall ME501 02 ODE Part2 PDFRej O-oneNo ratings yet
- The Neumann Problem for the Cauchy-Riemann Complex. (AM-75), Volume 75From EverandThe Neumann Problem for the Cauchy-Riemann Complex. (AM-75), Volume 75Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Electroceramics: Materials, Properties, ApplicationsFrom EverandElectroceramics: Materials, Properties, ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Anantadrishti Physics Classes: Sheet-2 Cbse and Isc Target-25 MinuteDocument2 pagesAnantadrishti Physics Classes: Sheet-2 Cbse and Isc Target-25 MinuteArchanaNo ratings yet
- Violation of Privacy in Computers and It'S Prevention: by I ArchanaDocument7 pagesViolation of Privacy in Computers and It'S Prevention: by I ArchanaArchanaNo ratings yet
- Sex Determination Class 12Document2 pagesSex Determination Class 12ArchanaNo ratings yet
- 14 H.D.A. Solid State 18-07-2021 PaperDocument5 pages14 H.D.A. Solid State 18-07-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 26 H.D.A. 07-10-2021 PaperDocument4 pages26 H.D.A. 07-10-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 05 Solution 16-05-2021Document4 pages05 Solution 16-05-2021ArchanaNo ratings yet
- Inheritance: 441 Linkage Exception To Independent Assortment)Document3 pagesInheritance: 441 Linkage Exception To Independent Assortment)ArchanaNo ratings yet
- 15 H.D.A. Solid State 25-07-2021Document3 pages15 H.D.A. Solid State 25-07-2021ArchanaNo ratings yet
- 13 H.D.A. Solid State 11-07-2021 PaperDocument4 pages13 H.D.A. Solid State 11-07-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 04 Some Basic Concept of Chemistry 09-05-2021 PaperDocument3 pages04 Some Basic Concept of Chemistry 09-05-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 19 H.D.A. 15-08-2021 PaperDocument3 pages19 H.D.A. 15-08-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 3511815545AFMC MBBS Information Brrochure 2018Document25 pages3511815545AFMC MBBS Information Brrochure 2018ArchanaNo ratings yet
- 12 H.D.A. Chemical Kinetics 04-07-2021 PaperDocument5 pages12 H.D.A. Chemical Kinetics 04-07-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Appendix-Iii: Colligative PropertiesDocument3 pagesClass Xii Appendix-Iii: Colligative PropertiesSrijan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Multikomponen DistilasiDocument24 pagesMultikomponen DistilasiBunga Rajhana Ragil GayatriNo ratings yet
- 5991 7531enDocument8 pages5991 7531enAlberto Alvarado PonceNo ratings yet
- 2 Solutions 97cDocument66 pages2 Solutions 97cRubiNo ratings yet
- LPG7Document9 pagesLPG7AremzyNo ratings yet
- Module 4 G7 Science Q1 Wk6Document16 pagesModule 4 G7 Science Q1 Wk6Ryza GloryNo ratings yet
- Classification of SolventsDocument4 pagesClassification of Solventsmohan raoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Quizz 2Document7 pagesChemistry Quizz 2leonardo orozcoNo ratings yet
- Residual SolventsDocument13 pagesResidual SolventsWillian SilvaNo ratings yet
- New Call 1234Document3 pagesNew Call 1234marketing hydroNo ratings yet
- Rate Processes Assignment OneDocument4 pagesRate Processes Assignment OneShifaz SikkanderNo ratings yet
- Polaritas Pelarut PDFDocument1 pagePolaritas Pelarut PDFMuflih Federick JacksonNo ratings yet
- Organic Vapour List PDFDocument1 pageOrganic Vapour List PDFDrGurkirpal Singh MarwahNo ratings yet
- 1pCRlAWRVB 50PyNhewz9gl6nwqJMTJP5Document27 pages1pCRlAWRVB 50PyNhewz9gl6nwqJMTJP5Rica Mae EsmenosNo ratings yet
- Joc NMR Solvent Peaks Very Important-1Document5 pagesJoc NMR Solvent Peaks Very Important-1jyotibamaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 (Solution)Document4 pagesChapter - 2 (Solution)Acoustify -MusicNo ratings yet
- Extraction Problem SetDocument1 pageExtraction Problem SetdiRkdARyLNo ratings yet
- Concentration of Solution Lecture PDFDocument5 pagesConcentration of Solution Lecture PDFLouis Fetilo FabunanNo ratings yet
- Colligative 1Document20 pagesColligative 1bruhNo ratings yet
- PYQS CH Solutions Class 12 ChemistryDocument9 pagesPYQS CH Solutions Class 12 Chemistryanshuman.panda.odmNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx 9.1 Exercise 1 Act 4Document4 pagesPhysioEx 9.1 Exercise 1 Act 4Juan AlemánNo ratings yet
- Green Solvents PresDocument74 pagesGreen Solvents PresTDSNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument5 pagesChemistryLevi AckermanNo ratings yet
- Crystal Free Presentation TemplateDocument90 pagesCrystal Free Presentation TemplateTrần Thu ThảoNo ratings yet
- Chem 1332Document4 pagesChem 1332geoffreyrascherNo ratings yet
- 1 QP SolutionDocument6 pages1 QP SolutionsachinNo ratings yet
- MeasurIT Flexim Sound Velocity and Density 0910Document1 pageMeasurIT Flexim Sound Velocity and Density 0910cwiejkowskaNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin Calcium Trihydrate Farmacopea BPDocument3 pagesAtorvastatin Calcium Trihydrate Farmacopea BPGuadalupe EnriquezNo ratings yet
- 010-Membrane Transport 2Document16 pages010-Membrane Transport 2Stephie GhassanNo ratings yet