Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Marking Scheme Sahodaya 2022 Physics-1
Marking Scheme Sahodaya 2022 Physics-1
Uploaded by
Shaba TaskeenCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Foot Atomic Solutions by Zhao, C.Document32 pagesFoot Atomic Solutions by Zhao, C.Jacob Francis94% (16)
- 2004 RX8 Parts ManualDocument15 pages2004 RX8 Parts Manualgo0n80% (10)
- Atterbergs Limit Sample ProblemDocument25 pagesAtterbergs Limit Sample ProblemCarlo Consuegra33% (3)
- Useful Formulas For Astronomy & Astrophysics OlympiadDocument1 pageUseful Formulas For Astronomy & Astrophysics Olympiadvosmera83% (6)
- MS Phy PB1 2023-24 Set 3Document5 pagesMS Phy PB1 2023-24 Set 3HarshwardhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ExamplesDocument11 pagesChapter 6 ExamplesSurya NarasimanNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument10 pagesSolutionSneha SamantaNo ratings yet
- Belcher-Feynman Cylinder ParadoxDocument9 pagesBelcher-Feynman Cylinder ParadoxH LNo ratings yet
- Sol Apts-20Document4 pagesSol Apts-20thangavelgomathi55No ratings yet
- XII Physics EveningDocument12 pagesXII Physics EveningPiyush Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Technical Test - 01 - SOL - PDFDocument13 pagesTechnical Test - 01 - SOL - PDFVamshiNo ratings yet
- Physics Set-1 MSDocument3 pagesPhysics Set-1 MSSURAJ GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 4 AnswerDocument17 pagesSample Paper 4 AnswermuthuNo ratings yet
- Hints & Solution: Answer Sheet (Physics)Document10 pagesHints & Solution: Answer Sheet (Physics)CalmestNo ratings yet
- Lec 5Document7 pagesLec 5Mohammad Yusril Iqbal HabibanaNo ratings yet
- Physics Sample Papers 2022-23 KeyDocument28 pagesPhysics Sample Papers 2022-23 KeyOJASisLiveNo ratings yet
- Past Papers Solutions OutputDocument35 pagesPast Papers Solutions OutputCharlie Biopunk AlesNo ratings yet
- Isc 100% Success in PhysicsDocument194 pagesIsc 100% Success in PhysicsAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- CBSE-Physcis 12-SP 14Document8 pagesCBSE-Physcis 12-SP 14Shorya PorwalNo ratings yet
- +2 Five Mark QuestionsDocument10 pages+2 Five Mark QuestionsAshwin KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Physics EquationsDocument3 pagesPhysics Equationsanam abidNo ratings yet
- 26 July Slot 1 1Document25 pages26 July Slot 1 1Hmingsanga HauhnarNo ratings yet
- Test 11p Full Syllabus Latest Pattern SolutionDocument12 pagesTest 11p Full Syllabus Latest Pattern SolutionHardik ChhabraNo ratings yet
- MCAT Physics Equations SheetDocument4 pagesMCAT Physics Equations SheetAshley ShanaéNo ratings yet
- At STRC DPP 14Document3 pagesAt STRC DPP 14Mofazzel HussainNo ratings yet
- Jee-2024 Part Test-02 SolutionsDocument13 pagesJee-2024 Part Test-02 Solutionsarmaankaushik310No ratings yet
- Torus Magnetic MomentDocument6 pagesTorus Magnetic MomentBen WaterglowNo ratings yet
- 13 Guided Waves 2014mkDocument67 pages13 Guided Waves 2014mkTrần ĐứcAnhNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Formulae For Physics Proficiency Exams: Motion, Forces, Work, Energy and MomentumDocument4 pagesMechanics Formulae For Physics Proficiency Exams: Motion, Forces, Work, Energy and MomentumeiufjojNo ratings yet
- ATOMSDocument5 pagesATOMSajith nairNo ratings yet
- XII Physics MorningDocument8 pagesXII Physics MorningKashish PandeyNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual Keeler 1st EditionDocument101 pagesSolutions Manual Keeler 1st EditionPerez Diaz Pedro AlejandroNo ratings yet
- PDF PDFDocument176 pagesPDF PDFMD AJMALNo ratings yet
- Hamrle - Spin Orbit CouplingDocument19 pagesHamrle - Spin Orbit Couplingsushil kumarNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 (Solution) - Modern Physics NJ - 247Document3 pagesDPP - 01 (Solution) - Modern Physics NJ - 247jayeshmali9459No ratings yet
- Pages From NTA JEE MAIN 101 Speed Tests (Crackjee - Xyz)Document5 pagesPages From NTA JEE MAIN 101 Speed Tests (Crackjee - Xyz)YuvarajNo ratings yet
- IITian Pace Phy1&2Document8 pagesIITian Pace Phy1&2Lokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- AIEEE 2002 SolutionDocument14 pagesAIEEE 2002 SolutionAditya RamNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuits: 1. (30pts.) The Core Shown Below Has Two Coils of N Turns Each Connected So TheDocument6 pagesMagnetic Circuits: 1. (30pts.) The Core Shown Below Has Two Coils of N Turns Each Connected So TheSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- Phys1122 202200 1Document7 pagesPhys1122 202200 1Amritraj DashNo ratings yet
- Ap2011 Solutions 03Document10 pagesAp2011 Solutions 03soniaxNo ratings yet
- 50998502ZXW6 Power Electronics Solution ManualDocument14 pages50998502ZXW6 Power Electronics Solution ManualchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- PH8103 Presentation 3Document13 pagesPH8103 Presentation 3Rishav SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Equation SheetDocument4 pagesEquation SheetBhaskar TupteNo ratings yet
- CSSC-MS - Physics Code ADocument15 pagesCSSC-MS - Physics Code Aashishmeher899No ratings yet
- Charged, Rotating Black HolesDocument21 pagesCharged, Rotating Black HolesFrancisco Tello OrtizNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Physics PB I 2023-24Document2 pagesMarking Scheme Physics PB I 2023-24rishirajkaran2006No ratings yet
- 12 Physics EveningDocument11 pages12 Physics EveningoREpTiONNo ratings yet
- Sol Manual Atomic PhysicsDocument33 pagesSol Manual Atomic PhysicsBIBI HUDANo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Physical Chemistry Quantum Chemistry and Molecular Interactions 1st Edition Andrew Cooksy Solutions Manual PDFDocument7 pagesDwnload Full Physical Chemistry Quantum Chemistry and Molecular Interactions 1st Edition Andrew Cooksy Solutions Manual PDFsithprisus100% (14)
- Physical Chemistry Quantum Chemistry and Molecular Interactions 1st Edition Andrew Cooksy Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesPhysical Chemistry Quantum Chemistry and Molecular Interactions 1st Edition Andrew Cooksy Solutions Manuallelandsmith4rzm100% (28)
- A. Using Eq. (2) Derive The Density of States of The Conducton Band Only To First-Order in The Parameter B. Also To First-Order in SolutionDocument10 pagesA. Using Eq. (2) Derive The Density of States of The Conducton Band Only To First-Order in The Parameter B. Also To First-Order in SolutionMainzaNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document5 pagesPaper 2karim salimiNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics Departmental Written Examination FALL, 2004 Updated Solution Set: 9/28/04Document55 pagesDepartment of Physics Departmental Written Examination FALL, 2004 Updated Solution Set: 9/28/04pusa123No ratings yet
- Solution of Question Paper For Class 12 PhysicsDocument6 pagesSolution of Question Paper For Class 12 PhysicsRohan KolhatkarNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines: 1 Single Transmission-Line EquationsDocument5 pagesTransmission Lines: 1 Single Transmission-Line EquationsIoan TudosaNo ratings yet
- 2-50 CC (Key & Sol) 08.07.2022Document8 pages2-50 CC (Key & Sol) 08.07.2022mocoking007No ratings yet
- Chap 12Document13 pagesChap 12api-3702256100% (4)
- MIT8 03SCF16 PracticeFinalExam1 Solutions 3Document18 pagesMIT8 03SCF16 PracticeFinalExam1 Solutions 3Kevin Erique Solano JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Xi Ansewer Key Confidence IDocument10 pagesXi Ansewer Key Confidence IAnsh RajputNo ratings yet
- SAIFR 2023 EXAM School 1Document6 pagesSAIFR 2023 EXAM School 1Carlos Eduardo Díaz JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Neet Full Test - 01 Time:3 Hours Full Mark: 720Document24 pagesNeet Full Test - 01 Time:3 Hours Full Mark: 720Shaba TaskeenNo ratings yet
- Hand Book of Chemistry - Term II - Whole SyllabusDocument20 pagesHand Book of Chemistry - Term II - Whole SyllabusShaba TaskeenNo ratings yet
- Mother'S Public School: Mid-Term Examination - 2021 (Offline)Document1 pageMother'S Public School: Mid-Term Examination - 2021 (Offline)Shaba TaskeenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test - 2Document5 pagesChemistry Test - 2Shaba TaskeenNo ratings yet
- Xii - B - Test - 10 ResultDocument2 pagesXii - B - Test - 10 ResultShaba TaskeenNo ratings yet
- Stampella 2022Document15 pagesStampella 2022Pablo StampellaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Exercise: Foundation & Techniques: Resource Person: Dr. Rahat Ayub PT SHS.326.Lec.15Document31 pagesTherapeutic Exercise: Foundation & Techniques: Resource Person: Dr. Rahat Ayub PT SHS.326.Lec.15Fatima YasirNo ratings yet
- ZYD CatalogueDocument13 pagesZYD CatalogueKevin Wenger MwangiNo ratings yet
- Mr. Birendra Bhagat EstimationDocument6 pagesMr. Birendra Bhagat EstimationTanmay RakshitNo ratings yet
- Habitat For Sten IDocument18 pagesHabitat For Sten IErwinNo ratings yet
- Concept For Colored StonesDocument2 pagesConcept For Colored Stonessaxon zvinaNo ratings yet
- Ejection System: Advantage DisadvantageDocument5 pagesEjection System: Advantage DisadvantageRaj ThakurNo ratings yet
- The Religious Meaning of Culture. Paul PDFDocument16 pagesThe Religious Meaning of Culture. Paul PDFEvandro Vieira OuriquesNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker ListDocument6 pagesCircuit Breaker ListOscar PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Control Industrial PDFDocument2 pagesControl Industrial PDFJose David Alava CedeñoNo ratings yet
- TEST 1 - Answer Scheme - Complete GeotechDocument10 pagesTEST 1 - Answer Scheme - Complete Geotechfaraeiin57No ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals: For The First CircuitDocument16 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals: For The First CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- MJPRU Exam SchemeDocument9 pagesMJPRU Exam SchemePrabhat SharmaNo ratings yet
- CV FORMAT 2Document2 pagesCV FORMAT 2useforfreelanceworkNo ratings yet
- Influence of Welding Parameters On Weld Characteristics of 5052 Aluminium Alloy Sheet Using TIG WeldingDocument5 pagesInfluence of Welding Parameters On Weld Characteristics of 5052 Aluminium Alloy Sheet Using TIG WeldingInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Final Test For MC Physics 1 (Fluid Mechanics)Document3 pagesFinal Test For MC Physics 1 (Fluid Mechanics)fj damayoNo ratings yet
- DWDM AbbDocument28 pagesDWDM AbbEfraim Torres100% (1)
- Ôn Tập Chia Thì Đủ LoạiDocument51 pagesÔn Tập Chia Thì Đủ LoạiNguyễn Minh NgọcNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument57 pagesSolutionssamiaahsNo ratings yet
- Datasheet RACKOM 21U IP55 Outdoor CabinetDocument2 pagesDatasheet RACKOM 21U IP55 Outdoor CabinetPrem Singh MehtaNo ratings yet
- We Take You To The Next Level.Document12 pagesWe Take You To The Next Level.Pradeep SreedharanNo ratings yet
- ACEA Oil SequencesDocument14 pagesACEA Oil Sequencesctiiin100% (1)
- Ig Chem CH 2 QP Core v.2Document6 pagesIg Chem CH 2 QP Core v.2Ankit MistryNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV Green Building Rating System in IndiaDocument26 pagesUNIT IV Green Building Rating System in IndiavishalakshiNo ratings yet
- ENG - Policy Paper - Neo Extractivism in Indonesias Nickel EpicenterDocument44 pagesENG - Policy Paper - Neo Extractivism in Indonesias Nickel Epicentersatirraja530No ratings yet
- The Characteristic Golden Brown Colour Associated With Baked Food Is Due To Maillard ReactionsDocument2 pagesThe Characteristic Golden Brown Colour Associated With Baked Food Is Due To Maillard ReactionsDenzHackNo ratings yet
- Pauwels SLIM® Transformers Lead The Way To Wind-Power in FranceDocument2 pagesPauwels SLIM® Transformers Lead The Way To Wind-Power in FranceLuminita CodreanuNo ratings yet
- Manual de Operación 5ecdDocument56 pagesManual de Operación 5ecdRicardo ArandaNo ratings yet
Marking Scheme Sahodaya 2022 Physics-1
Marking Scheme Sahodaya 2022 Physics-1
Uploaded by
Shaba TaskeenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Marking Scheme Sahodaya 2022 Physics-1
Marking Scheme Sahodaya 2022 Physics-1
Uploaded by
Shaba TaskeenCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYSICS MARKING SCHEME-SAHODAYA PREBOARD 2022
TERM-II
Q.NO VALUE POINTS MARKS
½
½
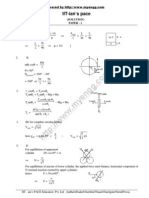
It is a photodiode and hence operated preferably in reverse bias.
1
Justification
h h2
(i) λ = V = ½
2mqV 2mqλ2
As mα = 4mp and qα= 2qp ½
V p mα qα 4m p × 2q p
= = = 8 :1
Vα m p q p mp q p
h h ½
2 (ii) λ = v=
mv mλ
v p mα 4m p ½
= = = 4 :1
vα m p mp
1
OR
(a) cot(θ / 2) =0, θ / 2 =90 Therefore θ =1800
0
1
(b) θ decreases 1
Since the resulting extrinsic semiconductor is a p-type semiconductor, holes are ½
the majority charge carriers.
However, the net charge of the p-type semiconductor is zero. ½
SAHODAYA PREBOARD EXAM 2022 PHYSICS MARKING SCHEME 1
c 3 ×108
(a) Wavelength λ = = = 1.5 ×10−3 m 1
ν 2 ×1011
E0 48
4 (b) B0 = = 8
= 1.6 × 10−7 T 1
c 3 ×10
(c) Microwave and two uses. ½+½
(a)Nuclear radius R=R0A1/3
1/3
RFe AFe
1/3
125 ½
= =
RAl AAl 27 1
5 5
RFe = RAl = × 3.6 fm = 6 fm
3 3
5 (b) Proof of constancy of nuclear density
1½
OR
(a) Definition of mass defect
Energy released per second = n X 200 MeV
1
Therefore, n X 200 MeV=106
2
So, n= 3.125 X 1016
n2h2 1½
(a)Derivation of the expression rn =
4 πmkZe 2
hc hc hc ½
6 (b) EC − EB = , EB − E A = and EC − E A =
λ1 λ2 λ3
½
But EC − E A = ( EC − EB ) + ( EB − E A )
hc hc hc 1 1 1 ½
= + or = +
λ 3 λ1 λ 2 λ 3 λ1 λ 2
Consider the refraction of the first surface(rarer to denser)
1½
3 4 4 3
−
= 3 + 2 v1 = 9 R
µ 2 − µ1 µ1 µ2 2 3
= +
R −u v1 R ∞ v1
Now consider refraction at the second surface ( denser to rarer)
7 1½
3 3
1−
2 = − 2 + 1 v = 3R
2
−R 9 R v2 2
OR
(a) Ray diagram
SAHODAYA PREBOARD EXAM 2022 PHYSICS MARKING SCHEME 2
1
(b) Derivation of magnifying power m = -fO/fE
(a) According to Einstein’s photoelectric equation K max = hν − W0
½
hc hc 1 W
eV0 = − W0 ∴V0 = + − 0
λ e λ e
Comparing with the straight line equation y=mx+c, we find the slope of 1
hc me
8 V0 ~1/λ is m = h=
e c ½
(b) Stopping potential won’t be affected.
When the distance between the light source and the metal surface A is
increased, the intensity of radiation decreases but the stopping potential V0 will
remain same as it depends on the frequency of the incident radiation and not on 1
its intensity.
(a) Intensity~x graph for single slit diffraction and YDSE ½+½
(b) The interference patterns due to different component colors of white light
overlap incoherently and we obtain a white central fringe accompanied by 1
9
colored fringes.
(c) For best contrast, both the sources need to have same intensity/amplitude.
In such situation, Imax = 4I0 and Imin = 0 where I0 is the intensity of each source. 1
Wavefront definition ½
10 Diagram of incident and reflected wavefront 1
Proof of Laws of Reflection 1½
½+½
(a) Two processes are Diffusion and Drift
1
11 Explanation of the process
1
(b) Since the diode is reverse biased, it does not conduct. Hence current is zero.
(i) c 1
(ii) d 1
12 (iii) b 1
(iv) c 1
(v) a 1
SAHODAYA PREBOARD EXAM 2022 PHYSICS MARKING SCHEME 3
You might also like
- Foot Atomic Solutions by Zhao, C.Document32 pagesFoot Atomic Solutions by Zhao, C.Jacob Francis94% (16)
- 2004 RX8 Parts ManualDocument15 pages2004 RX8 Parts Manualgo0n80% (10)
- Atterbergs Limit Sample ProblemDocument25 pagesAtterbergs Limit Sample ProblemCarlo Consuegra33% (3)
- Useful Formulas For Astronomy & Astrophysics OlympiadDocument1 pageUseful Formulas For Astronomy & Astrophysics Olympiadvosmera83% (6)
- MS Phy PB1 2023-24 Set 3Document5 pagesMS Phy PB1 2023-24 Set 3HarshwardhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ExamplesDocument11 pagesChapter 6 ExamplesSurya NarasimanNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument10 pagesSolutionSneha SamantaNo ratings yet
- Belcher-Feynman Cylinder ParadoxDocument9 pagesBelcher-Feynman Cylinder ParadoxH LNo ratings yet
- Sol Apts-20Document4 pagesSol Apts-20thangavelgomathi55No ratings yet
- XII Physics EveningDocument12 pagesXII Physics EveningPiyush Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Technical Test - 01 - SOL - PDFDocument13 pagesTechnical Test - 01 - SOL - PDFVamshiNo ratings yet
- Physics Set-1 MSDocument3 pagesPhysics Set-1 MSSURAJ GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 4 AnswerDocument17 pagesSample Paper 4 AnswermuthuNo ratings yet
- Hints & Solution: Answer Sheet (Physics)Document10 pagesHints & Solution: Answer Sheet (Physics)CalmestNo ratings yet
- Lec 5Document7 pagesLec 5Mohammad Yusril Iqbal HabibanaNo ratings yet
- Physics Sample Papers 2022-23 KeyDocument28 pagesPhysics Sample Papers 2022-23 KeyOJASisLiveNo ratings yet
- Past Papers Solutions OutputDocument35 pagesPast Papers Solutions OutputCharlie Biopunk AlesNo ratings yet
- Isc 100% Success in PhysicsDocument194 pagesIsc 100% Success in PhysicsAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- CBSE-Physcis 12-SP 14Document8 pagesCBSE-Physcis 12-SP 14Shorya PorwalNo ratings yet
- +2 Five Mark QuestionsDocument10 pages+2 Five Mark QuestionsAshwin KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Physics EquationsDocument3 pagesPhysics Equationsanam abidNo ratings yet
- 26 July Slot 1 1Document25 pages26 July Slot 1 1Hmingsanga HauhnarNo ratings yet
- Test 11p Full Syllabus Latest Pattern SolutionDocument12 pagesTest 11p Full Syllabus Latest Pattern SolutionHardik ChhabraNo ratings yet
- MCAT Physics Equations SheetDocument4 pagesMCAT Physics Equations SheetAshley ShanaéNo ratings yet
- At STRC DPP 14Document3 pagesAt STRC DPP 14Mofazzel HussainNo ratings yet
- Jee-2024 Part Test-02 SolutionsDocument13 pagesJee-2024 Part Test-02 Solutionsarmaankaushik310No ratings yet
- Torus Magnetic MomentDocument6 pagesTorus Magnetic MomentBen WaterglowNo ratings yet
- 13 Guided Waves 2014mkDocument67 pages13 Guided Waves 2014mkTrần ĐứcAnhNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Formulae For Physics Proficiency Exams: Motion, Forces, Work, Energy and MomentumDocument4 pagesMechanics Formulae For Physics Proficiency Exams: Motion, Forces, Work, Energy and MomentumeiufjojNo ratings yet
- ATOMSDocument5 pagesATOMSajith nairNo ratings yet
- XII Physics MorningDocument8 pagesXII Physics MorningKashish PandeyNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual Keeler 1st EditionDocument101 pagesSolutions Manual Keeler 1st EditionPerez Diaz Pedro AlejandroNo ratings yet
- PDF PDFDocument176 pagesPDF PDFMD AJMALNo ratings yet
- Hamrle - Spin Orbit CouplingDocument19 pagesHamrle - Spin Orbit Couplingsushil kumarNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 (Solution) - Modern Physics NJ - 247Document3 pagesDPP - 01 (Solution) - Modern Physics NJ - 247jayeshmali9459No ratings yet
- Pages From NTA JEE MAIN 101 Speed Tests (Crackjee - Xyz)Document5 pagesPages From NTA JEE MAIN 101 Speed Tests (Crackjee - Xyz)YuvarajNo ratings yet
- IITian Pace Phy1&2Document8 pagesIITian Pace Phy1&2Lokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- AIEEE 2002 SolutionDocument14 pagesAIEEE 2002 SolutionAditya RamNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuits: 1. (30pts.) The Core Shown Below Has Two Coils of N Turns Each Connected So TheDocument6 pagesMagnetic Circuits: 1. (30pts.) The Core Shown Below Has Two Coils of N Turns Each Connected So TheSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- Phys1122 202200 1Document7 pagesPhys1122 202200 1Amritraj DashNo ratings yet
- Ap2011 Solutions 03Document10 pagesAp2011 Solutions 03soniaxNo ratings yet
- 50998502ZXW6 Power Electronics Solution ManualDocument14 pages50998502ZXW6 Power Electronics Solution ManualchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- PH8103 Presentation 3Document13 pagesPH8103 Presentation 3Rishav SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Equation SheetDocument4 pagesEquation SheetBhaskar TupteNo ratings yet
- CSSC-MS - Physics Code ADocument15 pagesCSSC-MS - Physics Code Aashishmeher899No ratings yet
- Charged, Rotating Black HolesDocument21 pagesCharged, Rotating Black HolesFrancisco Tello OrtizNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Physics PB I 2023-24Document2 pagesMarking Scheme Physics PB I 2023-24rishirajkaran2006No ratings yet
- 12 Physics EveningDocument11 pages12 Physics EveningoREpTiONNo ratings yet
- Sol Manual Atomic PhysicsDocument33 pagesSol Manual Atomic PhysicsBIBI HUDANo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Physical Chemistry Quantum Chemistry and Molecular Interactions 1st Edition Andrew Cooksy Solutions Manual PDFDocument7 pagesDwnload Full Physical Chemistry Quantum Chemistry and Molecular Interactions 1st Edition Andrew Cooksy Solutions Manual PDFsithprisus100% (14)
- Physical Chemistry Quantum Chemistry and Molecular Interactions 1st Edition Andrew Cooksy Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesPhysical Chemistry Quantum Chemistry and Molecular Interactions 1st Edition Andrew Cooksy Solutions Manuallelandsmith4rzm100% (28)
- A. Using Eq. (2) Derive The Density of States of The Conducton Band Only To First-Order in The Parameter B. Also To First-Order in SolutionDocument10 pagesA. Using Eq. (2) Derive The Density of States of The Conducton Band Only To First-Order in The Parameter B. Also To First-Order in SolutionMainzaNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document5 pagesPaper 2karim salimiNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics Departmental Written Examination FALL, 2004 Updated Solution Set: 9/28/04Document55 pagesDepartment of Physics Departmental Written Examination FALL, 2004 Updated Solution Set: 9/28/04pusa123No ratings yet
- Solution of Question Paper For Class 12 PhysicsDocument6 pagesSolution of Question Paper For Class 12 PhysicsRohan KolhatkarNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines: 1 Single Transmission-Line EquationsDocument5 pagesTransmission Lines: 1 Single Transmission-Line EquationsIoan TudosaNo ratings yet
- 2-50 CC (Key & Sol) 08.07.2022Document8 pages2-50 CC (Key & Sol) 08.07.2022mocoking007No ratings yet
- Chap 12Document13 pagesChap 12api-3702256100% (4)
- MIT8 03SCF16 PracticeFinalExam1 Solutions 3Document18 pagesMIT8 03SCF16 PracticeFinalExam1 Solutions 3Kevin Erique Solano JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Xi Ansewer Key Confidence IDocument10 pagesXi Ansewer Key Confidence IAnsh RajputNo ratings yet
- SAIFR 2023 EXAM School 1Document6 pagesSAIFR 2023 EXAM School 1Carlos Eduardo Díaz JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Neet Full Test - 01 Time:3 Hours Full Mark: 720Document24 pagesNeet Full Test - 01 Time:3 Hours Full Mark: 720Shaba TaskeenNo ratings yet
- Hand Book of Chemistry - Term II - Whole SyllabusDocument20 pagesHand Book of Chemistry - Term II - Whole SyllabusShaba TaskeenNo ratings yet
- Mother'S Public School: Mid-Term Examination - 2021 (Offline)Document1 pageMother'S Public School: Mid-Term Examination - 2021 (Offline)Shaba TaskeenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test - 2Document5 pagesChemistry Test - 2Shaba TaskeenNo ratings yet
- Xii - B - Test - 10 ResultDocument2 pagesXii - B - Test - 10 ResultShaba TaskeenNo ratings yet
- Stampella 2022Document15 pagesStampella 2022Pablo StampellaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Exercise: Foundation & Techniques: Resource Person: Dr. Rahat Ayub PT SHS.326.Lec.15Document31 pagesTherapeutic Exercise: Foundation & Techniques: Resource Person: Dr. Rahat Ayub PT SHS.326.Lec.15Fatima YasirNo ratings yet
- ZYD CatalogueDocument13 pagesZYD CatalogueKevin Wenger MwangiNo ratings yet
- Mr. Birendra Bhagat EstimationDocument6 pagesMr. Birendra Bhagat EstimationTanmay RakshitNo ratings yet
- Habitat For Sten IDocument18 pagesHabitat For Sten IErwinNo ratings yet
- Concept For Colored StonesDocument2 pagesConcept For Colored Stonessaxon zvinaNo ratings yet
- Ejection System: Advantage DisadvantageDocument5 pagesEjection System: Advantage DisadvantageRaj ThakurNo ratings yet
- The Religious Meaning of Culture. Paul PDFDocument16 pagesThe Religious Meaning of Culture. Paul PDFEvandro Vieira OuriquesNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker ListDocument6 pagesCircuit Breaker ListOscar PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Control Industrial PDFDocument2 pagesControl Industrial PDFJose David Alava CedeñoNo ratings yet
- TEST 1 - Answer Scheme - Complete GeotechDocument10 pagesTEST 1 - Answer Scheme - Complete Geotechfaraeiin57No ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals: For The First CircuitDocument16 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals: For The First CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- MJPRU Exam SchemeDocument9 pagesMJPRU Exam SchemePrabhat SharmaNo ratings yet
- CV FORMAT 2Document2 pagesCV FORMAT 2useforfreelanceworkNo ratings yet
- Influence of Welding Parameters On Weld Characteristics of 5052 Aluminium Alloy Sheet Using TIG WeldingDocument5 pagesInfluence of Welding Parameters On Weld Characteristics of 5052 Aluminium Alloy Sheet Using TIG WeldingInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Final Test For MC Physics 1 (Fluid Mechanics)Document3 pagesFinal Test For MC Physics 1 (Fluid Mechanics)fj damayoNo ratings yet
- DWDM AbbDocument28 pagesDWDM AbbEfraim Torres100% (1)
- Ôn Tập Chia Thì Đủ LoạiDocument51 pagesÔn Tập Chia Thì Đủ LoạiNguyễn Minh NgọcNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument57 pagesSolutionssamiaahsNo ratings yet
- Datasheet RACKOM 21U IP55 Outdoor CabinetDocument2 pagesDatasheet RACKOM 21U IP55 Outdoor CabinetPrem Singh MehtaNo ratings yet
- We Take You To The Next Level.Document12 pagesWe Take You To The Next Level.Pradeep SreedharanNo ratings yet
- ACEA Oil SequencesDocument14 pagesACEA Oil Sequencesctiiin100% (1)
- Ig Chem CH 2 QP Core v.2Document6 pagesIg Chem CH 2 QP Core v.2Ankit MistryNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV Green Building Rating System in IndiaDocument26 pagesUNIT IV Green Building Rating System in IndiavishalakshiNo ratings yet
- ENG - Policy Paper - Neo Extractivism in Indonesias Nickel EpicenterDocument44 pagesENG - Policy Paper - Neo Extractivism in Indonesias Nickel Epicentersatirraja530No ratings yet
- The Characteristic Golden Brown Colour Associated With Baked Food Is Due To Maillard ReactionsDocument2 pagesThe Characteristic Golden Brown Colour Associated With Baked Food Is Due To Maillard ReactionsDenzHackNo ratings yet
- Pauwels SLIM® Transformers Lead The Way To Wind-Power in FranceDocument2 pagesPauwels SLIM® Transformers Lead The Way To Wind-Power in FranceLuminita CodreanuNo ratings yet
- Manual de Operación 5ecdDocument56 pagesManual de Operación 5ecdRicardo ArandaNo ratings yet