Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chart 1
Chart 1
Uploaded by
tantalizin marieOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chart 1
Chart 1
Uploaded by
tantalizin marieCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|7259008
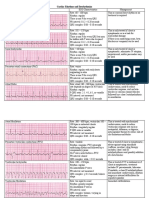
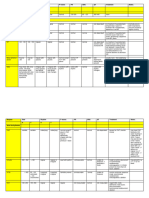
V&A rate V&A rhythm QRS shape P wave PR P:QRS Common Causes Interventions/
and interval ratio Medications
duration
Normal Sinus 60 – 100 Regular Normal Normal; 0.12 – 0.20 1:1 N/A N/A
Rhythm bpm in front of secs
QRS
Sinus < 60 bpm Regular Normal Normal; 0.12 – 0.20 1:1 Well-conditioned P: pacing
Bradycardia in front of secs athletes, Vagal A: atropine
QRS stimulation, decreased E: epinephrine
metabolic rate, heart D: dopamine
disease, Amiodarone,
Beta blockers, Ca
channel blockers,
Digoxin
Sinus Node
Dysrhythmias Sinus > 100 but < Regular Normal Normal; 0.12 – 0.20 1:1 Stress, acute blood loss, Hemodynamic
Tachycardia 150 bpm in front of secs anemia, shock, hyper & instability
QRS hypovolemia, heart cardioversion;
failure, pain, fever, if narrow QRS
exercise, anxiety, Beta blockers & Ca
caffeine, nicotine, channel blockers;
amphetamines, cocaine, if wide QRS
E pills, POTS adenosine *only if
QRS is monomorphic
& regular rhythm
Downloaded by Ethel Hubbard (ehubbard1981@yahoo.com)
lOMoARcPSD|7259008
V&A rate V&A rhythm QRS shape P wave PR P:QRS Common Causes Interventions/
and interval ratio Medications
duration
1st Degree AV Depends Depends on Normal or In front of > 0.20 secs 1:1 Occurs when all atrial Initial Tx is IV bolus
Block on under- under-lying abnormal QRS impulses are conducted of atropine
lying rhythm through the AV node into
rhythm the ventricles at a rate If pt doesn't respond
slower than normal to atropine
transcutaneous
2nd Degree AV Depends Regular PP Normal or In front of PR interval 3:2, Occurs when there is a pacing is indicated
Block Type on under- interval if abnormal QRS becomes 4:3, repeating pattern in
1(Mobitz 1 or lying normal sinus longer w/ 5:4, which all but one of a If pt doesn't have a
Wenchkebach) rhythm; rhythm; goes each ECG and so series of atrial impulses pulse, Tx is the same
V rate < A from longest complex forth are conducted through as ventricular
rate RR interval until no P the AV node into the asystole.
and gradually wave ventricles
shortens until visible; Pacemaker may be
next long RR becomes indicated
Conduction interval irregular
Abnormalities 2nd Degree AV Depends Regular PP Abnormal In front of Constant 2:1, Occurs when only some Tx is directed
Block Type 2 on under- same as above; but can be QRS for those P 3:1, of the atrial impulses are toward increasing
(Mobitz 2) lying RR interval is normal waves just 4:1, conducted through the the HR to maintain
rhythm; usually before QRS 5:1, AV node into the normal CO.
V rate < A regular or complex and so ventricles
rate irregular forth If pt is stable and
depending on no symptoms, no
P:QRS ratio treatment.
3rd Degree AV Depends Regular PP & Depends on Depends Very P waves Occurs when no atrial
Block on escape RR intervals, escape on under- irregular > QRS impulse is conducted
rhythm but PP interval rhythm lying complex through the AV node into
and does not equal rhythm the ventricle
underlying RR interval
atrial
rhythm;
V rate < A
rate
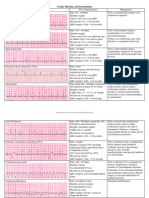
V&A rate V&A rhythm QRS shape P wave PR P:QRS Common Causes Interventions/
Downloaded by Ethel Hubbard (ehubbard1981@yahoo.com)
lOMoARcPSD|7259008
and interval ratio Medications
duration
Premature Atrial Depends Irregular Normal, Early & 0.12 – 0.20 1:1 Increased If in frequent, no
Contraction on under- abnormal or different secs catecholamine levels, Tx needed.
(PAC), lying absent P wave heart disease,
Supraventricular rhythm or caffeine, alcohol, If frequent (more
Tachycardia hidden nicotine, stretched than 6/min) treat
(SVT) in T atrial myocardium, underlying cause.
wave anxiety, hypokalemia,
atrial injury, Consider using vagal
ischemia, infarction maneuvers,
synchronized
cardioversion,
Adenosine, Beta
Blockers, Calcium
Channel Blockers
Atrial A rate: Highly Normal or No dis- Cannot Many:1 Unknown cause Vagal maneuvers,
Fibrillation 300 – 600 irregular abnormal cernible measure synchronized
Atrial
bpm; P waves Risk Factors: cardioversion, Beta
Dysrhythmias
V rate: increased age, male, Blockers, Calcium
120 – 200 high BMI, Channel Blockers;
bpm systolic BP 160 if HF present:
mmHG, Amiodarone, Digoxin
PR interval 160
milliseconds, HTN,
grade 3 or higher
heart murmur, HF &
heart diseases
Atrial Flutter A rate: Atrial rhythm Normal, Saw- Cannot 2:1, Occurs in pts w/
250 – 400 is regular; abnormal or toothed determine 3:1, COPD, pulmonary
bpm; ventricular absent shaped 4:1 HTN, valvular disease
V rate: rhythm is & thyrotoxicosis
75 – 150 regular or
bpm irregular due
to change in
AV conduction
V&A rate V&A rhythm QRS shape P wave PR P:QRS Common Causes Interventions/
Downloaded by Ethel Hubbard (ehubbard1981@yahoo.com)
lOMoARcPSD|7259008
and interval ratio Medications
duration
Premature Depends Irregular due 0.12 secs or Depends If P wave is 0:1, Caffeine, nicotine, If frequent &
Ventricular on the to early QRS longer on in front of 1:1 alcohol, cardiac persistent:
Contraction under- shorter RR timing of QRS; ischemia, infarction, Amiodarone or
(PVC) lying interval PVC interval is increased workload, Sotalol
rhythm < 0.12 secs. digitalis toxicity,
*Couplets, hypoxia, acidosis,
Bigeminy, hypokalemia,
Trigeminy mechanical irritation
of myocardium with
catheters/wires
Ventricular V rate: Regular 0.12 secs or Very Very Difficult to Electrolyte Synchronized
Tachycardia 100 – 200 more difficult irregular determine disturbances, hypoxia, cardioversion,
(V Tach w/ bpm; to detect mechanical irritation defibrillation for
pulse) A rate of myocardium w/ Polymorphic V tach,
depends on catheters/wires Amiodarone or
*3 or more PVCs under- Lidocaine,
Ventricular in a row lying Procainamide,
Dysrhythmias **Monomorphic rhythm Sotalol
or Polymorphic
Ventricular Cardiac Arrest: CPR & immediate
Tachycardia immediate defibrillation,
(Pulseless V interventions needed Epinephrine (IV
Tach) to prevent irreversible push), Amiodarone
brain death or Lidocaine
*3 or more PVCs
in a row
Ventricular > 300 bpm Extremely Irregular; CAD #1, V Tach, CPR & immediate
Fibrillation irregular, w/ undulating cardiomyopathy, Defib, Epinephrine
(V Fib) out specific waves w/ out valvular heart (IV push),
pattern recognizable disease, several Amiodarone or
QRS proarrhythmic meds, Lidocaine
complexes acid-base &
electrolyte abnorms,
electrical shock,
hypoxia
Asystole Cardiac Arrest CPR (No defib), confirm asystole in more than one lead, Epinephrine, Identify and treat reversible causes
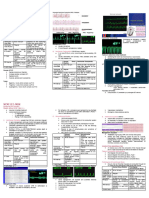
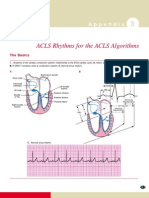
Normal EKG Waves
Downloaded by Ethel Hubbard (ehubbard1981@yahoo.com)
lOMoARcPSD|7259008
***includes P wave, QRS complex, T wave, possible U wave
***PR interval, ST segment & QT interval
Each small box represents 0.04 sec. or 1 mm
5 small boxes = 0.20 secs or 5 mm
Measurements:
PR interval = beginning of P wave to the beginning of QRS complex
o Represents time needed for sinus node stimulation, atrial depolarization and conduction through the AV node before ventricular depolarization
o Normal = 0.12 – 0.20 secs in duration
ST segment = end of QRS complex to beginning of T wave
o Above or below isometric line cardiac ischemia
QRS complex = beginning of Q wave to the end of the S wave
QT interval = beginning of the Q wave to the end of the T wave
o Represents total time for ventricular depolarization and repolarization
o Normal = 0.32 – 0.40 secs in duration if HR is between 65 – 95 BPM
TP interval = end of the T wave to the beginning of the next P wave
PP interval = beginning of one P wave to the beginning of the next P wave
o Determines atrial rate and rhythm
RR interval = measures QRS complex to the next QRS complex
o Determines ventricular rate and rhythm
Waves, Complexes and Intervals:
P wave = electrical impulse starting in the SA node and spreading through the atria; represents atrial depolarization
o Normal = 2.5 mm tall & 0.11 secs or < in duration
QRS complex = ventricular depolarization
o Normal = < 0.12 secs in duration
o If < 5 mm tall small qrs is used
o If > 5 mm tall large QRS is used
Q wave = 1st negative deflection after the P wave; normally < 0.04 secs
R wave = first positive deflection after P wave
S wave = 1st negative deflection after the R wave
T wave = ventricular repolarization; when cells regain a (-) charge
o Both atrial & ventricular repolarization occur at the same time
o Tall T wave occurs in patients with HYPERkalemia
U wave = repolarization of the Purkinje fibers
o Occurs in patients with HYPOkalemia, HTN or heart disease
Downloaded by Ethel Hubbard (ehubbard1981@yahoo.com)
You might also like
- Basic EKG ECG Rhythms CheatsheetDocument1 pageBasic EKG ECG Rhythms CheatsheetAhmad86% (7)
- Cardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med Surg NUR4 PDFDocument3 pagesCardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med Surg NUR4 PDFlml100% (1)
- Thorsten and ImaniDocument390 pagesThorsten and ImaniDoRo Thy79% (43)
- Basic Arrhythmia RulesDocument3 pagesBasic Arrhythmia Rulesgreenflames0997% (30)
- EKG RhythmsDocument10 pagesEKG RhythmsQueenNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Sinus BradycardiaDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Sinus BradycardiaPascal St Peter NwaorguNo ratings yet
- Heart Dysrhythmias Cheat Sheet PDFDocument5 pagesHeart Dysrhythmias Cheat Sheet PDFpcmundotNo ratings yet
- NCM 104 Cellular Aberration Lecture 2007Document104 pagesNCM 104 Cellular Aberration Lecture 2007api-378278992% (26)
- JD Guided Surgery Kit Instruction For UseDocument21 pagesJD Guided Surgery Kit Instruction For UseTeaca DumitruNo ratings yet
- Raihah Nabilah Hashim - ENGLISH FOR ACADEMIC WRITING ASSESSMENT 3Document9 pagesRaihah Nabilah Hashim - ENGLISH FOR ACADEMIC WRITING ASSESSMENT 3Raihah Nabilah HashimNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disorders: Types of DysrythmiasDocument3 pagesCardiovascular Disorders: Types of Dysrythmiasjamie carpioNo ratings yet
- KEY EKG Study Sheet FA 18Document2 pagesKEY EKG Study Sheet FA 18Anesa SyNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DysrhythmiasDocument3 pagesCardiac DysrhythmiasWilbert GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Rhythms and DysrhythmiasDocument14 pagesCardiac Rhythms and DysrhythmiasShawn Gaurav Jha100% (1)
- Cardiac Dysrhythmias For Heart PatientsDocument3 pagesCardiac Dysrhythmias For Heart PatientsAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 MSN Prelim Topic 4 Cardiac Rhythm DisordersDocument5 pagesNCM 112 MSN Prelim Topic 4 Cardiac Rhythm DisordersKim Erida QuezonNo ratings yet
- Rhythm EKG Rate (BPM) Rhythm EKG InterventionsDocument6 pagesRhythm EKG Rate (BPM) Rhythm EKG InterventionsRawabi rawabi1997No ratings yet
- Assignment Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument7 pagesAssignment Cardiac ArrhythmiasGail Lian Santos100% (1)
- Atrial Arrhythmias Definition and Pathology Significance Etiology Clinical Manifestations InterventionDocument5 pagesAtrial Arrhythmias Definition and Pathology Significance Etiology Clinical Manifestations Interventionmakyofrancis20No ratings yet
- Atrial Dysrhythmias: Type of Dysrhythmia Ecg Characteristics Causes Signs & Symptoms TreatmentDocument3 pagesAtrial Dysrhythmias: Type of Dysrhythmia Ecg Characteristics Causes Signs & Symptoms TreatmentTifanie Cyrine MerneloNo ratings yet
- ArrhyDocument26 pagesArrhyMouriyan AmanNo ratings yet
- Atrial DysrhythmiasDocument1 pageAtrial DysrhythmiasTracy Ables-TatroNo ratings yet
- Nclex RN Review Notes 2018 Triple eDocument30 pagesNclex RN Review Notes 2018 Triple eEndla SriniNo ratings yet
- Osce PDFDocument51 pagesOsce PDFAlfonso PeñarroyaNo ratings yet
- CardiacDocument37 pagesCardiacRebecca TapiaNo ratings yet
- Normal Ecg & ArrhythmiaDocument33 pagesNormal Ecg & ArrhythmiaEric AryantoNo ratings yet
- Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualDocument3 pagesIntensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualgalaxytwyNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Cardiac Arrhythmias: Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualDocument3 pagesNeonatal Cardiac Arrhythmias: Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualAhmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- ECGs LectureDocument16 pagesECGs LectureMike GNo ratings yet
- Quick Ekg ReferenceDocument23 pagesQuick Ekg Referencekowaikowar100% (2)
- EKG 2 Lead Interp RefresherDocument9 pagesEKG 2 Lead Interp RefresherDaniel GeduquioNo ratings yet
- Sinus Rhythm and Sinus and Atrial DysrhythmiasDocument41 pagesSinus Rhythm and Sinus and Atrial Dysrhythmiasclaudia brongNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenDocument23 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenItsMe AJNo ratings yet
- APPROACH TO ACLS RHYTHMS by Dra. Adviento 11.11.16Document92 pagesAPPROACH TO ACLS RHYTHMS by Dra. Adviento 11.11.16Rye CalderonNo ratings yet
- Basic ArrythmiasDocument58 pagesBasic ArrythmiasZachary Cohen100% (2)
- Types of DysrhythmiasDocument15 pagesTypes of DysrhythmiasKevin VillaranteNo ratings yet
- ACLS Rhythms For The ACLS Algorithms: AppendixDocument32 pagesACLS Rhythms For The ACLS Algorithms: Appendixyan_ricci19100% (4)
- Approach To ArrhythmiasDocument1 pageApproach To ArrhythmiasADITYA SARANGINo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia Rule S/S Causes TreatmentsDocument6 pagesArrhythmia Rule S/S Causes TreatmentsBrandi WorleyNo ratings yet
- EKG Study GuideDocument14 pagesEKG Study GuidesydNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 - Lesson 11 (Arrhythmia)Document5 pagesNCM 118 - Lesson 11 (Arrhythmia)Bobby Christian DuronNo ratings yet
- Acc Ecg ChallengeDocument91 pagesAcc Ecg ChallengeMiguel LizarragaNo ratings yet
- Algo Pals TachycardiaDocument1 pageAlgo Pals TachycardiaArdie FratamaNo ratings yet
- Cardiology-5 DysrhythmiaDocument16 pagesCardiology-5 DysrhythmiaMahmoud RamadanNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: 1A: Prolong AP & Increase Refractory Period Moderate Effects On Conduction in Normal CellsDocument4 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs: 1A: Prolong AP & Increase Refractory Period Moderate Effects On Conduction in Normal CellsSaulNo ratings yet
- 40 - Arrythmias (PICU COURSE)Document44 pages40 - Arrythmias (PICU COURSE)surasuarezlopezNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmia Study Sheet 2016Document5 pagesDysrhythmia Study Sheet 2016Geena sekhonNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi EKGDocument81 pagesInterpretasi EKGGalihNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookFrom EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo ratings yet
- Essential Cardiac Electrophysiology: The Self-Assessment ApproachFrom EverandEssential Cardiac Electrophysiology: The Self-Assessment ApproachNo ratings yet
- Community Health Paper Template-March 15Document43 pagesCommunity Health Paper Template-March 15tantalizin marieNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument7 pagesChronic Renal Failuretantalizin marieNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument5 pagesFluid and Electrolytestantalizin marieNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmias: Cardiac Conduction System Rhythm Strip RecognitionDocument5 pagesDysrhythmias: Cardiac Conduction System Rhythm Strip Recognitiontantalizin marieNo ratings yet
- Low BP - Decreased Cardiac Output - Improved Renal Blood FlowDocument2 pagesLow BP - Decreased Cardiac Output - Improved Renal Blood Flowtantalizin marieNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmias 1: Cardiac Conduc1on System Rhythm Strip Recogni1onDocument4 pagesDysrhythmias 1: Cardiac Conduc1on System Rhythm Strip Recogni1ontantalizin marieNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Pediatric PatientDocument7 pagesAssessment of The Pediatric Patienttantalizin marieNo ratings yet
- Rev. Enf. Ref. RIV14081T INGDocument8 pagesRev. Enf. Ref. RIV14081T INGFernando AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Modul: Intensive Care IDocument62 pagesModul: Intensive Care IHandayu GanitafuriNo ratings yet
- BWS - Ultimate Pull-Ups GuideDocument17 pagesBWS - Ultimate Pull-Ups GuideDebabrata BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- NCM 100 - Theoretical Foundation of NursingDocument13 pagesNCM 100 - Theoretical Foundation of NursingM StarkNo ratings yet
- CS Basket WeavingDocument76 pagesCS Basket Weavingamado cayNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Pharmacology ANS Pharmacology Question PaperDocument5 pagesVeterinary Pharmacology ANS Pharmacology Question PaperG S RaoNo ratings yet
- Developing A Civic Action Plan WorksheetDocument3 pagesDeveloping A Civic Action Plan WorksheetMirella CostaNo ratings yet
- Learners Logbook SITHKOP005Document105 pagesLearners Logbook SITHKOP005Lalit AyerNo ratings yet
- Menopause - RajonivrittiDocument13 pagesMenopause - RajonivrittiSivaram Shanmugha VilasNo ratings yet
- Racism Essay Thesis StatementDocument5 pagesRacism Essay Thesis Statementjfepyntgg100% (2)
- Radiology of Acute Mastoiditis and Its Complications: A Pictorial Review and Interpretation ChecklistDocument6 pagesRadiology of Acute Mastoiditis and Its Complications: A Pictorial Review and Interpretation ChecklistSalma Nurisna UfairohNo ratings yet
- Nursing Competency Program: Medications AdministrationDocument4 pagesNursing Competency Program: Medications Administrationpmnh nqpsNo ratings yet
- DC 221622Document6 pagesDC 221622juanraNo ratings yet
- Consept and Theory of Florence NightingaleDocument7 pagesConsept and Theory of Florence NightingaleWidimongar W. JarqueNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tract System NotesDocument8 pagesGastrointestinal Tract System NotesCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (1)
- Clinebell Howard J., Jr. - The Mental Health Ministry of The Local ChurchDocument211 pagesClinebell Howard J., Jr. - The Mental Health Ministry of The Local ChurchGuilherme EmilioNo ratings yet
- Fe SO4 Feosol. Gonzaga.Document2 pagesFe SO4 Feosol. Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- NSE 121 Clinical Assessment Tool POP Final1Document4 pagesNSE 121 Clinical Assessment Tool POP Final1ramyharoon2004No ratings yet
- 845-Physical Activity TrainerDocument16 pages845-Physical Activity Traineramrishjai9125No ratings yet
- Boiler Inspection PreparationDocument1 pageBoiler Inspection PreparationMirso100% (2)
- Jurnal SinusitisDocument49 pagesJurnal SinusitisAramanda Dian100% (1)
- EMS Result AsDocument2 pagesEMS Result Asjesinmathew123No ratings yet
- The Benefits of Yoga For Mental HealthDocument1 pageThe Benefits of Yoga For Mental HealthAero GlobalNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal FinalDocument6 pagesResearch Proposal Finalapi-408377873No ratings yet
- Essential Newborn Care Protocol: Warsame, Ahmed Sebanes, Kimberky Mae Silao, Emee JoyDocument35 pagesEssential Newborn Care Protocol: Warsame, Ahmed Sebanes, Kimberky Mae Silao, Emee JoyKathlyn SunicoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Foot AnkleDocument13 pagesAnatomy Foot AnkleLalaNo ratings yet