Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 viewsTypes of GMO Genetic Traits Genetic Change
Types of GMO Genetic Traits Genetic Change
Uploaded by
ameenaThis document summarizes different types of genetically modified organisms and their genetic traits. It describes how apples were modified to not brown when cut by inserting genes from other apple species. It also discusses how potatoes were engineered to be resistant to the Colorado potato beetle by inserting genes from Bacillus thuringiensis to produce Bt toxin. Additionally, the document outlines how alfalfa, soybeans, rainbow papaya, cotton, sugar beets, sweet corn, summer squash, and papaya were modified to resist insects or viruses through the insertion of genes from other organisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- CAPE Unit 1 Mark Scheme 2021Document14 pagesCAPE Unit 1 Mark Scheme 2021Armaggedon0% (2)
- The Macadamia Industry in MalawiDocument77 pagesThe Macadamia Industry in Malawiwarlord_ckNo ratings yet
- 3.06 Activity TemplateDocument2 pages3.06 Activity TemplateCommenter •••No ratings yet
- Of The Rise and Split of The Borean IIDocument61 pagesOf The Rise and Split of The Borean IINicolas BruneteauNo ratings yet
- Ashley EalsDocument8 pagesAshley Ealsaye plazaNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument30 pagesGenetic EngineeringDustin RojasNo ratings yet
- Activity GMODocument6 pagesActivity GMOJireh Mae JavierNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified OrganismDocument8 pagesGenetically Modified OrganismAnnhtak PNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18-19. Plant-Pathogen Interactions (Read p1103-1113)Document36 pagesLecture 18-19. Plant-Pathogen Interactions (Read p1103-1113)ganesh kumar penumajjiNo ratings yet
- Topic To Be Presented:: 1. R' GENESDocument3 pagesTopic To Be Presented:: 1. R' GENESChiranjit DebbarmaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Transgenic PlantsDocument48 pagesApplications of Transgenic PlantsAbhi Shetye0% (1)
- Samantha Enopia: Performance TaskDocument4 pagesSamantha Enopia: Performance TaskSamantha EnopiaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnologia MSC 2017 Ora3 MGDocument24 pagesBiotechnologia MSC 2017 Ora3 MGbendezsanetttNo ratings yet
- 7-Transgenic Crops With Biotic, Abiotic and Stress Resistance-2Document11 pages7-Transgenic Crops With Biotic, Abiotic and Stress Resistance-2younusjugnoNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology: and Its ApplicationDocument19 pagesBiotechnology: and Its ApplicationRanjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and Its Applications 01 - Classnotes - Yakeen Fastrack 2023Document23 pagesBiotechnology and Its Applications 01 - Classnotes - Yakeen Fastrack 2023Sarthak RajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 31 - Text, Summar, Objectives, Glossary and FAQ200323060603031111Document12 pagesLecture 31 - Text, Summar, Objectives, Glossary and FAQ200323060603031111biotechdeptNo ratings yet
- Edible Vaccines: Let Thy Food Be Thy MedicineDocument23 pagesEdible Vaccines: Let Thy Food Be Thy MedicineVirendra JoshiNo ratings yet
- Trancegenic PlantsDocument17 pagesTrancegenic PlantsKalyani Sawarkar SatoneNo ratings yet
- 1 Tritrophic InteractionsDocument54 pages1 Tritrophic InteractionskhalidxysNo ratings yet
- Zoology: Biotechnology & It'S ApplicationsDocument16 pagesZoology: Biotechnology & It'S ApplicationsDhanishtaNo ratings yet
- Application of Recombinant DNA Technology Agricultural BiotechnologyDocument27 pagesApplication of Recombinant DNA Technology Agricultural BiotechnologyAnastacio Elston EusoresNo ratings yet
- 2 Biotechnology ApplicationsDocument38 pages2 Biotechnology Applicationsvishal vishalNo ratings yet
- Welcome: Topic To Be PresentedDocument29 pagesWelcome: Topic To Be PresentedChiranjit DebbarmaNo ratings yet
- Breeding Vegetable by DR Jag Paul Sharma Assoc. DirectorDocument25 pagesBreeding Vegetable by DR Jag Paul Sharma Assoc. Directorjagpaul100% (1)
- Are Gmos Tested For Safety?: C. Are They Safe?Document5 pagesAre Gmos Tested For Safety?: C. Are They Safe?Jinjer Ann LanticanNo ratings yet
- Production Technology of TomatoDocument61 pagesProduction Technology of TomatoABHIJITH NAIK S100% (1)
- Viruses 13 02100 v2Document11 pagesViruses 13 02100 v2Tesa SembiringNo ratings yet
- Plant Immunology Lecture 9Document30 pagesPlant Immunology Lecture 9Lavander BlushNo ratings yet
- GM Crops/Livestocks Description Image Advantages DisadvantagesDocument4 pagesGM Crops/Livestocks Description Image Advantages DisadvantagesCarlo Lopez CantadaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3. GMODocument29 pagesLesson 3. GMOEden Faith Aggalao67% (3)
- Pdis 94 5 0551Document6 pagesPdis 94 5 0551Joel JoseNo ratings yet
- Systemic Acquired Resistance (SAR)Document38 pagesSystemic Acquired Resistance (SAR)Arulsia ANo ratings yet
- A Transgenic PlantsDocument6 pagesA Transgenic PlantsDR. YOGESHNo ratings yet
- Plant BiotechnologyDocument52 pagesPlant BiotechnologyMai LinhNo ratings yet
- Stas Week 15 GmoDocument2 pagesStas Week 15 GmoZyra PascualNo ratings yet
- Heath Ann Bot 80, 713Document26 pagesHeath Ann Bot 80, 713Gustavo MarinNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Ms. Jeniffer O. Garcia RN: I. What Is GMO?Document12 pagesSubmitted By: Ms. Jeniffer O. Garcia RN: I. What Is GMO?Jhenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Links and Relationships Between Nutrition, Symbionts and Infection (Fleur, Kawsar, Zach)Document4 pagesThe Links and Relationships Between Nutrition, Symbionts and Infection (Fleur, Kawsar, Zach)rkoed80No ratings yet
- Genetic Manipulationherbicide ToleranceDocument27 pagesGenetic Manipulationherbicide Tolerancefariha pervaizNo ratings yet
- The First Crop Plant Genetically Engineered To Release An Insect Pheromone For DefenceDocument9 pagesThe First Crop Plant Genetically Engineered To Release An Insect Pheromone For DefenceKencana MebelNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Capture HybridizationDocument21 pagesMagnetic Capture HybridizationVageeshbabu HanurNo ratings yet
- Morton Et Al 2000Document6 pagesMorton Et Al 2000Awawawawa UwuwuwuwuNo ratings yet
- Module 11 STSDocument8 pagesModule 11 STSROYYETTE F. FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Crop Protection Product List 1/11Document11 pagesCrop Protection Product List 1/11billu khanNo ratings yet
- Week-3 0Document2 pagesWeek-3 0ioperez1868qcNo ratings yet
- Rice Blast Resistance by SA Pathway by Catangui, Llamson, Pontejos, TrinidadDocument4 pagesRice Blast Resistance by SA Pathway by Catangui, Llamson, Pontejos, TrinidadGlen TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified Organism Intended Learning OucomesDocument8 pagesGenetically Modified Organism Intended Learning OucomesLemuel Glen DacuyanNo ratings yet
- Gene For Genehypothesisitsvalidtyinthepresentscenario 141129111805 Conversion Gate02Document48 pagesGene For Genehypothesisitsvalidtyinthepresentscenario 141129111805 Conversion Gate02BasavarajNo ratings yet
- Stress Breeding-Disease ResistanceDocument6 pagesStress Breeding-Disease ResistanceYASHPAL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Gmo 1Document45 pagesGmo 1Meziel LamanilaoNo ratings yet
- Pathogen Evolution: and Its Effects On Pathogens and Pests: Resistance Gene PyramidingDocument27 pagesPathogen Evolution: and Its Effects On Pathogens and Pests: Resistance Gene Pyramidingदिप्ती मंदा चंद्रभान गवईNo ratings yet
- Scientia Horticulturae PotatoDocument8 pagesScientia Horticulturae PotatoUMA MAHESWARINo ratings yet
- Hypericum Perforatum Plant Cells Reduce Agrobacterium ViabilityDocument8 pagesHypericum Perforatum Plant Cells Reduce Agrobacterium ViabilityFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Antrax (Carbunco)Document21 pagesAntrax (Carbunco)Ginna RuanoNo ratings yet
- Vikaspathania 140922060224 Phpapp02Document18 pagesVikaspathania 140922060224 Phpapp02Nguyễn ĐoànNo ratings yet
- Applications of Genetic Engineering in AgricultureDocument10 pagesApplications of Genetic Engineering in AgricultureDeepika KVNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas Spp. From FoodDocument6 pagesIsolation of Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas Spp. From FoodValentina RondonNo ratings yet
- Entomobicidal Toxins and Proteins of Bacillus Thuringiensis Bacillus ThuringiensisDocument5 pagesEntomobicidal Toxins and Proteins of Bacillus Thuringiensis Bacillus ThuringiensisPravin SurendranNo ratings yet
- Breeding StrategiesDocument53 pagesBreeding StrategiesRazelle Manceras100% (1)
- Elicitation of PRProteinDocument50 pagesElicitation of PRProteinRuben NetcoffNo ratings yet
- Fungi As FoodDocument4 pagesFungi As Fooddd6893452No ratings yet
- Verticle and Horizontal ResistanceDocument10 pagesVerticle and Horizontal Resistanceankit2147No ratings yet
- (English) Long Term Potentiation and Memory Formation, Animation (DownSub - Com)Document3 pages(English) Long Term Potentiation and Memory Formation, Animation (DownSub - Com)Mohammad Reza VaeziNo ratings yet
- Sam Goldstein, Cecil R ReynoldsDocument617 pagesSam Goldstein, Cecil R Reynoldssarhang talebaniNo ratings yet
- Microbial Morphology and TaxonomyDocument6 pagesMicrobial Morphology and TaxonomyJasmin Pearl AndayaNo ratings yet
- CodonChart 1Document3 pagesCodonChart 1ESCUETA John RobertNo ratings yet
- Evolution:: The Origin and Evolution of ManDocument39 pagesEvolution:: The Origin and Evolution of ManManisha Bisht100% (4)
- TigerDocument5 pagesTigerAndreea SimonaNo ratings yet
- Kendra Cherry: The Age Old Debate of Nature vs. NurtureDocument4 pagesKendra Cherry: The Age Old Debate of Nature vs. NurtureCharles Duke100% (1)
- TO Biochemistry TO Biochemistry: Basic Biomolecules and Their Polymers Basic Biomolecules and Their PolymersDocument7 pagesTO Biochemistry TO Biochemistry: Basic Biomolecules and Their Polymers Basic Biomolecules and Their PolymersShubhAm Pal100% (1)
- Octopuses: Quick GuideDocument2 pagesOctopuses: Quick GuideHarshitaNo ratings yet
- Cancer, Stem Cells and Development BiologyDocument2 pagesCancer, Stem Cells and Development Biologysicongli.leonleeNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Sci QRTR 2 Module 4 Intro To Life Student Edition Grade II DescartesDocument53 pagesEarth and Life Sci QRTR 2 Module 4 Intro To Life Student Edition Grade II Descartesmelvin madronalNo ratings yet
- Clicker Case - Down SyndromeDocument44 pagesClicker Case - Down Syndromeshyguy21No ratings yet
- Effect of Different Types of Abiotic Stress On The Growth and Productivity of Linseed (Linum Usitatissimum L.)Document7 pagesEffect of Different Types of Abiotic Stress On The Growth and Productivity of Linseed (Linum Usitatissimum L.)michael 65No ratings yet
- Abera & Mossie. 2022. A Review On Pneumonic Pasteurellosis in Small RuminantsDocument11 pagesAbera & Mossie. 2022. A Review On Pneumonic Pasteurellosis in Small RuminantsFREDY GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of The Cell, Sixth Edition Chapter 7: Control of Gene ExpressionDocument36 pagesMolecular Biology of The Cell, Sixth Edition Chapter 7: Control of Gene ExpressionIsmael Torres-Pizarro100% (2)
- Biol 210 1 Rogge Sum18Document5 pagesBiol 210 1 Rogge Sum18Ronie MarquezNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 Nov 2012 Version 2 Memo EngDocument10 pagesLife Sciences P1 Nov 2012 Version 2 Memo EngedwardnephNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Microbial GrowthDocument18 pagesChapter 5 Microbial GrowthMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Course Outline in Medical MicrobiologyDocument5 pagesCourse Outline in Medical MicrobiologyRami Tounsi100% (2)
- Perspective and Approaches in The Study of Human DevelopmentDocument50 pagesPerspective and Approaches in The Study of Human DevelopmentArguilles, Alexis C.No ratings yet
- Metabolism of LipidsDocument37 pagesMetabolism of LipidsSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Allan-Herndon-Dudley Syndrome MedlinePlus GenetiDocument1 pageAllan-Herndon-Dudley Syndrome MedlinePlus Geneti6ww9fmdccbNo ratings yet
- WordDocument6 pagesWordJonel SorianoNo ratings yet
- Biological Rhythms and SleepDocument50 pagesBiological Rhythms and SleepChaz JosephsNo ratings yet
- QMF27.0160.R6840 v4.1Document24 pagesQMF27.0160.R6840 v4.1Gustavo HoppeNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Earth & Life ScienceDocument16 pagesModule 3 Earth & Life ScienceNicole Mae SumaltaNo ratings yet
Types of GMO Genetic Traits Genetic Change
Types of GMO Genetic Traits Genetic Change
Uploaded by
ameena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesThis document summarizes different types of genetically modified organisms and their genetic traits. It describes how apples were modified to not brown when cut by inserting genes from other apple species. It also discusses how potatoes were engineered to be resistant to the Colorado potato beetle by inserting genes from Bacillus thuringiensis to produce Bt toxin. Additionally, the document outlines how alfalfa, soybeans, rainbow papaya, cotton, sugar beets, sweet corn, summer squash, and papaya were modified to resist insects or viruses through the insertion of genes from other organisms.
Original Description:
Original Title
Types of GMO
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes different types of genetically modified organisms and their genetic traits. It describes how apples were modified to not brown when cut by inserting genes from other apple species. It also discusses how potatoes were engineered to be resistant to the Colorado potato beetle by inserting genes from Bacillus thuringiensis to produce Bt toxin. Additionally, the document outlines how alfalfa, soybeans, rainbow papaya, cotton, sugar beets, sweet corn, summer squash, and papaya were modified to resist insects or viruses through the insertion of genes from other organisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesTypes of GMO Genetic Traits Genetic Change
Types of GMO Genetic Traits Genetic Change
Uploaded by
ameenaThis document summarizes different types of genetically modified organisms and their genetic traits. It describes how apples were modified to not brown when cut by inserting genes from other apple species. It also discusses how potatoes were engineered to be resistant to the Colorado potato beetle by inserting genes from Bacillus thuringiensis to produce Bt toxin. Additionally, the document outlines how alfalfa, soybeans, rainbow papaya, cotton, sugar beets, sweet corn, summer squash, and papaya were modified to resist insects or viruses through the insertion of genes from other organisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
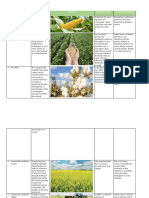
Types of GMO Genetic Traits Genetic Change
To stop browning due to oxidation when diced,
APPLE Non-browning the GMO apple is modified and inserted with
other species of apple.
Reduced Bruising and Amflora (also known as EH92-527-1) was
Black Spot Non- designed to resist attack from the Colorado
POTATO browning potatobeetle due to the insertion of Bt toxin
Low Acrylamide producing genes from the bacterium Bacillus
Blight Resistance thuringiensis.
Glyphosate herbicide (Roundup) tolerance
conferred by expression of a glyphosate-tolerant
ALFALFA Herbicide Tolerance form of the plant enzyme 5-
enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase
(EPSPS) isolated from the soil bacterium
Agrobacterium tumefaciens, strain CP4
Resistance to insect pests, specifically the
SOYBEAN Insect Resistance European corn borer, through expression of the
Herbicide Tolerance insecticidal protein Cry1Ab from Bacillus
thuringiensis
Mutation of P1 and HC-Pro genes resulted in
RAINBOW Disease Resistance the attenuation of PRSV symptoms in papaya.
PAPAYA Expressing the coat protein gene of PRSV are
resistant to the virus.
Resistance to insect pests, specifically the
COTTON Insect Resistance European corn borer, through expression of the
Herbicide Tolerance insecticidal protein Cry1Ab from Bacillus
thuringiensis
Sugar beets H7-1 was developed by first
making a piece of DNA, called an expression
SUGAR BEET Herbicide Tolerance cassette, that contains the cp4 epsps gene for
tolerance to the herbicide glyphosate, which is
the active ingredient in Roundup agricultural
herbicides.
Resistance to insect pests, specifically the
SWEET CORN Insect Resistance European corn borer, through expression of the
Herbicide Tolerance insecticidal protein Cry1Ab from Bacillus
thuringiensis
The virus is immune to the transition of GE virus
SUMMER SQUASH Virus Resistance resistance from yellow squash to zucchini
through traditional breeding (yellow squash and
zucchini are the same species and are readily
available for breeding).
A genetic sequence was used from the virus
PAPAYA Virus Resistance and inserted it into the genome of the papaya. A
number of species of aphids transmit the virus in
a non-persistent manner.
You might also like
- CAPE Unit 1 Mark Scheme 2021Document14 pagesCAPE Unit 1 Mark Scheme 2021Armaggedon0% (2)
- The Macadamia Industry in MalawiDocument77 pagesThe Macadamia Industry in Malawiwarlord_ckNo ratings yet
- 3.06 Activity TemplateDocument2 pages3.06 Activity TemplateCommenter •••No ratings yet
- Of The Rise and Split of The Borean IIDocument61 pagesOf The Rise and Split of The Borean IINicolas BruneteauNo ratings yet
- Ashley EalsDocument8 pagesAshley Ealsaye plazaNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument30 pagesGenetic EngineeringDustin RojasNo ratings yet
- Activity GMODocument6 pagesActivity GMOJireh Mae JavierNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified OrganismDocument8 pagesGenetically Modified OrganismAnnhtak PNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18-19. Plant-Pathogen Interactions (Read p1103-1113)Document36 pagesLecture 18-19. Plant-Pathogen Interactions (Read p1103-1113)ganesh kumar penumajjiNo ratings yet
- Topic To Be Presented:: 1. R' GENESDocument3 pagesTopic To Be Presented:: 1. R' GENESChiranjit DebbarmaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Transgenic PlantsDocument48 pagesApplications of Transgenic PlantsAbhi Shetye0% (1)
- Samantha Enopia: Performance TaskDocument4 pagesSamantha Enopia: Performance TaskSamantha EnopiaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnologia MSC 2017 Ora3 MGDocument24 pagesBiotechnologia MSC 2017 Ora3 MGbendezsanetttNo ratings yet
- 7-Transgenic Crops With Biotic, Abiotic and Stress Resistance-2Document11 pages7-Transgenic Crops With Biotic, Abiotic and Stress Resistance-2younusjugnoNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology: and Its ApplicationDocument19 pagesBiotechnology: and Its ApplicationRanjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and Its Applications 01 - Classnotes - Yakeen Fastrack 2023Document23 pagesBiotechnology and Its Applications 01 - Classnotes - Yakeen Fastrack 2023Sarthak RajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 31 - Text, Summar, Objectives, Glossary and FAQ200323060603031111Document12 pagesLecture 31 - Text, Summar, Objectives, Glossary and FAQ200323060603031111biotechdeptNo ratings yet
- Edible Vaccines: Let Thy Food Be Thy MedicineDocument23 pagesEdible Vaccines: Let Thy Food Be Thy MedicineVirendra JoshiNo ratings yet
- Trancegenic PlantsDocument17 pagesTrancegenic PlantsKalyani Sawarkar SatoneNo ratings yet
- 1 Tritrophic InteractionsDocument54 pages1 Tritrophic InteractionskhalidxysNo ratings yet
- Zoology: Biotechnology & It'S ApplicationsDocument16 pagesZoology: Biotechnology & It'S ApplicationsDhanishtaNo ratings yet
- Application of Recombinant DNA Technology Agricultural BiotechnologyDocument27 pagesApplication of Recombinant DNA Technology Agricultural BiotechnologyAnastacio Elston EusoresNo ratings yet
- 2 Biotechnology ApplicationsDocument38 pages2 Biotechnology Applicationsvishal vishalNo ratings yet
- Welcome: Topic To Be PresentedDocument29 pagesWelcome: Topic To Be PresentedChiranjit DebbarmaNo ratings yet
- Breeding Vegetable by DR Jag Paul Sharma Assoc. DirectorDocument25 pagesBreeding Vegetable by DR Jag Paul Sharma Assoc. Directorjagpaul100% (1)
- Are Gmos Tested For Safety?: C. Are They Safe?Document5 pagesAre Gmos Tested For Safety?: C. Are They Safe?Jinjer Ann LanticanNo ratings yet
- Production Technology of TomatoDocument61 pagesProduction Technology of TomatoABHIJITH NAIK S100% (1)
- Viruses 13 02100 v2Document11 pagesViruses 13 02100 v2Tesa SembiringNo ratings yet
- Plant Immunology Lecture 9Document30 pagesPlant Immunology Lecture 9Lavander BlushNo ratings yet
- GM Crops/Livestocks Description Image Advantages DisadvantagesDocument4 pagesGM Crops/Livestocks Description Image Advantages DisadvantagesCarlo Lopez CantadaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3. GMODocument29 pagesLesson 3. GMOEden Faith Aggalao67% (3)
- Pdis 94 5 0551Document6 pagesPdis 94 5 0551Joel JoseNo ratings yet
- Systemic Acquired Resistance (SAR)Document38 pagesSystemic Acquired Resistance (SAR)Arulsia ANo ratings yet
- A Transgenic PlantsDocument6 pagesA Transgenic PlantsDR. YOGESHNo ratings yet
- Plant BiotechnologyDocument52 pagesPlant BiotechnologyMai LinhNo ratings yet
- Stas Week 15 GmoDocument2 pagesStas Week 15 GmoZyra PascualNo ratings yet
- Heath Ann Bot 80, 713Document26 pagesHeath Ann Bot 80, 713Gustavo MarinNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Ms. Jeniffer O. Garcia RN: I. What Is GMO?Document12 pagesSubmitted By: Ms. Jeniffer O. Garcia RN: I. What Is GMO?Jhenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Links and Relationships Between Nutrition, Symbionts and Infection (Fleur, Kawsar, Zach)Document4 pagesThe Links and Relationships Between Nutrition, Symbionts and Infection (Fleur, Kawsar, Zach)rkoed80No ratings yet
- Genetic Manipulationherbicide ToleranceDocument27 pagesGenetic Manipulationherbicide Tolerancefariha pervaizNo ratings yet
- The First Crop Plant Genetically Engineered To Release An Insect Pheromone For DefenceDocument9 pagesThe First Crop Plant Genetically Engineered To Release An Insect Pheromone For DefenceKencana MebelNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Capture HybridizationDocument21 pagesMagnetic Capture HybridizationVageeshbabu HanurNo ratings yet
- Morton Et Al 2000Document6 pagesMorton Et Al 2000Awawawawa UwuwuwuwuNo ratings yet
- Module 11 STSDocument8 pagesModule 11 STSROYYETTE F. FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Crop Protection Product List 1/11Document11 pagesCrop Protection Product List 1/11billu khanNo ratings yet
- Week-3 0Document2 pagesWeek-3 0ioperez1868qcNo ratings yet
- Rice Blast Resistance by SA Pathway by Catangui, Llamson, Pontejos, TrinidadDocument4 pagesRice Blast Resistance by SA Pathway by Catangui, Llamson, Pontejos, TrinidadGlen TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified Organism Intended Learning OucomesDocument8 pagesGenetically Modified Organism Intended Learning OucomesLemuel Glen DacuyanNo ratings yet
- Gene For Genehypothesisitsvalidtyinthepresentscenario 141129111805 Conversion Gate02Document48 pagesGene For Genehypothesisitsvalidtyinthepresentscenario 141129111805 Conversion Gate02BasavarajNo ratings yet
- Stress Breeding-Disease ResistanceDocument6 pagesStress Breeding-Disease ResistanceYASHPAL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Gmo 1Document45 pagesGmo 1Meziel LamanilaoNo ratings yet
- Pathogen Evolution: and Its Effects On Pathogens and Pests: Resistance Gene PyramidingDocument27 pagesPathogen Evolution: and Its Effects On Pathogens and Pests: Resistance Gene Pyramidingदिप्ती मंदा चंद्रभान गवईNo ratings yet
- Scientia Horticulturae PotatoDocument8 pagesScientia Horticulturae PotatoUMA MAHESWARINo ratings yet
- Hypericum Perforatum Plant Cells Reduce Agrobacterium ViabilityDocument8 pagesHypericum Perforatum Plant Cells Reduce Agrobacterium ViabilityFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Antrax (Carbunco)Document21 pagesAntrax (Carbunco)Ginna RuanoNo ratings yet
- Vikaspathania 140922060224 Phpapp02Document18 pagesVikaspathania 140922060224 Phpapp02Nguyễn ĐoànNo ratings yet
- Applications of Genetic Engineering in AgricultureDocument10 pagesApplications of Genetic Engineering in AgricultureDeepika KVNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas Spp. From FoodDocument6 pagesIsolation of Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas Spp. From FoodValentina RondonNo ratings yet
- Entomobicidal Toxins and Proteins of Bacillus Thuringiensis Bacillus ThuringiensisDocument5 pagesEntomobicidal Toxins and Proteins of Bacillus Thuringiensis Bacillus ThuringiensisPravin SurendranNo ratings yet
- Breeding StrategiesDocument53 pagesBreeding StrategiesRazelle Manceras100% (1)
- Elicitation of PRProteinDocument50 pagesElicitation of PRProteinRuben NetcoffNo ratings yet
- Fungi As FoodDocument4 pagesFungi As Fooddd6893452No ratings yet
- Verticle and Horizontal ResistanceDocument10 pagesVerticle and Horizontal Resistanceankit2147No ratings yet
- (English) Long Term Potentiation and Memory Formation, Animation (DownSub - Com)Document3 pages(English) Long Term Potentiation and Memory Formation, Animation (DownSub - Com)Mohammad Reza VaeziNo ratings yet
- Sam Goldstein, Cecil R ReynoldsDocument617 pagesSam Goldstein, Cecil R Reynoldssarhang talebaniNo ratings yet
- Microbial Morphology and TaxonomyDocument6 pagesMicrobial Morphology and TaxonomyJasmin Pearl AndayaNo ratings yet
- CodonChart 1Document3 pagesCodonChart 1ESCUETA John RobertNo ratings yet
- Evolution:: The Origin and Evolution of ManDocument39 pagesEvolution:: The Origin and Evolution of ManManisha Bisht100% (4)
- TigerDocument5 pagesTigerAndreea SimonaNo ratings yet
- Kendra Cherry: The Age Old Debate of Nature vs. NurtureDocument4 pagesKendra Cherry: The Age Old Debate of Nature vs. NurtureCharles Duke100% (1)
- TO Biochemistry TO Biochemistry: Basic Biomolecules and Their Polymers Basic Biomolecules and Their PolymersDocument7 pagesTO Biochemistry TO Biochemistry: Basic Biomolecules and Their Polymers Basic Biomolecules and Their PolymersShubhAm Pal100% (1)
- Octopuses: Quick GuideDocument2 pagesOctopuses: Quick GuideHarshitaNo ratings yet
- Cancer, Stem Cells and Development BiologyDocument2 pagesCancer, Stem Cells and Development Biologysicongli.leonleeNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Sci QRTR 2 Module 4 Intro To Life Student Edition Grade II DescartesDocument53 pagesEarth and Life Sci QRTR 2 Module 4 Intro To Life Student Edition Grade II Descartesmelvin madronalNo ratings yet
- Clicker Case - Down SyndromeDocument44 pagesClicker Case - Down Syndromeshyguy21No ratings yet
- Effect of Different Types of Abiotic Stress On The Growth and Productivity of Linseed (Linum Usitatissimum L.)Document7 pagesEffect of Different Types of Abiotic Stress On The Growth and Productivity of Linseed (Linum Usitatissimum L.)michael 65No ratings yet
- Abera & Mossie. 2022. A Review On Pneumonic Pasteurellosis in Small RuminantsDocument11 pagesAbera & Mossie. 2022. A Review On Pneumonic Pasteurellosis in Small RuminantsFREDY GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of The Cell, Sixth Edition Chapter 7: Control of Gene ExpressionDocument36 pagesMolecular Biology of The Cell, Sixth Edition Chapter 7: Control of Gene ExpressionIsmael Torres-Pizarro100% (2)
- Biol 210 1 Rogge Sum18Document5 pagesBiol 210 1 Rogge Sum18Ronie MarquezNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 Nov 2012 Version 2 Memo EngDocument10 pagesLife Sciences P1 Nov 2012 Version 2 Memo EngedwardnephNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Microbial GrowthDocument18 pagesChapter 5 Microbial GrowthMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Course Outline in Medical MicrobiologyDocument5 pagesCourse Outline in Medical MicrobiologyRami Tounsi100% (2)
- Perspective and Approaches in The Study of Human DevelopmentDocument50 pagesPerspective and Approaches in The Study of Human DevelopmentArguilles, Alexis C.No ratings yet
- Metabolism of LipidsDocument37 pagesMetabolism of LipidsSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Allan-Herndon-Dudley Syndrome MedlinePlus GenetiDocument1 pageAllan-Herndon-Dudley Syndrome MedlinePlus Geneti6ww9fmdccbNo ratings yet
- WordDocument6 pagesWordJonel SorianoNo ratings yet
- Biological Rhythms and SleepDocument50 pagesBiological Rhythms and SleepChaz JosephsNo ratings yet
- QMF27.0160.R6840 v4.1Document24 pagesQMF27.0160.R6840 v4.1Gustavo HoppeNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Earth & Life ScienceDocument16 pagesModule 3 Earth & Life ScienceNicole Mae SumaltaNo ratings yet