Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Commonly Used Metric System Units
Commonly Used Metric System Units
Uploaded by
Paola Andrea Fdezds Abdul-Rahim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views3 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views3 pagesCommonly Used Metric System Units
Commonly Used Metric System Units
Uploaded by
Paola Andrea Fdezds Abdul-RahimCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
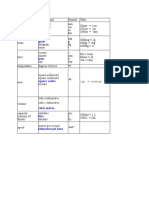
Commonly used metric system units, symbols, and prefixes
In the International System of Units — SI — each physical quantity — length, mass, volume, etc. — is represented by a specific SI
unit. Larger and smaller multiples of that unit are made by adding SI prefixes.
Commonly used metric system units and symbols
Quantity Unit Symbol Relationship
measured
millimeter mm 10 mm = 1 cm
Length, width,
distance, thickness, centimeter cm 100 cm = 1m
girth, etc. meter m
kilometer km 1 km = 1000 m
milligram mg 1000 mg = 1g
Mass gram g
(“weight”)* kilogram kg 1 kg = 1000 g
metric ton t 1t = 1000 kg
Time second s
Temperature degree Celsius °C
square meter m²
Area hectare ha 1 ha = 10 000 m²
square kilometer km² 1 km² = 100 ha
milliliter mL 1000 mL = 1L
Volume cubic centimeter cm³ 1 cm³ = 1 mL
liter L 1000 L = 1 m³
cubic meter m³
meter per second m/s
Speed, velocity
kilometer per hour km/h 1 km/h = 0.278 m/s
kilogram per cubic kg/m³
Density
meter
Force newton N
Pressure, stress kilopascal kPa
watt W
Power
kilowatt kW 1 kW = 1000 W
kilojoule kJ
Energy megajoule MJ 1 MJ = 1000 kJ
kilowatt hour kW·h 1 kW·h = 3.6 MJ
Electric current ampere A
* See Is it “weight” or “mass”? in the FAQ.
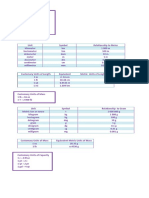
The most commonly used metric prefixes
This table shows the most commonly used SI prefixes.
Prefix Symbol Factor Numerically Name
giga G 109 1 000 000 000 billion**
mega M 106 1 000 000 million
kilo k 103 1 000 thousand
-2
centi c 10 0.01 hundredth
-3
milli m 10 0.001 thousandth
micro μ 10-6 0.000 001 millionth
nano n 10-9 0.000 000 001 billionth**
** The terms billion, trillion, etc., can be ambiguous. The terms are used here in the American English sense, but British English traditionally
defined billion as a million million, rather than a thousand million. However, recent British usage tends to match the American meanings.
A note about usage
Although unit names are ordinary words, note that unit symbols
• are case-sensitive, so uppercase and lowercase letters have different meanings — for example, mm is the millimeter (one-thousandth of a
meter), but Mm is the megameter (one million meters);
• don't have singular and plural forms — it's 1 mL, 2 mL (no “s” at the end); and
• aren't abbreviations, so there's no period after a unit symbol (unless it happens to fall at the end of a sentence).
Some examples and relationships among units
.
1 liter of water weighs 1 kilogram, so 1 cubic meter — 1000 liters — of water weighs 1000 kilograms or 1 metric ton.
A US cent weighs exactly 2.5 g, while the nickel weighs exactly 5 g.
1 mL = 1 cm3
1 milliliter is the same volume as 1 cubic centimeter.
1 mL of water has a mass of approximately 1 g
The mass of 1 milliliter of water is approximately 1 gram.
1 L of water has a mass of approximately 1 kg
The mass of 1 liter of water is therefore approximately 1 kilogram.
1 m3 of water has a mass of approximately 1 t
There are 1000 liters in a cubic meter, so the mass of 1 cubic meter of water is approximately 1000 kilograms or 1 metric ton.
A typical doorknob is 1 m high
Although there's no precise standard for doorknob heights, they're often about 1 meter above the floor.
The diameter of a CD or DVD is 12 cm
A CD or DVD is 12 centimeters (120 millimeters) across. The diameter of the center hole is 15 millimeters.
1 ha is 1002 m2
1 hectare is 10 000 square meters, equivalent to the area of a square 100 meters on a side. A football field is about 100 meters long, so imagine a
square the length of a football field on each side, and that's 1 hectare.
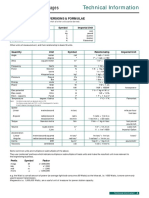
Approximate conversion factors from inch-pound to metric units
This table gives easily remembered, approximate conversion factors for some common units, as well as more precise factors. Boldfaced values are
exact. But remember, estimated values don't warrant precise conversions. If “it was about 100 yards away,” then it was about 100 meters away.
Only if it was exactly 100 yards away would one convert the measurement to 91.44 meters.
More precisely,
To convert from to multiply by Note
multiply by
acres (US survey) hectares (ha) 0.4 0.404 687 3
feet (ft) meters (m) 0.3 0.3048
fluid ounces (fl oz) milliliters (mL) 30 29.573 53 2
gallons (gal) liters (L) 3.8 3.785 411 784 2
inches (in) centimeters (cm) 2.54 2.54
knots kilometers per hour (km/h) 1.852
miles (mi) kilometers (km) 1.6 1.609 344
divide 235.215
miles per gallon (mi/gal) liters per 100 km (L/(100 km))
by mi/gal
miles per hour (mi/h) kilometers per hour (km/h) 1.6 1.609 344
nautical miles kilometers 1.852
ounces (oz) grams (g) 28 28.349 52 1
pound-force (lbf) newtons (N) 4.448 222
0.45
pounds (lb) kilograms (kg) 0.453 592 37 1
or divide by 2.2
pounds per square inch (lbf/in2) kilopascals (kPa) 6.894 757
quarts (qt) liters (L) 0.9 0.946 352 946 2
square feet (ft2) square meters (m2) 0.1 0.092 903 04
2 2
square miles (mi ) square kilometers (km ) 2.6 2.589 988
yards (yd) meters (m) 0.9 0.9144
Note 1. Ounces and pounds refer to avoirdupois units.
Note 2. Fluid ounces, quarts, and gallons refer to US liquid measures.
Info taken from: Copyright © 1998-2007, U.S. Metric Association (USMA), Inc. All rights reserved.
http://lamar.colostate.edu/~hillger/common.html
You might also like
- Full Download Textbook of Biochemistry With Clinical Correlations 7th Edition Devlin Test BankDocument21 pagesFull Download Textbook of Biochemistry With Clinical Correlations 7th Edition Devlin Test Bankisaaccastrole100% (28)
- Definition:: Eg Hyderabad Is 800km From ChennaiDocument6 pagesDefinition:: Eg Hyderabad Is 800km From ChennaiVisalakshi VenkatNo ratings yet
- Conversion TableDocument3 pagesConversion TableEdna Legaspi ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used Metric System Units and SymbolsDocument2 pagesCommonly Used Metric System Units and Symbolsgaylmm100% (2)
- Conversion TableDocument3 pagesConversion TableCrystL SnowNo ratings yet
- Free Kids Metric Conversion PDF FormatDocument1 pageFree Kids Metric Conversion PDF FormatTaner YasavNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factors To Memorize: Unit 02 Honors ChemistryDocument1 pageConversion Factors To Memorize: Unit 02 Honors Chemistry김동주No ratings yet
- English To Metric Sytem ConversionDocument1 pageEnglish To Metric Sytem ConversionRanz RodgerNo ratings yet
- Units and Conversions PDFDocument33 pagesUnits and Conversions PDFiayamaeNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Concept of ThermodynamicseditDocument19 pagesFundamental Concept of ThermodynamicseditMohamad Radhahudin100% (1)
- Technical Information: Back To Contents PagesDocument8 pagesTechnical Information: Back To Contents PagesAditya PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Conversions - Part1Document23 pagesConversions - Part1Kgothatso LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Metric Conversion Chart UsDocument1 pageMetric Conversion Chart UsYerrinn JungNo ratings yet
- Metric Conversion Chart UsDocument1 pageMetric Conversion Chart UsRishel AlamaNo ratings yet
- Unit Conversion of Base and Derived Quantities PDFDocument6 pagesUnit Conversion of Base and Derived Quantities PDFLEONNo ratings yet
- Q2 - MeasurementsDocument4 pagesQ2 - MeasurementsgundamstrikejusticeNo ratings yet
- Technical Information: Engineering Units, Conversions & FormulaeDocument8 pagesTechnical Information: Engineering Units, Conversions & FormulaePeterNo ratings yet
- Notes On Measurements1Document9 pagesNotes On Measurements1tmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Conversion Chart: Length Units How To ConvertDocument2 pagesConversion Chart: Length Units How To Convertdaisuke ʕ•ᴥ•ʔNo ratings yet
- Conversions: Volume Conversion ToolDocument8 pagesConversions: Volume Conversion ToolglsemsNo ratings yet
- Jhango Physics Book3 Corrected - Copy-1Document308 pagesJhango Physics Book3 Corrected - Copy-1Thoko SimbeyeNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Phy 1 MeasurementDocument22 pagesWeek 1 Phy 1 MeasurementAngelica Marie DiegoNo ratings yet
- Gen Physics 1Document2 pagesGen Physics 1Clyde SingsonNo ratings yet
- Converting Units of Base QuantityDocument2 pagesConverting Units of Base QuantityZi Song100% (1)
- Converting Units of Base QuantityDocument2 pagesConverting Units of Base QuantityZi SongNo ratings yet
- 012 MetricConverstion PDFDocument1 page012 MetricConverstion PDFTon FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Customary Units of LengthDocument2 pagesCustomary Units of LengthBea CiriloNo ratings yet
- SI Unit Conversion TableDocument4 pagesSI Unit Conversion TableGhazali ZuberiNo ratings yet
- International System of UnitsDocument2 pagesInternational System of UnitsHerbert Quinto SolisNo ratings yet
- Conversion Units, SI and MetricDocument1 pageConversion Units, SI and MetricbstfrndyrNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument16 pagesScienceshauki.mangontraNo ratings yet
- Converting Measurements HandoutsDocument2 pagesConverting Measurements HandoutsReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Examples:: M KG SDocument8 pagesExamples:: M KG SKCrs100% (1)
- Metric ConversionDocument1 pageMetric Conversionp tanNo ratings yet
- General Physics Module 1 ReviewerDocument9 pagesGeneral Physics Module 1 ReviewerIca Safra100% (2)
- Measurement Conversions: 1 Year 365 Days 1 Day 24 Hours 1 Hour 60 Minutes 1 Minute 60 SecondsDocument4 pagesMeasurement Conversions: 1 Year 365 Days 1 Day 24 Hours 1 Hour 60 Minutes 1 Minute 60 SecondsHalieem YousefNo ratings yet
- Measurement LessonDocument15 pagesMeasurement LessonMatthew SonntagNo ratings yet
- Units of MeasurementDocument2 pagesUnits of MeasurementCatherine Joy BesanaNo ratings yet
- Useful Information-Conversion TablesDocument19 pagesUseful Information-Conversion Tablesshapkov1995No ratings yet
- Conversion TablesDocument2 pagesConversion TablesKumarNo ratings yet
- Units of Measurement ObjectivesDocument6 pagesUnits of Measurement ObjectivesErienne IbanezNo ratings yet
- Besaran Pokok Simbol Besaran Satuan Simbol Satuan Dimensi: PanjangDocument4 pagesBesaran Pokok Simbol Besaran Satuan Simbol Satuan Dimensi: PanjangRizkaadeliaNo ratings yet
- ConversionsDocument2 pagesConversionsRose Marie DaganteNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS1111Document201 pagesPHYSICS1111Kaone LakayNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factors G: For de Common Unit SystemsDocument7 pagesConversion Factors G: For de Common Unit SystemsCintya Stefany Rivadeneyra BurgosNo ratings yet
- Unit Conversion Tables: Length PressureDocument1 pageUnit Conversion Tables: Length PressureJed JunioNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used Prefixes and Numerical Values For SI Units Prefix Symbol Value ExampleDocument4 pagesCommonly Used Prefixes and Numerical Values For SI Units Prefix Symbol Value ExampleJilliane PascualNo ratings yet
- Metric Metric ConversionsDocument3 pagesMetric Metric Conversionsapi-296414340No ratings yet
- CONVERSIONSDocument5 pagesCONVERSIONSAmier-Qhaf Jumadil Hiya-HiyaNo ratings yet
- SI Units and Conversion FactorsDocument6 pagesSI Units and Conversion FactorsbasithalNo ratings yet
- Imperial Vs MetricDocument3 pagesImperial Vs MetricahmedNo ratings yet
- Carry Out Simple Measurment & CalculationDocument56 pagesCarry Out Simple Measurment & Calculationyirgalemle ayeNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Topic 1Document11 pagesThermodynamics Topic 1Sunshine FelongcoNo ratings yet
- Metric System: Prefix Symbol Multiplication Factor Scientific NotationDocument2 pagesMetric System: Prefix Symbol Multiplication Factor Scientific Notationjohn FlanneryNo ratings yet
- Olevel Physics Revised Edition 2016Document426 pagesOlevel Physics Revised Edition 2016rasheedlukman9No ratings yet
- CH 5 MeasurementDocument62 pagesCH 5 MeasurementHarry White100% (1)
- UnconsciousnessDocument6 pagesUnconsciousnessSeema RahulNo ratings yet
- Important Questions TPSDocument3 pagesImportant Questions TPSAnonymous QlZBYqlSqZNo ratings yet
- BITH203 Computer Repair and MaintenanceDocument191 pagesBITH203 Computer Repair and MaintenanceNyashaNo ratings yet
- E-Therapeutics+ - Minor Ailments - Therapeutics - Central Nervous System Conditions - Heat-Related DisordersDocument7 pagesE-Therapeutics+ - Minor Ailments - Therapeutics - Central Nervous System Conditions - Heat-Related DisordersSamMansuriNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument4 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel BanagNo ratings yet
- Seminarul 8Document38 pagesSeminarul 8Alexandra GeantaNo ratings yet
- Post Assesment Question 1Document7 pagesPost Assesment Question 1Ganesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Manual Book GEA Gas Compressor Grasso SCDocument56 pagesManual Book GEA Gas Compressor Grasso SCabedurahmanNo ratings yet
- Dana - Illustrated Parts List PDFDocument38 pagesDana - Illustrated Parts List PDFGonzalo PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation (Physics)Document43 pagesNewton's Law of Universal Gravitation (Physics)Maryanne100% (1)
- 2130o1921s1d81e1Document26 pages2130o1921s1d81e1Balraj MyakaNo ratings yet
- Centrale À Cycle Combiné Bi-Arbres Rades C 1 X 450MW: GT Control Oil Jib Crane Installation ProcedureDocument3 pagesCentrale À Cycle Combiné Bi-Arbres Rades C 1 X 450MW: GT Control Oil Jib Crane Installation ProcedureWajdi MansourNo ratings yet
- Structural Evaluation of Pavements in Eastern India Using Falling Weight DeflectometerDocument19 pagesStructural Evaluation of Pavements in Eastern India Using Falling Weight DeflectometerRakesh Ranjan0% (1)
- Boiling and CondensationDocument16 pagesBoiling and CondensationJunnaid NissarNo ratings yet
- TS-999 v1.5.2 User Manual PDFDocument8 pagesTS-999 v1.5.2 User Manual PDFJari VNo ratings yet
- Como Experimento Falho Teria Provado Que Livre Arbítrio Não Existe Steve Taylor SciamDocument10 pagesComo Experimento Falho Teria Provado Que Livre Arbítrio Não Existe Steve Taylor SciamGardenia AndradeNo ratings yet
- Ma8452 NOTES - by WWW - Easyengineering.net 3Document240 pagesMa8452 NOTES - by WWW - Easyengineering.net 3YUVARAJ YUVANo ratings yet
- Artificial PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesArtificial PhotosynthesisJavier OrnaNo ratings yet
- Backward ClassesDocument101 pagesBackward ClassesSmmch forensic medicineNo ratings yet
- AI Tech Agency - by SlidesgoDocument9 pagesAI Tech Agency - by SlidesgoSULOCHNA KUJURNo ratings yet
- Masteremaco S 488: Dual Shrinkage Compensated, Trowelable Fibre Reinforced Thixotropic Repair MortarDocument2 pagesMasteremaco S 488: Dual Shrinkage Compensated, Trowelable Fibre Reinforced Thixotropic Repair Mortarsurendra_pangaNo ratings yet
- Teacher Resource Bank: GCE Physics A Sample A2 ISA: Damped Harmonic Motion - Question PaperDocument9 pagesTeacher Resource Bank: GCE Physics A Sample A2 ISA: Damped Harmonic Motion - Question PaperAbdul-Ahad LockhartNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationDocument7 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1 Identification조용기No ratings yet
- Earthdawn House and Optional RulesDocument12 pagesEarthdawn House and Optional RulesjasonstierleNo ratings yet
- Order PhthirapteraDocument3 pagesOrder PhthirapteraLawrence LagartoNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Pharmacy: Concepts For Alzheimer's Disease Drug DevelopmentDocument4 pagesInternational Journal of Pharmacy: Concepts For Alzheimer's Disease Drug DevelopmentIndra HedarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 To 2Document169 pagesUnit 1 To 2tbijleNo ratings yet
- Incoming Inspection SOPDocument1 pageIncoming Inspection SOPharishg 213No ratings yet
- Hartley 1980Document8 pagesHartley 1980Alexes Paul TancioNo ratings yet