Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fire Insurance
Fire Insurance
Uploaded by
vaishaliOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fire Insurance
Fire Insurance
Uploaded by
vaishaliCopyright:
Available Formats
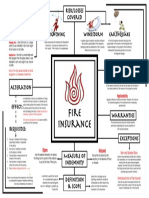
Introduction:
A fire insurance is a contract under which the insurer in return for a consideration (premium)
agrees to indemnify the insured for the financial loss which the latter may suffer due to
destruction of or damage to property or goods, caused by fire, during a specified period. The
contract specifies the maximum amount, agreed to by the parties at the time of the contract,
which the insured can claim in case of loss. This amount is not, however, the measure of the loss.
The loss can be ascertained only after the fire has occurred. The insurer is liable to make good
the actual amount of loss not exceeding the maximum amount fixed under the policy.
The types of losses covered by fire insurance are:-
1. Goods spoiled or property damaged by water used to extinguish the fire.
2. Pulling down of adjacent premises by the fire brigade in order to prevent the progress of
flame.
3. Breakage of goods in the process of their removal from the building where fire is raging
e.g. damage caused by throwing furniture out of window.
4. Wages paid to persons employed for extinguishing fire.
The types of losses not covered by a fire insurance policy are:-
1. Loss due to fire caused by earthquake, invasion, act of foreign enemy, hostilities or war,
civil strife, riots, mutiny, martial law, military rising or rebellion or insurrection.
2. Loss caused by subterranean (underground) fire.
3. Loss caused by burning of property by order of any public authority.
4. Loss by theft during or after the occurrence of fire.
5. Loss or damage to property caused by its own fermentation or spontaneous combustion
e.g. exploding of a bomb due to an inherent defect in it.
6. Loss or damage by lightening or explosion is not covered unless these cause actual
ignition which spread into fire.
A claim for loss by fire must satisfy the following conditions:-
1. The loss must be caused by actual fire or ignition and not just by high temperature.
2. The proximate cause of loss should be fire.
3. The loss or damage must relate to subject matter of policy.
4. The ignition must be either of the goods or of the premises where goods are kept.
5. The fire must be accidental, not intentional.
6. If the fire is caused through a malicious or deliberate act of the insured or his agents, the
insurer will not be liable for the loss.
Properties that are covered:
All moveable/ immoveable properties of the proposer on land (excluding those in transit) broadly
categorized as follows:
i. Building (including plinth and foundations, if required):
• Whether completed or in course of construction (excluding the value of land).
Interiors, Partitions and Electricals.
• Plant & Machinery, Equipments & Accessories (including foundations, if required)
• Bought Second hand.
• Bought New
• Obsolete Machinery
Stocks:
• Raw Material
• Finished Goods
• In process
• In trade belonging to Wholesaler, Manufacturer and Retailer.
Other Contents such as
• Furniture, Fixtures and Fittings • Cables, Piping‘s • Spares, Tools and Stores •
Household goods etc.
Types of Fire Insurance Policies:-
1. Specific policy:- is a policy which covers the loss up to a specific amount which is less
than the real value of the property. The actual value of the property is not taken into
consideration while determining the amount of indemnity.
2. Comprehensive policy:- is also known as 'all in one' policy and covers risks like fire,
theft, burglary, third party risks, etc. It may also cover loss of profits during the period the
business remains closed due to fire.
3. Valued policy: - is a departure from the contract of indemnity. Under it the insured can
recover a fixed amount agreed to at the time the policy is taken. In the event of loss, only
the fixed amount is payable, irrespective of the actual amount of loss.
4. Floating policy:- is a policy which covers loss by fire caused to property belonging to the
same person but located at different places under a single sum and for one premium. Such
a policy might cover goods lying in two warehouses at two different locations. This
policy is always subject to 'average clause.
5. Replacement or Re-instatement policy:- is a policy in which the insurer inserts a re-
instatement clause, whereby he undertakes to pay the cost of replacement of the property
damaged or destroyed by fire. Thus, he may re-instate or replace the property instead of
paying cash. In such a policy, the insurer has to select one of the two alternatives, i.e.
either to pay cash or to replace the property, and afterwards he cannot change to the other
option.
6. Stock declaration policy : This policy is taken for covering the stock where great
fluctuations in the value can happen throughout the contract period. On such policy 75%
of the premium has to be deposited in advance. The maximum liability of insurance
company is specified in the policy by the insured. At the end of year the average stock
and final premium is calculated.
7. Loss of profit policy : Such type of policy covers the loss of profit which sustains as a
result of fire. This policy is also known as consequential loss policy.
8. Sprinkler leakage policy :This type of policy covers the loss of building as a result of
the damage by the leakage of liquid or water.
9. Maximum value with Discount policy :Under this policy one third discount of the
premium paid is refundable to the insured at the maturity of the policy. This policy covers
the risk for maximum amount
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- E93 Examination Guide For Exams From 1 May 2018 To 30 April 2019Document20 pagesE93 Examination Guide For Exams From 1 May 2018 To 30 April 2019tamzNo ratings yet
- Presentation On FIRE InsuranceDocument19 pagesPresentation On FIRE InsuranceAda Sheikh88% (17)
- 114-Insurance and Risk ManagementDocument17 pages114-Insurance and Risk ManagementRobin ThomasNo ratings yet
- Statistics Chapter 3Document30 pagesStatistics Chapter 3Ishaan ChotaiNo ratings yet
- SYBBIDocument24 pagesSYBBIshekhar landageNo ratings yet
- Icici 1Document118 pagesIcici 1sknagarNo ratings yet
- Fire InsuranceDocument4 pagesFire Insuranceজাহিদ হৃদয়No ratings yet
- Bir Ruling Da 288 2005Document4 pagesBir Ruling Da 288 2005Eunice SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Insurance 211883506Document2 pagesCertificate of Insurance 211883506Sam VeeversNo ratings yet
- 1st Shift Rejected Calls Form 09-27-2023Document3 pages1st Shift Rejected Calls Form 09-27-2023Reign Emmanuelle Gabriel ConsorteNo ratings yet
- Rizal Surety Vs CaDocument7 pagesRizal Surety Vs CazaneNo ratings yet
- Fire InsuranceDocument3 pagesFire InsuranceTokie Toki100% (1)
- Revised English Edition IC-34 QA - v1 3 - 8Document16 pagesRevised English Edition IC-34 QA - v1 3 - 8Rajendra UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Notice of LossDocument2 pagesNotice of LossmarwinjsNo ratings yet
- Fire InsuranceDocument21 pagesFire InsuranceJaime DaliuagNo ratings yet
- Q&A's Word FileDocument26 pagesQ&A's Word FileShubham NagpalNo ratings yet
- Gaisano Cagayan Vs Insurance Company of AmericaDocument2 pagesGaisano Cagayan Vs Insurance Company of AmericaPaulo VillarinNo ratings yet
- Fire InsuranceDocument1 pageFire InsuranceBryan RicaldeNo ratings yet
- Functional Definition of Insurance: MeaningDocument6 pagesFunctional Definition of Insurance: MeaningShubham DhimaanNo ratings yet
- 131 General Lnsurance V NG Hua Double InsuranceDocument2 pages131 General Lnsurance V NG Hua Double InsuranceJovelan V. Escaño0% (1)
- Fire Insurance - Types, Coverage, Exclusions & Claim ProcessDocument8 pagesFire Insurance - Types, Coverage, Exclusions & Claim ProcessDrShiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- General InsuranceDocument44 pagesGeneral InsuranceVinitGupta100% (1)
- Alfalah InsuranceDocument38 pagesAlfalah InsuranceMohsan Sheikh0% (1)
- Elements of Marine Insurance ContractDocument6 pagesElements of Marine Insurance ContractSucharitaNo ratings yet
- Global Claims Review 2015:: Business Interruption in FocusDocument40 pagesGlobal Claims Review 2015:: Business Interruption in FocusdianletjNo ratings yet
- FC ProjectDocument13 pagesFC ProjectDipesh GharatNo ratings yet
- What Is Commercial Insurance?Document3 pagesWhat Is Commercial Insurance?Adan HoodaNo ratings yet
- INSURANCEDocument116 pagesINSURANCE시석인한No ratings yet
- Start of Black BookDocument39 pagesStart of Black Bookvipul sutharNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Fire InsuranceDocument18 pages2.0 Fire InsuranceSneha SinhaNo ratings yet