Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C. Sociological Perspectives: Unit 1: Society and Education
C. Sociological Perspectives: Unit 1: Society and Education
Uploaded by
Kayla AlbayOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C. Sociological Perspectives: Unit 1: Society and Education
C. Sociological Perspectives: Unit 1: Society and Education
Uploaded by
Kayla AlbayCopyright:
Available Formats
PROF ED 106 – THE TEACHER AND THE COMMUNITY, SCHOOL CULTURE, AND ORGANIZATIONAL LEADERSHIP
UNIT 1 – SOCIETY AND EDUCATION (A. SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES) DATE SUBMITTED: APRIL 1, 2022
Republic of the Philippines
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY
Bayambang Campus
College of Teacher Education
Bayambang, Pangasinan
A.Y. 2021-2022
Unit 1: Society and Education
C. SOCIOLOGICAL
PERSPECTIVES
(Written Report)
Submitted by:
Albay, Kayla L.
Baladad, Elena
Versoza, Bernadette I.
BEE-EGE II-2
Submitted to:
Assoc. Prof. Gemma D. Escaño
Instructor
April 1, 2022
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 1
PROF ED 106 – THE TEACHER AND THE COMMUNITY, SCHOOL CULTURE, AND ORGANIZATIONAL LEADERSHIP
UNIT 1 – SOCIETY AND EDUCATION (A. SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES) DATE SUBMITTED: APRIL 1, 2022
UNIT 1: SOCIETY AND EDUCATION
A. SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES
OVERVIEW
Sociology is the systematic and scientific study of society and social interaction. In order
to carry out their studies, sociologists identify cultural patterns and social forces and determine
how they affect individuals and groups. They also develop ways to apply their findings to the real
world. Sociologists develop theories to explain social events, interactions, and patterns. A theory
is a proposed explanation of those social interactions. Theories have different scales. Macro-level
theories, such as structural functionalism and conflict theory, attempt to explain how societies
operate as a whole. Micro-level theories, such as symbolic interactionism, focus on interactions
between individuals. Studying sociology is beneficial both for the individual and for society. By
studying sociology people learn how to think critically about social issues and problems that
confront our society. The study of sociology enriches students’ lives and prepares them for careers
in an increasingly diverse world. Society benefits because people with sociological training are
better prepared to make informed decisions about social issues and take effective action to deal
with them.
OBJECTIVES
At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
a) Define what is Sociological Perspectives, its concepts and Theories
b) Identify the progress of Education and Trends implemented in today’s generation
c) Understand the meaning, characteristics and major social institutions
CONTENTS
SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE
A. SOCIAL DIMENSION OF EDUCATION
Sociology
The word Sociology originates from latin prefix :socius, "companion"; and the suffix -ology, "the
study of", from Greek lógos, "knowledge" . Sociology is the systematic study of society.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 2
PROF ED 106 – THE TEACHER AND THE COMMUNITY, SCHOOL CULTURE, AND ORGANIZATIONAL LEADERSHIP
UNIT 1 – SOCIETY AND EDUCATION (A. SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES) DATE SUBMITTED: APRIL 1, 2022
Man is by nature a social animal
Aristotle
The Sociological Perspective is one that observes society through a lens without personal
opinions. It generalizes the causes and actions of individuals into patterns and categories. However,
it not only observes these patterns of society but also tries to explain such patterns or behaviours.
SOCIETY
Group of people who shares teretory and culture,and has common rules and regulations.
"A society is a relatively independent,self perpetuating human group which occupies a territory,
shares a culture and has most of its association within the group"
Horton Hunt
"Society is a system of usagesand procedures, authority and mutual aid,of many groupings and
division,of human behavior and of liberties"
Maciver and Page.
STRUCTURAL FUNCTIONALISM
Society has a complex whole composed of groups working together to achieve stability.
Structural functionalism, in sociology and other social sciences, a school of thought according to
which each of the institutions, relationships, roles, and norms that together constitute a society serves
a purpose, and each is indispensable for the continued existence of the others and of society as a
whole.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 3
PROF ED 106 – THE TEACHER AND THE COMMUNITY, SCHOOL CULTURE, AND ORGANIZATIONAL LEADERSHIP
UNIT 1 – SOCIETY AND EDUCATION (A. SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES) DATE SUBMITTED: APRIL 1, 2022
FUNCTION
Manifest function
- given, obvious
Latent function
- not obvious, covert
DYSFUNCTION
Behavior that disrupt the smooth flow of society
CONFLICT THEORY
Society is composed of groups that compete for limited resources. Focuses on the concept of
social inequality in the division of resources and therefore.the conflict that exist between classes,
which will eventually trigger social change.
CLASS CONFLICT THEORY
Inequality between two classes under capitalism.
Bourgeoisie - owner of means of production such as machines and factory.
Proletariat - the working class sell service to the burgeousie
Racial conflict Theory
Inequality due to the conflict of races and ethnic groups
Gender conflict Theory
Inequality between men and women
SYMBOLIC INTERACTIONISM
Society is composed of people interacting through the use of symbols.A framework on
sociological theory regarding social behavior that emphasizes linguistic or gestural communication
as well as its subjective understanding.
Focus more on actions and reactions of people in society and how and why people defined their
situation.
B. SCHOOLS AND SOCIAL INSTITUTIONS
Social Institution
Is a social structures and social mechanisms of social order and cooperation that govern the behavior
of its members. Is a group of social positions, connected by social relations, performing a social role
Any institution in a society that works to socialize the group of people in it?
Characteristics of an Institution
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 4
PROF ED 106 – THE TEACHER AND THE COMMUNITY, SCHOOL CULTURE, AND ORGANIZATIONAL LEADERSHIP
UNIT 1 – SOCIETY AND EDUCATION (A. SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES) DATE SUBMITTED: APRIL 1, 2022
Palispis ( 2015)
Institutions are purposive.
Relatively permanent in content.
Institutions are structured.
Institutions are a unified structure.
Institutions are necessarily value-laden.
Functions of an Institutions
Palispis (2015)
Institutions simplify social behavior for the individual person.
Provide ready-made forms of social relations and social roles for individual.
Act as agencies of coordination and stability for the total culture.
Control behavior.
Major Social Institutions
The Family
Education
Religion
Economic Institutions
Government as a Social Institution
THE FAMILY
The smallest social institution with the unique function. It is the basic unit of Philippine society
and the educational system where the child begins to learn his ABC. The basic agent of socialization
because it is here where the individual develops values, behaviors, and ways of life through
interaction with members of the family.
Characteristics of a Filipino Family
The family is closely knit and has strong family ties.
The Filipino family is usually extended one and therefore, big.
Kinship ties are extended to include the “compadre’ or sponsors.
Social Functions of the Family
The primary unit for socializing children.
Source of practical and emotional support.
Helps regulate sexual activity and sexual reproduction.
Provides social identity.
Providing Care and Protection
Kinds of Family
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 5
PROF ED 106 – THE TEACHER AND THE COMMUNITY, SCHOOL CULTURE, AND ORGANIZATIONAL LEADERSHIP
UNIT 1 – SOCIETY AND EDUCATION (A. SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES) DATE SUBMITTED: APRIL 1, 2022
a. Nuclear Family
- the primary family consisting of husband, wife and children
b. Extended Family
- it is a family that extends beyond the nuclear family. Consisting of husband, wife, children,
aunts, uncles, grandparents and cousin.
EDUCTION
- a form of learning in which the knowledge, skills, and habits of a group of people are
transferred from one generation to the next through teaching, training, or research.
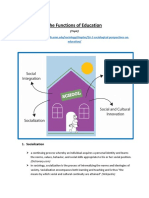
SOCIAL FUNCTION OF SCHOOL
Socialization
Social Integration
Social Placement
Social and Cultural Innovation
INTELLECTUAL PURPOSE
- to teach basic cognitive skills and to transmit specific knowledge.
POLITICAL PURPOSES
to inculcate allegiance to the existing political order(patriotism).
to prepare citizens who will participate in the political order.
to assimilate diverse cultural groups into political order.
to teach children the basic laws of society
SOCIAL PURPOSE
- to socialize children into the various roles, behavior, and values of society.
ECONOMIC PURPOSE
- to prepare students for their later occupational roles, and to select, train, and allocate
individuals into the division of labor.
RELIGION
- is a system of beliefs and rituals that serves to bind people together through shared worship,
thereby creating a social group.
THREE ASPECTS OF RELIGION
RITUALS
- Ceremonies or festivals to express the beliefs.
Example: Praying, chanting, eating some kind of food.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 6
PROF ED 106 – THE TEACHER AND THE COMMUNITY, SCHOOL CULTURE, AND ORGANIZATIONAL LEADERSHIP
UNIT 1 – SOCIETY AND EDUCATION (A. SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES) DATE SUBMITTED: APRIL 1, 2022
BELIEFS
- Faith upon a religion by a community of believers, trust, faith, or confidence in something
called God or supernatural entity.
CODE OF CONDUCTS
- Methods of worshiping set of symbols, methods of living a way of life.
ROLE OF RELIGION IN SOCIETY
giving meaning and purpose to life,
reinforcing social unity and stability,
serving as an agent of social control of behavior,
promoting physical and psychological well-being,
motivating people to work for positive social change.
ECONOMIC INCTITUTIONS
- - Economy is the social institution that ensures maintenance of society through the
production, distribution and consumption of goods and services.
MICOECONOMICS
- Concerned with the specific economic units of parts that makes an economic system and the
relationship between those parts.
MACROECONOMICS
- Concerned with the economy as a whole, or large segments of it.
GOVERNMENT AS ASOCIAL INSTITUTION
- Is the institution which solves conflicts that are public in nature and involve more than a few
people.
THREE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT
1. The executive branch
- headed by the President who functions as both the head of state and the head of government
2. The legislative branch
- enacts legislation, confirms or rejects Presidential appointments, and has the authority to
declare war.
3. Judiciary Branch
- is headed by the Supreme Court
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 7
PROF ED 106 – THE TEACHER AND THE COMMUNITY, SCHOOL CULTURE, AND ORGANIZATIONAL LEADERSHIP
UNIT 1 – SOCIETY AND EDUCATION (A. SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES) DATE SUBMITTED: APRIL 1, 2022
EDUCATION 4.0: RESPONDING TO THE DEMANDS OF SOCIETY
What is Education 4.0?
Education 4.0 is a purposeful approach to learning that lines up with the fourth industrial
revolution and about transforming the future of education using advanced technology and
automation.
Creativity is the foundation of Education 4.0. It emphasizes the need to prepare
students to take on challenges, head-on.
Major trends of Education 4.0
1. A more personalized learning
Education 4.0 appreciates the individuality of every single student and their own pace of
learning. Having a personalized way of teaching will have a greater impact on students to
achieve their outcomes easily.
2. More remote learning opportunities
The cornerstone of Education 4.0 is making learning available anywhere, anytime with the
set of e-learning tools that promote remote and self-paced learning.
3. The plethora of education tools
Education 4.0 offers a clear route to students by making tools and techniques handy in their
learning environment.
4. Project-based learning
The project-driven approach that Education 4.0 supports helps students learn in a fun and
interesting way!
5. Easy and accurate assessment
A more practical way of assessment comes into place with Education 4.0.
6. Data at the fingertips
There are greater insights into the students learning journey with data analytics and reporting
in Education 4.0.
How industry 4.0 affect the education industry?
Why do education institutions need curriculum 4.0?
Education 4.0 is nothing but the curriculum of the future. It is about evolving with the times, and for
higher education institutions, this means understanding what is required of their future graduates.
A majority of hiring managers believe that AI will impact the types of skills their companies
need.
How can education institutions prepare students for Education 4.0?
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 8
PROF ED 106 – THE TEACHER AND THE COMMUNITY, SCHOOL CULTURE, AND ORGANIZATIONAL LEADERSHIP
UNIT 1 – SOCIETY AND EDUCATION (A. SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES) DATE SUBMITTED: APRIL 1, 2022
Remodeling of Curriculum - with special stress on futuristic subjects. With digitization and
automation, a skill-based curriculum is an order of the day. Employers are running short of
skilled workforce and bank on universities and educational institutions to upskill the present
workforce.
Building digital skills - Institutions should have modern workplace skills and focus on
training their faculty to build digital skills to develop fully able students for their workplace.
Soft skills should be made indispensable with a mix of problem-solving, social skills, and
process skills.
Top 10 Digital Skills Education 4.0 demands:
1. Complex Problem Solving.
2. Critical Thinking.
3. Creativity.
4. People Management.
5. Coordinating with Others.
6. Emotional Intelligence.
7. Judgment & Decision Making.
8. Service Orientation.
9. Negotiation
10. Cognitive Flexibility
opt for digital tools for virtual learning (face to face) environments (VLEs) - This is
picking up across the world where students and faculty gain remote access for teaching
through LMS. Learning and teaching, accessing course content, online chat facilities,
discussions, collaborations, peer teaching, blended learning, all happen in flexible hours.
Tweaking of course delivery - There should be a synchronization between the Faculty and
the curriculum taught. Faculty should be open to using technological applications to improve
students’ cognitive learning abilities.
Technology built classrooms - to be initiated across universities, colleges, and higher
education institutions to deliver successful graduates for the cyber-physical systems prevalent
across all industries.
LEARNING POINTS
Some pointers to remember:
Bourgeoisie-owner of means of production such as machines and factory.
Conflict Theory-Society is composed of groups that compete for limited resources. We have
3 conflict theories first is class conflict theory-Inequality between two classes under
capitalism.
Education-Education is a broad concept, referring to all the experiences in which learners
can learn something.
Gender conflict Theory - Inequality between men and women
Proletariat-the working class sell service to the bourgeoisie.
Sociology-The word Sociology originates from Latin prefix :socius, "companion"; and the
suffix -ology, "the study of", from Greek logos, "knowledge".
Society-Group of people who shares territory and culture, and has common rules and
regulations.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 9
PROF ED 106 – THE TEACHER AND THE COMMUNITY, SCHOOL CULTURE, AND ORGANIZATIONAL LEADERSHIP
UNIT 1 – SOCIETY AND EDUCATION (A. SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES) DATE SUBMITTED: APRIL 1, 2022
Structural functionalism-Society has a complex whole composed of groups working
together to achieve stability.
Symbolic interactionism- Society is composed of people interacting through the use of
symbols.
We also have Dysfunction-Behavior that disrupt the smooth flow of society.
We have 2 type of function the manifest function-obvious, given and the latent function-not
obvious, covert.
Social Institution has 5 major, first family, second education, third religion, fourth economic
institution and lastly government.
There are also 6 major trends in Education 4.0, 1. A more personalized learning 2. More
remote learning opportunities 3. The plethora of education tools 4. Project-based learning 5.
Easy and accurate assessment 6. Data at the fingertips
LEARNING ACTIVITIES
Exercise
Multiple Choice
1. It is a form of learning in which knowledge, skills, and habits of a group of people are
transferred from one generation to the next through teaching, training, or research.
A. Family B. Education C. Religion
2. A group of people living together, by the bonds of marriage, blood, adaptation etc.
A. Government B. Religion C. Family
3. Concerned with the economy as a whole, or large segments of it.
A. Microeconomics B. Macroeconomics C. Economics
4. People in general thought of as living together in organized communities with shared
laws, traditions, and values
A. Society B. Institutions C. Function
5. It is the systematic study of society
A. Psychology B. Mythology C. Sociology
6. This branch is headed by the President who functions as both the head of state and the
head of government
A. The Executive Branch B. The Legislative Branch C. Judiciary Branch
7. It is the development of industries in a country or region on a wide scale.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 10
PROF ED 106 – THE TEACHER AND THE COMMUNITY, SCHOOL CULTURE, AND ORGANIZATIONAL LEADERSHIP
UNIT 1 – SOCIETY AND EDUCATION (A. SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES) DATE SUBMITTED: APRIL 1, 2022
A. Sociological B. Function C. Industrialization
8. The use of digital technologies to change a business model and provide new revenue and
value-producing opportunities
A. Digitalization B. 3-D Printing C. Robotics
9. ____ is headed by the Supreme Court.
A. Judiciary Branch B. The Executive Branch C. The Legislative Branch
10. Is a system of beliefs and rituals that serves to bind people together through shared
worship, thereby creating a social group .
A. Government B. Religion C. Economic Institution
ASSESSMENT
Constructed Response
1. Of the several functions of family that were discussed, which function do you think is the
most important? Why?
2. How social changes affect you?
3. In Gender conflict Theory, what are your insights about inequality between men and
women?
SUMMARY
In sociological perspective discussed the social dimension of education including the conflict
theories, structural functionalism and interactionist theories and in school and in social institutions
including family, education, religion, government and economic institutions. It also discussed the
Education 4.0 Responding to the demands of society,This are parts of The sociological perspective
that will invites us to look at our familiar surroundings in a fresh way. It encourages us to take a new
look at the world we have always taken for granted, to examine our social environment with the
same curiosity that we might bring to an exotic foreign culture. The study of sociology leads us into
areas of society that we might otherwise have ignored or misunderstood. Since our world view is
shaped by our personal experience and since people with different social experiences have different
definitions of social reality, sociology helps us to appreciate viewpoints other than our own and to
understand how these viewpoints came into being.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 11
PROF ED 106 – THE TEACHER AND THE COMMUNITY, SCHOOL CULTURE, AND ORGANIZATIONAL LEADERSHIP
UNIT 1 – SOCIETY AND EDUCATION (A. SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES) DATE SUBMITTED: APRIL 1, 2022
REFERENCES
Authored by: OpenStax CNX (N/A), Introduction to Sociology, Retrieved from,
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/sociology/chapter/the-sociological-approach-to-
religion/#:~:text=While%20some%20people%20think%20of,basic%20social
%20needs%20and%20values
Ellway, P. (2005). “The Rational Choice Theory of Religion: Shopping for Faith or
Dropping your Faith?” Retrieved from,
http://www.csa.com/discoveryguides/religion/overview.php
I. Robertson, Sociology, NY: Worth Pub. (1981), The Sociological Perspective,
Retrieved from, https://www.geneseo.edu/sociology/about
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 12
PROF ED 106 – THE TEACHER AND THE COMMUNITY, SCHOOL CULTURE, AND ORGANIZATIONAL LEADERSHIP
UNIT 1 – SOCIETY AND EDUCATION (A. SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES) DATE SUBMITTED: APRIL 1, 2022
Violeta,V.(2002)The Social Dimensions of Philippine Education, Retrieved from,
http://www.merriam-webster.com
Violeta A.Vega Social Dimensions of Philippine Education, Dr. Adelaide Bago
Suvin, C. (2020, Sept. 30) Why should higher education institutions focus on
Education 4.0? Retrieved from: https://www.creatrixcampus.com/blog/Education-4.0?
fbclid=IwAR3VHnfEbxlao6UE7gttueBkMBW_Mv9rlIikcu8omefUtRvkvYI-
VuUR0lE#:~:text=Education%204.0%20is%20a%20purposeful,on%20challenges
%2C%20head%2Don
ZUNHAID TAPIA (N/A), What is family institution and its Characteristics, Retrieved from,
https://www.sociologygroup.com/family-institution-definition-characteristics/
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 13
You might also like
- The Teacher and The Community School Culture and Organizational Leadership Soledad R. TaguibaoDocument31 pagesThe Teacher and The Community School Culture and Organizational Leadership Soledad R. TaguibaoGlenzchie Taguibao91% (55)
- Five Dysfunctions of A Team Assessment Questions - Lencioni - DysfunctionsDocument3 pagesFive Dysfunctions of A Team Assessment Questions - Lencioni - DysfunctionsZeeshan Kazmi100% (2)
- Unit V. Sociological Foundations of Education A. Sociology and Sociology in EducationDocument99 pagesUnit V. Sociological Foundations of Education A. Sociology and Sociology in EducationJamy Dizon Taganas100% (2)
- Socio-Anthropological Foundations of EducationDocument20 pagesSocio-Anthropological Foundations of EducationNestor Balboa100% (2)
- M.A. Sociology of Edu PDFDocument143 pagesM.A. Sociology of Edu PDFRaúlDavidUgaldeDelgado100% (1)
- UCSP DLL Week 2Document7 pagesUCSP DLL Week 2Lev Mazed Sulio83% (6)
- Sociological Foundation of Education-ReportDocument10 pagesSociological Foundation of Education-ReportEric Estrella Silandote100% (5)
- Pangasinan State University Bayambang, Campus College of Teacher Education Bayambang, PangasinanDocument16 pagesPangasinan State University Bayambang, Campus College of Teacher Education Bayambang, PangasinanCha ChaNo ratings yet
- Ed 304 STUDY GUIDE 3 Lesson 5Document6 pagesEd 304 STUDY GUIDE 3 Lesson 5Jireck SibucoNo ratings yet
- Sociology of Education in Philippine SettingDocument21 pagesSociology of Education in Philippine SettingJanice SenseiNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Education 13Document7 pagesDay 1 Education 13Amethyst ChiongNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 104 SG 1 Introduction To Society Community and Education Defining The Basic Concept Unit 1 Society and EducationDocument17 pagesProf Ed 104 SG 1 Introduction To Society Community and Education Defining The Basic Concept Unit 1 Society and EducationWellyn Macaroy100% (3)
- Bae Sociology NotesDocument44 pagesBae Sociology NotesSsentongo Nazil0% (1)
- SOCIOLOGICAL BASIS OF EDUCATION - RemovedDocument20 pagesSOCIOLOGICAL BASIS OF EDUCATION - Removedgouravsuthar379No ratings yet
- Sociological Basis of EducationDocument58 pagesSociological Basis of EducationstellagrecianNo ratings yet
- Social Foundation PDFDocument94 pagesSocial Foundation PDFSelvamSelvam100% (1)
- Course Note and Outline SOC 226 EditedDocument59 pagesCourse Note and Outline SOC 226 EditediobiwoleNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - The Teacher & The Com. SCHL Culture & Orgl. LeadershipDocument33 pagesModule 1 - The Teacher & The Com. SCHL Culture & Orgl. LeadershipPrinces Aubrey Dumpit100% (1)
- Social Dimension PointersDocument18 pagesSocial Dimension PointersJohann EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Educ 213 Prelim ModuleDocument30 pagesEduc 213 Prelim ModuleKarenjoy DuayNo ratings yet
- Paper 16 PDFDocument97 pagesPaper 16 PDFKavani HekhaNo ratings yet
- Functions of EducationDocument5 pagesFunctions of EducationKarren Joy Savuro PalmaNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 104 Written Report Group 1Document11 pagesProf Ed 104 Written Report Group 1Dave Matthew LibiranNo ratings yet
- M.A. Education-103 (1st Semester)Document126 pagesM.A. Education-103 (1st Semester)gouravsuthar379No ratings yet
- (FINAL) Social Institutions-Education, Government, EconomyDocument17 pages(FINAL) Social Institutions-Education, Government, EconomyMariel Paz MartinoNo ratings yet
- HCC 08 SociologyDocument69 pagesHCC 08 SociologySankari ShivaNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER IN EDUC 60 Week 1 To 17Document35 pagesREVIEWER IN EDUC 60 Week 1 To 17Sherlyn Llanera HiguerraNo ratings yet
- M.A. Sociology of Edu.Document143 pagesM.A. Sociology of Edu.Deen Ul HaqqNo ratings yet
- Learning Material 1 Basic Concepts in Educ 147: Read and Understand The Text BelowDocument5 pagesLearning Material 1 Basic Concepts in Educ 147: Read and Understand The Text BelowMark DaveNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document6 pagesModule 1balanopaulamae4No ratings yet
- Sociology Social InstitutionDocument39 pagesSociology Social InstitutionGOUTAM DESHWALINo ratings yet
- Running Head: SOCIOLOGY 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: SOCIOLOGY 1Juma OgutuNo ratings yet
- St. Alexius College Integrated School DepartmentDocument7 pagesSt. Alexius College Integrated School DepartmentKrisTin Magbanua JocsonNo ratings yet
- Social Dimension Final ReportDocument33 pagesSocial Dimension Final ReportLeopoldo Reuteras Morte IINo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Social Science Theories and Their Implications To EducationDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 3 Social Science Theories and Their Implications To EducationJames Arnold TapiaNo ratings yet
- Social Science Sem 1Document123 pagesSocial Science Sem 1faizu vlogNo ratings yet
- Sociological Dimensions of EducationDocument11 pagesSociological Dimensions of EducationSai GuyoNo ratings yet
- Social Dimension SummaryDocument18 pagesSocial Dimension Summarykat agustinNo ratings yet
- Sociology of Education 2Document60 pagesSociology of Education 2ayshakats24No ratings yet
- St. Paul University Philippines: Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500 Basic Education Unit Senior High SchoolDocument27 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines: Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500 Basic Education Unit Senior High SchoolEunicel Balane100% (1)
- Educ 103 The Teacher and The Community School Culture and Organizational LeadershipDocument32 pagesEduc 103 The Teacher and The Community School Culture and Organizational LeadershipPatriciaNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed N5 Social DimensionsDocument15 pagesProf Ed N5 Social DimensionsLance FloreceNo ratings yet
- Florentinos Group Sed Ss 315 Chapter 3Document26 pagesFlorentinos Group Sed Ss 315 Chapter 3Prince Jedi LucasNo ratings yet
- Education Honours Elective Rev1Document69 pagesEducation Honours Elective Rev1Alok Kumar RathNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and The Community, School Culture and Organizational LeadershipDocument34 pagesThe Teacher and The Community, School Culture and Organizational LeadershipAngelica CanapiNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 104 SG 2Document19 pagesProf Ed 104 SG 2jellaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 What Is SocialDocument23 pagesWEEK 1 What Is SocialYda Nur ImanNo ratings yet
- Community Engagement DLP Week 2Document6 pagesCommunity Engagement DLP Week 2Jovan Salibay100% (3)
- SociologyDocument9 pagesSociologyCHeartNo ratings yet
- Group 5 ResearchDocument19 pagesGroup 5 ResearchjeaxhedarNo ratings yet
- Education From SociologicalDocument44 pagesEducation From SociologicalMaria Lorelie100% (1)
- Sociology of EducationDocument7 pagesSociology of EducationDsk ReddyNo ratings yet
- Philippine Society and CultureDocument31 pagesPhilippine Society and CultureMar-Elen Fe Guevara Reñosa100% (1)
- SHS HUMSS UCSP Wk2 1-4Document4 pagesSHS HUMSS UCSP Wk2 1-4Jandeil GurreaNo ratings yet
- Community Engagement DLP Week 2 PDF FreeDocument6 pagesCommunity Engagement DLP Week 2 PDF FreeDexter Jess Dag-umanNo ratings yet
- Sociological Foundation of EdducationDocument187 pagesSociological Foundation of EdducationROMELONo ratings yet
- Study Guide 3-1Document5 pagesStudy Guide 3-1Aegee Cedrick ManicaoNo ratings yet
- Tcsol - C3-C6Document28 pagesTcsol - C3-C6abegail libuitNo ratings yet
- CESC Wks 1 3Document6 pagesCESC Wks 1 3juarezchristoff24No ratings yet
- Summary Of "Education And Society. Consensus Or Conflict" By Carlos Ornelas: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "Education And Society. Consensus Or Conflict" By Carlos Ornelas: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "Scientific Theory Of Culture" By Bronislaw Malinovski: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "Scientific Theory Of Culture" By Bronislaw Malinovski: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Performance Assessment - Written ReportDocument18 pagesUnit 2 Performance Assessment - Written ReportKayla Albay100% (1)
- Albay Kayla L TTL Semi Detailed Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesAlbay Kayla L TTL Semi Detailed Lesson PlanKayla AlbayNo ratings yet
- Albay Kayla L - BEE-EGED ll-2 Intellectual Revolution in AfricaDocument5 pagesAlbay Kayla L - BEE-EGED ll-2 Intellectual Revolution in AfricaKayla AlbayNo ratings yet
- IMRAD by RomeDocument20 pagesIMRAD by RomeKayla AlbayNo ratings yet
- New Conception of Global Relations Emerged From Latin American CountriesDocument11 pagesNew Conception of Global Relations Emerged From Latin American CountriesKayla Albay50% (2)
- Easy Guide To MeditationDocument49 pagesEasy Guide To Meditationapextrader_955187937100% (1)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux-6Document809 pagesRed Hat Enterprise Linux-6lamsal123No ratings yet
- Identity Crisis and Its Impact On Teache1Document11 pagesIdentity Crisis and Its Impact On Teache1Vunti ShardaNo ratings yet
- Math11 SP Q3 M8 PDFDocument12 pagesMath11 SP Q3 M8 PDFJessa Banawan EdulanNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary Education in Pakistan - Key Issues and ChallengesDocument26 pagesPrimary and Secondary Education in Pakistan - Key Issues and ChallengesAhsan 1188% (8)
- Gaurav Jain: Work ExperienceDocument2 pagesGaurav Jain: Work ExperienceGaurav JainNo ratings yet
- RPP-04 / Prosedur Perlaksanaan KuliahDocument9 pagesRPP-04 / Prosedur Perlaksanaan KuliahichirokaguyaNo ratings yet
- Review Center of The Philippines V ErmitaDocument3 pagesReview Center of The Philippines V ErmitaatoydequitNo ratings yet
- Facilitate Learning SessionDocument6 pagesFacilitate Learning SessionReysia Mae B. QuibeteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Civics EduDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Civics EduAulia RahmaNo ratings yet
- Piano Suite Class RM Lesson 24Document4 pagesPiano Suite Class RM Lesson 24geniunetNo ratings yet
- Educational Benefits of Online LearningDocument6 pagesEducational Benefits of Online LearningmalkanthithenabaduNo ratings yet
- Revised Summative Test Based On TOS English 11 2021Document6 pagesRevised Summative Test Based On TOS English 11 2021Henry Kahal Orio Jr.No ratings yet
- Cohen Ndejje CVDocument4 pagesCohen Ndejje CVfedwredNo ratings yet
- LearningDistanceGuidance 686455 7-1Document24 pagesLearningDistanceGuidance 686455 7-1JENNIFER MAGPANTAYNo ratings yet
- 1T Capacitor-Less DRAM Cell Based OnDocument6 pages1T Capacitor-Less DRAM Cell Based OnmaheshNo ratings yet
- Pfeffer Hard Facts Dangerous Half-Truths and Total NonsenseDocument10 pagesPfeffer Hard Facts Dangerous Half-Truths and Total Nonsenselydgry100% (1)
- Proposal of HospitalDocument22 pagesProposal of HospitalShraddhaNo ratings yet
- En Paris Campus Other ProgramsDocument14 pagesEn Paris Campus Other ProgramsPinakpani DasNo ratings yet
- 1 - 2015 NCAE OverviewDocument27 pages1 - 2015 NCAE OverviewGirlie Mae Drilon FloresNo ratings yet
- Avinash Degree College, L.B.Nagar: Department of Management BBA II Yr Curriculum CalendarDocument1 pageAvinash Degree College, L.B.Nagar: Department of Management BBA II Yr Curriculum CalendarNIMMANAGANTI RAMAKRISHNANo ratings yet
- New PTET - SyllabusDocument4 pagesNew PTET - SyllabusSourav Subramanya ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- S4 ScholDocument231 pagesS4 ScholTara ShettigarNo ratings yet
- Math Year Planning Form 5 CVQ 22-23Document6 pagesMath Year Planning Form 5 CVQ 22-23Mencarty DocentNo ratings yet
- Nursing Intervention and Smoking Cessation: A Meta-AnalysisDocument17 pagesNursing Intervention and Smoking Cessation: A Meta-AnalysisingevelystareslyNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Teachers' Perceived Readiness For Online Collaborative Learning: A Case Study in MalaysiaDocument13 pagesFactors Affecting Teachers' Perceived Readiness For Online Collaborative Learning: A Case Study in MalaysiaSulaini OmbiNo ratings yet
- Unit 11-Looking BackDocument18 pagesUnit 11-Looking BackMarlon Gonzales DagaNo ratings yet
- IT Curriculum Guide Grade 9Document39 pagesIT Curriculum Guide Grade 9Paul Jaisingh67% (3)
- Borrego (2017) PDFDocument10 pagesBorrego (2017) PDFBryan TorresNo ratings yet