Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Map Final Copy1
Concept Map Final Copy1
Uploaded by
api-608271845Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concept Map Final Copy1
Concept Map Final Copy1
Uploaded by
api-608271845Copyright:
Available Formats
1
Concept Mapping
4832 Nursing Care of Children and Families
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis
2
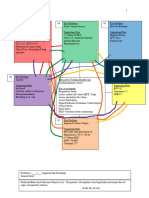
Key Problem 1
Impaired Gas Exchange Key Problem 5 Key Problem 2
Supporting Data: SLOPPY COPY
Impaired Urinary Ineffective Airway
O2 reported at 80-88 before Elimination Clearance
oxygen administration Supporting Data: Supporting Data:
Respiratory panel film array INC BUN: 29 Increased production of
positive for INC Creatinine: 1.54 secretions
Rhinovirus/Enterovirus Anuria Use of suctioning
X-Ray of chest showed lungs Reduced glomerular Abnormal breath
hyperinflated filtration rate resulting in sounds: wheeze
Continuous Oxygen the kidney’s inability to Bronchospasm
Administration through nasal excrete Meds: Albuterol
cannula- only .325L d/t weening
off
Nasal Suctioning
Nebulizer used- Albuterol
Destruction of alveoli
Inability to move secretions
Reduced tolerance for activity Reason For Needing Health Care Key Problem 7
Acute on Chronic Respiratory Failure + Acute Pain
End Stage Renal Failure Supporting data:
Key Problem 4 Key Assessments Facial Grimacing
Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Skin: Nasal Cannula taped to face Crying
Body Requirements GI :I&O, d/t kidney dysfunction RR & BP
Supporting Care Respiratory: lung sounds, respiratory effort increased while
Weight in 1st%ile, (6.185kg) and pulse oximetry d/t respiratory failure suctioning
Loss of muscle mass Nutritional Status FLACC scale used
Poor muscle tone Temp + Vitals score 8
Hypotonia
Height in 68th%ile
Key Problem 3 Key Problem 6
Risk for infection Decreased Cardiac Output
Supporting Data: Supporting data:
Malnutrition: Fluid imbalances affecting
Key Problem 8 weight in 1st%ile circulating volume,
Caregiver Role Strain Decreased myocardial workload
Supporting data: platelets: 202 Alteration in rate, rhythm,
Lack of visitation by Decreased cardiac conduction
parents Lymphocytes: 34 Electrolyte imbalances:
Chronically Ill child Inadequate Sodium 130, Chloride 90
Child loves to be held primary defenses: Urea
due to lack of parent stasis of secretions Deposition of calcium
phosphate
Broviac Catheter in right
upper chest
Use of Alteplase (Cathflo)
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis
3
Problem # 1: Impaired gas Exchange
General Goal: Participate in treatment regimen within the level of ability/situation.
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will Demonstrate improved ventilation
and adequate oxygenation of tissues by ABG’s WNR and be free of symptoms of respiratory
distress on day of care.
Nursing Interventions:
1. Assess and record respiratory rate, depth. Note the use of accessory muscles,
pursed-lip breathing, inability to speak or converse.
2. Monitor O2 saturation and titrate oxygen to maintain Sp02 between 88% to 92%
3. Provide humidified oxygen as ordered
Patient Responses:
1. Patient showed a normal respiratory rate and depth
2. Patient’s O2 saturation was maintained within normal limits
3. Patient was administered oxygen as ordered and did not show signs of respiratory
distress
4. Patient was suctioned as ordered and showed signs of a clearer airway and
reduction of productive cough.
Evaluation of outcomes objectives: The interventions in this situation helped the patient maintain an adequate
gas exchange and kept vital signs within normal limits. Goal met.
Problem # 2: Ineffective Airway Clearance
General Goal: Maintain airway patency with breath sounds clear/clearing.
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will demonstrate behaviors to improve
airway clearance, cough effectively and expectorate secretions on day of care.
on the day of care.
Nursing interventions: The nurse will….
1. Observe characteristics of cough (persistent, hacking, moist). Assist with measures
to improve the effectiveness of cough effort.
2. Suction the patient to break up and reduce secretions
3. Administer bronchodilators
Patient Responses:
1. Improved coughing effort
2. Patient showed lack of productive cough after suctioning
3. Patient showed less labored breathing after administration of Albuterol
Evaluation of outcomes objectives: The interventions in this situation allowed for the patient to maintain
airway patency with breath sounds and improved airway clearance. Goal Met.
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis
4
Problem 3: Risk for infection
General Goal: Patient remains free of infection
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): Patient will remain free of infection by
participating in breathing exercises and finishing prescribed feeds on day of care
Nursing Interventions, The nurse will…
1. Obtain sputum specimen by deep coughing or suctioning for Gram’s stain,
culture, and sensitivity
2. Demonstrate and assist the patient in the disposal of tissues and sputum. Stress
proper handwashing, and use gloves when handling or disposing of tissues,
sputum containers
3. Limit visitors. provide masks and gowns as indicated.
Patient responses:
1. Patient was negative for infection upon cultures
2. Patient was not exposed to improper handwashing, absence of gloves, or any
other means of infectious disease.
3. Patient was protected by being cleaned and having visitors wear PPE as indicated
due to risk for infection.
Evaluation of outcomes objectives: The interventions in this situation allowed for
the patient to remain free of infection when previously listed as a high risk for
infection. Goal met.
Problem 4: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements
General Goal: Display progressive weight gain toward the goal as appropriate.
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): Patient will Demonstrate
behaviors/lifestyle changes to regain and/or maintain an appropriate weight.
Nursing Interventions: Nurse will…
1. Auscultate bowel sounds to assess for gastric motility and constipation related to
limited fluid intake and hypoxemia
2. Feed the patient high calorie foods to maintain body weight and muscle mass
3. Weigh the patient and record
Patient responses:
1. Patient had bowel sounds present and did not show diminished or hypoactive
bowl sounds
2. Patient ate the prescribed feedings fully
3. Patient was cooperative in taking weight related to caloric needs which is helpful
in the adequacy of developing a nutritional plan
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis
5
Evaluation of outcomes objectives: These interventions helped the patient
regain and maintain an appropriate weight and showed a progressive gain
towards appropriate weight. Goal Met.
Problem 5: Decreased Cardiac Output
General Goal: Improve cardiac output
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): Maintain cardiac output as
evidenced by BP and heart rate within patient’s normal range; peripheral
pulses strong and equal with prompt capillary refill time.
Nursing interventions: Nurse will...
1. Evaluate heart sounds, BP, peripheral pulses, capillary refill, vascular
congestion, temperature, and sensorium or mentation.
2. Assess activity level, response to activity.
3. Monitor Electrolytes (potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium), BUN and
Creatinine
Patient Responses:
1. Patient did not show signs of sudden hypotension, narrow pulse, diminished
or absent peripheral pulses, JVD, pallor, or medical emergencies
2. Patient did not show signs of weakness associated with heart failure and
anemia
3. Patient’s electrolytes were still out of normal range but did not get worse and
most of them improved including creatinine and sodium.
Evaluation of outcomes objectives: These interventions helped the patient
maintain cardiac output and avoid signs of decreased cardiac output. Goal
met.
Problem 6: Impaired Urinary Elimination
General Goal: Patient shows signs of healthy urinary elimination
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): Patient will urinate without
bladder distention, urine retention, pain or discomfort, and will eliminate a
normal amount of urine on day of care.
Nursing interventions: Nurse will…
1. Review for laboratory test for changes in renal function.
2. Palpate bladder and assess color of urine
3. Determine client’s usual daily fluid intake
Patient Responses:
1. Patient did not show any negative changes in renal function on day of
care.
2. Patient did not show signs of urinary retention or increased urination.
Patient’s urine was also appropriately colored
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis
6
3. Patient took in the required number of fluids for the day based on weight
of 6.2 kg
Evaluation of outcomes objectives: These interventions helped the
patient remain free of impaired urinary elimination, bladder distention,
urine retention, pain, and discomfort. Goal met.
Problem 7: Acute Pain
General goal: Patient will be without pain
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will remain
free of unpleasant emotional and sensory experience and show a lower
sign of pain on the FLACC scale by end of shift
Nursing Interventions: The nurse will:
1. Monitor and record patient’s vital signs to report an increase of pain if
necessary
2. Perform a comprehensive assessment of pain location, onset,
characteristics, and frequency
3. Nurse will rate the patient’s pain on the FLACC scale
Patient responses:
1. Patient did not show an increase in vital signs such as HR, BP, RR,
regarding pain
2. Patient did not show signs of pain during assessment of specific
locations.
3. Patient showed a FLACC rating of 4 at the end of shift-improving
from 8 at the beginning
Evaluation of outcome objectives: These interventions helped the
patient remain fee of pain and through assessment the patient was
able to be evaluated for acute pain during the shift. Goal met.
Problem 8: Caregiver Role Strain
General Goal: Assess for neglect and abuse of the care recipient
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The caregiver-care
recipient relationship will be improved, and the care recipient will
receive more safety and bonding by end of stay in hospital.
Nurse interventions. Nurse will…
1. Ascertain the caregiver’s knowledge and ability to implement
patient care, including bathing, skin care, safety, nutrition,
medications, and ambulation.
2. Evaluate the family communication pattern.
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis
7
3. Evaluate the caregiver’s appraisal of the caregiving situation, the
level of understanding, and willingness to assume caregiver role.
Patient Responses
1. Patient caregiver is informed of the fundamental guidance needed
to enhance the relationship to the recipient
2. Patient is informed that mutually satisfying relationships promote a
therapeutic caregiving experience.
3. Patient caregiver did not show up during the day of care.
Evaluation of outcome objectives: These interventions are good
means of helping the child-parent relationship healthily. These
planned interventions could not be fulfilled fully because of the
lack of presence of the caregiver. Goal not met.
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis
You might also like
- Assessment & Reasoning Cardiac System: Suggested Cardiac Nursing Assessment Skills To Be DemonstratedDocument8 pagesAssessment & Reasoning Cardiac System: Suggested Cardiac Nursing Assessment Skills To Be DemonstratedSharon Tanveer100% (1)
- Ebersole and Hess Toward Healthy Aging 9th Edition Touhy Test BankDocument6 pagesEbersole and Hess Toward Healthy Aging 9th Edition Touhy Test BankThomasClinewpsix100% (13)
- St. Anthony College of Roxas City, Inc.: Case Study For Pediatric Nursing Clinical RotationDocument15 pagesSt. Anthony College of Roxas City, Inc.: Case Study For Pediatric Nursing Clinical RotationJudy Mae ObamosNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Finished 2Document6 pagesConcept Map Finished 2api-352785497100% (1)
- Questions NursingDocument8 pagesQuestions NursingJeyarajasekar Ttr100% (3)
- OSCE Stop - Lecture Long HistoryDocument18 pagesOSCE Stop - Lecture Long HistorycrystalsheNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Concept Map Care Plan For Critical Care PatientDocument11 pagesAssessment and Concept Map Care Plan For Critical Care Patientapi-546697029No ratings yet
- Concept Map 2020Document4 pagesConcept Map 2020api-546505804No ratings yet
- 4832 Concept MapDocument7 pages4832 Concept Mapapi-508446364No ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument10 pagesConcept Mapapi-608044542No ratings yet
- Brooke Baker Concept Map 4840 Complex Care: P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002Document10 pagesBrooke Baker Concept Map 4840 Complex Care: P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002api-546799391No ratings yet
- Concept Map FinalDocument5 pagesConcept Map Finalapi-545001894No ratings yet
- Concept Map Complex Care 2017Document7 pagesConcept Map Complex Care 2017api-401537905No ratings yet
- Concept Map RSV 4Document10 pagesConcept Map RSV 4api-546577761No ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument5 pagesConcept Mapapi-662323379No ratings yet
- Peds Concept Map - FinalDocument6 pagesPeds Concept Map - Finalapi-660321588No ratings yet
- 4832 Concept MapDocument9 pages4832 Concept Mapapi-663135887No ratings yet
- Concept Map PedsDocument6 pagesConcept Map Pedsapi-498759347No ratings yet
- Concept Map Critical CareDocument5 pagesConcept Map Critical Careapi-546401036No ratings yet
- Concept Map Critical CareDocument6 pagesConcept Map Critical Careapi-508559825No ratings yet
- Resume of Respiratory ProblemDocument5 pagesResume of Respiratory ProblemIbi Yulia SetyaniNo ratings yet
- Rle RequirementsDocument8 pagesRle RequirementsUzziel Galinea TolosaNo ratings yet
- Clustering Data Sheet and Concept Map and Nursing Care Plan HTNDocument4 pagesClustering Data Sheet and Concept Map and Nursing Care Plan HTNAyman NabilNo ratings yet
- CC - Concept MapDocument2 pagesCC - Concept Mapapi-546518436No ratings yet
- 4832 Concept MapDocument3 pages4832 Concept Mapapi-498427226No ratings yet
- 4832 Concept MapDocument7 pages4832 Concept Mapapi-739571122No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Ineffective Airway Clearance: Arranged byDocument9 pagesNursing Care Ineffective Airway Clearance: Arranged byAlri LestariNo ratings yet
- CC Concept MapDocument6 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-741058487No ratings yet
- Group 2B: A Pulmonary Histoplasmosis CaseDocument58 pagesGroup 2B: A Pulmonary Histoplasmosis CaseAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Concept Map Template Final 2Document6 pagesCritical Care Concept Map Template Final 2api-740444719No ratings yet
- CC Concept MapDocument5 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-663024375No ratings yet
- Complex Care Clinical Concept Map Sara Ciletti Youngstown State UniversityDocument9 pagesComplex Care Clinical Concept Map Sara Ciletti Youngstown State Universityapi-590353096No ratings yet
- RLE Simulation Scenario For Clinical Practice: (Care of Patients With Alterations in Oxygenation)Document13 pagesRLE Simulation Scenario For Clinical Practice: (Care of Patients With Alterations in Oxygenation)Biway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Labrato - Kayla AHN596-801 SOAP#1Document10 pagesLabrato - Kayla AHN596-801 SOAP#1Kayla LabratoNo ratings yet
- Careplan 2 NSG 434 CCDocument8 pagesCareplan 2 NSG 434 CCapi-509642710No ratings yet
- Critical Care Concept Map FinishedDocument7 pagesCritical Care Concept Map Finishedapi-604156447No ratings yet
- (ACC ENGLISH) ASKEP HiperglikemiaDocument11 pages(ACC ENGLISH) ASKEP HiperglikemiaWenNo ratings yet
- Case Study Jim SandersonDocument6 pagesCase Study Jim SandersonJessica McAlexanderNo ratings yet
- Darunday NCP Rot 3Document12 pagesDarunday NCP Rot 3Ezra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- The Nursing Process FormatDocument11 pagesThe Nursing Process FormatMichelle Gee MagdaleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument22 pagesNursing Care Planaln00550% (2)
- RLE Simulation Scenario For Clinical Practice: (Care of Patients With Alterations in Oxygenation)Document12 pagesRLE Simulation Scenario For Clinical Practice: (Care of Patients With Alterations in Oxygenation)Biway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Brooke Baker Concept Map 4832 Nursing Care of Children and FamiliesDocument10 pagesBrooke Baker Concept Map 4832 Nursing Care of Children and Familiesapi-546799391No ratings yet
- Concept Map Template - Andreanna TocickiDocument5 pagesConcept Map Template - Andreanna Tocickiapi-741174198No ratings yet
- Concept Map CCDocument4 pagesConcept Map CCapi-738778945No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Patient With ArrhythmiasDocument30 pagesNursing Care Patient With ArrhythmiasSalma Eka OktaryzaNo ratings yet
- Askep CKD Bhs InggrisDocument15 pagesAskep CKD Bhs InggrisFitri MulyaNo ratings yet
- B IngDocument8 pagesB IngFikriNo ratings yet
- Kegawatan Napas Pada AnakDocument43 pagesKegawatan Napas Pada AnakRaelna SahaarNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument16 pagesBronchial AsthmaMOLINA, TANJA JAYNENo ratings yet
- Concept Map f21 FinishedDocument5 pagesConcept Map f21 Finishedapi-601070065No ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- Cretenism Case StudyDocument8 pagesCretenism Case StudyMonica Marie MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis: Primary Concept Nutrition Interrelated Concepts (In Order of Emphasis)Document12 pagesCirrhosis: Primary Concept Nutrition Interrelated Concepts (In Order of Emphasis)Peggy100% (1)
- SlideDocument19 pagesSlideMuslih FerecovNo ratings yet
- FG 6 - Assessment Form For The Older AdultsDocument7 pagesFG 6 - Assessment Form For The Older AdultsALFI NURUL IMANINo ratings yet
- UtsaDocument17 pagesUtsaCallie ParkNo ratings yet
- PST Partum HemorrhageDocument15 pagesPST Partum HemorrhageSampat Kumawat100% (1)
- Concept Map Templatef21Document4 pagesConcept Map Templatef21api-741272284No ratings yet
- SOAP Note TemplateDocument5 pagesSOAP Note TemplateSyed Shams Haider MashhadiNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa Case StudyDocument7 pagesPlacenta Previa Case StudyKing NavsunNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument5 pagesDocumentMayMay AscadoFNo ratings yet
- Orchidoscopy Journal FixDocument23 pagesOrchidoscopy Journal FixAgung IndraNo ratings yet
- Impact of Digital Media On Sleep Pattern Disturbance in Medical and Nursing StudentsDocument7 pagesImpact of Digital Media On Sleep Pattern Disturbance in Medical and Nursing StudentsValarmathiNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Diseases PDFDocument41 pagesNeonatal Diseases PDFmomobelle100% (1)
- 2020-21 P3 UPPER-INTERMEDIATE GLOBED ACHIEVE 3000 ArrangementsDocument3 pages2020-21 P3 UPPER-INTERMEDIATE GLOBED ACHIEVE 3000 ArrangementsJust QuotesNo ratings yet
- Pamphlet Template - Prevention of SmokingDocument1 pagePamphlet Template - Prevention of SmokingDamia insyirah Norman (Esss)No ratings yet
- Mathematical Modeling of Seir Type To Co 751ddd02Document10 pagesMathematical Modeling of Seir Type To Co 751ddd02Ayu AyuNo ratings yet
- Pemakaian April 2022Document9 pagesPemakaian April 2022nurulNo ratings yet
- Simplify Insulin Therapy With IDegAsp Co-FormulationDocument31 pagesSimplify Insulin Therapy With IDegAsp Co-FormulationRiamintan SihotangNo ratings yet
- Robert G. Gish, MD CV - May 2014Document221 pagesRobert G. Gish, MD CV - May 2014Robert G. Gish, MDNo ratings yet
- Multinational Pharmaceutical Companies in BangladeshDocument1 pageMultinational Pharmaceutical Companies in BangladeshXd Dip100% (1)
- Labiaplasty: A Guide For WomenDocument3 pagesLabiaplasty: A Guide For WomenBudi Iman SantosoNo ratings yet
- Ethics of DentistryDocument20 pagesEthics of DentistrytayabakhanNo ratings yet
- Renal Transplant ThesisDocument8 pagesRenal Transplant Thesisicatryhig100% (2)
- Resume Allyssa FarrisDocument3 pagesResume Allyssa Farrisapi-239462063No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document13 pagesUnit 2jamilaakhatunnNo ratings yet
- DClinPsy Course InformationDocument2 pagesDClinPsy Course InformationAlice NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ve Efn2 TB U03Document9 pagesVe Efn2 TB U03Milka Rocha FloresNo ratings yet
- MAPEH (Health) : Quarter 1 - Module 1: Consumer Health: Assessment of Health Information, Products, and ServicesDocument15 pagesMAPEH (Health) : Quarter 1 - Module 1: Consumer Health: Assessment of Health Information, Products, and ServicesAlbert Ian Casuga100% (1)
- Natural History of Aortic StenosisDocument81 pagesNatural History of Aortic StenosisLioraNo ratings yet
- Doh Ao 2020-0022Document17 pagesDoh Ao 2020-0022Mohrein H. Ismael VINo ratings yet
- Nurs 252 Critical Thinking SummaryDocument5 pagesNurs 252 Critical Thinking Summaryapi-284824610No ratings yet
- Betty Neuman ReportDocument5 pagesBetty Neuman ReportKathleen BatallerNo ratings yet
- JoeoeoeoeDocument31 pagesJoeoeoeoeBSRT1A BERBANO, IAN JEWEL M.No ratings yet
- LEPTOSPIROSISDocument14 pagesLEPTOSPIROSISNica Paredes MiravallesNo ratings yet
- CD HandoutsDocument80 pagesCD HandoutsMayflor GuiyabNo ratings yet