Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What's A Carboxyl Group?: Carboxyl Remains Stable When Ionized
What's A Carboxyl Group?: Carboxyl Remains Stable When Ionized
Uploaded by
Jen AdvientoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What's A Carboxyl Group?: Carboxyl Remains Stable When Ionized
What's A Carboxyl Group?: Carboxyl Remains Stable When Ionized
Uploaded by
Jen AdvientoCopyright:
Available Formats
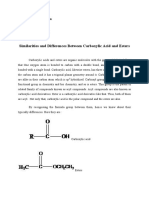
With a molecular formula of COOH, structure is of utmost importance when it comes to
carboxyl groups. Discover how to identify the properties of this functional group. Updated:
10/11/2021
What's a Carboxyl Group?
A carboxyl group is a very common functional group seen in chemistry. A carboxyl group is
defined as having a carbonyl and hydroxyl group both linked to a carbon atom. To refresh your
memory, a carbonyl group is a carbon double-bonded to an oxygen, and a hydroxyl group is an
OH group. As a side note, don't be fooled by the term carboxy group. This is just another way
to say carboxyl group.
A great way to make sure you know you are dealing with carboxyl is to be on the lookout for
two things: an OH and a carbon double-bonded to an oxygen. Better yet, if you look at the word
carboxyl we can break it down into two parts: 'carb' and 'oxyl.' When you see 'carb' think carbon
atom. When you see '-oxyl' think hydroxyl group. The molecular formula for a carboxyl group is
COOH.
Carboxyl Group Formula
When you hang out with carboxyl as an organic compound, you receive the benefit of joining
the club of acidity. Carboxyl groups will make organic compounds acidic because of their own
ionizing property. Let's dig a little deeper on this subject of carboxyl's ionizing property.
Carboxyl groups will ionize themselves by letting go of the hydrogen atom on the hydroxyl
group. This process of ionizing themselves occurs often. When the hydrogen atom is free
floating, it is now called a free proton. It is the release of this hydrogen atom that makes a
carboxyl group acidic.
But what does that mean for the oxygen atom? Well, instead of remaining lonely and sad that
hydrogen left, the oxygen atom will become negatively charged. As a comeback to losing his pal
hydrogen, the oxygen atom will go as far as sharing this negative charge with the second
oxygen atom present. By sharing a negative charge between both oxygen atoms, the carboxyl is
able to remain stable while ionized.
Carboxyl remains stable when ionized.
Wait, so why is the carboxyl group so willing to let the hydrogen go? The answer goes back to
stability. When hydrogen is present, carboxyl is linked by a single bond to the hydroxyl group
and a double bond to the oxygen atom. These two different bonds make carboxyl feel uneasy
as more energy is required to maintain its configuration. When hydrogen leaves, the double
bond is broken, and now carboxyl is free to not only lower its energy state but also increase its
stability. Hence, it makes perfect sense why carboxyl is so quick to let hydrogen go and turn
into an acid.
Properties of carboxyl groups
Carboxyl vs. Carbonyl
Now I am sure you probably already thought, 'Hey carboxyl sounds similar to the term
carbonyl.' There is actually some truth to that statement. Think of carbonyl and carboxyl groups
as part of the same functional group family. The carbonyl does not have a hydroxyl group, like
carboxyl does. So, although they may sound very similar, they are quite different. Here's a
reference to make sure you can see the difference between carbonyl and carboxyl groups.
Carbonyl and carboxyl groups
There is a good reason why carboxyl and carboxylic acid are best buddies. When you see an
organic compound with a carboxyl group, guess what it is called? That's right, a carboxylic acid.
If this sounds confusing, here you see the difference between a carboxylic acid and a carboxyl
group. Just remember, you will never a see a carboxylic acid compound without a carboxyl
group present. They are best buds - glued to each other's hips!
Carboxyl and carboxylic acid
Lesson Summary
Let's Review. Carboxyl groups are functional groups with a carbon atom double-bonded to an
oxygen atom and single bonded to a hydroxyl group. The molecular formula is COOH. Carboxyl
groups missing a hydrogen atom are de-protonated and ionized. Ionized carboxyl groups act as
acids, require less energy and are more stable. Electron sharing between oxygen atoms on
ionized carboxyl groups increases stability. Carboxyl groups are different from carboxylic acids
and carbonyl groups because of their side chains.
Learning Outcomes
The process of memorizing this lesson's details about carboxyl groups could prepare you to:
Recognize the properties of carboxyl groups
Identify the molecular formula for carboxyl groups
Distinguish between carboxyl groups, carboxylic acids and carbonyl groups4
You might also like
- Black Belt Wireless Presales Stage 1 Quiz 1 2021Document3 pagesBlack Belt Wireless Presales Stage 1 Quiz 1 2021Jen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Meat Inspection in The Abattoir in CameroonDocument122 pagesMeat Inspection in The Abattoir in CameroonKevine Kenmoe MocheNo ratings yet
- nstp1 Activity 1Document3 pagesnstp1 Activity 1Jen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Haier in India Building Presence in A Mass Market Beyond ChinaDocument14 pagesHaier in India Building Presence in A Mass Market Beyond ChinaArun Kumar80% (5)
- Cold Call Scripts - Coaching SessionDocument3 pagesCold Call Scripts - Coaching SessionDianeNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids - 2023Document15 pagesCarboxylic Acids - 2023Sangay ChodenNo ratings yet
- Tugas B.inggris HerlisyaDocument3 pagesTugas B.inggris HerlisyatrisnadewiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 6Document4 pagesChemistry Module 6angelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids Class XII NotesDocument43 pagesCarboxylic Acids Class XII NotesAditya BhattNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 6Document4 pagesChemistry Module 6angelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- BioChem - GlucoseDocument58 pagesBioChem - GlucoseKYLE ANDREW SAWITNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompundsDocument8 pagesCarbon and Its CompundsAjeet YadavNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4. Alkyl Halides, Alcohols, Ethers and Carbonyl CompoundsDocument30 pagesLesson 4. Alkyl Halides, Alcohols, Ethers and Carbonyl Compoundsann wamburaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids: Nomenclature, Preparation, Physical Properties, and Chemical ReactionsDocument22 pagesCarboxylic Acids: Nomenclature, Preparation, Physical Properties, and Chemical ReactionsDivyansh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Organic Molecules Chemistry Grade 12: Everything Science WWW - Everythingscience.co - ZaDocument16 pagesOrganic Molecules Chemistry Grade 12: Everything Science WWW - Everythingscience.co - ZaAbhi SinghNo ratings yet
- Modern Minimalist Black and White Report PresentationDocument72 pagesModern Minimalist Black and White Report PresentationPRINCESS NOELLEE TRAYVILLANo ratings yet
- Oleh: Prof. Dr. Hj. Maulidiyah, M.Si: Jurusan Kimia FMIPA UHO 2019Document21 pagesOleh: Prof. Dr. Hj. Maulidiyah, M.Si: Jurusan Kimia FMIPA UHO 2019ANDI ELSYA WIDIYA PRASTIKA WEMPI F1C117065No ratings yet
- Carboxylic EstersDocument2 pagesCarboxylic Esterssophia del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Cac Bo EngliDocument4 pagesCac Bo EngliLinh ĐồngNo ratings yet
- Unit 15A: Carboxylic AcidsDocument21 pagesUnit 15A: Carboxylic AcidsKazel Lyca SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids: Group Iv - A Aleta - Bangaoan - Pascuac - Ramil - UrmanitaDocument15 pagesCarboxylic Acids: Group Iv - A Aleta - Bangaoan - Pascuac - Ramil - UrmanitaShawn Francis TabiosNo ratings yet
- Carboxylate - WikipediaDocument1 pageCarboxylate - WikipediaBadhon Chandra SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document70 pagesChap 4Irfan AzaharNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates LectureDocument74 pagesCarbohydrates LectureLars JayhawkNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument2 pagesCarboxylic AciddemNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds Part2Document8 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds Part2www.luciannarikaNo ratings yet
- Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument2 pagesAromatic HydrocarbonsHalloNo ratings yet
- Notes C16 121Document13 pagesNotes C16 121Amir HussainNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chapter 4 NotesDocument9 pagesClass 10 Chapter 4 Notesrachitagar.officialNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid and Derivatives PDFDocument12 pagesCarboxylic Acid and Derivatives PDFÏt's RîçkgãrçīäNo ratings yet
- Functional Groups: Bio 1 X-1LDocument32 pagesFunctional Groups: Bio 1 X-1LAeron Jade ParenaNo ratings yet
- Sch4uc Unit 2 Lesson 08Document28 pagesSch4uc Unit 2 Lesson 08Luis David Lazo CondoriNo ratings yet
- CHM 113Document17 pagesCHM 113danielexoskelentonNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Gr.1Document71 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes Gr.1HarijaNo ratings yet
- Laporan IGF AlimDocument11 pagesLaporan IGF Alimppg.risdaniar99130No ratings yet
- CH 117 Notes 3Document6 pagesCH 117 Notes 3Benson ShayoNo ratings yet
- Topic 11: Organic Chemistry 11.1 Homologous SeriesDocument8 pagesTopic 11: Organic Chemistry 11.1 Homologous SeriesbnNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Carboxylic Acids & EstersDocument133 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Carboxylic Acids & EstersWai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Module On Carboxylic AcidDocument1 pageModule On Carboxylic AcidPaula CaborubiasNo ratings yet
- More Functional Groups - Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesMore Functional Groups - Organic ChemistrysrdjanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry and The Organization of CellsDocument32 pagesBiochemistry and The Organization of CellsAinsssNo ratings yet
- Functional G Chem 15th FebDocument64 pagesFunctional G Chem 15th FebAndrew GordonNo ratings yet
- More Types of Organic CompoundDocument2 pagesMore Types of Organic CompoundkalloliNo ratings yet
- 01 - Biochemistry & Biomolecules PDFDocument25 pages01 - Biochemistry & Biomolecules PDFNURDAYANA NADHIRAH HAFIZANo ratings yet
- 10.1 - Introduction To Organic Chemistry PDFDocument9 pages10.1 - Introduction To Organic Chemistry PDFVũ Đức DuyNo ratings yet
- Notes CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesNotes CarbohydratesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Carboxylic Acids: Chapter 10 Lecture Notes: Carboxylic Acids, Amines, and AmidesDocument20 pagesCarboxylic Acids: Chapter 10 Lecture Notes: Carboxylic Acids, Amines, and AmidesABHISHEK MISHRANo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument9 pagesCarboxylic AcidAbiot DibabaNo ratings yet
- Fuctional GroupsDocument12 pagesFuctional GroupsNina HamadaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids Homologous Series Information SheetDocument1 pageCarboxylic Acids Homologous Series Information SheetAli r24No ratings yet
- 1 Organic ChemistryDocument15 pages1 Organic ChemistryKeizel Anne MananguNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemDocument13 pagesOrganic ChemsumaiyahNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids ..Document27 pagesCarboxylic Acids ..Mariam HamedNo ratings yet
- G10 - Handout - Organic - Makeup Handout - First WeekDocument4 pagesG10 - Handout - Organic - Makeup Handout - First WeekSheela BatterywalaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Assessment: Determine What Is Asked. Encircle The Correct Letter of The Best AnswerDocument20 pagesPre-Assessment: Determine What Is Asked. Encircle The Correct Letter of The Best AnswerRNee AlfnsoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 HydrocarbonsDocument13 pagesUnit 4 HydrocarbonsRicame GaringNo ratings yet
- Different Functional Groups and Their Uses in Organic Compounds 2Document25 pagesDifferent Functional Groups and Their Uses in Organic Compounds 2Belaro JennyNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument9 pagesCarboxylic AcidjohnsmithprayNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument26 pagesCarboxylic AcidDavid ParkNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument15 pagesUntitlednatNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Lesson 7 Organic Chemistry and Functional Groups 1Document71 pagesQuarter 2 Lesson 7 Organic Chemistry and Functional Groups 1Lhyn DE Leon DumayaNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds PDFDocument31 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds PDFHari kumarNo ratings yet
- Ch20 PDFDocument30 pagesCh20 PDFPilar CaleroNo ratings yet
- CH 20Document31 pagesCH 20syedhasnainrazanustNo ratings yet
- The Dynamic World of Chemical Reactions with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Dynamic World of Chemical Reactions with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Ray Harroun - ExpositionDocument3 pagesRay Harroun - ExpositionJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Rana Bahadur Shah - CompositionDocument4 pagesRana Bahadur Shah - CompositionJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- OL Lab 5 Stoichiometric Calculations Identify An Unknown Compound Using Gravimetric Analysis 1Document4 pagesOL Lab 5 Stoichiometric Calculations Identify An Unknown Compound Using Gravimetric Analysis 1Jen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Art AppDocument2 pagesArt AppJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Visa Inc. - PaperDocument12 pagesVisa Inc. - PaperJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Intacc 1Document4 pagesIntacc 1Jen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 2Document23 pagesWeek 1 2Jen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Arrieta Francis Mae R. Module 5 Work Immersion Ethics PDFDocument3 pagesArrieta Francis Mae R. Module 5 Work Immersion Ethics PDFJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- DumaogABM402BS SRDocument2 pagesDumaogABM402BS SRJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- 03quiz1 DionidoDocument2 pages03quiz1 DionidoJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- M3 Post Task Critical ThinkingDocument2 pagesM3 Post Task Critical ThinkingJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Leadership in OrganizationsDocument4 pagesChapter 11 Leadership in OrganizationsJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- 03 Quiz 1Document3 pages03 Quiz 1Jen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Career Path Reflection PaperDocument4 pagesCareer Path Reflection PaperJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Conagra S Recipe For A Better Human Resource SystemDocument5 pagesConagra S Recipe For A Better Human Resource SystemJen Adviento100% (1)
- Experiment 4 SSB Demodulation - PdfaefaefaDocument5 pagesExperiment 4 SSB Demodulation - PdfaefaefaJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Elms CPARDocument5 pagesElms CPARJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Point of View: Subsistence NeedsDocument3 pagesPoint of View: Subsistence NeedsJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Activity 8 The Cell Cycle Answer Sheet Rev2021Document5 pagesActivity 8 The Cell Cycle Answer Sheet Rev2021Jen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- EtikDocument3 pagesEtikJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Hydroxyl Group: EthanolDocument7 pagesHydroxyl Group: EthanolJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- LabAct8 1 PDFDocument14 pagesLabAct8 1 PDFJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Ammonia: A Close Cousin: Single Bonds To Either Hydrogen or Carbon. Let's Take A Look at Some ExamplesDocument3 pagesAmmonia: A Close Cousin: Single Bonds To Either Hydrogen or Carbon. Let's Take A Look at Some ExamplesJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Philhis - Edited PDFDocument7 pagesGroup 2 Philhis - Edited PDFJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- 2022 QB ProDocument31 pages2022 QB ProJen Adviento50% (2)
- What Is A Phosphate Group?: Phosphorylated. That Means Its Function Has Changed Usually, Phosphorylation Activates ThatDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Phosphate Group?: Phosphorylated. That Means Its Function Has Changed Usually, Phosphorylation Activates ThatJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Napul ResumeDocument2 pagesNapul ResumeNp LbNo ratings yet
- Read The Following Text and Answer The QuestionsDocument10 pagesRead The Following Text and Answer The QuestionsNixon RestrepoNo ratings yet
- Thompson Nadler Lount Judgmental BiasesDocument27 pagesThompson Nadler Lount Judgmental BiasesWazeerullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Week 4 PDFDocument8 pagesWeek 4 PDFChelsea RoqueNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CommunityDocument43 pagesIntroduction To CommunityRyan Rojas Ricablanca100% (1)
- User Manual IvmsDocument223 pagesUser Manual IvmsGerardo AltobelliNo ratings yet
- Manual Bluetti Eb150Document12 pagesManual Bluetti Eb150Rafa Lozoya AlbacarNo ratings yet
- Java Array: Logic Formulation and Intro. To ProgrammingDocument9 pagesJava Array: Logic Formulation and Intro. To ProgrammingklintNo ratings yet
- 1Q Planificación Microcurricular 8thDocument1 page1Q Planificación Microcurricular 8thAbigail Sisalema BastidasNo ratings yet
- Grasso: Ammonia Liquid Chiller Series FX PP, LP, VP 200 - 6000 KWDocument65 pagesGrasso: Ammonia Liquid Chiller Series FX PP, LP, VP 200 - 6000 KWManuel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Winkler Test For Dissolved OxygenDocument3 pagesWinkler Test For Dissolved OxygenDOMINICNo ratings yet
- Mobile Jumper Solution 2020Document12 pagesMobile Jumper Solution 2020Gils Alain HountondjiNo ratings yet
- Section Capacity Section Capacity: AbutmentDocument4 pagesSection Capacity Section Capacity: AbutmentGajendra SNo ratings yet
- Connx October 2008Document2 pagesConnx October 2008ScamsIntrernetNo ratings yet
- Doordash Agreement Contract October 25Document13 pagesDoordash Agreement Contract October 25wagaga papapaNo ratings yet
- B P S U: Ataan Eninsula Tate NiversityDocument10 pagesB P S U: Ataan Eninsula Tate NiversityCharles Vincent DavidNo ratings yet
- Personal Branding Workbook - Ext - 2nd EdDocument23 pagesPersonal Branding Workbook - Ext - 2nd EdMiguelito JeromeNo ratings yet
- Swathi Palanichamy - 2013072Document33 pagesSwathi Palanichamy - 2013072Tanisha PokarnaNo ratings yet
- 7th History Workbook English Medium Maharashtra BoardDocument12 pages7th History Workbook English Medium Maharashtra Boardpankarvi6100% (1)
- Gfps 9182 Product Range PVC U en PDFDocument568 pagesGfps 9182 Product Range PVC U en PDFjj bagzNo ratings yet
- Wiley American Anthropological AssociationDocument3 pagesWiley American Anthropological AssociationSimeon Pol'shinNo ratings yet
- Characterization RO NF MembranesDocument13 pagesCharacterization RO NF MembranesEri Dwi ListiantoNo ratings yet
- PF100/PF150 Manual Postformers: Process For Postforming A Waterfall (90°) EdgeDocument1 pagePF100/PF150 Manual Postformers: Process For Postforming A Waterfall (90°) EdgeAngel CazaresNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Integral TheoryDocument24 pagesAn Overview of Integral TheoryRytis JuozapavičiusNo ratings yet
- Book 14 PDFDocument242 pagesBook 14 PDFAndres Perez71% (7)
- Extended Abstract Comparison of Effectiveness of The Various Species of Citrus' Peels As Styrofoam DecomposerDocument3 pagesExtended Abstract Comparison of Effectiveness of The Various Species of Citrus' Peels As Styrofoam DecomposerKen EzekielNo ratings yet
- Establishing A Change RelationshipDocument10 pagesEstablishing A Change Relationshipravelyn bresNo ratings yet