Professional Documents
Culture Documents
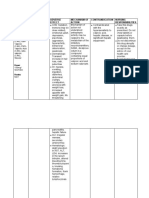
Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name
Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name
Uploaded by
SHEILA MAE SACLOTOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name
Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name
Uploaded by
SHEILA MAE SACLOTCopyright:
Available Formats
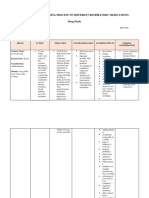
Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility
Generic Name: Ranitidine is a specific, It is to treat ulcers of History of acute •headache - Check/ask client if he/she has
Ranitidine rapidly acting histamine the stomach and porphyria •constipation allergies.
H2-antagonist. It inhibits intestines and prevent Hypersensitivity •diarrhea
basal and stimulated them from coming back to ranitidine or •nausea and - Check the label and dosage
secretion of gastric acid, after they have healed. components of vomiting prior to administration.
reducing both the volume, This medication is also the formulation •dizziness Interventions:
and the acid and pepsin used to treat certain •hair loss
content of the secretion. stomach and throat •Inflammation of •Injection may be given as a
(esophagus) problems liver slow.
(such as erosive •Changes in brain •Be alert for early signs of
esophagitis, function hepatotoxicity
Drug Classification:
gastroesophageal reflux •Abnormal heart •Potential toxicity results from
Histamine H2
disease-GERD, Zollinger- rate decreased clearance
Antagonists
Ellison syndrome). (elimination) and therefore
Dosage: prolonged action; greatest in the
50mg IV q8 x 3 doses older adult patients or those
with hepatic or renal
Route of dysfunction.
administration:
IV injection Teaching points:
•May experience constipation or
diarrhea, nausea and vomiting,
enlargement of breasts,
impotence or decreased libido,
and headache.
•Report sore throat, fever
unusual bruising or bleeding,
tarry stool, confusion,
hallucinations, dizziness, severe
headache and muscle or joint
pain.
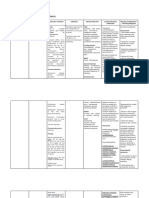
Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility
Generic Name: Omeprazole is a proton To treat certain • Hypersensitivity to >Dizziness -Nurse should use a double-
Omeprazole pump inhibitor. It inhibits stomach omeprazole, other >Rash ended transfer needle and
the parietal cell H+ / K+ and esophagus proton pump inhibitors. >Headache attach to the injection
Brand Name: ATP pump, the final step problems • Concomitant use with >Nausea membrane of the infusion
Losec, Prilosec of acid production. In (such as acid reflux, products containing >Vomiting bag. Connect the other
turn, omeprazole ulcers). It relieves rilpivirine. >Constipation needle-end from the vial with
suppresses gastric basal symptoms such as >Upper respiratory freeze-dried omeprazole.
and stimulated acid heartburn, difficulty Cautions: tract Make sure all omeprazole is
secretion. On the other swallowing, and May increase risk >infection dissolved.
hand, it reduces acid persistent cough. of fractures, >Back pain
secretion gastrointestinal infections. >Abdominal pain - Advise patient to avoid
in the stomach by binding infections. alcohol and foods that may
irreversibly to the enzyme cause an increase in GI
Drug class: H+,K+- ATPase. It inhibits irritation.
proton-pump the final pathway
inhibitors involved in acid secretion - Instruct client to take 30-60
and effectively inhibits minutes prior to eating. And if
Dosage: the capsule it should be swallowed
40mg IV active proton pumps. whole.
Route of - Nurse should advise the
administration client to promptly report any
Intravenous infusion sign of adverse reactions.
and PO
- Nurse should instruct client
to report pain at the IV site.
- Nurse should advise client to
report immediately when GI
discomfort, nausea, diarrhea
occurs.
- Nurse should evaluate for
therapeutic response (relief of
GI symptoms).
Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility
Generic name: Paracetamol has a central Reduce fever in viral and Hypersensitivity to Anorexia - Nurse should assess for
Paracetamol analgesic effect that is bacterial infections paracetamol. Severe hepatic Nausea clinical improvement and
mediated through Temporary relief of mild to impairment or severe active Diaphoresis, fatigue relief of pain, fever.
activation of descending moderate pain, headache, liver disease. Vomiting,
serotonergic pathways. fever. Management of Right upper quadrant - If there is fever, assess
Debate exists about its moderate to severe pain Cautions: tenderness, temperature and diaphoresis.
primary site of action, when combined with Severe renal Elevated lfts within
which may be inhibition of opioid analgesia. impairment; alcohol 48–72 hrs - Nurse should not exceed
prostaglandin (PG) dependency, hepatic after ingestion. maximum daily recommended
synthesis or through an impairment, or active dose.
Brand Name: active metabolite hepatic
Biogesic influencing cannabinoid disease; chronic - Assess allergic reactions:
receptors. malnutrition rash, urticaria; if these occur, drug
Drug class: and hypovolemia may have to be discontinued.
Analgesics and Limit dose to less than 4
antipyretics g/day - Nurse should assess for fecal
occult blood and nephritis.
Dosage:
300mg IV - Avoid giving patient aspirin or
500mg tab aspirin-like analgesics because it
inhibits platelet aggregation.
Route of
administration: - Nurse should watch for
PO, rectal, intravenous cyanosis, shortness of breath and
(IV) abdominal pain as these are signs
of toxicity.
- Do not exceed the
recommended dosage.
- Nurse should report watch for
weakness, abdominal pain,
jaundice, dark urine, itchiness, or
clay colored stools.
- Discontinue drug if
hypersensitivity reactions occur.
You might also like
- Parales, Danish Stephanie C. BSN 3Y1-2: Her Home Medications Include MonthlyDocument8 pagesParales, Danish Stephanie C. BSN 3Y1-2: Her Home Medications Include MonthlyJanaica Juan0% (1)
- Pharmacology For PhysiotherapyDocument278 pagesPharmacology For PhysiotherapyEllaBembea78% (9)
- Omeprazole Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOmeprazole Drug StudyjoanneNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Pharmaceutical Unit (Tablet, Capsules, Syrups, Lotion Etc.)Document6 pagesProject Report On Pharmaceutical Unit (Tablet, Capsules, Syrups, Lotion Etc.)EIRI Board of Consultants and Publishers100% (3)
- Indusyunic MedicineDocument575 pagesIndusyunic MedicineHakeem Kashif Naeem Qureshi100% (8)
- Pharmacy Management: Misbah Biabani, PH.DDocument3 pagesPharmacy Management: Misbah Biabani, PH.DGame MerNo ratings yet
- MCQs With Key 50 Qs On ANSDocument10 pagesMCQs With Key 50 Qs On ANSshhahhmurad6592% (12)
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic NameSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Adu Drug Study Edited 1Document3 pagesAdu Drug Study Edited 1Lerry Claire LimosNo ratings yet
- Dengue DRUG StudyDocument4 pagesDengue DRUG Studyjaninenicole100% (1)
- Generic NameDocument3 pagesGeneric NameShainaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OmeprazoleDocument1 pageDrug Study OmeprazoleCzarina Santok GasparNo ratings yet
- MCN Form 014Document4 pagesMCN Form 014jericho dinglasanNo ratings yet
- MS Drug Study 1Document6 pagesMS Drug Study 1Elijah MarfilNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTramadol Drug StudyPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Camillus MabiniDocument5 pagesDrug Study Camillus MabiniJonh Carlo LopezNo ratings yet
- PantoprazoleDocument1 pagePantoprazolehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Name of Patient: Mr. DG U Date: January 12, 201Document2 pagesDrug Study: Name of Patient: Mr. DG U Date: January 12, 201ceian230% (1)
- Case Study 3 WorduDocument5 pagesCase Study 3 WorduMelissa Andrea JajallaNo ratings yet
- Diclofenalac Sodium (Fenac)Document3 pagesDiclofenalac Sodium (Fenac)karenmichellelecarozNo ratings yet
- Brand/ Generic Name LACTULOSEDocument3 pagesBrand/ Generic Name LACTULOSEjgc18No ratings yet
- LACTULOSEDocument2 pagesLACTULOSEkhelxoNo ratings yet
- Hydrochlorothiazide, Allopurinol, KetosterilDocument9 pagesHydrochlorothiazide, Allopurinol, KetosterilcotyboyNo ratings yet
- Print MeDocument4 pagesPrint MeDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Dosage / Frequency Action Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument9 pagesGeneric Name Dosage / Frequency Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilityorhocelo6908No ratings yet
- Drugs Study Drugs Classification Adverse Effect Mechanism of Action Contrandication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesDrugs Study Drugs Classification Adverse Effect Mechanism of Action Contrandication Nursing ResponsibilitiesRachel BotonNo ratings yet
- Furosemid Citicoline Clexane, LevofloxacinDocument9 pagesFurosemid Citicoline Clexane, Levofloxacincotyboy50% (2)
- Rani Ti DineDocument2 pagesRani Ti Dinejordan11111111No ratings yet
- Drug Study YyyDocument7 pagesDrug Study YyyIanjoyce OlivarNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyAllysa Megan OrpillaNo ratings yet
- OMEPRAZOLEDocument2 pagesOMEPRAZOLERea LynNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Med Ward Duty)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Med Ward Duty)Kimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- DSDocument18 pagesDSAngelica Murillo Ang-AngcoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Nausea & VomitingDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Nausea & Vomitingderic87% (47)
- Name of DrugDocument4 pagesName of DrugMicahEuranneCastillo-GoliNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyejpics29No ratings yet
- Application of Nursing Process To Different Respiratory MedicationsDocument13 pagesApplication of Nursing Process To Different Respiratory MedicationssharedNo ratings yet
- Drug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFDocument4 pagesDrug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasNo ratings yet
- Abas Drug Study Nicu PDFDocument4 pagesAbas Drug Study Nicu PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFDocument4 pagesDrug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study orDocument4 pagesDrug Study orChristine Katherine LibuitNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Narcotics & NMJDocument7 pagesActivity 2 Narcotics & NMJKristineNo ratings yet
- ANTIPSYCHOTICSDocument25 pagesANTIPSYCHOTICSCheetahboi Shopee100% (4)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormatDocument3 pagesDrug Study FormatMeryl MarcosNo ratings yet
- New DrugsDocument6 pagesNew DrugsZymer Lee AbasoloNo ratings yet
- Rani Ti DineDocument2 pagesRani Ti DineJeffNo ratings yet
- SimvastatinDocument1 pageSimvastatinGracia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MMMCDocument14 pagesDrug Study MMMCKathleen Pagulayan Intalan-GloriosoNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole (FSW)Document3 pagesOmeprazole (FSW)khelxoNo ratings yet
- Pain and Mobility Medication CardsDocument8 pagesPain and Mobility Medication CardsJamie O.No ratings yet
- Drug Study-PsychDocument5 pagesDrug Study-Psychrc_lacampuinganyahooNo ratings yet
- Kayexalate Drug StudyDocument3 pagesKayexalate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred Congreso100% (1)
- FUROSEMIDEDocument6 pagesFUROSEMIDEPark JeongyeonNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Perfect Insulin Resistance Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Losing Weight, Reversing Insulin Resistant And And Preventing Pre-Diabetes With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Perfect Insulin Resistance Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Losing Weight, Reversing Insulin Resistant And And Preventing Pre-Diabetes With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Gastritis and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Gastritis and Related ConditionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Complete Guide to Chronic Constipation: Symptoms, Risks, Treatments & CuresFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Chronic Constipation: Symptoms, Risks, Treatments & CuresNo ratings yet
- The Complete Dysphagia Diet Cookbook:The Ultimate Nutrition Guide For People With Swallowing And Chewing Difficulties With Foodlist, Meal Plan And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Complete Dysphagia Diet Cookbook:The Ultimate Nutrition Guide For People With Swallowing And Chewing Difficulties With Foodlist, Meal Plan And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Esophagus Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Esophagus Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Gallbladder Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Gallbladder Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip and PalateDocument8 pagesCleft Lip and PalateSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToDocument2 pagesDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular AccidentDocument7 pagesCardiovascular AccidentSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Seminar - This Is A Type of Academic Activity Happened Within An Instruction orDocument13 pagesSeminar - This Is A Type of Academic Activity Happened Within An Instruction orSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument5 pagesRRLSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- CATARACTDocument8 pagesCATARACTSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- DELIRIUMDocument7 pagesDELIRIUMSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Curriculum-Vitae RicoDocument2 pagesCurriculum-Vitae RicoSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Letters & ResumeDocument4 pagesLetters & ResumeSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- ATORVASTATINDocument1 pageATORVASTATINSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Saturn: Significant Events in The Philippines From 1521-1861Document5 pagesSaturn: Significant Events in The Philippines From 1521-1861SHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAzithromycin Drug StudySHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Case Study CHF Final Output Group 2Document83 pagesCase Study CHF Final Output Group 2SHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Elaborate The QuoteDocument1 pageElaborate The QuoteSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Elaborate The QuoteDocument1 pageElaborate The QuoteSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Elaborate The QuoteDocument1 pageElaborate The QuoteSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NCM 118 FinalDocument15 pagesDrug Study NCM 118 FinalSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Guiding PrincipleDocument1 pageGuiding PrincipleSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic NameSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Psychia Case Study Group 2 July 4 2021Document75 pagesPsychia Case Study Group 2 July 4 2021SHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy: Chathannoor FHCDocument31 pagesPharmacy: Chathannoor FHCKrishnanunni KLNo ratings yet
- Pemakaian Obat RasionalDocument62 pagesPemakaian Obat RasionalMARTININo ratings yet
- Milk of Magnesia PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLETDocument2 pagesMilk of Magnesia PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLETralphael obodoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in ParkinsonismDocument16 pagesDrugs Used in ParkinsonismShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- Form Stok OpnameDocument7 pagesForm Stok OpnameIka RahayuNo ratings yet
- Format BaruDocument500 pagesFormat BarugunawanNo ratings yet
- Serotonin, Psilocybin and Body Dysmorphic Disorder - A Case ReportDocument2 pagesSerotonin, Psilocybin and Body Dysmorphic Disorder - A Case ReportDayon BochniaNo ratings yet
- 2023-2024 İngilizce Ders Programı 2023-2024 Güz - İngilizce DuyuruDocument1 page2023-2024 İngilizce Ders Programı 2023-2024 Güz - İngilizce Duyurudeviee008No ratings yet
- Pharmacy Notes PDFDocument9 pagesPharmacy Notes PDFEnzo VasquezNo ratings yet
- Medications: By: Mrs. Mae G. Mallorca, R.N., M.A.N Ms. Jo Maree Pearl J. Oyco, R.NDocument66 pagesMedications: By: Mrs. Mae G. Mallorca, R.N., M.A.N Ms. Jo Maree Pearl J. Oyco, R.NGia Espinosa OcbeñaNo ratings yet
- FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FAST DISSOLVING SUBLINGUAL FILM CONTAINING ARIPIPRAZOLE" By. Bhusari A.CDocument108 pagesFORMULATION DEVELOPMENT AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FAST DISSOLVING SUBLINGUAL FILM CONTAINING ARIPIPRAZOLE" By. Bhusari A.CAdinath BhusariNo ratings yet
- Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery SystemDocument10 pagesGastro Retentive Drug Delivery SystemKrunal SamejaNo ratings yet
- FDA Orphan Drug ReviewDocument49 pagesFDA Orphan Drug ReviewpdgcssNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For Multiple Sclerosis (Betaseron)Document4 pagesDrug Study For Multiple Sclerosis (Betaseron)Leslie Lagat PaguioNo ratings yet
- A Compilation of Bioactive Compounds From AyurvedaDocument11 pagesA Compilation of Bioactive Compounds From AyurvedaAhmed Ismail SabriNo ratings yet
- PPSC FaysalDocument24 pagesPPSC FaysalJoseph Jackson100% (3)
- Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs: College of Pharmacy Our Lady of Fatima UniversityDocument27 pagesSedative-Hypnotic Drugs: College of Pharmacy Our Lady of Fatima UniversityK WangNo ratings yet
- Clozapine and The Role of Therapeutic Drug MonitoringDocument5 pagesClozapine and The Role of Therapeutic Drug MonitoringNicolás LescanoNo ratings yet
- OmeprazoleDocument4 pagesOmeprazoleRéka JankovitsNo ratings yet
- Websitecompanies NewDocument33 pagesWebsitecompanies NewRajiv JulakantiNo ratings yet
- Ans PracticalDocument40 pagesAns PracticalJeevs MusicNo ratings yet
- GA Dengan Intubasi EndotrachealDocument21 pagesGA Dengan Intubasi EndotrachealMuhammad Nur AlamsyahNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY: Metoprolol - BetalocDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY: Metoprolol - BetalocYum C100% (1)
- PONV Prophylaxis Guidelines: Risk Factor OR 95% CIDocument4 pagesPONV Prophylaxis Guidelines: Risk Factor OR 95% CIHerly NurrahmaNo ratings yet
- Drug Certificate-of-Suitability-of-premises-RegulationDocument24 pagesDrug Certificate-of-Suitability-of-premises-RegulationAkampurira Moses BlessedNo ratings yet