Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4th Quarter Lesson Plan
4th Quarter Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
Bernard GundranOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4th Quarter Lesson Plan
4th Quarter Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
Bernard GundranCopyright:
Available Formats
School Grade 6
School LESSON Level
Logo EXEMPLAR Teacher Learning Science
Area
Teaching Date and Time Week 6 Quarter 4th
I. OBJECTIVES
The learner demonstrates understanding of the earth’s
A. Content Standards
rotation and revolution
The Learners should be able to demonstrate the eath’s
B. Performance Standards
rotaion and revolution
Differentiate between the rotation and revolution and
C. Learning Competencies or
describe the effects of the earth’s motions.
Objectives
a. Most Essential Learning
Differentiate between the rotation and revolution and
Competencies (MELC)
describe the effects of the earth’s motions.
(If available, write the indicated
MELC)
b. Enabling Competencies
(If available, write the attached
enabling competencies)
c. Enrichment Competencies
(If available, write the attached
enrichment competencies)
II. CONTENT
A. Topic: MOTIONS OF THE EARTH
MELC Science Grade 6, 4th quarter p. 510
B. Reference: The New Science Links: Worktext in Science and Technology for
Grade 6 pg. 432-437
a. Teacher’s Guide Pages
b. Learner’s Material Pages
The New Science Links: Worktext in Science and Technology for
c. Textbook Pages Grade 6 pg. 315- 319
d. Additional Materials from
Learning Resources
C. List of Learning Resources for
PowerPoint Presentation, laptop, cellphone, ballpen,
Development and Engagement
Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) and paper
Activities
D. Concepts Motion, rotation, revolution
oral reading, communication, collaboration, critical thinking,
E. Skills
technological skills
F. Values Giving the importance of the earth’s motion
ANNOTATION
III. PROCEDURES
What can you say about the movement of the INDICATOR 1. Apply
A. ENGAGE knowledge of content
following objects?
within and across
curriculum teaching
areas.
English- analyzing
pictures.
These are example of objects that
rotates.
Rotation means “to spin.”
How about this picture?
What can you say about the car’ movement?
The car is moving around the tree
The car is revolving around the tree.
Revolution means “to go around
something.”
the learners into four. INDICATOR 1. Apply
B. EXPLORE knowledge of content
Distribute the activity sheets.
Remind the learners about the norms/standards to be within and across
followed in doing the activity. curriculum teaching
- Read and understand the instructions properly. areas.
- Cooperate with your group. Values- Values
- Do not disturb the other groups integration like
- Maintain cleanliness in your workplace. Group cooperating with
- Seek the guidance of the teacher if needed. group mates,
- Minimize your noise cleanliness and
- Submit your output on time. practicing being on
Present the scoring rubric to be used for group activity. time.
ACTIVITY 10.1
Demonstrating Rotation and Revolution
Problem:
What is the difference between the rotation and the
revolution of the earth?
What you need: COT-RPMS Indicator
Globe 3. Use effective verbal
Wide area or space and non-verbal
Flashlight classroom
communication
What you need to do: strategies to support
learning
1. Draw a circle to serve as the orbit of earth. Let understanding,
one person in the group go to the center. participation,
He/she will represent the sun. engagement and
2. Let one person hold the globe and spin it achievement
Providing an
evenly counter clockwise not too fast, while
easy and
he/she walks completely around the person at enjoyable yet
the center of the circle. (As it revolves around very educative
the sun, north end of the earth’s axis continues activity that will
to point toward a relatively stationery object. In adapt to all
the sky, it is called the North Star.) The person kind of
at the center is revolving around him/her. learners.
3. Notice the part lighted by the flashlight when
the earth rotates sand revolves around the
sun.
What have you found out?
1. Do all parts of Earth receive light as it
rotate on its axis? Why?
2. What is the effect of Earth’s rotation?
3. What have you noticed about the amount
of light received by Earth as it revolves
around the sun?
4. What do you think are the occurences
when Earth revolves around the sun?
Conclusion:
Make a conclusion based from the given problem.
One representative from each group will present their
C. EXPLAIN output. A scoring rubric will be used in rating the group
output. (Please see attached scoring rubrics on appendix
A and B.)
Process the output of every group.
1. Do all parts of Earth receive light as it rotate on
its axis? Why?
No. The “fixed” tilt means that, during our
orbit around our Sun each year, different
parts of Earth receive sunlight for
different lengths of time. It also means
that the angle at which sunlight strikes
different parts of Earth's surface changes
through the year.
2. What is the effect of Earth’s rotation?
The spinning of the Earth causes day to
turn to night
3. What have you noticed about the amount of
light received by Earth as it revolves around
the sun?
As the earth revolves around the
sun, the place where light shines
the brightest changes. This motion
gives us the different seasons. For
instance, the poles receive less
light than does the equator
because of the angle that the land
around the poles receive the sun's
light.
4. What do you think are the occurrences when
Earth revolves around the sun?
The Earth is constantly in motion, revolving
around the Sun and rotating on its axis.
These motions account for many of the
phenomenon we see as normal
occurrences: night and day, changing of
the seasons, and different climates in
different regions.
Show a video of Earth’s rotation and revolution. COT-RPMS Indicator
D. ELABORATE INDICATOR 1. Apply
Discuss: knowledge of content
within and across
Rotation- is the movement of earth on its axis. Earth curriculum teaching
rotates from west to east. It is clockwise as seen above areas.
the North Pole and Counter Clockwise as seen above ICT- letting the pupils
South Pole. The period of one complete rotation is defined to learn by viewing
as a day and takes 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4.2 through the use of
seconds. Earth’s rotation is inclined or tilted 23.5 degrees gadgets.
relative to its plane of revolution around the sub. The sun,
moon, planets, and stars do not orbit around Earth
everyday. It appears that the way to us because we
observe the sky from a planet that rorates once every day,
or 15 degrees per hour.
Results from Earth’s Rotation
The occurrence of day and night. Places facing
the sun experience daytime while those facing COT-RPMS
away from the sun experience nighttime. The 3. Use effective verbal
length of daytime and nighttime varies as Earth and non-verbal
revolves around the sun. classroom
The daily rising and setting of the sun, stars communication
and the moon are the pattern of motion visible strategies to support
in the sky. The sun rises in the east and sets in learning
the west, as do the moon, planets, and the stars. understanding,
These daily motions are the result from the earth’s participation,
rotation. engagement and
Earth’s rotation affects the flow of air and water achievement
on earth. Flowing air and water are diverted from Using the
north-south direction to an east-west direction mother-
because of Earth’s rotation. The diversion of tongue,
direction is called the Coriolis effect. Filipino and
English to
ensure that the
Revolution is the movement of an object around the pupils fully
bigger object. Earth revolves around the sun. Its orbit understand the
around the sun is in the form of a slightly flattened cirle lesson
called an ellipse. The sun is hot at the center of the orbit,
but is slightly off to one side. This explains why Earth’s
distance from the sun varies. It is closest to the sun at 147
million kilometers when it is in its orbit’s perihelion. It is
farthest from the sun at 152 million kilometers when it is in
its orbit’s aphelion.
Earth revolves around the sun as it roates, or spins, on its
axis. The period of one revolution around the sun is
defined as a year. One complete revolution of earth is
365.24 solar days or 365 days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, and
46 seconds. Earth’s axis is tilted. As it orbits the sun,
Earth’s axis remains fixed in space so that at one poinr,
the northern hemisphere of earth is tilted.
Results from Earth’s Revolution
Occurrence of Seasonal Changes
The seasons change through the year; the length of
days varies; and the temperature may range from
cold to hot depending on the latitude where you live.
The annual changes are the result of Earth’s orbital
motion around the sun is called a revolution. Our
seasons are created by this orbit tilt and by Earth’s
orbital motion around the sun.
Identify the words being referred to. Choose your
E. EVALUATE
answer from the words below.
Aphelion rotation perihelion
Axis orbit
_______1. Earth’s motion around the sun.
_______2. Imaginary line describing earth’s tilt
_______3.Earth’s path around the sun
_______4. Earth’s orbit closest to the sun
_______5. Earth’s orbit farthest from the sun
6-10. Give five effects of earth’s rotation and
revolution
Essay. Write your answer in an ½ sheet of paper. INDICATOR 1. Apply
IV. ADDITIONAL knowledge of content
1. Explain the occurrence of the different
ACTIVTY within and across
seasons.
curriculum teaching
areas.
English-Writing an
essay, organizing
ideas, and expressing
thoughts in English
language
IV. REFLECTION ____ ML
___Lesson carried. Move on to the next objective.
___Lesson not carried.
(Reflection on the
Type of Formative
Assessment Used for
This Particular
Lesson)
Prepared by: Checked by:
Teacher I Principal I
You might also like
- Earth's Rotation and Revolution (Grade 6) - Free Printable Tests and WorksheetsDocument2 pagesEarth's Rotation and Revolution (Grade 6) - Free Printable Tests and WorksheetsCarl Maramag100% (8)
- Grades VI Lesson Plan Subject Science 6 School Ligayan Elementary School Date June, 2022 Teacher Judyleen D. FulgencioDocument8 pagesGrades VI Lesson Plan Subject Science 6 School Ligayan Elementary School Date June, 2022 Teacher Judyleen D. FulgencioJudyleen Fulgencio100% (2)
- Lesson Plan - Particles Model of The States of MatterDocument6 pagesLesson Plan - Particles Model of The States of MatterRezelyn AnnNo ratings yet
- GNAV Questions by LessonDocument83 pagesGNAV Questions by LessonLucasNo ratings yet
- Engineering Dynamics 2.0 - Fundamentals and Numerical Solutions, 2019Document715 pagesEngineering Dynamics 2.0 - Fundamentals and Numerical Solutions, 2019DCRAING201675% (4)
- 4th Quarter Lesson PlanDocument7 pages4th Quarter Lesson PlanRienaly Bustamante100% (2)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument8 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Sciencedeseree abendanio100% (1)
- A Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7Document6 pagesA Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7France MonaresNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 2NDDocument11 pagesGrade 6 2NDRomielyn MenguezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Biodiversity 4asDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Biodiversity 4asRaymond Escuzar100% (1)
- (Science 6 WK 2 L2) - Differentiating A Solute From A SolventDocument53 pages(Science 6 WK 2 L2) - Differentiating A Solute From A SolventRhea Ocite100% (2)
- DLP Science Q2 W4Document6 pagesDLP Science Q2 W4Julieann MarceloNo ratings yet
- DLL Sci 7 Phil EnviDocument5 pagesDLL Sci 7 Phil EnviivonneNo ratings yet
- 7e's DLL Grade 7 ADocument2 pages7e's DLL Grade 7 AJaneth de Juan100% (2)
- Detailed Lesson Plan: (S6FE-III d-f-2)Document4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan: (S6FE-III d-f-2)mailyn Pareja100% (2)
- A Detailed Less-WPS OfficeDocument11 pagesA Detailed Less-WPS OfficeRoshelle Jhane L. SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Cot Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesCot Lesson Planjuvelyn abugan100% (1)
- For DemoDocument15 pagesFor DemoGrace T Kalif100% (1)
- I. Objectives: Write The LC Code For EachDocument3 pagesI. Objectives: Write The LC Code For EachNica Joy AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Editable SCIENCE 7 DETAILED LESSON PLAN 4TH QUARTERDocument9 pagesEditable SCIENCE 7 DETAILED LESSON PLAN 4TH QUARTERZenny Jean MordenoNo ratings yet
- Maria Angela LapidezDocument9 pagesMaria Angela LapidezDanivie JarantaNo ratings yet
- DLP Global WarmingDocument3 pagesDLP Global WarmingReyna Myra EstradaNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument8 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogSherwin PhillipNo ratings yet
- Final Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesFinal Lesson PlanTeodorico LacsonNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Science Cot LPDocument7 pagesGrade 4 Science Cot LPKeith Kathe100% (1)
- Cot FinalDocument3 pagesCot FinalAlleen Joy Solivio100% (1)
- Grade 6 DLL SCIENCE 6 Q3 Week 6Document5 pagesGrade 6 DLL SCIENCE 6 Q3 Week 6Mark neil a. GalutNo ratings yet
- Science LPDocument3 pagesScience LPEva Reataza Acero-Odtujan100% (1)
- DLL G7 W1Document4 pagesDLL G7 W1LENETTE ALAGONNo ratings yet
- Cot Sci4 3RDQDocument5 pagesCot Sci4 3RDQjoanna marie limNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanGspr BoJoyNo ratings yet
- Cot 2021 Ap6Document9 pagesCot 2021 Ap6Alyssa Lae Cabildo Feliciano - TolentinoNo ratings yet
- BoW - Science 7Document3 pagesBoW - Science 7John EviotaNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Science Fourth Quarter Exam Edited FinalDocument7 pagesGrade 6 Science Fourth Quarter Exam Edited FinalJulaton JericoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science About MotionDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in Science About MotionFloramae SeradorNo ratings yet
- Cot PPT ScienceDocument31 pagesCot PPT ScienceEllen Orilloza Alcorin100% (1)
- DLL - Science 4 - Q4 - W8Document3 pagesDLL - Science 4 - Q4 - W8Anna Lou S. DuronNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document18 pagesModule 1Shane Catherine Besares100% (1)
- 3rd-7e's - LOCATING PLACESDocument3 pages3rd-7e's - LOCATING PLACESRod ReyesNo ratings yet
- DLL Grade 6 Fourth Quarter Week 2 Day 1Document6 pagesDLL Grade 6 Fourth Quarter Week 2 Day 1BRIGIDA V.ADOPTANTE100% (1)
- DLL - Science 6 - Q4 - W2Document10 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q4 - W2Amado SandoyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan SCIENCE 5 (WEEK 7, DAY 2)Document3 pagesLesson Plan SCIENCE 5 (WEEK 7, DAY 2)Angel rose reyes100% (1)
- Moon Phases Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesMoon Phases Lesson Planapi-297185099No ratings yet
- Cot 1Document7 pagesCot 1Frinces Mae CristalNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of Some Important Properties of SolutionsDocument4 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of Some Important Properties of Solutionsjennelyn malaynoNo ratings yet
- Procedure: Activity 2: Where in The World Is The Philippines? Part IiDocument28 pagesProcedure: Activity 2: Where in The World Is The Philippines? Part Iisamn cadNo ratings yet
- Science 4Document3 pagesScience 4RichardCastrenceParagas0% (1)
- DLL SCIENCE Week 7Document6 pagesDLL SCIENCE Week 7Elizza GuerraNo ratings yet
- DLL Science Grade 7 2nd Grading 2docxDocument28 pagesDLL Science Grade 7 2nd Grading 2docxMarivic OrdonezNo ratings yet
- LANDMASSES AND BODIES OF WATER Simple Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLANDMASSES AND BODIES OF WATER Simple Detailed Lesson PlanMonica Grace ManaloNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 7 - AccelerationDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Science 7 - Accelerationangeline vacalaresNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter COT Q2 Week 1 Skeletal SystemDocument9 pages1st Quarter COT Q2 Week 1 Skeletal SystemJesbeel Ramirez-Pimentel100% (1)
- DLP Science 6 Q2 W2 Day 5Document5 pagesDLP Science 6 Q2 W2 Day 5Rubie Jane Aranda100% (1)
- Science 6 CotDocument4 pagesScience 6 CotRonel Mariano100% (2)
- Week 2 - Day 4 I. Objectives: V Xkmhs4Qlj - S Tsyo4Z0EDocument8 pagesWeek 2 - Day 4 I. Objectives: V Xkmhs4Qlj - S Tsyo4Z0EBRIGIDA V.ADOPTANTENo ratings yet
- Module 9: The Hero in Me My Heroic Deeds: Activity 1: Let's Explore This!Document4 pagesModule 9: The Hero in Me My Heroic Deeds: Activity 1: Let's Explore This!Justiniana BisanaNo ratings yet
- MIINHS Science 8 WHLP Week 4 JMAPDocument2 pagesMIINHS Science 8 WHLP Week 4 JMAPJERIZZA MAGNE PARAFINANo ratings yet
- Kayang Kaya Yan!Document4 pagesKayang Kaya Yan!Judah Ben Ng Ducusin100% (1)
- Third Quarter Lesson Plan in Science VI Week 4 Day 1 ContentDocument15 pagesThird Quarter Lesson Plan in Science VI Week 4 Day 1 ContentRobieDeLeon100% (1)
- GRAND DEMO DLP - 035152mDocument10 pagesGRAND DEMO DLP - 035152mArreza Riche E.No ratings yet
- Sample Lesson Plan in Science V Using Explicit InstructionDocument6 pagesSample Lesson Plan in Science V Using Explicit InstructionKrimson Mike DolorzoNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Lesson Plan SCIENCE 6Document8 pages4th Quarter Lesson Plan SCIENCE 6Rhoda Mae DelaCruz YpulongNo ratings yet
- 3RD QUARTER SCIENCE 6 FRICTION Lesson ExemplarDocument5 pages3RD QUARTER SCIENCE 6 FRICTION Lesson ExemplarMerlizah DeligNo ratings yet
- FLAT TemplatesDocument7 pagesFLAT TemplatesBernard GundranNo ratings yet
- DLL English g6 q2 w2Document17 pagesDLL English g6 q2 w2Bernard GundranNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: EsophagusDocument14 pagesDigestive System: EsophagusBernard GundranNo ratings yet
- Multigrade SchoolDocument1 pageMultigrade SchoolBernard GundranNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 PPT - Science - Q2 - W4 - Parts of Circulatory System and Its FuynctionDocument1 pageGrade 6 PPT - Science - Q2 - W4 - Parts of Circulatory System and Its FuynctionBernard GundranNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Region 02, Cagayan Valley: Department of Education Schools Division Office of Nueva VizcayaDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Region 02, Cagayan Valley: Department of Education Schools Division Office of Nueva VizcayaBernard GundranNo ratings yet
- TransfereeDocument1 pageTransfereeBernard GundranNo ratings yet
- Report On Als Enrolment: Pao Elementary SchoolDocument2 pagesReport On Als Enrolment: Pao Elementary SchoolBernard GundranNo ratings yet
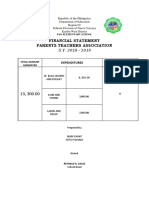
- Financial Statement Parents Teachers Association: Expenditures DifferenceDocument1 pageFinancial Statement Parents Teachers Association: Expenditures DifferenceBernard GundranNo ratings yet
- List of Non - Numerates, Result of Each Activities Given, Projects MonitoredDocument4 pagesList of Non - Numerates, Result of Each Activities Given, Projects MonitoredBernard GundranNo ratings yet
- Natural ScienceDocument6 pagesNatural ScienceJandro KareemNo ratings yet
- Systems in Space Lessons 1-3 Kahoot Review QuestionsDocument10 pagesSystems in Space Lessons 1-3 Kahoot Review Questionsapi-159752083No ratings yet
- Earth Represent Test ADocument8 pagesEarth Represent Test AAnonymous tYRXs9No ratings yet
- TutorialDocument69 pagesTutorialManoj MahendrakarNo ratings yet
- Springer - Methods of Celestial Mechanics, Volume II - Application To Planetary System, Geodynamics, Satellite Geodesy (G. Beutler 2005)Document452 pagesSpringer - Methods of Celestial Mechanics, Volume II - Application To Planetary System, Geodynamics, Satellite Geodesy (G. Beutler 2005)Daniel ComeglioNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Articles Earth and Space: St. Anthony Montessori Inc. 2070 E. Pascua St. Brgy. Kasilawan Makati CityDocument28 pagesCompilation of Articles Earth and Space: St. Anthony Montessori Inc. 2070 E. Pascua St. Brgy. Kasilawan Makati CityKevin Joseph PerfectoNo ratings yet
- Science 6-Q4-Module 3-Weeks 3-4Document34 pagesScience 6-Q4-Module 3-Weeks 3-4John Bunay100% (4)
- Science6 - Q4 - Module 4 - WK 4-5 - ADMDocument32 pagesScience6 - Q4 - Module 4 - WK 4-5 - ADMerwin_bacha67% (3)
- Marković-Topalović, Eur J Phys 37, 065801 (2016)Document18 pagesMarković-Topalović, Eur J Phys 37, 065801 (2016)Marcelo CabralNo ratings yet
- APhO2001 Theory Prob 1Document3 pagesAPhO2001 Theory Prob 1Hermawan MulyonoNo ratings yet
- LL3 Universe and Solar SystemDocument31 pagesLL3 Universe and Solar SystemPrincess PabualanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Rotation and Revolution of The Earth 1Document19 pagesLesson 4 Rotation and Revolution of The Earth 1axilrich8No ratings yet
- Gravity Causes Climate ChangeDocument13 pagesGravity Causes Climate ChangeJohn Dodds0% (1)
- I PU Geography English Medium PDFDocument211 pagesI PU Geography English Medium PDFMADEGOWDA BSNo ratings yet
- Earths Patterns Rotation and RevolutionDocument8 pagesEarths Patterns Rotation and Revolutionapi-407875476No ratings yet
- Rotation of Earth in Holy Qur'anDocument9 pagesRotation of Earth in Holy Qur'anrahmanhadiqNo ratings yet
- Rotation and Revolution: What Causes Night and Day? What Causes The Seasons To Change?Document5 pagesRotation and Revolution: What Causes Night and Day? What Causes The Seasons To Change?ajay_competitionNo ratings yet
- Time NotesDocument11 pagesTime NotesUlan JavierNo ratings yet
- Earth: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search World Earth (Disambiguation) Planet Earth (Disambiguation)Document18 pagesEarth: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search World Earth (Disambiguation) Planet Earth (Disambiguation)DarthV2No ratings yet
- The Earth's Movements PDFDocument37 pagesThe Earth's Movements PDFEnola PearlNo ratings yet
- Q4 Rotation and RevolutionDocument4 pagesQ4 Rotation and Revolutionmarites gallardoNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Q4 - Module 5-6Document12 pagesScience 6 - Q4 - Module 5-6Hahayuf GangaNo ratings yet
- G7 Science Q4 - Week 5 Evidence of Rotation of The Earth-1Document33 pagesG7 Science Q4 - Week 5 Evidence of Rotation of The Earth-1laurenmartinez0913No ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Lesson PlanDocument7 pages4th Quarter Lesson PlanBernard Gundran100% (2)
- Experimental Proofs of The Earth's Rotation-William F. RIGGE-1913PA 21 267R-CompletDocument19 pagesExperimental Proofs of The Earth's Rotation-William F. RIGGE-1913PA 21 267R-CompletchavanneNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Worksheet Q4 Science 6 - Week 5: Name: - Section: - Rating/ScoreDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Worksheet Q4 Science 6 - Week 5: Name: - Section: - Rating/ScoreEfmarie De Guzman RufinoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument258 pagesUntitledArthe MisNo ratings yet