Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Powders VS Tablets: Powder
Powders VS Tablets: Powder
Uploaded by
Evelina NastasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Powders VS Tablets: Powder
Powders VS Tablets: Powder
Uploaded by
Evelina NastasCopyright:
Available Formats
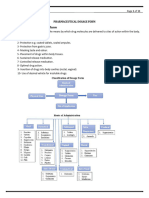
Powders VS Tablets
Powder
Powders are intimate mixtures of dry, finely divided drugs and or chemical that may be
intended for internal or external use (e. g. external applications to the skin). Powder are the
simplest dosage forms and the basis of many other solid dosage forms , powder were originally
designed as a convenient mode of administering hard vegetable drugs such as roots, bark and
woods. Powder dosage forms are versatile flexible in dosage strength relatively stable and also
convenient to manufacture, store, handle and use. It is possible to reduce them to desired
particle size and thus facilitate rapid absorption. Thus from biopharmaceutical consideration
powder are convenient and useful for prescribing drugs. Advantage: 1)Good chemical stability
compared with fluids. 2) Useful for bulky drugs with large dose, e. g. indigestion powder. 3)
Easy to swallow even in large bulk, especially if mixed with drink food (useful for stomach-tube
feeding). 4)The smaller particle size of powders causes more rapid dissolution in body fluids,
increases drug bioavailability, and decreases gastric irritation compared with tablets.
Disadvantage: 1)Not suitable for drugs unstable in atmospheric conditions. 2)Not suitable for
bitter, nauseating , delinquent and corrosive drugs. 3) Inaccuracy of dose in case of bulk
powder. 4) Inconvenient to carry.
Tablet
A tablet is a pharmaceutical oral dosage form or solid unit dosage form. Tablets may be
defined as the solid unit dosage form of medicament or medicaments with suitable excipients.
It comprises a mixture of active substances and excipients, usually in powder form, pressed or
compacted from a powder into a solid dose. Tablets are often stamped with symbols, letters,
and numbers, which enable them to be identified. Sizes of tablets to be swallowed range from a
few millimetres to about a centimetre . Advantages and disadvantages: Tablets are simple and
convenient to use. They provide an accurately measured dosage of the active ingredient in a
convenient portable package, and can be designed to protect unstable medications or disguise
unpalatable ingredients. Some drugs may be unsuitable for administration by the oral route.
For example, protein drugs such as insulin may be denatured by stomach acids. Some drugs
may be deactivated by the liver when they are carried there from the gastrointestinal tract by
the hepatic portal vein (the "first pass effect"), making them unsuitable for oral use. Drugs
which can be taken sublingually are absorbed through the oral mucosa, so that they bypass the
liver and are less susceptible to the first pass effect. The oral bioavailability of some drugs may
be low due to poor absorption from the gastrointestinal tract.
You might also like
- TabletsDocument174 pagesTabletsAhmed Ali100% (1)
- X - Problem Prioritization and NCPDocument5 pagesX - Problem Prioritization and NCPMartin Lєtmaku Espina100% (2)
- Medical TerminologyDocument33 pagesMedical TerminologySusanBernardNo ratings yet
- 1 Teori Sediaan Serbuk Dan GranulDocument13 pages1 Teori Sediaan Serbuk Dan GranulMia FitrianaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics I Dosage FormsDocument20 pagesPharmaceutics I Dosage FormsShweta Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Phar 24 NotesDocument22 pagesPhar 24 NotesSherry LynnNo ratings yet
- Basic Dispensing Theory For Pharmacy TechnicianDocument18 pagesBasic Dispensing Theory For Pharmacy TechnicianIfeanyichukwu HenryNo ratings yet
- Zinc, Starch, and Talc Dusting Powder-QuestionsDocument4 pagesZinc, Starch, and Talc Dusting Powder-QuestionsChristianNo ratings yet
- Powders As Dosage FormsDocument4 pagesPowders As Dosage Formssyedamaryamali19No ratings yet
- TabletsDocument127 pagesTabletsAltamash SheikhNo ratings yet
- Abq Pharmaceutics Nidhi MishraDocument11 pagesAbq Pharmaceutics Nidhi MishranidhiNo ratings yet
- 4.1 - Doge and Doges FormsDocument28 pages4.1 - Doge and Doges FormsNo IdeaNo ratings yet
- Types of Dosage FormsDocument92 pagesTypes of Dosage Formsneha_dand1591No ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Drug Dosage Forms II Lecture 1 09-10. - 2Document12 pagesMicrosoft Word - Drug Dosage Forms II Lecture 1 09-10. - 2princeamitNo ratings yet
- Dosage FormDocument4 pagesDosage Formnevelle4667No ratings yet
- Dosage FormDocument6 pagesDosage FormAmaila Ch100% (1)
- Solid Dosage Forms-59983Document12 pagesSolid Dosage Forms-59983Evelina NastasNo ratings yet
- A Review On Effervescent TabletDocument6 pagesA Review On Effervescent TabletInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- TABLETSDocument21 pagesTABLETStayyabasultan100% (1)
- PharmocodynamicsDocument48 pagesPharmocodynamicsflash.43612No ratings yet
- Lecture On Pharmaceutical Powders Unit-V: National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and ResearchDocument43 pagesLecture On Pharmaceutical Powders Unit-V: National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and ResearchShumaila QadirNo ratings yet
- Tablet Technology EditedDocument42 pagesTablet Technology EditedPramod Kc100% (1)
- Assignment Enteral Topikal Dosage Form (REV 7-12-2022-Edit)Document22 pagesAssignment Enteral Topikal Dosage Form (REV 7-12-2022-Edit)Mark Frost HDNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument220 pagesIlovepdf MergedhamzawiNo ratings yet
- Tablets and CapsuleDocument23 pagesTablets and CapsuleAnoosha FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Common Disk-Shaped Tablets A Tablet Is A Mixture of ActiveDocument8 pagesCommon Disk-Shaped Tablets A Tablet Is A Mixture of Activenasser9876No ratings yet
- Dosage Forms (Also Called Unit Doses) Are PharmaceuticalDocument8 pagesDosage Forms (Also Called Unit Doses) Are PharmaceuticalDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical PowdersDocument12 pagesPharmaceutical PowdersThomas Niccolo Filamor ReyesNo ratings yet
- Enteral Dosage Forms-Tri Murini (2016) - 2Document48 pagesEnteral Dosage Forms-Tri Murini (2016) - 2RobertOktaChandraNo ratings yet
- TabletsDocument25 pagesTabletsAsif KhanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument16 pagesUntitledIssac GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Dosage FormDocument7 pagesDosage FormKawtar MenjraNo ratings yet
- TABLETSDocument9 pagesTABLETSKeith OmwoyoNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Technology-II: Dr. Nargis Sultana ChowdhuryDocument26 pagesPharmaceutical Technology-II: Dr. Nargis Sultana ChowdhuryRokonuzzaman Ripon100% (1)
- INTRODUCTIONS PharmDocument5 pagesINTRODUCTIONS Pharmathankasoka18No ratings yet
- Drug Delivery SystemDocument15 pagesDrug Delivery SystemC-Net WorksNo ratings yet
- Know Your Medicine UPH654: Nur Sabiha MD HussinDocument176 pagesKnow Your Medicine UPH654: Nur Sabiha MD HussinSyafiyatulMunawarahNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical TabletDocument44 pagesPharmaceutical TabletMurtaza Choudhary100% (4)
- Formulation and Evaluation of Poly Herbal Chewable Tablets From Ayurvedic Ingredients Having Cough Relieving ActivityDocument8 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Poly Herbal Chewable Tablets From Ayurvedic Ingredients Having Cough Relieving ActivityInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Tablets Part 1Document23 pagesTablets Part 1Taleda AloranNo ratings yet
- Tablet 1Document24 pagesTablet 1Anis Yahya100% (1)
- Lec 1 Industrial Pharmacy II 2023Document36 pagesLec 1 Industrial Pharmacy II 2023saifmohanad.usNo ratings yet
- Tyden Drug Dosage Forms in Veterinary PracticeDocument6 pagesTyden Drug Dosage Forms in Veterinary PracticeZakariya Mohammed ZakoNo ratings yet
- Tablets Part 1 - MergedDocument185 pagesTablets Part 1 - MergedTaleda AloranNo ratings yet
- L-1 Tablet-1..Document11 pagesL-1 Tablet-1..Sun ShineNo ratings yet
- AshokaDocument40 pagesAshokaAnish Kumar ANo ratings yet
- 502t Ip2 Unit - IIDocument50 pages502t Ip2 Unit - IIHarshNo ratings yet
- Clinical Relevance of Drug Dosage FormsDocument37 pagesClinical Relevance of Drug Dosage FormsAnthony ChidomNo ratings yet
- Some of The Advantages and Disadvantages of Tablets Are Given BelowDocument17 pagesSome of The Advantages and Disadvantages of Tablets Are Given BelowTasmih Rob MowNo ratings yet
- Dosage FormsDocument21 pagesDosage Formsyashaswim4No ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Dosage FormsDocument77 pagesPharmaceutical Dosage Formsester juanitaNo ratings yet
- A Tablet Is A Pharmaceutical Dosage FormDocument2 pagesA Tablet Is A Pharmaceutical Dosage FormAnonymous Yhe5vFeidHNo ratings yet
- Dosage FormsDocument26 pagesDosage Formsafeworksintayehu477No ratings yet
- Tablets Solid Dosage FormsDocument4 pagesTablets Solid Dosage FormsRamdas Dolas0% (1)
- Dosage Form - WikipediaDocument4 pagesDosage Form - WikipediaMohamed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- L-1 Tablet-1Document10 pagesL-1 Tablet-1igrg382No ratings yet
- Recent Advancement in Drug Technology1 ChabgesDocument45 pagesRecent Advancement in Drug Technology1 ChabgesBirjesh KumarNo ratings yet
- TabletsDocument22 pagesTabletsabwlyfysl05No ratings yet
- PowdersDocument16 pagesPowdersShumaila Qadir100% (2)
- The best supplement of different types of dangerous Disease.From EverandThe best supplement of different types of dangerous Disease.No ratings yet
- History of ImmunologyDocument6 pagesHistory of ImmunologyCatherine MerillenoNo ratings yet
- Salicylic AcidDocument5 pagesSalicylic AcidMarrauNo ratings yet
- AtacandDocument4 pagesAtacandljubodragNo ratings yet
- Marvin T Reyes MD - Google SearchDocument1 pageMarvin T Reyes MD - Google SearchMicah TidwellNo ratings yet
- PharmacistDocument2 pagesPharmacistcrisjavaNo ratings yet
- Ventilator ModesDocument3 pagesVentilator ModesLudmila CrenshawNo ratings yet
- Ethnobotanical Survey of Markanda Forest Range of Gadchiroli District Maharashtra IndiaDocument8 pagesEthnobotanical Survey of Markanda Forest Range of Gadchiroli District Maharashtra IndiaInsightmedpubNo ratings yet
- MSDS K-Othrine 20 EWDocument8 pagesMSDS K-Othrine 20 EWSadhana SentosaNo ratings yet
- 22 Anafilaksise4ed2018Document52 pages22 Anafilaksise4ed2018David HartantoNo ratings yet
- Nacsys 600 MG Effervescent Tablets: Package Leaflet: Information For The UserDocument5 pagesNacsys 600 MG Effervescent Tablets: Package Leaflet: Information For The UserJrj TrestizaNo ratings yet
- Presidential Theme: 66 (LXVI) Annual Conference of Indian Orthopaedic AssociationDocument17 pagesPresidential Theme: 66 (LXVI) Annual Conference of Indian Orthopaedic AssociationnipundaveNo ratings yet
- Putaringonit: Slouchy StudiesDocument15 pagesPutaringonit: Slouchy StudiesThe University Daily KansanNo ratings yet
- Perubahan Fisiologi Ibu HamilDocument20 pagesPerubahan Fisiologi Ibu HamilMarisa IzzaNo ratings yet
- Volume 7, Issue 2, August 2006 - The Nepean Dyspepsia Index - Translation and Validation in Indonesian LanguageDocument4 pagesVolume 7, Issue 2, August 2006 - The Nepean Dyspepsia Index - Translation and Validation in Indonesian LanguageHenderaNo ratings yet
- Aetna Hmo 20 GeorgiaDocument94 pagesAetna Hmo 20 Georgiabill_w85081No ratings yet
- History and Development of Play TherapyDocument1 pageHistory and Development of Play TherapyLingNo ratings yet
- NCP VOL 33 No 1Document159 pagesNCP VOL 33 No 1Marwah RifahNo ratings yet
- Parameters of Care Dentoalveolar Surgery 2012Document22 pagesParameters of Care Dentoalveolar Surgery 2012api-265532519No ratings yet
- Where Did You Last Spend Your Money? What Kind of Service Did You Last Avail?Document20 pagesWhere Did You Last Spend Your Money? What Kind of Service Did You Last Avail?Rose Marie GabrielNo ratings yet
- Hiatal HerniaDocument2 pagesHiatal Hernianursegian13No ratings yet
- Medicalguidancenotes 1Document292 pagesMedicalguidancenotes 1fcordNo ratings yet
- April2017Personal Support PackageDocument10 pagesApril2017Personal Support PackageGail WardNo ratings yet
- Fallpxtoolkit PDFDocument202 pagesFallpxtoolkit PDFjmoncusNo ratings yet
- PFS A RolePlay Group9Document7 pagesPFS A RolePlay Group9j250592No ratings yet
- Slow Sand Filtration For Community Water Supply in Developing Countries No-11 1978Document181 pagesSlow Sand Filtration For Community Water Supply in Developing Countries No-11 1978Muhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Fits, Faints and Funny Turns in Children - Mark MackayDocument6 pagesFits, Faints and Funny Turns in Children - Mark MackayOwais Khan100% (1)
- Upload To Get Her BackDocument19 pagesUpload To Get Her BackBenjamin DsilvaNo ratings yet
- Medication Safety ReconciliationDocument117 pagesMedication Safety ReconciliationIndra WijayaNo ratings yet