Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Statistics: Lesson 1 Activity 1
Statistics: Lesson 1 Activity 1
Uploaded by
Marjie Bay-asenCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Rizal Technological University College of Arts and Sciences: Research MethodologyDocument10 pagesRizal Technological University College of Arts and Sciences: Research MethodologyMarie Fe Sario100% (1)
- Brian Kemp Audit Inconsistencies Report Joe Rossi 11.18.2021Document40 pagesBrian Kemp Audit Inconsistencies Report Joe Rossi 11.18.2021kmonclaNo ratings yet
- S4800 Supplementary Notes1 PDFDocument26 pagesS4800 Supplementary Notes1 PDFTanu OhriNo ratings yet
- Describing Sample Size and Sampling ProceduresDocument17 pagesDescribing Sample Size and Sampling ProceduresJoyce Bondoc100% (1)
- SamplingDocument7 pagesSamplingwilson philipoNo ratings yet
- Sampling Design: Dr. Eunice B. Custodio PhilippinesDocument30 pagesSampling Design: Dr. Eunice B. Custodio PhilippinesJerico Refamonte ValezaNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Data Collection: Lecture 19-20 Research Methods (Business) Isp-AhtDocument6 pagesSampling and Data Collection: Lecture 19-20 Research Methods (Business) Isp-AhtPiyam RazaNo ratings yet
- Sampling (Public Opinion) PDFDocument5 pagesSampling (Public Opinion) PDFMuskan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sampling DistributionDocument10 pagesSampling DistributionvarunNo ratings yet
- Research Methods and Sampling Design: (Document Subtitle)Document11 pagesResearch Methods and Sampling Design: (Document Subtitle)Komal SoomroNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument5 pagesSamplingSaif FazalNo ratings yet
- Stat II Chapter 1 and 2Document31 pagesStat II Chapter 1 and 2habtamubiniam897No ratings yet
- 5.3 - Data Collection and Presentation Part 1Document39 pages5.3 - Data Collection and Presentation Part 1GERRYNo ratings yet
- Methods of SamplingDocument8 pagesMethods of SamplingPriya GaurNo ratings yet
- Alex Financial Term PaperDocument7 pagesAlex Financial Term PaperAlex MainaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 SamplingDocument5 pagesChapter 6 SamplingAsaminow GirmaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document5 pagesTopic 3Lugalia KelvinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Sampling and Sampling DistributionDocument36 pagesChapter 1: Sampling and Sampling Distributionnasriibraahim507No ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Business Statistics For Contemporary Decision Making Canadian 2nd Edition Black Test Bank Full ChapterDocument52 pages(Download PDF) Business Statistics For Contemporary Decision Making Canadian 2nd Edition Black Test Bank Full Chapternausikicki100% (8)
- Study Material On Unit-IDocument19 pagesStudy Material On Unit-IBALAJI VARA PRASADNo ratings yet
- PR1 Q4 WK2 WorktextDocument2 pagesPR1 Q4 WK2 WorktextMONIQUE LEMENTENo ratings yet
- Business Statistics for Contemporary Decision Making Canadian 2nd Edition Black Test Bank instant download all chapterDocument52 pagesBusiness Statistics for Contemporary Decision Making Canadian 2nd Edition Black Test Bank instant download all chaptermezaknaskoo100% (3)
- SamplingDocument7 pagesSamplingrmdn32529732No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - SamplingDocument32 pagesLesson 3 - SamplingrelebohilemochesaneNo ratings yet
- Practical Research Q2 Week 2Document10 pagesPractical Research Q2 Week 2Rhynz BanastonNo ratings yet
- Concept of SamplingDocument20 pagesConcept of SamplingVishnupriyaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document5 pagesModule 3nasninass67No ratings yet
- UNIT V Sampling Theory: ParameterDocument8 pagesUNIT V Sampling Theory: ParameterebenesarbNo ratings yet
- Sampling Mixed Research MethodsDocument10 pagesSampling Mixed Research MethodsNana Ama Donkor-boatengNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Sampling Is Part of Daily LifeDocument13 pagesSampling: Sampling Is Part of Daily LifeSheetal ShettyNo ratings yet
- Gatheringofdata2 150513082553 Lva1 App6892Document45 pagesGatheringofdata2 150513082553 Lva1 App6892Caryl Mae BocadoNo ratings yet
- Sample Module Layout in Math 1Document24 pagesSample Module Layout in Math 1YapieeNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument11 pagesSamplingcilovNo ratings yet
- What Is SamplingDocument11 pagesWhat Is SamplingFatman RulesNo ratings yet
- LP4 - Unit4 - GE10-Methods of ResearchDocument12 pagesLP4 - Unit4 - GE10-Methods of ResearchCza Mae ArsenalNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Sample Design and ProcedureDocument5 pagesCH 4 Sample Design and ProcedureTasfa ZarihunNo ratings yet
- Bus Research Chapter SixDocument10 pagesBus Research Chapter Sixhaymanot gizachewNo ratings yet
- Definition of StatisticsDocument7 pagesDefinition of StatisticsLavinia Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Data CollectionDocument19 pagesLesson 2 Data CollectionningcordelNo ratings yet
- Engaging Activity NoDocument3 pagesEngaging Activity NoMary Joy MallongaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 RMDocument20 pagesModule 3 RMAman KhanNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem 2nd Q W2 Sampling Techniques PDFDocument53 pages1st Sem 2nd Q W2 Sampling Techniques PDFJian FrankNo ratings yet
- Research Ch4Document25 pagesResearch Ch4Bantamkak FikaduNo ratings yet
- RME-chapter 3Document22 pagesRME-chapter 3demilieNo ratings yet
- Sampling TechniquesDocument4 pagesSampling TechniquesANAM RAUF (GCUF)No ratings yet
- MethodsDocument36 pagesMethodsJimin parkNo ratings yet
- Collection of Data: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesCollection of Data: Objectivesapple gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Business Research MethodologiesDocument21 pagesSampling: Business Research MethodologiesJames DavisNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument45 pagesUnit Iii05Bala SaatvikNo ratings yet
- Sampling Design - Group ThreeDocument38 pagesSampling Design - Group ThreeWasihunNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument4 pagesResearchKriza EstocadoNo ratings yet
- Statistics in ResearchDocument11 pagesStatistics in ResearchJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Its Types Part - 2 - Ajay KumarDocument5 pagesSampling and Its Types Part - 2 - Ajay KumarAashis TamangNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter 3Document17 pages09 - Chapter 3Chandan TiwariNo ratings yet
- NUSS 500 - Part4Document50 pagesNUSS 500 - Part4Suraj NaikNo ratings yet
- Sampling Methods 5Document31 pagesSampling Methods 5akoeljames8543No ratings yet
- HandoutDocument4 pagesHandoutNemwel CapolNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Dept. of Psychology Kurukshetra UniversityDocument38 pagesSampling: Dept. of Psychology Kurukshetra UniversityPradeep M VineetaNo ratings yet
- Final SamplingDocument5 pagesFinal SamplingChristian BalodongNo ratings yet
- Uma Simple Random SamplingDocument3 pagesUma Simple Random SamplingRathai RagupathyNo ratings yet
- Research Ch2, Ch3 and Ch4Document29 pagesResearch Ch2, Ch3 and Ch4mengistu malkeNo ratings yet
- Participatory Action Research for Evidence-driven Community DevelopmentFrom EverandParticipatory Action Research for Evidence-driven Community DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Learning MaterialsDocument2 pagesPreparation of Learning MaterialsMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- RubricsDocument2 pagesRubricsMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Letter B TableDocument2 pagesLetter B TableMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense 22Document7 pagesSimple Past Tense 22Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Preparation 09-27-2022Document3 pagesPreparation 09-27-2022Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Simple Past TenseDocument7 pagesSimple Past TenseMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- April ARDocument2 pagesApril ARMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Bibliography Lesson Plan - Docx (1) 335Document13 pagesBibliography Lesson Plan - Docx (1) 335Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Transition SignalsDocument24 pagesTransition SignalsMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Pliant BambooDocument8 pagesPliant BambooMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Course Audit Test Questions22Document8 pagesCourse Audit Test Questions22Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Lugaw Is Essential PDFDocument1 pageLugaw Is Essential PDFMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Final Walk SpeechDocument2 pagesFinal Walk SpeechMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- A SemiDocument1 pageA SemiMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5Document2 pagesWorksheet 5Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Mythology TimelineDocument1 pageMythology TimelineMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Authorization LetterDocument1 pageAuthorization LetterMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Population of Poblacion, Sagada Second Quarter 2021: Activity 1Document4 pagesPopulation of Poblacion, Sagada Second Quarter 2021: Activity 1Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Sonnet 29 g9Document2 pagesSonnet 29 g9Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Couurse AuditDocument58 pagesCouurse AuditMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Building and Enhancing Literacy Skills Across CurriculumDocument7 pagesBuilding and Enhancing Literacy Skills Across CurriculumMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- MODULE HihiDocument2 pagesMODULE HihiMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Curriculum FinalsDocument18 pagesCurriculum FinalsMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Final Answersheet Readings StudentDocument14 pagesFinal Answersheet Readings StudentMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Research Paper For WebinarDocument7 pagesResearch Paper For WebinarMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument6 pagesArt AppreciationMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Statistics: It'S Your TurnDocument7 pagesStatistics: It'S Your TurnMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- RythmicDocument2 pagesRythmicMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Marjie Bay-Asen Bsed-E2 Sched: 9-10am MW Class Code: E71Document14 pagesMarjie Bay-Asen Bsed-E2 Sched: 9-10am MW Class Code: E71Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Scope of Marketing ResearchDocument19 pagesMeaning and Scope of Marketing ResearchNardsdel RiveraNo ratings yet
- Week 2 LecturesDocument13 pagesWeek 2 LecturesBethany LongNo ratings yet
- Item Analysis - CSS 10 - 1st Summative TestDocument2 pagesItem Analysis - CSS 10 - 1st Summative TestMBSRA DiscoveryNo ratings yet
- Regression ExampleDocument7 pagesRegression ExamplerasnimNo ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument38 pagesQuestion PaperKrishi ShahNo ratings yet
- Unofficial Results of Brookline's 2019 ElectionDocument9 pagesUnofficial Results of Brookline's 2019 ElectionAbby PatkinNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of HDFC and Icici BankDocument4 pagesComparative Analysis of HDFC and Icici BankSukhjeet Kaur BatthNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Mutu TerpaduDocument21 pagesManajemen Mutu Terpadu033IMAS TININo ratings yet
- An Example of A HypothesisDocument2 pagesAn Example of A HypothesisAjibade TaofikNo ratings yet
- Peran Stakeholders Dalam Proses Pemberdayaan Usaha Mikro Kecil Dan Menengah (UMKM) Alas Kaki Unggulan Melalui Program Pembiayaan Usaha Syariah (PUSYAR) Di Kota MojokertoDocument15 pagesPeran Stakeholders Dalam Proses Pemberdayaan Usaha Mikro Kecil Dan Menengah (UMKM) Alas Kaki Unggulan Melalui Program Pembiayaan Usaha Syariah (PUSYAR) Di Kota MojokertoFox IncNo ratings yet
- 16 pf2009Document4 pages16 pf2009Cristian gzNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Designs: Narrative Review Systematic Review Meta-AnalysisDocument80 pagesLiterature Review Designs: Narrative Review Systematic Review Meta-AnalysisAnonymous 12cE2wKNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: CH 10 TestDocument7 pagesThis Study Resource Was: CH 10 TestIlham SaputraNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Pr1 Week 3Document14 pagesDaily Lesson Log Pr1 Week 3Rosalvie Dante100% (1)
- Grayson Race Orange County by Precinct 11 3Document5 pagesGrayson Race Orange County by Precinct 11 3Mark A. Adams JD/MBANo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Tata Kelola Sistem Informasi Akademik Berbasis COBIT 5 Di Universitas Pendidikan GaneshaDocument10 pagesEvaluasi Tata Kelola Sistem Informasi Akademik Berbasis COBIT 5 Di Universitas Pendidikan GaneshaRidho HardiansyahNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1 (Need Analysis Questionnaire For Teacher) : Agree DisagreeDocument174 pagesAppendix 1 (Need Analysis Questionnaire For Teacher) : Agree DisagreeMeiti RizkiNo ratings yet
- Preliminary English Test: Carlos Rafael Monroy AlonsoDocument1 pagePreliminary English Test: Carlos Rafael Monroy AlonsoCarlos MonroyNo ratings yet
- Value of A Pilot StudyDocument3 pagesValue of A Pilot StudyXiaoqian ChuNo ratings yet
- PSRP Quiz-2 SolutionDocument3 pagesPSRP Quiz-2 SolutionarindamNo ratings yet
- 3 - Election in ChsDocument2 pages3 - Election in ChsAnamika Rai PandeyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) : W&W, Chapter 10Document20 pagesAnalysis of Variance (ANOVA) : W&W, Chapter 10sarangpandeNo ratings yet
- 1 Nature of StatisticsDocument7 pages1 Nature of StatisticsJay SerdonNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Research Review: Dr. Galvez PLM NotesDocument171 pagesEpidemiology and Research Review: Dr. Galvez PLM NotesPatty Reyes100% (1)
- Lesson 2-WPS Office 2Document6 pagesLesson 2-WPS Office 2Kent MarianitoNo ratings yet
- Reliability and Validity of Instruments Measuring Job Satisfaction-A Systematic ReviewDocument10 pagesReliability and Validity of Instruments Measuring Job Satisfaction-A Systematic ReviewFira Charming VerinaNo ratings yet
- Practical Statistical Data Analysis 1Document51 pagesPractical Statistical Data Analysis 1NurhadiNo ratings yet
- Test Constructiion FRIEDMAN TESTDocument13 pagesTest Constructiion FRIEDMAN TESTmonica bualNo ratings yet
Statistics: Lesson 1 Activity 1
Statistics: Lesson 1 Activity 1
Uploaded by
Marjie Bay-asenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Statistics: Lesson 1 Activity 1
Statistics: Lesson 1 Activity 1
Uploaded by
Marjie Bay-asenCopyright:
Available Formats
STATISTICS
MODULE 2
Pre-test
1. B
2. A
3. C
4. C
5. D
6. A
7. B
8. D
9. C
10. B
LESSON 1
Activity 1
1. If you will conduct your research study, what method of data collection
are you going to use then identify what type of data collection?
I would like to prefer Indirect Method because it does not consume
too much time and that the respondents express more their opinions and
they have the freedom to express also their views and the fact that they
maybe want to answer the question since anonymity is maintained. They
will have a lot more confidence to answer rather keeping shy and just
thinking of what to say and stutter all the time.
It’ll be primary data since, every time a questionnaire is floated the
answers usually came from the respondents themselves therefore the
data gathered are from primary sources. Although the data need retouch
but the fact that it is collected directly from the source.
2. Site a sample scenario in each data collection and identify if it is
secondary or primary data.
Example for Direct Method is that, when you go around having
interview, group discussion, Focus and participatory approach for your
research culture diversity in mountain province. Primary data is usually
used in here since it directly came from the source. The data gathered
are collected from people who are most certainly needed for the research.
Also, the researchers are involved in the study.
Sample scenario for indirect method will be questionnaires. You’ll
be floating questionnaire and it’ll serve as your survey guide to collect
data regarding if citrus extract does relieve stress. Primary may be used
also in this method since you are acquiring the data needed directly from
the source.
Registration method is enforced by law, example is the number of
patients died, recovered or on the process of healing during this
pandemic on COVID-19. These usually are primary data since they come
directly from the hospital and the respondents are the exact data
recovered from the patient’s file.
Observation method, from the word observation, an example is
that you are to observe from a certain place or community some cultural
practices and some possible behaviors that the particular place have
STATISTICS
similarities in some way. This is a secondary data since you are to look
beyond and not to collect directly instead you are to observe. The
observed qualities or traits you intended to observed came from the
primary source itself and you are just to articulate it and/or arrange it.
There are two types of experimental method which are scientific
and non-scientific. Scientific experimental method for example is the
effectivity of developed vaccine for COVID-19 from the Philippines versus
that from Germany. As for non- scientific, an example is the comparison
between the cultures of yesterday to today’s culture. This’ll be secondary
data since you’ll be observing and that they don’t come directly from the
sources and that you usually pick up the data from the people.
Activity 2
1. How many respondents per municipalities if the breakdown of
population is as follows:
Municipality Barli Bauk Besa Bonto Paraceli Sabanga Sadang Sagad Natoni Tadia
g o o c s n a a n n
Population
152 365 110 323 3450 1320 950 130 1100 200
0 5 0 0 0 0
Responden
ts 317 316 293 356 358 307 281 306 293 333
2. Can you site an example or scenario that non probability sampling
has advantage to probability sampling?
Non-probability sampling is a sampling technique where the odds
of any member being selected for a sample cannot be calculated. While
probability sampling you can calculate the odds. The major advantage of
non-probability over probability sampling is that compared to probability
sampling, it’s cost and time effective. It is easy to use and can also be
used when it’s impossible to conduct probability sampling. Example is
when you have a very small population to work with.
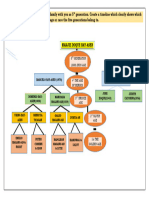
3. In your own, differentiate the Stratified random sampling and cluster
sampling by giving and explain and example.
Stratified random sampling, sampling is done on elements within
each stratum. A random sampling is drawn from each of strata, whereas
in the cluster sampling only the selected clusters are sampled.
For example, in stratified sampling, a sample is drawn from each
stratum (using a random sampling method like simple random sampling
or systematic sampling). In the image below, let's say you need a sample
size of 6. Two members from each group (yellow, red, and blue) are
selected randomly. Make sure to sample proportionally: In this simple
STATISTICS
example, 1/3 of each group (2/6 yellow, 2/6 red and 2/6 blue) has been
sampled. If you have one group that's a different size, make sure to
adjust your proportions. For example, if you had 9 yellow, 3 red and 3
blue, a 5-item sample would consist of 3/9 yellow (i.e. one third), 1/3 red
and 1/3 blue. In cluster sampling, the sampling unit is the whole
cluster; Instead of sampling individuals from within each group, a
researcher will study whole clusters. In the image below, the strata are
natural groupings by head color (yellow, red, blue). A sample size of 6 is
needed, so two of the complete strata are selected randomly (in this
example, groups 2 and 4 are chosen).
4. Applying the formula , compare the sample size if we are going to use
1%, 2%, 3%, 4% and 5% margin of error.
Margin of error Sample size
1%
2% 1668
3% 910
4% 556
5% 370
5. How many respondent can he/she have in the whole region? How many
respondent per province utilizing the proportional allocation stratified
random sampling? Utilizing equal allocation stratified random sampling.
POST TEST.
1. A
2. B
3. B
4. A
You might also like
- Rizal Technological University College of Arts and Sciences: Research MethodologyDocument10 pagesRizal Technological University College of Arts and Sciences: Research MethodologyMarie Fe Sario100% (1)
- Brian Kemp Audit Inconsistencies Report Joe Rossi 11.18.2021Document40 pagesBrian Kemp Audit Inconsistencies Report Joe Rossi 11.18.2021kmonclaNo ratings yet
- S4800 Supplementary Notes1 PDFDocument26 pagesS4800 Supplementary Notes1 PDFTanu OhriNo ratings yet
- Describing Sample Size and Sampling ProceduresDocument17 pagesDescribing Sample Size and Sampling ProceduresJoyce Bondoc100% (1)
- SamplingDocument7 pagesSamplingwilson philipoNo ratings yet
- Sampling Design: Dr. Eunice B. Custodio PhilippinesDocument30 pagesSampling Design: Dr. Eunice B. Custodio PhilippinesJerico Refamonte ValezaNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Data Collection: Lecture 19-20 Research Methods (Business) Isp-AhtDocument6 pagesSampling and Data Collection: Lecture 19-20 Research Methods (Business) Isp-AhtPiyam RazaNo ratings yet
- Sampling (Public Opinion) PDFDocument5 pagesSampling (Public Opinion) PDFMuskan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sampling DistributionDocument10 pagesSampling DistributionvarunNo ratings yet
- Research Methods and Sampling Design: (Document Subtitle)Document11 pagesResearch Methods and Sampling Design: (Document Subtitle)Komal SoomroNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument5 pagesSamplingSaif FazalNo ratings yet
- Stat II Chapter 1 and 2Document31 pagesStat II Chapter 1 and 2habtamubiniam897No ratings yet
- 5.3 - Data Collection and Presentation Part 1Document39 pages5.3 - Data Collection and Presentation Part 1GERRYNo ratings yet
- Methods of SamplingDocument8 pagesMethods of SamplingPriya GaurNo ratings yet
- Alex Financial Term PaperDocument7 pagesAlex Financial Term PaperAlex MainaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 SamplingDocument5 pagesChapter 6 SamplingAsaminow GirmaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document5 pagesTopic 3Lugalia KelvinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Sampling and Sampling DistributionDocument36 pagesChapter 1: Sampling and Sampling Distributionnasriibraahim507No ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Business Statistics For Contemporary Decision Making Canadian 2nd Edition Black Test Bank Full ChapterDocument52 pages(Download PDF) Business Statistics For Contemporary Decision Making Canadian 2nd Edition Black Test Bank Full Chapternausikicki100% (8)
- Study Material On Unit-IDocument19 pagesStudy Material On Unit-IBALAJI VARA PRASADNo ratings yet
- PR1 Q4 WK2 WorktextDocument2 pagesPR1 Q4 WK2 WorktextMONIQUE LEMENTENo ratings yet
- Business Statistics for Contemporary Decision Making Canadian 2nd Edition Black Test Bank instant download all chapterDocument52 pagesBusiness Statistics for Contemporary Decision Making Canadian 2nd Edition Black Test Bank instant download all chaptermezaknaskoo100% (3)
- SamplingDocument7 pagesSamplingrmdn32529732No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - SamplingDocument32 pagesLesson 3 - SamplingrelebohilemochesaneNo ratings yet
- Practical Research Q2 Week 2Document10 pagesPractical Research Q2 Week 2Rhynz BanastonNo ratings yet
- Concept of SamplingDocument20 pagesConcept of SamplingVishnupriyaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document5 pagesModule 3nasninass67No ratings yet
- UNIT V Sampling Theory: ParameterDocument8 pagesUNIT V Sampling Theory: ParameterebenesarbNo ratings yet
- Sampling Mixed Research MethodsDocument10 pagesSampling Mixed Research MethodsNana Ama Donkor-boatengNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Sampling Is Part of Daily LifeDocument13 pagesSampling: Sampling Is Part of Daily LifeSheetal ShettyNo ratings yet
- Gatheringofdata2 150513082553 Lva1 App6892Document45 pagesGatheringofdata2 150513082553 Lva1 App6892Caryl Mae BocadoNo ratings yet
- Sample Module Layout in Math 1Document24 pagesSample Module Layout in Math 1YapieeNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument11 pagesSamplingcilovNo ratings yet
- What Is SamplingDocument11 pagesWhat Is SamplingFatman RulesNo ratings yet
- LP4 - Unit4 - GE10-Methods of ResearchDocument12 pagesLP4 - Unit4 - GE10-Methods of ResearchCza Mae ArsenalNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Sample Design and ProcedureDocument5 pagesCH 4 Sample Design and ProcedureTasfa ZarihunNo ratings yet
- Bus Research Chapter SixDocument10 pagesBus Research Chapter Sixhaymanot gizachewNo ratings yet
- Definition of StatisticsDocument7 pagesDefinition of StatisticsLavinia Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Data CollectionDocument19 pagesLesson 2 Data CollectionningcordelNo ratings yet
- Engaging Activity NoDocument3 pagesEngaging Activity NoMary Joy MallongaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 RMDocument20 pagesModule 3 RMAman KhanNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem 2nd Q W2 Sampling Techniques PDFDocument53 pages1st Sem 2nd Q W2 Sampling Techniques PDFJian FrankNo ratings yet
- Research Ch4Document25 pagesResearch Ch4Bantamkak FikaduNo ratings yet
- RME-chapter 3Document22 pagesRME-chapter 3demilieNo ratings yet
- Sampling TechniquesDocument4 pagesSampling TechniquesANAM RAUF (GCUF)No ratings yet
- MethodsDocument36 pagesMethodsJimin parkNo ratings yet
- Collection of Data: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesCollection of Data: Objectivesapple gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Business Research MethodologiesDocument21 pagesSampling: Business Research MethodologiesJames DavisNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument45 pagesUnit Iii05Bala SaatvikNo ratings yet
- Sampling Design - Group ThreeDocument38 pagesSampling Design - Group ThreeWasihunNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument4 pagesResearchKriza EstocadoNo ratings yet
- Statistics in ResearchDocument11 pagesStatistics in ResearchJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Its Types Part - 2 - Ajay KumarDocument5 pagesSampling and Its Types Part - 2 - Ajay KumarAashis TamangNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter 3Document17 pages09 - Chapter 3Chandan TiwariNo ratings yet
- NUSS 500 - Part4Document50 pagesNUSS 500 - Part4Suraj NaikNo ratings yet
- Sampling Methods 5Document31 pagesSampling Methods 5akoeljames8543No ratings yet
- HandoutDocument4 pagesHandoutNemwel CapolNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Dept. of Psychology Kurukshetra UniversityDocument38 pagesSampling: Dept. of Psychology Kurukshetra UniversityPradeep M VineetaNo ratings yet
- Final SamplingDocument5 pagesFinal SamplingChristian BalodongNo ratings yet
- Uma Simple Random SamplingDocument3 pagesUma Simple Random SamplingRathai RagupathyNo ratings yet
- Research Ch2, Ch3 and Ch4Document29 pagesResearch Ch2, Ch3 and Ch4mengistu malkeNo ratings yet
- Participatory Action Research for Evidence-driven Community DevelopmentFrom EverandParticipatory Action Research for Evidence-driven Community DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Learning MaterialsDocument2 pagesPreparation of Learning MaterialsMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- RubricsDocument2 pagesRubricsMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Letter B TableDocument2 pagesLetter B TableMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense 22Document7 pagesSimple Past Tense 22Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Preparation 09-27-2022Document3 pagesPreparation 09-27-2022Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Simple Past TenseDocument7 pagesSimple Past TenseMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- April ARDocument2 pagesApril ARMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Bibliography Lesson Plan - Docx (1) 335Document13 pagesBibliography Lesson Plan - Docx (1) 335Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Transition SignalsDocument24 pagesTransition SignalsMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Pliant BambooDocument8 pagesPliant BambooMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Course Audit Test Questions22Document8 pagesCourse Audit Test Questions22Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Lugaw Is Essential PDFDocument1 pageLugaw Is Essential PDFMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Final Walk SpeechDocument2 pagesFinal Walk SpeechMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- A SemiDocument1 pageA SemiMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5Document2 pagesWorksheet 5Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Mythology TimelineDocument1 pageMythology TimelineMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Authorization LetterDocument1 pageAuthorization LetterMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Population of Poblacion, Sagada Second Quarter 2021: Activity 1Document4 pagesPopulation of Poblacion, Sagada Second Quarter 2021: Activity 1Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Sonnet 29 g9Document2 pagesSonnet 29 g9Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Couurse AuditDocument58 pagesCouurse AuditMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Building and Enhancing Literacy Skills Across CurriculumDocument7 pagesBuilding and Enhancing Literacy Skills Across CurriculumMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- MODULE HihiDocument2 pagesMODULE HihiMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Curriculum FinalsDocument18 pagesCurriculum FinalsMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Final Answersheet Readings StudentDocument14 pagesFinal Answersheet Readings StudentMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Research Paper For WebinarDocument7 pagesResearch Paper For WebinarMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument6 pagesArt AppreciationMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Statistics: It'S Your TurnDocument7 pagesStatistics: It'S Your TurnMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- RythmicDocument2 pagesRythmicMarjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Marjie Bay-Asen Bsed-E2 Sched: 9-10am MW Class Code: E71Document14 pagesMarjie Bay-Asen Bsed-E2 Sched: 9-10am MW Class Code: E71Marjie Bay-asenNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Scope of Marketing ResearchDocument19 pagesMeaning and Scope of Marketing ResearchNardsdel RiveraNo ratings yet
- Week 2 LecturesDocument13 pagesWeek 2 LecturesBethany LongNo ratings yet
- Item Analysis - CSS 10 - 1st Summative TestDocument2 pagesItem Analysis - CSS 10 - 1st Summative TestMBSRA DiscoveryNo ratings yet
- Regression ExampleDocument7 pagesRegression ExamplerasnimNo ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument38 pagesQuestion PaperKrishi ShahNo ratings yet
- Unofficial Results of Brookline's 2019 ElectionDocument9 pagesUnofficial Results of Brookline's 2019 ElectionAbby PatkinNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of HDFC and Icici BankDocument4 pagesComparative Analysis of HDFC and Icici BankSukhjeet Kaur BatthNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Mutu TerpaduDocument21 pagesManajemen Mutu Terpadu033IMAS TININo ratings yet
- An Example of A HypothesisDocument2 pagesAn Example of A HypothesisAjibade TaofikNo ratings yet
- Peran Stakeholders Dalam Proses Pemberdayaan Usaha Mikro Kecil Dan Menengah (UMKM) Alas Kaki Unggulan Melalui Program Pembiayaan Usaha Syariah (PUSYAR) Di Kota MojokertoDocument15 pagesPeran Stakeholders Dalam Proses Pemberdayaan Usaha Mikro Kecil Dan Menengah (UMKM) Alas Kaki Unggulan Melalui Program Pembiayaan Usaha Syariah (PUSYAR) Di Kota MojokertoFox IncNo ratings yet
- 16 pf2009Document4 pages16 pf2009Cristian gzNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Designs: Narrative Review Systematic Review Meta-AnalysisDocument80 pagesLiterature Review Designs: Narrative Review Systematic Review Meta-AnalysisAnonymous 12cE2wKNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: CH 10 TestDocument7 pagesThis Study Resource Was: CH 10 TestIlham SaputraNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Pr1 Week 3Document14 pagesDaily Lesson Log Pr1 Week 3Rosalvie Dante100% (1)
- Grayson Race Orange County by Precinct 11 3Document5 pagesGrayson Race Orange County by Precinct 11 3Mark A. Adams JD/MBANo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Tata Kelola Sistem Informasi Akademik Berbasis COBIT 5 Di Universitas Pendidikan GaneshaDocument10 pagesEvaluasi Tata Kelola Sistem Informasi Akademik Berbasis COBIT 5 Di Universitas Pendidikan GaneshaRidho HardiansyahNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1 (Need Analysis Questionnaire For Teacher) : Agree DisagreeDocument174 pagesAppendix 1 (Need Analysis Questionnaire For Teacher) : Agree DisagreeMeiti RizkiNo ratings yet
- Preliminary English Test: Carlos Rafael Monroy AlonsoDocument1 pagePreliminary English Test: Carlos Rafael Monroy AlonsoCarlos MonroyNo ratings yet
- Value of A Pilot StudyDocument3 pagesValue of A Pilot StudyXiaoqian ChuNo ratings yet
- PSRP Quiz-2 SolutionDocument3 pagesPSRP Quiz-2 SolutionarindamNo ratings yet
- 3 - Election in ChsDocument2 pages3 - Election in ChsAnamika Rai PandeyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) : W&W, Chapter 10Document20 pagesAnalysis of Variance (ANOVA) : W&W, Chapter 10sarangpandeNo ratings yet
- 1 Nature of StatisticsDocument7 pages1 Nature of StatisticsJay SerdonNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Research Review: Dr. Galvez PLM NotesDocument171 pagesEpidemiology and Research Review: Dr. Galvez PLM NotesPatty Reyes100% (1)
- Lesson 2-WPS Office 2Document6 pagesLesson 2-WPS Office 2Kent MarianitoNo ratings yet
- Reliability and Validity of Instruments Measuring Job Satisfaction-A Systematic ReviewDocument10 pagesReliability and Validity of Instruments Measuring Job Satisfaction-A Systematic ReviewFira Charming VerinaNo ratings yet
- Practical Statistical Data Analysis 1Document51 pagesPractical Statistical Data Analysis 1NurhadiNo ratings yet
- Test Constructiion FRIEDMAN TESTDocument13 pagesTest Constructiion FRIEDMAN TESTmonica bualNo ratings yet