Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsCarbohydrate Metabolism
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Uploaded by
Mark Zedrix MediarioThis document discusses carbohydrate metabolism. It defines carbohydrates and lists their various forms including polysaccharides, disaccharides, and monosaccharides. Key polysaccharides mentioned are glycogen, starch, cellulose, and nondigestive ones like pectin and alginates. The main disaccharides are sucrose, maltose, and lactose. Glucose, fructose, and galactose are named as the important monosaccharides. The document also outlines the processes of glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, and gluconeogenesis in carbohydrate metabolism. Glucose is said to be used as energy by entering the Krebs cycle in mitochondria to produce ATP through cellular respiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- PPNPSDocument4 pagesPPNPSMark Zedrix Mediario100% (2)
- Selective, Differential, & Enriched Media Lab ChartDocument2 pagesSelective, Differential, & Enriched Media Lab ChartFrankiesgirl6yr100% (6)
- Advocacy Programs Relevant To The Care of Older PersonsDocument6 pagesAdvocacy Programs Relevant To The Care of Older PersonsMark Zedrix Mediario100% (1)
- 10 Foods To Avoid When Trying To Lose WeightDocument5 pages10 Foods To Avoid When Trying To Lose WeightNikita DubeyNo ratings yet
- NCM105 Notes 2-CarbsDocument3 pagesNCM105 Notes 2-CarbsPaula TalaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Nutrition CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesNotes On Nutrition CarbohydratesFreewilly SternumNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument5 pagesCARBOHYDRATESGeorgina Rose JalagatNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three (Macronutrients)Document4 pagesChapter Three (Macronutrients)Kit Mendez BaccayNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Lec 3Document3 pagesNCM 105 Lec 3Rizaga, Carlos BenedictNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument15 pagesBio MoleculessofiajanineganalNo ratings yet
- Classification of Nutrients Macronurtients Classification of CarbohydratesDocument52 pagesClassification of Nutrients Macronurtients Classification of CarbohydratesAnna SantosNo ratings yet
- Biology Long TestDocument7 pagesBiology Long TestMarjorie AballaNo ratings yet
- NDT BsuDocument28 pagesNDT BsuAltea PasiaNo ratings yet
- NDT ReviewerDocument111 pagesNDT ReviewerMay RodeoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Macronutrients CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesChapter 2 Macronutrients Carbohydratesreajohn591No ratings yet
- 1 Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides (Simple Sugar)Document3 pages1 Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides (Simple Sugar)Kara AshleighNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate (STM)Document42 pagesCarbohydrate (STM)Jessica chiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - Energy Giving Food - Carbohydrates (CHO)Document4 pagesCHAPTER 3 - Energy Giving Food - Carbohydrates (CHO)Ruby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 - Macronutrient (CARBOHYDRATES)Document4 pagesMODULE 2 - Macronutrient (CARBOHYDRATES)Donna MarieNo ratings yet
- NCMA 215 PrelimsDocument30 pagesNCMA 215 PrelimsClaudine Jo B. TalabocNo ratings yet
- Charbohydrate: Unit - IiDocument8 pagesCharbohydrate: Unit - IiHemant SharmaNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument5 pagesCARBOHYDRATESMicah YapNo ratings yet
- Macronutrients: Carbohydrates (CHO) Proteins (CHON) FatsDocument32 pagesMacronutrients: Carbohydrates (CHO) Proteins (CHON) FatsGayle BocalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesChapter 4 - CarbohydratesIce Cream C0neNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument33 pagesCarbohydratesDeboo X Xavier100% (1)
- Science 10 Biomolecules ReviewerDocument9 pagesScience 10 Biomolecules ReviewerTasha Heart QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Handouts - CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesHandouts - CarbohydratesJerrold CruzNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument30 pagesCarbohydratesSheena Lou Regencia SalomonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MacronutrientsDocument3 pagesChapter 3 MacronutrientsMaxdjye EyjdxamNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument12 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolismbingbong2231No ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesbananakyuNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument43 pagesCarbohydratesEvangelene Esquillo Sana100% (1)
- Module 4 Cut CompressedDocument131 pagesModule 4 Cut CompressedLê Khuê TúNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument30 pagesCarbohydratesAvinash JakkulaNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument41 pagesCarbohydratesStrange Me100% (3)
- Macro Nutrients: Austin David O. Dumlao RN Instructor IDocument42 pagesMacro Nutrients: Austin David O. Dumlao RN Instructor IEmmanuel CuevasNo ratings yet
- GIT كتيب الطبعة الثانيةDocument56 pagesGIT كتيب الطبعة الثانيةdijla51No ratings yet
- المحاضرة الرابعة تغذية CarbohydrateDocument30 pagesالمحاضرة الرابعة تغذية Carbohydratedeminavictor8No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates PPT 1Document17 pagesCarbohydrates PPT 1Cristine Mae Pisquel TabunotNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Jameston S. Adorable, RND InstructorDocument51 pagesCarbohydrates: Jameston S. Adorable, RND InstructorMj AñascoNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument109 pagesMetabolismMai GaberNo ratings yet
- NUTMACRODocument9 pagesNUTMACROAliza Bea CastroNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Simple Sugars and Complex ChainsDocument44 pagesCarbohydrates: Simple Sugars and Complex ChainsBundi Gonzalez MartinNo ratings yet
- Macronutirents CPF With Prelim ProjectDocument78 pagesMacronutirents CPF With Prelim ProjectMONICA AGUIRRENo ratings yet
- MacronurientsDocument11 pagesMacronurientsDanah Grace SanchezNo ratings yet
- MacronurientsDocument11 pagesMacronurientsDanah Grace SanchezNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument59 pagesCarbohydratesChris Gift AkufunaNo ratings yet
- CC ChekDocument105 pagesCC ChekMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Carbohydrate 1 DIGESTION ABSORPTION AND METABOLISMDocument25 pagesChapter 3 Carbohydrate 1 DIGESTION ABSORPTION AND METABOLISMmaingcduNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument2 pagesBiological Moleculeshakdogiklog08No ratings yet
- 6 BiomoleculesDocument78 pages6 BiomoleculesPrecious Ryza G. BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter I: Food Components: CarbohydrateDocument14 pagesChapter I: Food Components: CarbohydrateJaylina MabulayNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesCarbohydratesBianca AzoresNo ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument75 pagesCombine PDFCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- Macro NutrientsDocument10 pagesMacro NutrientsClarke GriffinNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates 18.5.2022Document47 pagesCarbohydrates 18.5.2022Gourab NandaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Blood SugarDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Blood SugartagmanNo ratings yet
- Block 1 SummaryDocument230 pagesBlock 1 Summarymelisha.uysNo ratings yet
- KarbohidratDocument38 pagesKarbohidratRegina MunaamadaniNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument3 pagesCARBOHYDRATESjaizamaeenriquez59No ratings yet
- Digestion, Absorption and Metabolism of CarbohydratesDocument28 pagesDigestion, Absorption and Metabolism of CarbohydratesIzzuddienNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates LectureDocument31 pagesCarbohydrates LecturekushalNo ratings yet
- NCM 105-Macronutrients Carbohydrates ReviewerDocument6 pagesNCM 105-Macronutrients Carbohydrates ReviewerJustine AbongNo ratings yet
- NCP - MS FamilyDocument3 pagesNCP - MS FamilyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- FDAR SampleDocument1 pageFDAR SampleMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Disaster NursingDocument6 pagesDisaster NursingMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Disaster NursingDocument38 pagesDisaster NursingMark Zedrix Mediario100% (1)
- Carbohydrates ReviewDocument12 pagesCarbohydrates ReviewMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- 2 - Leadership and Management in NursingDocument4 pages2 - Leadership and Management in NursingMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- 3 - Modalities of NursingDocument6 pages3 - Modalities of NursingMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- 4 - Nursing Core Competency Standards 2012Document2 pages4 - Nursing Core Competency Standards 2012Mark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- 1 - ChedDocument2 pages1 - ChedMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - FractureDocument4 pagesDrug Study - FractureMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- FNCP Own FamilyDocument1 pageFNCP Own FamilyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Head NursingDocument2 pagesHead NursingMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument4 pagesDigestionMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy ActivityDocument4 pagesOxygen Therapy ActivityMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP Severe HypocalcemiaDocument4 pagesNCP Severe HypocalcemiaMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Maternal Health Framework ActDocument2 pagesMaternal Health Framework ActMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Program Mental HealthDocument10 pagesProgram Mental HealthMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument2 pagesNCP Rheumatoid ArthritisMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP ThoracostomyDocument3 pagesNCP ThoracostomyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient Knowledge of ROPDocument2 pagesNCP Deficient Knowledge of ROPMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP HypomagnesemiaDocument2 pagesNCP HypomagnesemiaMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Geriatric AssessmentDocument4 pagesGeriatric AssessmentMark Zedrix Mediario0% (1)
- Magnesium Deficit ActivityDocument4 pagesMagnesium Deficit ActivityMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP MixedDocument11 pagesNCP MixedMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Fat and Protein MetabolismDocument2 pagesFat and Protein MetabolismMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP LaminectomyDocument4 pagesNCP LaminectomyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument2 pagesVitamins and MineralsMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- FDAR Probable DengueDocument2 pagesFDAR Probable DengueMark Zedrix Mediario100% (1)
- Per Task TNCTDocument5 pagesPer Task TNCTDen Gesiefer LazaroNo ratings yet
- Monggo-Squash Cupcake Research StudyDocument12 pagesMonggo-Squash Cupcake Research StudyChin Sai100% (2)
- Curriculum Vitae Peter WilliamsDocument35 pagesCurriculum Vitae Peter Williamspetergw1No ratings yet
- Hypertensive DietDocument6 pagesHypertensive DietCarlos NiñoNo ratings yet
- Healthy Living 2017 Food TriangleDocument5 pagesHealthy Living 2017 Food TriangleAndrea CamachoNo ratings yet
- Make Kindness The Norm Neighborhood ChallengeDocument17 pagesMake Kindness The Norm Neighborhood ChallengeSzabados SándorNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Final de Ingles IDocument4 pagesTrabajo Final de Ingles IKatheryn MamaniNo ratings yet
- Naskah Soal Asas 9 2324 Tes TulisDocument8 pagesNaskah Soal Asas 9 2324 Tes TulisSalsa IvzahraNo ratings yet
- ATG Module 1Document5 pagesATG Module 1Inday Anne LptNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Grammar Revision Paper 2Document10 pagesGrade 6 Grammar Revision Paper 2Ting KimNo ratings yet
- ELPL NutraceuticalsDocument69 pagesELPL NutraceuticalsMascot pmtNo ratings yet
- What Is Food WebDocument1 pageWhat Is Food WebDashtan SalvosaNo ratings yet
- English Question Paper 1Document4 pagesEnglish Question Paper 1PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Capacity Layer ProjectDocument21 pagesCapacity Layer ProjectnilamaniNo ratings yet
- Cu2 Lab Module Diet ComputationDocument9 pagesCu2 Lab Module Diet ComputationCarl Jhelou AragonNo ratings yet
- Midwifery Exam PracticeDocument12 pagesMidwifery Exam Practicekristel ludangcoNo ratings yet
- Kaitlyn Greene Unit 9 Final ProjectDocument14 pagesKaitlyn Greene Unit 9 Final Projectapi-661682455No ratings yet
- REFERENCESDocument5 pagesREFERENCESRodeliza SolidiaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/32 March 2018Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/32 March 2018K KNo ratings yet
- Men's Health South Africa - November 2019Document134 pagesMen's Health South Africa - November 2019JulioNo ratings yet
- Mind Maps in Biochemistry - (Metabolism of Carbohydrates)Document23 pagesMind Maps in Biochemistry - (Metabolism of Carbohydrates)Gus LionsNo ratings yet
- Behavioral DirordersDocument14 pagesBehavioral DirordersranaNo ratings yet
- Biological Classification VedDocument13 pagesBiological Classification VedTanisha VarshneyNo ratings yet
- A Novel Healthy and Time Aware Food Recommender Syst - 2023 - Expert Systems Wit PDFDocument22 pagesA Novel Healthy and Time Aware Food Recommender Syst - 2023 - Expert Systems Wit PDFARVIEL DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- 01 Compendium Labelling Display 17 10 2022Document42 pages01 Compendium Labelling Display 17 10 2022sidhishwarr N RindheNo ratings yet
- Bombbar Swot Analysis: Opportunities ThreatsDocument9 pagesBombbar Swot Analysis: Opportunities ThreatsEkaterina ZuevaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Grade 9and10 FOOD PRODocument3 pages2nd Quarter Grade 9and10 FOOD PRODolly TrueemawnNo ratings yet
- Effects of Anthocyanin-Rich Purple Potato Flakes On Antioxidant StatuDocument8 pagesEffects of Anthocyanin-Rich Purple Potato Flakes On Antioxidant StatujbenavidesNo ratings yet
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Uploaded by
Mark Zedrix Mediario0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesThis document discusses carbohydrate metabolism. It defines carbohydrates and lists their various forms including polysaccharides, disaccharides, and monosaccharides. Key polysaccharides mentioned are glycogen, starch, cellulose, and nondigestive ones like pectin and alginates. The main disaccharides are sucrose, maltose, and lactose. Glucose, fructose, and galactose are named as the important monosaccharides. The document also outlines the processes of glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, and gluconeogenesis in carbohydrate metabolism. Glucose is said to be used as energy by entering the Krebs cycle in mitochondria to produce ATP through cellular respiration.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses carbohydrate metabolism. It defines carbohydrates and lists their various forms including polysaccharides, disaccharides, and monosaccharides. Key polysaccharides mentioned are glycogen, starch, cellulose, and nondigestive ones like pectin and alginates. The main disaccharides are sucrose, maltose, and lactose. Glucose, fructose, and galactose are named as the important monosaccharides. The document also outlines the processes of glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, and gluconeogenesis in carbohydrate metabolism. Glucose is said to be used as energy by entering the Krebs cycle in mitochondria to produce ATP through cellular respiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Uploaded by
Mark Zedrix MediarioThis document discusses carbohydrate metabolism. It defines carbohydrates and lists their various forms including polysaccharides, disaccharides, and monosaccharides. Key polysaccharides mentioned are glycogen, starch, cellulose, and nondigestive ones like pectin and alginates. The main disaccharides are sucrose, maltose, and lactose. Glucose, fructose, and galactose are named as the important monosaccharides. The document also outlines the processes of glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, and gluconeogenesis in carbohydrate metabolism. Glucose is said to be used as energy by entering the Krebs cycle in mitochondria to produce ATP through cellular respiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
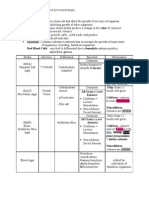
February 17, 2022 o Agar- used in laboratory or bacterial
cultures; gelatinous material prepared
NCM 116 – Metabolism
from salt water or algae; used for
thickening food
o Alginates- seaweeds
(3) Carbohydrate Metabolism o Carrageens- seaweeds
• Latin- “Assucre” Cellulose Amylose Amylopectin Glycogen
• Any of various neutral compound of CHO:
Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
• Constitutes a major class of animal food most
of which are produced by green plants (sugar,
starches, and cellulose)
Forms of Carbohydrates
Polysaccharides- a complex form of carb which can
be decomposed by hydrolysis into two or more
molecules of monosaccharides
Example:
• Dextrin- from starch made up of so many
molecules of glucose Disaccharides
• Starch- Amylose (plant components that 1. Sucrose- Fructose + Glucose
converts starch into sugar) and amylopectin
• Cellulose- framework of plants (wood, Sugar cane, the sweetest disaccharide
stalks, and leaves of all plants) 2. Maltose- Glucose + Glucose
Malt sugar from starch, fermentable sugar
3. Lactose- Galactose + Glucose
Milk sugar, yields lactic acid upon fermentation
Milk, eggnog, yogurt pudding, beer (sweet
stout), whey powder
Monosaccharides
- Smallest unit or monomer
• Glycogen- animal starch similar to - Combined by dehydration synthesis to form
amylopectin, made up of 30,000 glucose larger molecules like disaccharides and
which can be stored in the liver and in muscle polysaccharides
cells; most important polysaccharide; unused o Examples: Glucose, Galactose, and
glucose, converted and stored by liver Fructose
• Chemical formula: C6H1206
Nondigestive Polysaccharides
• Trioses
o Pectin- any group of colloidal • Tetroses
substances found in ripe fruits; used • Pentoses
to gel
1
• Hexoses (Glucose, Galactose, and Fructose) Glycogenesis
– most important for metabolism
• Glucose converted into Glycogen for storage
• Heptoses (Surbitol- used in making ice
in the liver and muscles, with the intervention
cream, Mannitol- a diuretic treating patients
of hormone, Insulin. This normalizes the
with brain inflammation)
blood sugar of a person after a meal.
Glycogenolysis
• Glycogen from liver and muscle will be
converted back again into Glucose to
normalize decreasing blood sugar, with the
intervention of Glucagon hormone
Gluconeogenesis
• Conversion of protein and fats into Glucose
as needed
Glucose/Dextrose
• The sweet colorless, soluble dextrorotary
form that occurs widely in nature and is the Glucose used as Energy
by smallest unit of carbohydrates present in
• Glucose yields 2 pyruvic acid… and with the
blood, used as energy by animals. Most come
action of acetylcholine enzyme A, it enters
from fruits, grains, and vegetables.
into the Krebs cycle with the help of Vitamin
Fructose/Levulose B
• Krebs cycle- happens inside the mitochondria
• From honey, sugar, and fruits
of the cell and makes ATP
• Agave, apple, pear, mango, honey, soda with
• Adenosine triphosphate when used result in
HFCS
energy, water, and CO2
Galactose
• Milk sugar
• Honey, yogurt, celery
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
• Carbo --- Salivary Amylase ---
(Polysaccharides converted to disaccharides)
--- Stomach Amylase --- by hydrolysis,
disaccharides will be converted to
monosaccharides
• Glucose readily absorbed in the microvillis of
intestines… Lactase, Maltase, and Sucrase
acts on Disacch to convert them into Glucose
You might also like
- PPNPSDocument4 pagesPPNPSMark Zedrix Mediario100% (2)
- Selective, Differential, & Enriched Media Lab ChartDocument2 pagesSelective, Differential, & Enriched Media Lab ChartFrankiesgirl6yr100% (6)
- Advocacy Programs Relevant To The Care of Older PersonsDocument6 pagesAdvocacy Programs Relevant To The Care of Older PersonsMark Zedrix Mediario100% (1)
- 10 Foods To Avoid When Trying To Lose WeightDocument5 pages10 Foods To Avoid When Trying To Lose WeightNikita DubeyNo ratings yet
- NCM105 Notes 2-CarbsDocument3 pagesNCM105 Notes 2-CarbsPaula TalaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Nutrition CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesNotes On Nutrition CarbohydratesFreewilly SternumNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument5 pagesCARBOHYDRATESGeorgina Rose JalagatNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three (Macronutrients)Document4 pagesChapter Three (Macronutrients)Kit Mendez BaccayNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Lec 3Document3 pagesNCM 105 Lec 3Rizaga, Carlos BenedictNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument15 pagesBio MoleculessofiajanineganalNo ratings yet
- Classification of Nutrients Macronurtients Classification of CarbohydratesDocument52 pagesClassification of Nutrients Macronurtients Classification of CarbohydratesAnna SantosNo ratings yet
- Biology Long TestDocument7 pagesBiology Long TestMarjorie AballaNo ratings yet
- NDT BsuDocument28 pagesNDT BsuAltea PasiaNo ratings yet
- NDT ReviewerDocument111 pagesNDT ReviewerMay RodeoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Macronutrients CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesChapter 2 Macronutrients Carbohydratesreajohn591No ratings yet
- 1 Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides (Simple Sugar)Document3 pages1 Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides (Simple Sugar)Kara AshleighNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate (STM)Document42 pagesCarbohydrate (STM)Jessica chiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - Energy Giving Food - Carbohydrates (CHO)Document4 pagesCHAPTER 3 - Energy Giving Food - Carbohydrates (CHO)Ruby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 - Macronutrient (CARBOHYDRATES)Document4 pagesMODULE 2 - Macronutrient (CARBOHYDRATES)Donna MarieNo ratings yet
- NCMA 215 PrelimsDocument30 pagesNCMA 215 PrelimsClaudine Jo B. TalabocNo ratings yet
- Charbohydrate: Unit - IiDocument8 pagesCharbohydrate: Unit - IiHemant SharmaNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument5 pagesCARBOHYDRATESMicah YapNo ratings yet
- Macronutrients: Carbohydrates (CHO) Proteins (CHON) FatsDocument32 pagesMacronutrients: Carbohydrates (CHO) Proteins (CHON) FatsGayle BocalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesChapter 4 - CarbohydratesIce Cream C0neNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument33 pagesCarbohydratesDeboo X Xavier100% (1)
- Science 10 Biomolecules ReviewerDocument9 pagesScience 10 Biomolecules ReviewerTasha Heart QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Handouts - CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesHandouts - CarbohydratesJerrold CruzNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument30 pagesCarbohydratesSheena Lou Regencia SalomonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MacronutrientsDocument3 pagesChapter 3 MacronutrientsMaxdjye EyjdxamNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument12 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolismbingbong2231No ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesbananakyuNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument43 pagesCarbohydratesEvangelene Esquillo Sana100% (1)
- Module 4 Cut CompressedDocument131 pagesModule 4 Cut CompressedLê Khuê TúNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument30 pagesCarbohydratesAvinash JakkulaNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument41 pagesCarbohydratesStrange Me100% (3)
- Macro Nutrients: Austin David O. Dumlao RN Instructor IDocument42 pagesMacro Nutrients: Austin David O. Dumlao RN Instructor IEmmanuel CuevasNo ratings yet
- GIT كتيب الطبعة الثانيةDocument56 pagesGIT كتيب الطبعة الثانيةdijla51No ratings yet
- المحاضرة الرابعة تغذية CarbohydrateDocument30 pagesالمحاضرة الرابعة تغذية Carbohydratedeminavictor8No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates PPT 1Document17 pagesCarbohydrates PPT 1Cristine Mae Pisquel TabunotNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Jameston S. Adorable, RND InstructorDocument51 pagesCarbohydrates: Jameston S. Adorable, RND InstructorMj AñascoNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument109 pagesMetabolismMai GaberNo ratings yet
- NUTMACRODocument9 pagesNUTMACROAliza Bea CastroNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Simple Sugars and Complex ChainsDocument44 pagesCarbohydrates: Simple Sugars and Complex ChainsBundi Gonzalez MartinNo ratings yet
- Macronutirents CPF With Prelim ProjectDocument78 pagesMacronutirents CPF With Prelim ProjectMONICA AGUIRRENo ratings yet
- MacronurientsDocument11 pagesMacronurientsDanah Grace SanchezNo ratings yet
- MacronurientsDocument11 pagesMacronurientsDanah Grace SanchezNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument59 pagesCarbohydratesChris Gift AkufunaNo ratings yet
- CC ChekDocument105 pagesCC ChekMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Carbohydrate 1 DIGESTION ABSORPTION AND METABOLISMDocument25 pagesChapter 3 Carbohydrate 1 DIGESTION ABSORPTION AND METABOLISMmaingcduNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument2 pagesBiological Moleculeshakdogiklog08No ratings yet
- 6 BiomoleculesDocument78 pages6 BiomoleculesPrecious Ryza G. BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter I: Food Components: CarbohydrateDocument14 pagesChapter I: Food Components: CarbohydrateJaylina MabulayNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesCarbohydratesBianca AzoresNo ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument75 pagesCombine PDFCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- Macro NutrientsDocument10 pagesMacro NutrientsClarke GriffinNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates 18.5.2022Document47 pagesCarbohydrates 18.5.2022Gourab NandaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Blood SugarDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Blood SugartagmanNo ratings yet
- Block 1 SummaryDocument230 pagesBlock 1 Summarymelisha.uysNo ratings yet
- KarbohidratDocument38 pagesKarbohidratRegina MunaamadaniNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument3 pagesCARBOHYDRATESjaizamaeenriquez59No ratings yet
- Digestion, Absorption and Metabolism of CarbohydratesDocument28 pagesDigestion, Absorption and Metabolism of CarbohydratesIzzuddienNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates LectureDocument31 pagesCarbohydrates LecturekushalNo ratings yet
- NCM 105-Macronutrients Carbohydrates ReviewerDocument6 pagesNCM 105-Macronutrients Carbohydrates ReviewerJustine AbongNo ratings yet
- NCP - MS FamilyDocument3 pagesNCP - MS FamilyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- FDAR SampleDocument1 pageFDAR SampleMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Disaster NursingDocument6 pagesDisaster NursingMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Disaster NursingDocument38 pagesDisaster NursingMark Zedrix Mediario100% (1)
- Carbohydrates ReviewDocument12 pagesCarbohydrates ReviewMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- 2 - Leadership and Management in NursingDocument4 pages2 - Leadership and Management in NursingMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- 3 - Modalities of NursingDocument6 pages3 - Modalities of NursingMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- 4 - Nursing Core Competency Standards 2012Document2 pages4 - Nursing Core Competency Standards 2012Mark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- 1 - ChedDocument2 pages1 - ChedMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - FractureDocument4 pagesDrug Study - FractureMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- FNCP Own FamilyDocument1 pageFNCP Own FamilyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Head NursingDocument2 pagesHead NursingMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument4 pagesDigestionMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy ActivityDocument4 pagesOxygen Therapy ActivityMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP Severe HypocalcemiaDocument4 pagesNCP Severe HypocalcemiaMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Maternal Health Framework ActDocument2 pagesMaternal Health Framework ActMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Program Mental HealthDocument10 pagesProgram Mental HealthMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument2 pagesNCP Rheumatoid ArthritisMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP ThoracostomyDocument3 pagesNCP ThoracostomyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient Knowledge of ROPDocument2 pagesNCP Deficient Knowledge of ROPMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP HypomagnesemiaDocument2 pagesNCP HypomagnesemiaMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Geriatric AssessmentDocument4 pagesGeriatric AssessmentMark Zedrix Mediario0% (1)
- Magnesium Deficit ActivityDocument4 pagesMagnesium Deficit ActivityMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP MixedDocument11 pagesNCP MixedMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Fat and Protein MetabolismDocument2 pagesFat and Protein MetabolismMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP LaminectomyDocument4 pagesNCP LaminectomyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument2 pagesVitamins and MineralsMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- FDAR Probable DengueDocument2 pagesFDAR Probable DengueMark Zedrix Mediario100% (1)
- Per Task TNCTDocument5 pagesPer Task TNCTDen Gesiefer LazaroNo ratings yet
- Monggo-Squash Cupcake Research StudyDocument12 pagesMonggo-Squash Cupcake Research StudyChin Sai100% (2)
- Curriculum Vitae Peter WilliamsDocument35 pagesCurriculum Vitae Peter Williamspetergw1No ratings yet
- Hypertensive DietDocument6 pagesHypertensive DietCarlos NiñoNo ratings yet
- Healthy Living 2017 Food TriangleDocument5 pagesHealthy Living 2017 Food TriangleAndrea CamachoNo ratings yet
- Make Kindness The Norm Neighborhood ChallengeDocument17 pagesMake Kindness The Norm Neighborhood ChallengeSzabados SándorNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Final de Ingles IDocument4 pagesTrabajo Final de Ingles IKatheryn MamaniNo ratings yet
- Naskah Soal Asas 9 2324 Tes TulisDocument8 pagesNaskah Soal Asas 9 2324 Tes TulisSalsa IvzahraNo ratings yet
- ATG Module 1Document5 pagesATG Module 1Inday Anne LptNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Grammar Revision Paper 2Document10 pagesGrade 6 Grammar Revision Paper 2Ting KimNo ratings yet
- ELPL NutraceuticalsDocument69 pagesELPL NutraceuticalsMascot pmtNo ratings yet
- What Is Food WebDocument1 pageWhat Is Food WebDashtan SalvosaNo ratings yet
- English Question Paper 1Document4 pagesEnglish Question Paper 1PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Capacity Layer ProjectDocument21 pagesCapacity Layer ProjectnilamaniNo ratings yet
- Cu2 Lab Module Diet ComputationDocument9 pagesCu2 Lab Module Diet ComputationCarl Jhelou AragonNo ratings yet
- Midwifery Exam PracticeDocument12 pagesMidwifery Exam Practicekristel ludangcoNo ratings yet
- Kaitlyn Greene Unit 9 Final ProjectDocument14 pagesKaitlyn Greene Unit 9 Final Projectapi-661682455No ratings yet
- REFERENCESDocument5 pagesREFERENCESRodeliza SolidiaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/32 March 2018Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/32 March 2018K KNo ratings yet
- Men's Health South Africa - November 2019Document134 pagesMen's Health South Africa - November 2019JulioNo ratings yet
- Mind Maps in Biochemistry - (Metabolism of Carbohydrates)Document23 pagesMind Maps in Biochemistry - (Metabolism of Carbohydrates)Gus LionsNo ratings yet
- Behavioral DirordersDocument14 pagesBehavioral DirordersranaNo ratings yet
- Biological Classification VedDocument13 pagesBiological Classification VedTanisha VarshneyNo ratings yet
- A Novel Healthy and Time Aware Food Recommender Syst - 2023 - Expert Systems Wit PDFDocument22 pagesA Novel Healthy and Time Aware Food Recommender Syst - 2023 - Expert Systems Wit PDFARVIEL DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- 01 Compendium Labelling Display 17 10 2022Document42 pages01 Compendium Labelling Display 17 10 2022sidhishwarr N RindheNo ratings yet
- Bombbar Swot Analysis: Opportunities ThreatsDocument9 pagesBombbar Swot Analysis: Opportunities ThreatsEkaterina ZuevaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Grade 9and10 FOOD PRODocument3 pages2nd Quarter Grade 9and10 FOOD PRODolly TrueemawnNo ratings yet
- Effects of Anthocyanin-Rich Purple Potato Flakes On Antioxidant StatuDocument8 pagesEffects of Anthocyanin-Rich Purple Potato Flakes On Antioxidant StatujbenavidesNo ratings yet