Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and Minerals
Uploaded by
Mark Zedrix Mediario0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views2 pagesVitamins and minerals are both micronutrients needed in small amounts. Vitamins are organic and can be destroyed by heat while minerals are inorganic. Water-soluble vitamins like B vitamins and C aid energy production, metabolism, and cell growth. Fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K build bones, protect vision, interact favorably in the body, and act as antioxidants. Major minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and iron are needed for bones, teeth, blood clotting, oxygen transport and more. Minor minerals also have key roles like chromium in glucose metabolism and fluoride for teeth. Vitamins and minerals work together, like vitamin D helping calcium absorption and vitamin C aiding iron absorption
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentVitamins and minerals are both micronutrients needed in small amounts. Vitamins are organic and can be destroyed by heat while minerals are inorganic. Water-soluble vitamins like B vitamins and C aid energy production, metabolism, and cell growth. Fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K build bones, protect vision, interact favorably in the body, and act as antioxidants. Major minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and iron are needed for bones, teeth, blood clotting, oxygen transport and more. Minor minerals also have key roles like chromium in glucose metabolism and fluoride for teeth. Vitamins and minerals work together, like vitamin D helping calcium absorption and vitamin C aiding iron absorption
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views2 pagesVitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and Minerals
Uploaded by
Mark Zedrix MediarioVitamins and minerals are both micronutrients needed in small amounts. Vitamins are organic and can be destroyed by heat while minerals are inorganic. Water-soluble vitamins like B vitamins and C aid energy production, metabolism, and cell growth. Fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K build bones, protect vision, interact favorably in the body, and act as antioxidants. Major minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and iron are needed for bones, teeth, blood clotting, oxygen transport and more. Minor minerals also have key roles like chromium in glucose metabolism and fluoride for teeth. Vitamins and minerals work together, like vitamin D helping calcium absorption and vitamin C aiding iron absorption
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
February 17, 2022 genetic diseases; for pregnancy, this is
needed thrice in amount. Normally, 0.4 mg
NCM 116 – Metabolism
only
• B12- Cyanocobalamin – RBC production;
amino acid synthesis
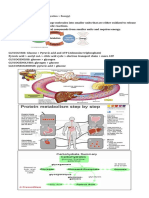
(3) VITAMINS AND MINERALS
• Vitamin C- Ascorbic Acid – combat
Difference Between Vitamins and Minerals infections and microorganisms
• Both are substances often times called Fat-soluble Vitamins
micronutrients since the body needs them in
A- Retinol – maintenance of eye function; avoid
tiny amounts.
night blindness
• Vitamins are organic (from plants) and can be
broken down by heat, air or acid. While D- Calciferol – bone strength; helps deposit calcium
minerals are inorganic (from water and soil) from diet into the bones
and eaten by animals.
E- Tocopherol - antioxidant
Water-soluble “B” Vitamins – can be absorbed by
K- Napthoquinones – blood clotting mechanism
villis of intestine
• B1- Thiamin – carb and amino acid
metabolism; growth and development; nerve Vitamins and Minerals Interaction
regeneration (important in peripheral
• Vitamin D magnetizes Calcium from food in
neuropathies in diabetic persons) – along
digestive tract
with B6 and B12 (Neurobion medication)
• Vitamin C helps absorb Iron
• B2- Riboflavin – citric acid cycle; blood
produces energy coming from ATP, we need • Vitamin C blocks body’s ability to assimilate
Copper (Low Vit C, High Cu, vice versa)
B2
• Overload of Manganese can lead to Iron
• B3- Niacin – comes from fish liver oil, red
Deficiency
meat, nuts; a component of Nicotinamide
Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) involved in Function of Water-soluble vitamins
glycolysis and carb metabolism; also in citric
acid cycle 1. Release energy
• B5- Panthothenic Acid – constituent of - Several B vitamins are coenzymes that
coenzyme glucose production from lipids; help release energy from food
Example, with gluconeogenesis, blood sugar 2. Produce energy
drops and you need glucose. B5 transforms - Thiamin, Riboflavin, niacin,
the proteins in body into glucose. panthothenic acid, and biotin engage in
energy production
• B6- Pyridoxine – amino acid metabolism;
- Any lack of any from these vitamins lead
produces essential and nonessential amino
to weakness
acids
3. Build proteins and cells
• B7- Biotin – fatty acid and nucleic acid
- B6, B12, and Folic acid metabolize
synthesis. Fatty acid comes from lipids (fats).
amino acid and helps cells multiply
Nucleic acid is involved in the movements of
4. Make Collagen
Pyruvic acid and into the citric acid cycle so
- The protein part of the bone that makes
that ATP can be utilized into energy.
skin resistant to infection; for strong
• B9- Folic Acid – nucleic acid synthesis and
bones, blood vessels, and teeth
making blood cells (hematopoiesis); combats
1
- Vitamin C makes Collagen, knits wound 10. Chromium – associated with the enzyme in
together, support blood vessel walls, form glucose metabolism
a base for teeth and bones 11. Fluoride - teeth
12. Manganese – absorption of food materials
Functions of Fat-soluble Vitamins
13. Copper – blood cell health
1. Builds bones 14. Iodine – thyroid function
- Bone formation is impossible without A, 15. Zinc - antioxidant
D, and K 16. Selenium – component to many enzymes; a
2. Protect vision coenzyme (helps others)
- Retinol keeps eye cells stay healthy
Functions of Minerals
3. Interact favorably
- Without Vitamin E, body will have • Maintain proper water balance
difficulty absorbing and storing Vitamin - A Sodium, Chloride, and Potassium role
A - Extracellular, Intra, and Intercellular
4. Protect the body fluid
- Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant • Healthy bones
- A function of Calcium, Phosphorus, and
Note: since these fat-soluble vitamins are
Magnesium
stored in the body for long periods, toxic
levels can build up. • Stabilize protein structures
- Sulfur helps stabilize protein such as
those found in hair, skin, and nails
Minerals • Transport of Oxygen
- Function of Iron
Major Minerals • Strengthen teeth
- Function of Fluoride
1. Calcium – for bone and teeth strength; blood
clotting mechanism; muscle activity; nerve • Helps blood clot and bolster immune system
function - Function of Zinc
2. Chloride – blood acid bone balance; • Hemoglobin production
Hydrochloric acid production, which helps in - Copper
protein absorption in body Notes:
3. Magnesium – blood formation; hemoglobin
synthesis; activation of enzymes o Salt overload. Calcium binds with
4. Phosphorus – bone and teeth formation; excess Sodium in the body and
energy transfer of ATP excreted when body senses that
5. Potassium – like the Calcium, for muscle sodium levels must be lowered
and bone function o Phosphorus can hamper body’s
6. Sodium – osmotic pressure regulation and ability to absorb Magnesium
nerve muscle function o Minor overload of Manganese can
7. Sulfur – components of hormones and exacerbate iron deficiency
several vitamins and proteins o Too little Iodine slows thyroid
8. Iron – important in hemoglobin hormone production- Goiter;
Seaweeds are rich in Iodine
Minor Minerals
9. Molybdenum – an enzyme component; with
minor symptoms during deficiency
You might also like
- Nebosh Igc1 Past ExamDocument15 pagesNebosh Igc1 Past Examkamy21481% (21)
- PPNPSDocument4 pagesPPNPSMark Zedrix Mediario100% (2)
- Advocacy Programs Relevant To The Care of Older PersonsDocument6 pagesAdvocacy Programs Relevant To The Care of Older PersonsMark Zedrix Mediario100% (1)
- Earth and LifeeDocument19 pagesEarth and LifeeShaine DelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument4 pagesVitamins and MineralsWillie Portacio Laron Jr.No ratings yet
- Nutrition: by DR Vipan GoyalDocument27 pagesNutrition: by DR Vipan GoyalAmit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Short Notes On Vitamins: Vitamin-D (Calciferol)Document3 pagesShort Notes On Vitamins: Vitamin-D (Calciferol)Aastha WankhadeNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument42 pagesVitamins and MineralsCawen TaponNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument48 pagesVitaminsBhumika ghimireNo ratings yet
- Fit MeDocument7 pagesFit MelouisesulagueNo ratings yet
- NUTRIDocument16 pagesNUTRIthisswannNo ratings yet
- Pcog Mod 11 VitaminsDocument7 pagesPcog Mod 11 VitaminsJeamel IgpuaraNo ratings yet
- Vitamins NutrientsDocument72 pagesVitamins NutrientsADITYA REZA PRIANUGRAHANo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 MICRONUTRIENTSDocument12 pagesChapter 4 MICRONUTRIENTSSami InglesNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Lesson Planchristian jade quijanoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Section 1 Chapter 1: The Relationship of Food and Health Nutrients VitaminsDocument32 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy: Section 1 Chapter 1: The Relationship of Food and Health Nutrients VitaminsAnonymousTargetNo ratings yet
- Nutrition, Heath and DiseasesDocument31 pagesNutrition, Heath and DiseaseskendoNo ratings yet
- Calories, Vitamins and Minerals: Nutrition - Finals Lesson 12Document12 pagesCalories, Vitamins and Minerals: Nutrition - Finals Lesson 12yoonie catNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Terms:: Changed To Active VitaminsDocument10 pagesVitamins: Terms:: Changed To Active VitaminsKaye Hayakawa CaibiganNo ratings yet
- Vit Mins NotesDocument7 pagesVit Mins NotesNirma BaneeNo ratings yet
- Vitamin: Djoko PriyatnoDocument39 pagesVitamin: Djoko Priyatnorahayu fujiNo ratings yet
- Basnut 2021 - Vitamin PDFDocument63 pagesBasnut 2021 - Vitamin PDFYUSRINA PUTRI NUGRAHAENI WIBOWONo ratings yet
- NDT Lab - Vitamins, Minerals, Water - UnaccomplishedDocument2 pagesNDT Lab - Vitamins, Minerals, Water - UnaccomplishedAlexandra AyneNo ratings yet
- NutritionalDocument4 pagesNutritionalperymeearumugamNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument21 pagesFat Soluble Vitaminskalpita joshiNo ratings yet
- CHN Nutrition of ChildDocument4 pagesCHN Nutrition of ChildJared Dela cruzNo ratings yet
- 2012-09-07 VitaminsDocument22 pages2012-09-07 Vitaminsaltemsahvetmed.85No ratings yet
- Macronutrients and Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals: L. SchefflerDocument34 pagesMacronutrients and Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals: L. SchefflerRuth Domingo AvedilloNo ratings yet
- Vitamins SlidesDocument91 pagesVitamins SlidesRhealyn Iligan100% (2)
- Fat Soluble Vitamin-1Document74 pagesFat Soluble Vitamin-1Himank RanaNo ratings yet
- Notes - Nutrition in MammalDocument15 pagesNotes - Nutrition in MammalEricNo ratings yet
- Fats and Water Soluble VitaminsDocument31 pagesFats and Water Soluble VitaminshafizahhoshniNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument54 pagesVitaminsAssasination ClassroomNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble Vit Lec-4Document38 pagesFat Soluble Vit Lec-4Anas siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - MicronutrientsDocument114 pagesChapter 4 - MicronutrientsSami InglesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document25 pagesLecture 5Liu IvyNo ratings yet
- VITAMINSDocument2 pagesVITAMINSthisswannNo ratings yet
- Akanksha Mittal I Year PGDocument111 pagesAkanksha Mittal I Year PGमोदी कृष्णाNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and VitaminDocument70 pagesNutrition and VitaminTob JurNo ratings yet
- Types of VitaminsDocument12 pagesTypes of VitaminsDesign worldNo ratings yet
- 041220190vit. K, E, A, D (E. Shaat) Lecture 1 Students-2019Document39 pages041220190vit. K, E, A, D (E. Shaat) Lecture 1 Students-2019slmen1269No ratings yet
- BIOCHEM, Vit. & Blood (Reviewer)Document8 pagesBIOCHEM, Vit. & Blood (Reviewer)michaelamontanielNo ratings yet
- "Vita" - Life, + AmineDocument91 pages"Vita" - Life, + AmineMaureen Chavez Kinney100% (1)
- Vitamins: Dr. Sara KhalifeDocument23 pagesVitamins: Dr. Sara KhalifeOmar F'KassarNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Week 10 - Vitamins and MineralsDocument3 pagesBiochemistry Week 10 - Vitamins and MineralsMicah JadeNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION - Micronutrients and Revision OfficialDocument25 pagesNUTRITION - Micronutrients and Revision OfficialAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Iqra Yasmeen 17975Document18 pagesVitamins: Iqra Yasmeen 17975Minahil SohailNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Biology Lesson Note SS1Document10 pagesWeek 3 Biology Lesson Note SS1Opeyemi AfolabiNo ratings yet
- Vitamin For Final MCQDocument14 pagesVitamin For Final MCQSajia Abedin 1821432649No ratings yet
- Vitamins Are An Organic Chemical Compound Which The Body Requires in Small Amounts For The Metabolism and To Protect Your HealthDocument130 pagesVitamins Are An Organic Chemical Compound Which The Body Requires in Small Amounts For The Metabolism and To Protect Your HealthAneesNo ratings yet
- Vitamins - It Must Be A Vital Organic Substance That Is Not An Energy-Producing Carbohydrate, Fat or Protein and Usually NecessaryDocument9 pagesVitamins - It Must Be A Vital Organic Substance That Is Not An Energy-Producing Carbohydrate, Fat or Protein and Usually NecessaryGia Espinosa OcbeñaNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument7 pagesVitaminsujeransariansari13No ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals: MicronutrientsDocument69 pagesVitamins and Minerals: MicronutrientsRajal PratapNo ratings yet
- Nutrition LectureDocument4 pagesNutrition LectureAce FernandezNo ratings yet
- Лекция 3 Витамины Минералы....Document213 pagesЛекция 3 Витамины Минералы....ibb ChattawNo ratings yet
- Macrominerals Sources Deficiency Toxicity FunctionsDocument3 pagesMacrominerals Sources Deficiency Toxicity FunctionsGia Espinosa OcbeñaNo ratings yet
- L 3 NutritionDocument120 pagesL 3 NutritionZara16No ratings yet
- BV300Document39 pagesBV300rajeevunnao100% (1)
- Carbsss 1652441181408Document41 pagesCarbsss 1652441181408Sameer Singh pariharNo ratings yet
- Food ChemDocument7 pagesFood ChemRaven RosalesNo ratings yet
- 5 Micronutrients Fat Soluble Vitamins 21-01-2022 (21 Jan 2022) Material - I - 21!01!2022 - VitaminsDocument21 pages5 Micronutrients Fat Soluble Vitamins 21-01-2022 (21 Jan 2022) Material - I - 21!01!2022 - VitaminsAksh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Gastrointestinal Tract System/BlockDocument38 pagesVitamins: Gastrointestinal Tract System/BlockjabirNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandVitamin B12 Deficiency, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- NCP - MS FamilyDocument3 pagesNCP - MS FamilyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- FDAR SampleDocument1 pageFDAR SampleMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Disaster NursingDocument38 pagesDisaster NursingMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates ReviewDocument12 pagesCarbohydrates ReviewMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- 3 - Modalities of NursingDocument6 pages3 - Modalities of NursingMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- 4 - Nursing Core Competency Standards 2012Document2 pages4 - Nursing Core Competency Standards 2012Mark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Head NursingDocument2 pagesHead NursingMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- 2 - Leadership and Management in NursingDocument4 pages2 - Leadership and Management in NursingMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- 1 - ChedDocument2 pages1 - ChedMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Disaster NursingDocument6 pagesDisaster NursingMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- FNCP Own FamilyDocument1 pageFNCP Own FamilyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP HypomagnesemiaDocument2 pagesNCP HypomagnesemiaMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - FractureDocument4 pagesDrug Study - FractureMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Program Mental HealthDocument10 pagesProgram Mental HealthMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP Severe HypocalcemiaDocument4 pagesNCP Severe HypocalcemiaMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Deficit ActivityDocument4 pagesMagnesium Deficit ActivityMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP LaminectomyDocument4 pagesNCP LaminectomyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy ActivityDocument4 pagesOxygen Therapy ActivityMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient Knowledge of ROPDocument2 pagesNCP Deficient Knowledge of ROPMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument2 pagesNCP Rheumatoid ArthritisMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP ThoracostomyDocument3 pagesNCP ThoracostomyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Maternal Health Framework ActDocument2 pagesMaternal Health Framework ActMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- NCP MixedDocument11 pagesNCP MixedMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Fat and Protein MetabolismDocument2 pagesFat and Protein MetabolismMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument2 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Geriatric AssessmentDocument4 pagesGeriatric AssessmentMark Zedrix Mediario0% (1)
- DigestionDocument4 pagesDigestionMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- FDAR Probable DengueDocument2 pagesFDAR Probable DengueMark Zedrix Mediario100% (1)
- Nucleobase: Nucleobases, Also Known As Nitrogenous BasesDocument5 pagesNucleobase: Nucleobases, Also Known As Nitrogenous BasesLuis Felipe Mera GrandasNo ratings yet
- 304 Stainless Steel Chemical Compatibility Chart From IsmDocument11 pages304 Stainless Steel Chemical Compatibility Chart From IsmchenNo ratings yet
- Ajin Sathyababu: Profile SummaryDocument2 pagesAjin Sathyababu: Profile SummaryAjin SNo ratings yet
- CA1 Online Class 2Document13 pagesCA1 Online Class 2kemerutNo ratings yet
- Form Hasil Pemeriksaan Laboratorium 2Document5 pagesForm Hasil Pemeriksaan Laboratorium 2puskesmas sarijadiNo ratings yet
- Artepillin C As An Outstanding Phenolic Compound of Brazilian Green Propolis For Disease Treatment: A Review On Pharmacological AspectsDocument13 pagesArtepillin C As An Outstanding Phenolic Compound of Brazilian Green Propolis For Disease Treatment: A Review On Pharmacological AspectslyviaNo ratings yet
- SGA Webinar 21nov2020 - InvitationDocument1 pageSGA Webinar 21nov2020 - InvitationSantoso 9JimmyNo ratings yet
- Pemerintah Kabupaten Klungkung Dinas Kesehatan: Jalan Gajah Mada No. 55 Semarapura Telp. (0366) 21150Document4 pagesPemerintah Kabupaten Klungkung Dinas Kesehatan: Jalan Gajah Mada No. 55 Semarapura Telp. (0366) 21150anggaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum 4 (Soil Washing)Document19 pagesLaporan Praktikum 4 (Soil Washing)Shinta AritonangNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 17Document17 pagesPage 1 of 17RamBabuMeenaNo ratings yet
- Science & Beyond Science Final1Document25 pagesScience & Beyond Science Final1Veeresh M Honnihal100% (2)
- Literature Review On Environmental DegradationDocument8 pagesLiterature Review On Environmental Degradationafmzaoahmicfxg100% (1)
- L6S Final Examination Students)Document12 pagesL6S Final Examination Students)Fazliawati MahayuddinNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fundamental Knowledge 2013Document10 pagesAssessment of Fundamental Knowledge 2013Jason PakNo ratings yet
- Hazard ManagementDocument18 pagesHazard Managementsthiyagu0% (1)
- Overflow With Hope - Joel OsteenDocument7 pagesOverflow With Hope - Joel OsteenJHON RAY OTAÑESNo ratings yet
- Habonim Valve CatalogDocument17 pagesHabonim Valve Catalogmushtaq1211No ratings yet
- Scpa Presentation December 15, 2014: Presented By: Chandra Brown, Internal Audit Monya Wyatt, SCPA Budget ManagerDocument20 pagesScpa Presentation December 15, 2014: Presented By: Chandra Brown, Internal Audit Monya Wyatt, SCPA Budget ManagerCincinnatiEnquirerNo ratings yet
- Grant AwardDocument15 pagesGrant AwardRay StillNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STO: Within 4 Hour of DX: DX: Sto: Goal MetDocument5 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STO: Within 4 Hour of DX: DX: Sto: Goal MetRussel SantosNo ratings yet
- Ecpg OrlapDocument258 pagesEcpg OrlapNoha Ibraheem HelmyNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Pharmacology in The Neonatal FoalDocument26 pagesAspects of Pharmacology in The Neonatal FoalAristoteles Esteban Cine VelazquezNo ratings yet
- (2003) Wels C. & Robertson A. MacG. - Conceptual Model For Estimating Water Recovery in Tailings Impoundments PDFDocument8 pages(2003) Wels C. & Robertson A. MacG. - Conceptual Model For Estimating Water Recovery in Tailings Impoundments PDFLuis Miguel La TorreNo ratings yet
- En - Techinfo - TRILITE SM210Document9 pagesEn - Techinfo - TRILITE SM210Emrh YsltsNo ratings yet
- 12 Week Holiday ChallengeDocument58 pages12 Week Holiday ChallengeHalison AriasNo ratings yet
- MTO MATERIAL OHL 20 KVDocument4 pagesMTO MATERIAL OHL 20 KVDacid ChalinkNo ratings yet
- Driving Exam NotesDocument7 pagesDriving Exam Notesreach2ashish5065No ratings yet
- Module 2-Curriculum PlanningDocument6 pagesModule 2-Curriculum PlanningAsuna SanNo ratings yet
- Gea Fes, Inc.: 4 Models 50 - 300 HPDocument2 pagesGea Fes, Inc.: 4 Models 50 - 300 HPVadimNo ratings yet