Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name: - Test Date: - : Digestive Unit Study Guide
Name: - Test Date: - : Digestive Unit Study Guide
Uploaded by
ameetdey100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
20 views3 pagesThe document provides information about the digestive system including:
- The parts of the digestive system and their functions such as the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines.
- Additional vocabulary like insulin, choking, and feces.
- Diseases and conditions that can affect the digestive system including cancer, ulcers, diabetes, and diarrhea.
- Ways to take care of the digestive system like eating fiber, drinking water, and exercising.
Original Description:
Original Title
Digestive Study Guide
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information about the digestive system including:
- The parts of the digestive system and their functions such as the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines.
- Additional vocabulary like insulin, choking, and feces.
- Diseases and conditions that can affect the digestive system including cancer, ulcers, diabetes, and diarrhea.
- Ways to take care of the digestive system like eating fiber, drinking water, and exercising.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
20 views3 pagesName: - Test Date: - : Digestive Unit Study Guide
Name: - Test Date: - : Digestive Unit Study Guide
Uploaded by
ameetdeyThe document provides information about the digestive system including:
- The parts of the digestive system and their functions such as the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines.
- Additional vocabulary like insulin, choking, and feces.
- Diseases and conditions that can affect the digestive system including cancer, ulcers, diabetes, and diarrhea.
- Ways to take care of the digestive system like eating fiber, drinking water, and exercising.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Name:__________________ Test Date:______________
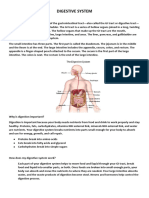
DIGESTIVE UNIT STUDY GUIDE
DIGESTION – The process of breaking down food into substances that can be
used by the body.
PARTS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Know where it is located and what
the function (job) of each part:
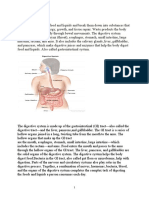
Mouth (teeth, tongue, saliva) Word together to break food into smaller pieces and
moisten food to make it easier to swallow.
Esophagus – The tube food passes through from the mouth to the stomach.
Epiglottis – The flap of skin that closes over the windpipe so food goes to the
stomach and not to the lungs.
Stomach – Turns and chemically breaks down food to go to the small intestine.
Small Intestines – The approximately 25-foot tube that absorbs nutrients into the
body.
Villi – Small finger-like projections in the small intestine that absorb nutrients.
Liver – Makes bile (helps digest food), stores minerals and vitamins, and helps get
rid of harmful substances in the blood.
Gall Bladder - Stores bile from the liver until it is released into the intestine.
Large Intestines (colon) – The 5-foot part of the digestive system that absorbs
fluids from undigested food into the body.
Rectum – The final section of the large intestine.
Anus – The opening where feces (waste) leaves the body
Appendix – No known cause
Pancreas – Makes insulin that controls sugar levels in the blood
ADDITIONAL VOCABULARY:
Insulin – A substance that regulates the amount of sugar in the blood.
Choking – What happens when an object blocks the windpipe (which runs parallel
to the esophagus) making it difficult to breath.
Heimlich Maneuver – A procedure where pressure is applied between the navel
and the rib cage to prevent choking.
Feces: Bodily waste eliminated through the rectum.
DISEASES AND CONDITIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM:
1. Cancer – The growth of abnormal cells. To help prevent, drink water, eat
foods high in fiber, and visit the doctor when sick or yearly.
2. Ulcer – A painful erosion of the stomach and intestines.
3. Diabetes – A condition where the body doesn’t produce the necessary
amount of insulin.
4. Hypoglycemia – a condition where there is not enough sugar in the blood.
5. Vomiting – Also known as throwing up or regurgitating.
6. Diarrhea – Watery feces
WAYS TO TAKE CARE OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: See Packet Page 10
- Eat foods high in fiber such as fruits, vegetables and whole grain foods.
- Drink between 6-8 glasses of water a day
- Exercise about 60 minutes a day
Additional computer site to study:
http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/health/anatomy/digestion/
digestion_tutorial.htm AND
http://www.frsd.k12.nj.us/cms/lib01/NJ01001104/Centricity/Domain/462/
digestive%20flash%20cards.pdf
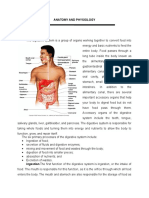
Anatomy:
You might also like
- Kaizen: A Tool For Continuous Improvement of Jollibee Foods Corp. Sanitation Procedures and PracticesDocument36 pagesKaizen: A Tool For Continuous Improvement of Jollibee Foods Corp. Sanitation Procedures and PracticesreiNo ratings yet
- News Lessons Sevilleoranges Worksheet Advanced 391522Document4 pagesNews Lessons Sevilleoranges Worksheet Advanced 391522Chiara Irene Thea CappellinaNo ratings yet
- Advance Sentence Correction 3 - TensesDocument2 pagesAdvance Sentence Correction 3 - Tensesdennis oh100% (1)
- Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesDigestive SystemChristine Joyce S. CruzNo ratings yet
- SCP Ebs Integration White Paper 12.1.3 VersionDocument23 pagesSCP Ebs Integration White Paper 12.1.3 Versionameetdey100% (1)
- LESSON 11 - 4th GradingDocument6 pagesLESSON 11 - 4th GradingRovy Insigne GacitaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER. 07 Animal NutritiondocxDocument6 pagesCHAPTER. 07 Animal Nutritiondocxsumana yeasminNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesDigestive SystemhlorenoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System (Autosaved)Document53 pagesDigestive System (Autosaved)Jeyger Borres BuadlartNo ratings yet
- Digestive System HandoutDocument6 pagesDigestive System HandoutMd. Jakir HossainNo ratings yet
- Digestive Sysytem: Basic Health CareDocument50 pagesDigestive Sysytem: Basic Health CareBecky GalanoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Reported By: Norjanisah B. BauteDocument41 pagesDigestive System: Reported By: Norjanisah B. BauteGwynethNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PresentationDocument20 pagesDigestive System Presentationrocky2219No ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesThe Digestive SystemSofia Reinne Ong LafortezaNo ratings yet
- Sistem Pencernaan ManusiaDocument8 pagesSistem Pencernaan ManusiaJovan Bimaa PramanaNo ratings yet
- SCI G8 Q4 Week 1 DIGESTIVE SYSTEMDocument114 pagesSCI G8 Q4 Week 1 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM• S h ı m m y •No ratings yet
- Digestive System ReviewerDocument2 pagesDigestive System ReviewerDivino BauzonNo ratings yet
- From Start ..... To FinishDocument55 pagesFrom Start ..... To Finishapi-240527437No ratings yet
- Nutrition & EnergyDocument13 pagesNutrition & EnergyJeyanthi ElaneshanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Key Terms:: Nutrition Quiz NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Key Terms:: Nutrition Quiz NotesThomas AssisNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument45 pagesDigestive SystemEzequiel ManluluNo ratings yet
- CH-2 (Nutrition in Animals) NotesDocument9 pagesCH-2 (Nutrition in Animals) NotespranavNo ratings yet
- NUTRITIONDocument11 pagesNUTRITIONRushana SadaqatNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument29 pagesDigestive Systemsugar kookie0% (1)
- Digestive System: Submitted By: Caimoso, Tricia Ann D. Quiambao, Aliyah Lourdes D. Bs Psychology 3-3Document9 pagesDigestive System: Submitted By: Caimoso, Tricia Ann D. Quiambao, Aliyah Lourdes D. Bs Psychology 3-3Tricia Ann CaimosoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE DIgestive SystemDocument7 pagesSCIENCE DIgestive SystemRichard MerkNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesThe Digestive SystemKashif KhokharNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiologydaculareyndel04No ratings yet
- FenieDocument32 pagesFenieLilacx ButterflyNo ratings yet
- Examen Final de InglesDocument3 pagesExamen Final de InglesCynthia SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument9 pagesNutrition in AnimalsrounakNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Report (Human Anatomy and Physiology)Document6 pagesDigestive System Report (Human Anatomy and Physiology)Cielo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Materi Digestive SystemDocument13 pagesMateri Digestive Systembetta putriNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Powerpoint 1227698045024899 8Document44 pagesThe Digestive System Powerpoint 1227698045024899 8Julia Rae Delos Santos100% (1)
- Human Digestive System-Note NewDocument7 pagesHuman Digestive System-Note Newtinsae tewodrosNo ratings yet
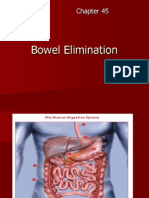
- Bowel EliminationDocument34 pagesBowel EliminationAnastasia LubertaNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative Colitis FinalDocument13 pagesUlcerative Colitis FinalAngelique100% (1)
- Digestive SystemDocument29 pagesDigestive SystemMaika JimenezNo ratings yet
- Class 7-Science-Nutrition in Animals-Additional NotesDocument13 pagesClass 7-Science-Nutrition in Animals-Additional NotesTestEmailForScribd TestEmailForScribdNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesDigestive SystemAntonella AguileraNo ratings yet
- GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM 1 Ngan 2Document14 pagesGASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM 1 Ngan 2Stephen Jil BocoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 NotesDocument14 pagesChapter 7 NotesSamaa Al busidiNo ratings yet
- StomachDocument4 pagesStomachtinsae tewodrosNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesThe Digestive SystemSabika HassanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 Bowl EliminationDocument72 pagesLecture 15 Bowl EliminationIsbelNo ratings yet
- دمج شباتر البالغين .....Document511 pagesدمج شباتر البالغين .....Abdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive SystemDocument34 pagesThe Human Digestive SystemKayla Denize GerardinoNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument14 pagesBiologyPinky RanaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesWeek 1 - Digestive Systemlau dashNo ratings yet
- Biology Sahil ArminDocument22 pagesBiology Sahil Arminarmin marandiNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument48 pagesDigestive SystemAlyanna Marie CarilloNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument25 pagesDigestive Systembazaar9No ratings yet
- Nutrition: What Is Malnutrition?Document43 pagesNutrition: What Is Malnutrition?Starpril_88No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Notes BioDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Notes BioArabella ShepherdNo ratings yet
- Digestive Tract of The PigDocument4 pagesDigestive Tract of The PiglsvcsbNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY (Second Term)Document55 pagesBIOLOGY (Second Term)carlaplana2008No ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument21 pagesHuman Digestive SystemazliniNo ratings yet
- Diet Assessment NBDocument6 pagesDiet Assessment NBnbaker2108No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The GDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Gbryan leguiabNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument11 pagesDigestiveSuahniNo ratings yet
- Document 70Document9 pagesDocument 70Malik Ghazi KhedirNo ratings yet
- Function of Digestive SystemDocument33 pagesFunction of Digestive SystemameetdeyNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & Physiology A & B Course SyllabusDocument6 pagesHuman Anatomy & Physiology A & B Course SyllabusameetdeyNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Notes: - Quiz Friday!Document18 pagesDigestive System Notes: - Quiz Friday!ameetdeyNo ratings yet
- Act 2010-3Document50 pagesAct 2010-3ameetdeyNo ratings yet
- BHEL Pay ScaleDocument1 pageBHEL Pay ScaleameetdeyNo ratings yet
- How To Update Service RequestDocument2 pagesHow To Update Service RequestameetdeyNo ratings yet
- SR Create API - ExampleDocument4 pagesSR Create API - ExampleameetdeyNo ratings yet
- KCS 2017 05 07 PDFDocument196 pagesKCS 2017 05 07 PDFameetdeyNo ratings yet
- KCS 2017 04 30 PDFDocument192 pagesKCS 2017 04 30 PDFameetdeyNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade ARMT - Item Specs PDFDocument133 pages7th Grade ARMT - Item Specs PDFameetdeyNo ratings yet
- Southbound Weekdays Southbound Weekdays: (Cont.)Document8 pagesSouthbound Weekdays Southbound Weekdays: (Cont.)ameetdeyNo ratings yet
- Rainbow RoutesDocument1 pageRainbow RoutesameetdeyNo ratings yet
- PDF 20221016 202706 0000Document53 pagesPDF 20221016 202706 0000CA Manoj Kumar SabatNo ratings yet
- Business Praposal-Pizza Restaurant Real PaprikaDocument19 pagesBusiness Praposal-Pizza Restaurant Real PaprikaHarikrushan DholariyaNo ratings yet
- OFFERINGDocument4 pagesOFFERINGZaki HananNo ratings yet
- Topic-Can I Transfer My Liquor Licence To Someone Else???Document2 pagesTopic-Can I Transfer My Liquor Licence To Someone Else???Neha SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Cookery-Nc-Ii-Long-Quiz Grade 11Document3 pagesCookery-Nc-Ii-Long-Quiz Grade 11Riza Ponce100% (1)
- 7 Reading Task 1. For Questions 1-6, Read The Text Below and Decide Which Answer (A, B, C or D) Best Fits Each Gap. Fill in The Table Below The TextDocument2 pages7 Reading Task 1. For Questions 1-6, Read The Text Below and Decide Which Answer (A, B, C or D) Best Fits Each Gap. Fill in The Table Below The TextСофия ТимофееваNo ratings yet
- DS 2021Document478 pagesDS 2021Farhat DurraniNo ratings yet
- A2 SınavDocument3 pagesA2 Sınavmerve.akkuss20No ratings yet
- 2021-2022 Assessment TLE8 Week3&4Document2 pages2021-2022 Assessment TLE8 Week3&4ARVIJOy ANDRESNo ratings yet
- CraniotomyDocument13 pagesCraniotomyVianca KoNo ratings yet
- 2024 Palacio de Maynila New Standard Proposal Letter For UP Manila April 17, 2024Document2 pages2024 Palacio de Maynila New Standard Proposal Letter For UP Manila April 17, 2024Arianne Grace AberdeNo ratings yet
- Cetak Soal Tugas - Sistem Informasi Pembelajaran (SIP) SMA Kusuma Bangsa Palemba 5Document4 pagesCetak Soal Tugas - Sistem Informasi Pembelajaran (SIP) SMA Kusuma Bangsa Palemba 5Gora Marondos Kayara SaragihNo ratings yet
- De Cuong Speaking TA4 TQDocument35 pagesDe Cuong Speaking TA4 TQdvu751763No ratings yet
- Module 3 G10 (Q4)Document4 pagesModule 3 G10 (Q4)Meco ChicaNo ratings yet
- Coca Cola - FinalDocument29 pagesCoca Cola - FinalShubham DixitNo ratings yet
- Fusion by Tala Select Food MenuDocument6 pagesFusion by Tala Select Food MenuArwa AlawadhiNo ratings yet
- AGP (W1) - Self-Study I - Present TensesDocument18 pagesAGP (W1) - Self-Study I - Present TensesMagdalena SzczukaNo ratings yet
- The TerminalDocument78 pagesThe TerminalDaniel Minsoo KimNo ratings yet
- INGLES IRIS YANEZ 2do Lapso ResueltoDocument2 pagesINGLES IRIS YANEZ 2do Lapso Resueltoザ 緩い100% (1)
- 604-Article Text-2332-1-10-20191127Document5 pages604-Article Text-2332-1-10-20191127Glen Homer Realin HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Vegetable C 2Document7 pagesHandbook of Vegetable C 2Sudip ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Asana - Pranayama - Japa - by GurumaaDocument5 pagesAsana - Pranayama - Japa - by GurumaaSuraj NikteNo ratings yet
- 6th Lecture Composition and Properties of MilkDocument24 pages6th Lecture Composition and Properties of MilkSankaNo ratings yet
- Cooking Method and Meat CutsDocument26 pagesCooking Method and Meat CutsAlexis VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- g7 Module Health q2 EdilynDocument44 pagesg7 Module Health q2 EdilynRYAN FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Bubbafood-'S All MSDocument7 pagesBubbafood-'S All MSAli AliNo ratings yet
- (123doc) Viet Tieng Anh 6 En41Document51 pages(123doc) Viet Tieng Anh 6 En41Dang Quoc DuNo ratings yet