Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Substantive Test Vs
Substantive Test Vs
Uploaded by
Princess Tolentino0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesAn auditor must choose between substantive tests and tests of controls. The higher the assessed control risk, the more substantive procedures need to be performed. Tests of controls examine the effectiveness of client controls, while substantive tests examine financial statements and supporting documentation for errors. There are three types of substantive tests: substantive tests of transactions, substantive tests of balances, and analytical procedures. Audit evidence is information used to support an auditor's opinion and can come from underlying accounting data, corroborating information, or be observed. The sufficiency, materiality, and risk involved impact how much evidence is needed.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn auditor must choose between substantive tests and tests of controls. The higher the assessed control risk, the more substantive procedures need to be performed. Tests of controls examine the effectiveness of client controls, while substantive tests examine financial statements and supporting documentation for errors. There are three types of substantive tests: substantive tests of transactions, substantive tests of balances, and analytical procedures. Audit evidence is information used to support an auditor's opinion and can come from underlying accounting data, corroborating information, or be observed. The sufficiency, materiality, and risk involved impact how much evidence is needed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesSubstantive Test Vs
Substantive Test Vs
Uploaded by
Princess TolentinoAn auditor must choose between substantive tests and tests of controls. The higher the assessed control risk, the more substantive procedures need to be performed. Tests of controls examine the effectiveness of client controls, while substantive tests examine financial statements and supporting documentation for errors. There are three types of substantive tests: substantive tests of transactions, substantive tests of balances, and analytical procedures. Audit evidence is information used to support an auditor's opinion and can come from underlying accounting data, corroborating information, or be observed. The sufficiency, materiality, and risk involved impact how much evidence is needed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Substantive Test Vs. Test of Controls. 2.
Substantive Tests of Balance – an
auditor focuses on substantiating
How to choose between them? It is based on the ending balance of an account.
the audit risk model – the higher the control 3. Analytical Procedures – using
risk assessment, the more substantive comparisons and relationships to
procedures performed. assess whether account balance
Test Control appear reasonable.
Is an audit procedure to test the Audit Evidence
effectiveness of a control used by a - Audit evidence refers to
client to prevent or detect material information or data use or collects
misstatements. by auditors as part of their audit
General Classification of test controls: works so that they could conclude
1. Reperformance – Auditors may their opinion on whether or not
initiate a new transaction, to see financial statements are prepared
which controls are used by the in material respect and accordance
client and effectiveness of the with the applicable financial
controls. reporting framework.
2. Observation – Auditors may
observe a business process in Types of Evidences
action, and in particular the control
1. Underlying Accounting Data – are
elements of the process.
3. Inspection – auditors may examine the books of entry and “source of
data” is the supporting document
business documents for approval
signatures, stamps, or review check based on which a transaction is
recorded.
mark, which indicate that controls
have been performed. 2. Corroborating information – refers
to the documents and other
Substantive Test information supporting the entity’s
accounting data obtained by client
Is an audit procedure that examines the and other sources.
financial statements and supporting
documentation to see if they contain Qualities of evidence
errors. These tests are needed as
evidence to support the assertion that 1. Sufficiency – is the measure of the
quantity of audit evidence should
the financial records of an entity are
complete, valid and accurate. accumulate.
Factors that may be considered in
3 types of Substantive Test
1. Substantive Test of Transaction – evaluating the sufficiency of
evidence:
auditors focuses on testing
individual transaction by verifying a. The competence of evidence –
refers to the quality of the
them to supporting documentation.
evidence, regardless of whether
the evidence is written, oral, or 1. Audit Evidence obtained from
observed. Written Evidence Independent Resources
includes the client’s books, 2. Effective accounting and internal
records, and other information control Systems
such as meeting minutes and 3. Audit evidence obtained directly by the
internal control manuals. Oral auditor
evidence is gathered during 4. Audit evidence in the form of
initial and subsequent inquiries documents and written
of the client’s employees and representations.
management. Observed
evidence includes watching the Cost/benefit consideration when obtaining
evidence.
client take the physical
inventory. As a guiding rule, there should be a rational
b. The Materiality of the item relationship between the cost of obtaining
being examined. The more the evidence and the usefulness of the information
financial statement amount obtained. Determining the appropriate type of
being examined is, the more evidence that should be obtained is a matter of
evidence will be needed to professional judgment.
support its validity. On the
other hand, if the account is
immaterial to the financial
statement, there is no need to
perform any procedure related
to that account.
c. The risk involved in a particular
account. As the risk of
misstatement in a particular
account increases, the more
evidence will be needed.
2. Appropriateness – is the measure of
the quality of audit evidence and its
relevance to a particular assertion
and its reliability.
Relevance relates the timeliness of
evidence and its ability to satisfy
the audit objective. Reliability
relates to the objectivity of
evidence and is influence by its
source and by its nature.
Generalization that may help an auditor in
Assessing the Reliability of Audit Evidence:
You might also like
- Auditing and Assurance Services 16th Edition Arens Solutions ManualDocument28 pagesAuditing and Assurance Services 16th Edition Arens Solutions Manualgloriaelfleda9twuoe100% (25)
- Red Light Camera Effectiveness EvaluationDocument33 pagesRed Light Camera Effectiveness EvaluationRochester Democrat and ChronicleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Evidential Matter and Its DocumentationDocument14 pagesChapter 4 - Evidential Matter and Its DocumentationKristine WaliNo ratings yet
- The Movie Patch AdamsDocument2 pagesThe Movie Patch AdamsPrincess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Muet 2006 To 2019 Past PapersDocument148 pagesMuet 2006 To 2019 Past PapersUmaid Ali Keerio100% (2)
- Measuring Team ProductivityDocument27 pagesMeasuring Team ProductivityAdhitya Setyo Pamungkas100% (1)
- Audit PrelimsDocument10 pagesAudit PrelimsMane NessyNo ratings yet
- Audit I CH IVDocument7 pagesAudit I CH IVAhmedNo ratings yet
- Audit Evidence and Documentation HandoutsDocument16 pagesAudit Evidence and Documentation Handoutsumar shahzadNo ratings yet
- Audit EvidenceDocument16 pagesAudit EvidenceDymphna Ann CalumpianoNo ratings yet
- Gathering and Evaluating Audit Evidence: What Is An Audit Procedures?Document4 pagesGathering and Evaluating Audit Evidence: What Is An Audit Procedures?Alyssa Abbas DiatorNo ratings yet
- At.3204 Nature and Type of Audit EvidenceDocument7 pagesAt.3204 Nature and Type of Audit EvidenceDenny June CraususNo ratings yet
- Auditing CHAPTER THREEDocument9 pagesAuditing CHAPTER THREEGetachew JoriyeNo ratings yet
- AT.3404 - Audit Evidence and DocumentationDocument6 pagesAT.3404 - Audit Evidence and DocumentationMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Jzanzig - Auditing CH 7 LectureDocument24 pagesJzanzig - Auditing CH 7 LectureMouna MoonyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Performing Substantive TestDocument5 pagesChapter 8: Performing Substantive TestJhondelNo ratings yet
- AA-Audit EvidenceDocument15 pagesAA-Audit EvidenceRafsan JazzNo ratings yet
- Audit-Evidence - Internal ControlDocument3 pagesAudit-Evidence - Internal ControlHarley Alburque MandapatNo ratings yet
- Audit Evidence AndTestingDocument15 pagesAudit Evidence AndTestingSigei LeonardNo ratings yet
- Audit TechniqueDocument8 pagesAudit TechniqueAllin John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- AUDI314 Week9Document14 pagesAUDI314 Week9miaNo ratings yet
- At.106.2 Audit Evidence Gathering My StudentsDocument7 pagesAt.106.2 Audit Evidence Gathering My StudentsLimuel NievoNo ratings yet
- Audit Working PapersDocument25 pagesAudit Working PapersImran MobinNo ratings yet
- Audit Evidence: Concept Checks P. 167Document32 pagesAudit Evidence: Concept Checks P. 167hsingting yuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Audit EvidenceDocument6 pagesChapter 5 Audit EvidencebiyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Audit EvidenceDocument10 pagesUnit 5: Audit EvidenceNigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Audit Procedures: Learning OutcomesDocument5 pagesAudit Procedures: Learning OutcomesKimberly parciaNo ratings yet
- Audit EvidenceDocument12 pagesAudit Evidencemuriithialex2030No ratings yet
- ACCO 30043 Assignment Number 5 Answer The Following Questions Briefly and ConciselyDocument3 pagesACCO 30043 Assignment Number 5 Answer The Following Questions Briefly and ConciselyYoung ManyNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL AUDIT (Final Exam - Portions) : RelevanceDocument5 pagesFINANCIAL AUDIT (Final Exam - Portions) : RelevanceSoniea DianiNo ratings yet
- Audit Evidence Procedures and DocumentationDocument46 pagesAudit Evidence Procedures and Documentationbobo kaNo ratings yet
- Substantive TestingDocument18 pagesSubstantive TestingMichelle SicangcoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Audit Evidence and DocumentatiDocument54 pagesChapter 5 Audit Evidence and Documentatipadma adrianaNo ratings yet
- Audit Evidence and Auditing ProceduresDocument64 pagesAudit Evidence and Auditing ProceduresMAAN SHIN ANGNo ratings yet
- Acctg 163 Review 4Document9 pagesAcctg 163 Review 4Tressa Salarza PendangNo ratings yet
- Unit 5. Audit PlanningDocument7 pagesUnit 5. Audit Planningzelalem kebedeNo ratings yet
- TYPES AND TESTS OF EVIDENCE and AUDIT PROCEDURESDocument6 pagesTYPES AND TESTS OF EVIDENCE and AUDIT PROCEDURESShady RainNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Substantive Test of Details of AccountsDocument12 pagesModule 8 - Substantive Test of Details of AccountsMark Angelo BustosNo ratings yet
- Ch. 7 - SM ACCDocument26 pagesCh. 7 - SM ACCkrstn_hghtwrNo ratings yet
- ACC 411 LECTURE 8 - Evidence and SamplingDocument11 pagesACC 411 LECTURE 8 - Evidence and SamplingOlarinde ColeNo ratings yet
- AT 08 PSA Audit EvidenceDocument7 pagesAT 08 PSA Audit EvidencePrincess Mary Joy LadagaNo ratings yet
- (EN) AU Ch7Document11 pages(EN) AU Ch7Māhmõūd ĀhmēdNo ratings yet
- AT Module 6A Audit Evidence T2AY2324Document10 pagesAT Module 6A Audit Evidence T2AY2324pht2airdropNo ratings yet
- At 11Document10 pagesAt 11Jean Fajardo BadilloNo ratings yet
- Audit Evidence and Audit ProcedureDocument9 pagesAudit Evidence and Audit Procedurevincent ottoNo ratings yet
- Audit OverviewDocument13 pagesAudit OverviewKei VenusaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Audit Procedures - ppt179107590Document8 pagesChapter 12 Audit Procedures - ppt179107590Clar Aaron BautistaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Ko HuhuDocument13 pagesReviewer Ko HuhuKei VenusaNo ratings yet
- CH14Document8 pagesCH14Joyce Anne GarduqueNo ratings yet
- Audit Evidence ReviewerDocument9 pagesAudit Evidence ReviewerJames LopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Audit ProceduresDocument8 pagesChapter 12 Audit ProceduresRichard de LeonNo ratings yet
- 12 Audit EvidenceDocument11 pages12 Audit EvidenceMoffat MakambaNo ratings yet
- Ch-3 Audit EvidenceDocument49 pagesCh-3 Audit EvidenceNuraddiin JaafarNo ratings yet
- AUD 1.4 Audit Objectives, Procedures, Evidence and Documentation - 2022Document11 pagesAUD 1.4 Audit Objectives, Procedures, Evidence and Documentation - 2022Aimee CuteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Audit EvidenceDocument7 pagesLesson 7 - Audit EvidenceAllaina Uy BerbanoNo ratings yet
- Audit - Isa 500Document6 pagesAudit - Isa 500Imran AsgharNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4Document7 pagesChapter - 4dejen mengstieNo ratings yet
- ACCO 30043 Assignment No.5Document7 pagesACCO 30043 Assignment No.5RoseanneNo ratings yet
- Ireneo Chapter 10 Ver 2020Document82 pagesIreneo Chapter 10 Ver 2020shanNo ratings yet
- Audit Evidence New SlidesDocument20 pagesAudit Evidence New SlidesAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance Services 17Th Edition Arens Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument54 pagesAuditing and Assurance Services 17Th Edition Arens Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFstephenthanh1huo100% (16)
- Auditing and Assurance Services 17th Edition Arens Solutions Manual instant download all chapterDocument55 pagesAuditing and Assurance Services 17th Edition Arens Solutions Manual instant download all chaptersytaripeddy100% (3)
- The Art and Science of Auditing: Principles, Practices, and InsightsFrom EverandThe Art and Science of Auditing: Principles, Practices, and InsightsNo ratings yet
- Stat Module 6Document3 pagesStat Module 6Princess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Basic Skills in ChessDocument3 pagesBasic Skills in ChessPrincess TolentinoNo ratings yet
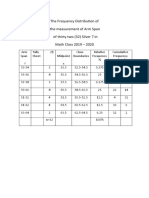
- The Frequency Distribution of The Measurement of Arm Span of Thirty Two (32) Silver 7 in Math Class 2019 - 2020Document3 pagesThe Frequency Distribution of The Measurement of Arm Span of Thirty Two (32) Silver 7 in Math Class 2019 - 2020Princess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- The International Covenant On Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (1966)Document6 pagesThe International Covenant On Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (1966)Princess Tolentino100% (1)
- Assignment in Stat Module 1Document4 pagesAssignment in Stat Module 1Princess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Rules and Regulations of TennisDocument3 pagesRules and Regulations of TennisPrincess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document2 pagesExercise 1Princess Tolentino100% (1)
- The Frequency Distribution of The Measurement of Arm Span of Thirty Two (32) Silver 7 in Math Class 2019 - 2020Document2 pagesThe Frequency Distribution of The Measurement of Arm Span of Thirty Two (32) Silver 7 in Math Class 2019 - 2020Princess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- This Life Is What We Make ItDocument1 pageThis Life Is What We Make ItPrincess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Why Study Business ResearchDocument5 pagesWhy Study Business ResearchPrincess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Future Value of Annuity, Continuous Compounding, and Geometric SeriesDocument2 pagesFuture Value of Annuity, Continuous Compounding, and Geometric SeriesPrincess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Water StationDocument14 pagesWater StationPrincess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Accounting Quiz 1Document26 pagesAccounting Quiz 1Princess Tolentino50% (2)
- Speaking Mathematically 2Document11 pagesSpeaking Mathematically 2Princess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- OceanofPDF - Com Strictly Research - Terry TowersDocument284 pagesOceanofPDF - Com Strictly Research - Terry TowersKenny SimNo ratings yet
- 10 Science NcertSolutions Chapter 8 ExercisesDocument4 pages10 Science NcertSolutions Chapter 8 ExercisesAnita GargNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With Nuvoton NUC140 32-Bit ARM Cortex-M0 Microcontroller PDFDocument7 pagesGetting Started With Nuvoton NUC140 32-Bit ARM Cortex-M0 Microcontroller PDFoktaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledGerard Phoenix MaximoNo ratings yet
- 1951 1obli ChronicleDocument18 pages1951 1obli Chronicleapi-198872914No ratings yet
- 2011 C1 CoMe ORGMIDocument8 pages2011 C1 CoMe ORGMIADJ ADJNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS For ExercisesDocument13 pagesANSWERS For ExercisesAlia HazwaniNo ratings yet
- Occupational StructureDocument3 pagesOccupational StructureEmirul FairuzNo ratings yet
- Astm A 1011 2005Document8 pagesAstm A 1011 2005gao yanminNo ratings yet
- Christmas Vigil MassDocument106 pagesChristmas Vigil MassMary JosephNo ratings yet
- 10 Best JobsitesDocument14 pages10 Best JobsitesHemansu PathakNo ratings yet
- 84501-9200-9L-008 Rev-0 Technical Inspection Services Company Final Documentation RequirementsDocument7 pages84501-9200-9L-008 Rev-0 Technical Inspection Services Company Final Documentation RequirementsPeni M. SaptoargoNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory Refers To The Idea That: MicrographiaDocument5 pagesCell Theory Refers To The Idea That: MicrographiadeltasixNo ratings yet
- Apuntes Ingles b2Document25 pagesApuntes Ingles b2Arancha ManeiroNo ratings yet
- Organic Halides Introduction Class-1 NotesDocument15 pagesOrganic Halides Introduction Class-1 Notessiddhartha singhNo ratings yet
- 4final Examination Prof Ed 10Document7 pages4final Examination Prof Ed 10Danelle EsparteroNo ratings yet
- SPB ClientDocument4 pagesSPB ClientRKNo ratings yet
- 03 - Literature ReviewDocument9 pages03 - Literature ReviewKhant Wai YanNo ratings yet
- VIETNAM. PROCESSING OF AROMA CHEMICALS AND FRAGRANCE MATERIALS. TECHNICAL REPORT - AROMA CHEMICALS AND PERFUME BLENDING (20598.en) PDFDocument83 pagesVIETNAM. PROCESSING OF AROMA CHEMICALS AND FRAGRANCE MATERIALS. TECHNICAL REPORT - AROMA CHEMICALS AND PERFUME BLENDING (20598.en) PDFOsamaAliMoussaNo ratings yet
- Sd10 Forecasting Free CashflowsDocument8 pagesSd10 Forecasting Free CashflowsDemi Tugano BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Housekeeping Management Practices and Standards of Selected Hotels and Restaurants of Ilocos Sur, PhilippinesDocument8 pagesHousekeeping Management Practices and Standards of Selected Hotels and Restaurants of Ilocos Sur, PhilippinesMehwish FatimaNo ratings yet
- Policy Copy 3005 314095178 00 000Document3 pagesPolicy Copy 3005 314095178 00 000alagardharshan2No ratings yet
- Admission LetterDocument7 pagesAdmission Letterduke cyberNo ratings yet
- Ozone Therapy Is Safest Known TherapyDocument35 pagesOzone Therapy Is Safest Known Therapyherdin2008100% (1)
- A Picture Is Worth A Thousand Words: The Benefit of Medical Illustration in Medical PublishingDocument6 pagesA Picture Is Worth A Thousand Words: The Benefit of Medical Illustration in Medical PublishingSinisa RisticNo ratings yet
- Comparative Investment ReportDocument8 pagesComparative Investment ReportNelby Actub MacalaguingNo ratings yet
- The Laws On Local Governments SyllabusDocument4 pagesThe Laws On Local Governments SyllabusJohn Kevin ArtuzNo ratings yet