Professional Documents
Culture Documents
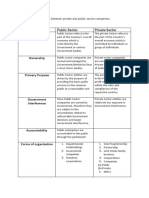
For Point 3
For Point 3
Uploaded by
Jigisha Singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views5 pagesThe document discusses government initiatives in Uttar Pradesh, India to support the handicrafts industry. It outlines various centers established to provide training, design guidance, testing facilities, and marketing assistance to artisans and entrepreneurs. These include centers in Moradabad, Saharanpur, Nagina, and Chunar that help improve products and promote handicrafts within India and abroad. The handicrafts sector employs over 2 million people in Uttar Pradesh, especially in carpet weaving, and initiatives aim to reduce underemployment and increase incomes.
Original Description:
Original Title
For point 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses government initiatives in Uttar Pradesh, India to support the handicrafts industry. It outlines various centers established to provide training, design guidance, testing facilities, and marketing assistance to artisans and entrepreneurs. These include centers in Moradabad, Saharanpur, Nagina, and Chunar that help improve products and promote handicrafts within India and abroad. The handicrafts sector employs over 2 million people in Uttar Pradesh, especially in carpet weaving, and initiatives aim to reduce underemployment and increase incomes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views5 pagesFor Point 3
For Point 3
Uploaded by
Jigisha SinghThe document discusses government initiatives in Uttar Pradesh, India to support the handicrafts industry. It outlines various centers established to provide training, design guidance, testing facilities, and marketing assistance to artisans and entrepreneurs. These include centers in Moradabad, Saharanpur, Nagina, and Chunar that help improve products and promote handicrafts within India and abroad. The handicrafts sector employs over 2 million people in Uttar Pradesh, especially in carpet weaving, and initiatives aim to reduce underemployment and increase incomes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
For point 3. Government initiative in Uttar Pradesh.
The Metal Handicrafts Service Centre at
Moradabad aims at achieving a qualitative
improvement of art metalware especially to
enhance their export worthiness. It offers
professional and technical advice for improving
manufacturing techniques and training facilities
for upgradation of skills of craft persons and
technicians, extends testing facilities to
entrepreneurs in order to help them meet
international standards of quality control and
setting up a common facility for research &
development programmes.The Centre has been
registered as a society and has received support
from the United Nations Development Fund as
well as Government of Uttar Pradesh.
• The National Centre for Design and Product
Development (NCDPD) at Moradabad has been
set up by the EPCH with assistance from UNDP
and Gol as well as active support from IGEP
(Indo-German Export Promotion Program). The
Centre provides services and technology in
computer-aided designs and modern management
for the benefit of entrepreneurs, manufacturers
and traders. The Centre has had the support of
two German designers assisted by another
Philipino designer.
• The wood seasoning plant and common facility
centre at Saharanpur and Nagina have been
extending useful services.
• The CDC (Crafts Development Centre) has been
conceived for artisans to get facilities of advance
training, design guidance and marketing, besides
raw material procurement
DC (H) formulated a scheme by establishing
emporia through state corporations/NGOs. Some
15 emporia have been established under the
scheme all over the country to market handicraft
product of Uttar Pradesh.
• The following CDCs are relevant:
• For carpet sector at Shahjahanpur, implemented
by Uttar Pradesh Export Corporation Ltd.
• For promotion of woodware at Saharanpur,
managed by the Uttar Pradesh Export
Corporation Ltd.
• For pottery/ceramic, at Chumar, implemented
by Unnayan Sansthan, Mirzapur for which an
amount of Rs. 21 lakh was sanctioned.
• For wood, at Gankheri, Bijnore, implemented by
Bijnore Sewa Sansthan. An amount of Rs. 27
lakh sanctioned.
• Another centre for wood at Nagina, Bijnore
managed by Nagina Crafts Development Society.
An amount of Rs. 25 lakh sanctioned.
Details of grant released for CDCs in Uttar Pradesh
during April-November 2001 are shown below:
CDCs Rs. in Lakh
CDC at Saharanpur (The UP Export Corp. Ltd.) 8.000
Chunar, Mirzapur (Unnayan sansthan) 10.385
Bijnor Seva Sansthan, Bijnor 13.465
Nagina Crafts Development Society 12.115
Total 43.965
IMPORTANT POINT
Promoting handicrafts threw fairs like,
Shilpgram fair in Agra
Awadh shilpgram in Lucknow.
Point 5 swot analysis completed
Uttar Pradesh: A Critical State for Crafts
The estimated number of persons employed in the
handicrafts sector in Uttar Pradesh was reported to be
about 2.03 million (full-time and part-time) in the year
1979-80. The carpet sector is pre-eminently represented
in Uttar Pradesh, with as many as 1125000 workers
being in the state in a countrywide total of 1500000
carpet weavers.
A large number of persons employed in the sector
are engaged in the production of crafts for only a part
of the year, who spend the rest of the year in
agricultural activities; ‘underemployment is widespread
—but despite this, handicraft production is the primary
source of income’ for them. Due to an extensive
division of labour in the production of most of the
crafts, even semi-skilled and unskilled family labour is
employed in their production.
Strengths
• Rich traditions of excellence in arts and crafts.
• Development of supply-chain with skill
specialisation.
• Component level manufacturing, providing it the
efficiency and skill requirements.
• Achievable/acceptable social standards.
• Labour laws conforming to ILO Conventions.
• High employment potential.
• Highly export-driven, for foreign exchange accrual.
Weaknesses
• Unorganised marketing and inadequate market
information.
• Inadequate support mechanism for product
development.
• Power interruptions and other infrastructural
deficiencies.
• Inadequacy of raw material at appropriate
prices.
• Lack of mechanism for dispersal of technology for
enhancing productivity and final finishing.
• Lack of investment for fulfilling international
requirements.
• A general poor image of the country as a supplier
of quality goods with consistency.
Opportunities
• A large trained, skilled manpower base.
• Existing international presence.
• Existing social interventions and structure.
• Traditional knowledge base.
• Growing export market for quality products and
reduction in acceptance of mass-produced
products, especially in Europe and USA.
• Growing environmental concerns.
• Growing sophistication and buying power of
Indian consumers.
Threats
• Competitors gaining market share on strength of
volume and price.
• Competitors edging out Indian exporters on
strength of quality.
• Growing environmental concerns in the country
affecting supply of raw material.
• International campaigns against child labour and
social standards.
• Lack of coordination between institutions
affecting production and exports.
• Increased competition among indigenous
suppliers leading to price wars, high
transportation costs.
• Excessive reliance on state incentives and
props.
References
https://irandoostan.com/role-handicrafts-tourism-development/
https://culturalindia.net/indian-crafts/index.html
https://www.ukessays.com/essays/economics/handicrafts.php
http://www.uphdmc.in/
You might also like
- Apm MCQSDocument31 pagesApm MCQSsaim buttNo ratings yet
- On Craft ClusterDocument50 pagesOn Craft ClusterTapas MondalNo ratings yet
- CRAFT VILLAGE, VELLAR THIRUVANANTHAPURAM, KERALA. Project Report by Sudheesh Kumar S S (Designer)Document104 pagesCRAFT VILLAGE, VELLAR THIRUVANANTHAPURAM, KERALA. Project Report by Sudheesh Kumar S S (Designer)anashwara80% (5)
- A) Intoduction: Jharcraft: A Strong Backbone of The Jharkhand StateDocument37 pagesA) Intoduction: Jharcraft: A Strong Backbone of The Jharkhand StateShree Cyberia0% (1)
- Weaver Service CenterDocument26 pagesWeaver Service CenterMitakshi mishraNo ratings yet
- Handicrafts From India: A Mirror of Rich Cultural Diversity .Document12 pagesHandicrafts From India: A Mirror of Rich Cultural Diversity .rishabh044No ratings yet
- Handicrafts Export Promotion Council Additional ExtraDocument27 pagesHandicrafts Export Promotion Council Additional ExtraManasa PriyaNo ratings yet
- Hon'ble Textiles Secretary Announces: 200 Export Promotion Programmes For 44 Craft StationsDocument40 pagesHon'ble Textiles Secretary Announces: 200 Export Promotion Programmes For 44 Craft Stationspriya4112No ratings yet
- Presentation Textile Craft Design PolicyDocument14 pagesPresentation Textile Craft Design PolicyPratyush PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- EPCHDocument20 pagesEPCHrahul867No ratings yet
- CITIZEN Charter Nagpur637618734445240021Document7 pagesCITIZEN Charter Nagpur637618734445240021AdarshNo ratings yet
- Taszeus Rajarshi Iiml Phase 1Document8 pagesTaszeus Rajarshi Iiml Phase 1Rajarshi DeyNo ratings yet
- Citizen'S Charter: Weavers' Service Centre, AhmedabadDocument9 pagesCitizen'S Charter: Weavers' Service Centre, AhmedabadPURVA BORKARNo ratings yet
- A Study On Brand Promotion Strategies of Handicrafts & Handlooms ProductsDocument60 pagesA Study On Brand Promotion Strategies of Handicrafts & Handlooms ProductsAshis karmakarNo ratings yet
- Government Schemes For Promotion of Craft and CraftDocument6 pagesGovernment Schemes For Promotion of Craft and Craftwajahatlone13No ratings yet
- WeaversDocument16 pagesWeaversSwayam Gaur100% (1)
- Bhutan - Presentation E-Business Pilot Project On Textile HandicraftsDocument21 pagesBhutan - Presentation E-Business Pilot Project On Textile HandicraftsarvvaioNo ratings yet
- From The Chairman's Desk: (Rohit R. Brandon)Document35 pagesFrom The Chairman's Desk: (Rohit R. Brandon)Soumya VardhanNo ratings yet
- Hanif Kanjer: L1. Generic StrategiesDocument19 pagesHanif Kanjer: L1. Generic StrategiesNehaMhatreNo ratings yet
- Hala Pottery: The Dying Art of SindDocument19 pagesHala Pottery: The Dying Art of Sindkausar_saeed1772100% (1)
- J-12012/279/2015-16/DS/NR/3081 Dated 18 March, 2016Document92 pagesJ-12012/279/2015-16/DS/NR/3081 Dated 18 March, 2016Joseph RalteNo ratings yet
- Capacity BuildingDocument5 pagesCapacity Buildinglopa70No ratings yet
- Trade and Skill Development Capacity Building For Orissa Appliqué CraftersDocument6 pagesTrade and Skill Development Capacity Building For Orissa Appliqué Crafterslopa70No ratings yet
- Incentive and Infrastructure Support From Central and StateDocument44 pagesIncentive and Infrastructure Support From Central and StateveenaaskiNo ratings yet
- About The A.H.V.Y. (The Scheme)Document35 pagesAbout The A.H.V.Y. (The Scheme)sukhnagNo ratings yet
- The Design and Technical Development Workshop Under AhvyDocument34 pagesThe Design and Technical Development Workshop Under AhvysukhnagNo ratings yet
- Export Possibilities For Light Engineering & Vendor IndustriesDocument60 pagesExport Possibilities For Light Engineering & Vendor IndustriesShaheenNo ratings yet
- The Loom of Tradition: "Shawls As Artware"Document13 pagesThe Loom of Tradition: "Shawls As Artware"Sabrina SuptiNo ratings yet
- Group 12 - MADocument16 pagesGroup 12 - MARakshitaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Export Promotion CouncilDocument38 pagesAssignment On Export Promotion CouncilPooja BansalNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Development UNIT 6Document7 pagesEntrepreneurship Development UNIT 6Jasjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Realizing The Growth Potential of North-EastDocument12 pagesRealizing The Growth Potential of North-EastadityahongkongNo ratings yet
- Aarong Business Research ProposalDocument13 pagesAarong Business Research Proposaltanvir1674100% (4)
- By: Shailja Gurung (Sec B-31) Somna (Sec B-33) Raksha Pal (Sec C-23) Alka Tripathi (Sec D-53)Document23 pagesBy: Shailja Gurung (Sec B-31) Somna (Sec B-33) Raksha Pal (Sec C-23) Alka Tripathi (Sec D-53)alka1010No ratings yet
- 2015-Australian Journal of Commerce Study - Science and Technology Program Implementation For Crafts Export ProductDocument7 pages2015-Australian Journal of Commerce Study - Science and Technology Program Implementation For Crafts Export ProductTri Wahyuningsih FEBNo ratings yet
- Project On: Small Scale Industry: - By: Prof - RupalDocument24 pagesProject On: Small Scale Industry: - By: Prof - Rupalshweta_zNo ratings yet
- A Study On Role of Handicraft Association in Export Promotion of ThankaDocument8 pagesA Study On Role of Handicraft Association in Export Promotion of ThankaromanNo ratings yet
- NHDP (Final) Anex-III DT 01.01.2016 (Handicraft)Document52 pagesNHDP (Final) Anex-III DT 01.01.2016 (Handicraft)Jash PatelNo ratings yet
- Shri Odop-1Document28 pagesShri Odop-1Manas DudhaniNo ratings yet
- Incense Stick IndustryDocument13 pagesIncense Stick IndustrySahil63% (8)
- Export Promotion Schemes For HandicraftsDocument63 pagesExport Promotion Schemes For HandicraftsHasna HafizaNo ratings yet
- Jute and Jute ProductsDocument25 pagesJute and Jute ProductsAbhinav VermaNo ratings yet
- PURA Providing Urban Amenities in Rural AreaDocument40 pagesPURA Providing Urban Amenities in Rural ArealastbudNo ratings yet
- Project Completion Report Feb June 2010Document19 pagesProject Completion Report Feb June 2010Kumar RaviNo ratings yet
- Project Progress Report: Skill Development Program Under Narsapur Mega ClusterDocument22 pagesProject Progress Report: Skill Development Program Under Narsapur Mega ClusterS.M RajuNo ratings yet
- Srivastava Handmade Carpet5 PDFDocument20 pagesSrivastava Handmade Carpet5 PDFaghorbanzadehNo ratings yet
- Export Promotion Council: by Anuj GuptaDocument31 pagesExport Promotion Council: by Anuj GuptaKailash DograNo ratings yet
- Marketing Organization of OdishaDocument9 pagesMarketing Organization of Odishaavilipsaswain2004No ratings yet
- TDAPDocument27 pagesTDAPRaza023No ratings yet
- Coir Board of IndiaDocument9 pagesCoir Board of IndiaNennissa(NIHARIKA BARUAH)No ratings yet
- Export Promotion CouncilDocument31 pagesExport Promotion Councilashrafsiddiqui2007No ratings yet
- Conclusions of Birbhum Handicraft IndustryDocument4 pagesConclusions of Birbhum Handicraft IndustrycutemuktaNo ratings yet
- TenderDocument14 pagesTenderBrajendra MohanNo ratings yet
- Indian Silk Promotion CouncilDocument22 pagesIndian Silk Promotion CouncilDEEPAKNo ratings yet
- OU 24 Ppts OU-OAC-KDocument32 pagesOU 24 Ppts OU-OAC-Kapi-3774915No ratings yet
- Handicraft Buisness PlanDocument14 pagesHandicraft Buisness PlanjananiNo ratings yet
- Short Visit To The Aditya Birla Industry House Short Visit To The Aditya Birla Industry HouseDocument41 pagesShort Visit To The Aditya Birla Industry House Short Visit To The Aditya Birla Industry HouseDeepthi ChenjeriNo ratings yet
- Cluster ActivitiesDocument7 pagesCluster Activitiesaeioums4391No ratings yet
- Fractal Modernisation Model of Industrial Areas’ Environment in Developing CountriesFrom EverandFractal Modernisation Model of Industrial Areas’ Environment in Developing CountriesNo ratings yet
- Rang de Basanti ReviewDocument7 pagesRang de Basanti ReviewJigisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Internship Work Hadiya'S CaseDocument4 pagesInternship Work Hadiya'S CaseJigisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Internal Evaluations:: Agency ManagementDocument11 pagesInternal Evaluations:: Agency ManagementJigisha SinghNo ratings yet
- This Content Downloaded From 103.59.198.110 On Thu, 12 May 2022 23:09:41 UTCDocument5 pagesThis Content Downloaded From 103.59.198.110 On Thu, 12 May 2022 23:09:41 UTCJigisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management in Aviation MaintenanceDocument8 pagesTotal Quality Management in Aviation MaintenanceConsejero TerapeutaNo ratings yet
- CALGARY FIRE DEPARTMENT ZEROBASED REVIEW and ADMI Attach 3 Calgary Fire Department ZeroBased Review Report From Behr Energy Services LTDDocument124 pagesCALGARY FIRE DEPARTMENT ZEROBASED REVIEW and ADMI Attach 3 Calgary Fire Department ZeroBased Review Report From Behr Energy Services LTDDarren KrauseNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Your Email MarketingDocument2 pagesEvaluating Your Email MarketingIdham MuqoddasNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Exam "Disney Production": Graduate School of Business MBA ProgramDocument13 pagesComprehensive Exam "Disney Production": Graduate School of Business MBA ProgrammenoushNo ratings yet
- Business Plan For TeachersDocument19 pagesBusiness Plan For TeachersMelita Stephen NatalNo ratings yet
- Five Forces Model of Aarong, SMDocument4 pagesFive Forces Model of Aarong, SMRocky misuNo ratings yet
- Word c2Document15 pagesWord c2sariNo ratings yet
- Fdnmark - c48 - Group 6 - Final PaperDocument24 pagesFdnmark - c48 - Group 6 - Final PaperClarissa Mae BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Eko Ganis Sukoharsono - Caroll Pyramid and CSRDocument8 pagesEko Ganis Sukoharsono - Caroll Pyramid and CSRTheGilmoreBuddiesNo ratings yet
- Simpsons Movie PosterDocument1 pageSimpsons Movie PosterkierantatumNo ratings yet
- R2301F PDF ENG CompressedDocument18 pagesR2301F PDF ENG CompressedMarioAbuyeresNo ratings yet
- Business Studies QA Chapter 3Document2 pagesBusiness Studies QA Chapter 3Gehna JainNo ratings yet
- The Best Books For Graphic DesignersDocument1 pageThe Best Books For Graphic DesignersNama DepanNo ratings yet
- CHUA - Exercise 3 - BudgetingDocument1 pageCHUA - Exercise 3 - BudgetingClaudeen Jade Antoinette ChuaNo ratings yet
- Industry Economics Market ModelsDocument10 pagesIndustry Economics Market ModelsrosheelNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World - Page 53-54Document2 pagesContemporary World - Page 53-54Aurioule DepaysoNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On: Customer Preference & Attributes Towards Saving-AccountDocument55 pagesA Project Report On: Customer Preference & Attributes Towards Saving-Accountamit-183% (6)
- How Do You Feel About Having Management Responsibilities in TodayDocument2 pagesHow Do You Feel About Having Management Responsibilities in TodayJoseph JacintoNo ratings yet
- Babz 1Document31 pagesBabz 1Tiana TillaNo ratings yet
- Aregay Editd ProposalDocument25 pagesAregay Editd ProposalFasiko AsmaroNo ratings yet
- 2023 05 08 - Plan Onondaga Full Draft - Digital PDFDocument258 pages2023 05 08 - Plan Onondaga Full Draft - Digital PDFCNY CentralNo ratings yet
- UPM (Company)Document13 pagesUPM (Company)Min SaNo ratings yet
- Verify SGS Documents - SGS Portugal-2Document3 pagesVerify SGS Documents - SGS Portugal-2Salvador SilvaNo ratings yet
- Kayes Arman11-6265-Term PaperDocument7 pagesKayes Arman11-6265-Term PaperTAWHID ARMAN100% (1)
- International Trade FinanceDocument33 pagesInternational Trade FinanceHaji AliNo ratings yet
- MTR Food: (Mavalli Tiffin Rooms)Document8 pagesMTR Food: (Mavalli Tiffin Rooms)KARTIK BABREKARNo ratings yet
- Blue & Yellow Professional Future Technology PresentationDocument11 pagesBlue & Yellow Professional Future Technology PresentationJoaquin PalominoNo ratings yet
- Events After The Reporting Period: Adjusting Events Non-Adjusting EventsDocument1 pageEvents After The Reporting Period: Adjusting Events Non-Adjusting EventsDora the ExplorerNo ratings yet
- Dombivli Shikshan Prasarak Mandals K. V. Pendharkar College of Arts, Science and Commerce (Autonomous)Document7 pagesDombivli Shikshan Prasarak Mandals K. V. Pendharkar College of Arts, Science and Commerce (Autonomous)Sujal BedekarNo ratings yet