Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solved Chapter 8 Problem 39P Solution Engineer
Solved Chapter 8 Problem 39P Solution Engineer
Uploaded by
Robby KurniawanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Mad English TV Celpip 8-9Document95 pagesMad English TV Celpip 8-9john huo100% (6)
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.46. A Flexible Circular Area of Radi...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.46. A Flexible Circular Area of Radi...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow SimulationDocument5 pagesCircular Flow Simulationsamira2702No ratings yet
- Solved For A Given Soil, The Following Are Known Gs 2.74, M...Document1 pageSolved For A Given Soil, The Following Are Known Gs 2.74, M...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Tango's Tamales Is A Small Restaurant On A Busy St...Document1 pageTango's Tamales Is A Small Restaurant On A Busy St...rizqighaniNo ratings yet
- Solved - Determine The Real Root of F (X) 5x3 - 5x2 + 6x - 2 - (...Document6 pagesSolved - Determine The Real Root of F (X) 5x3 - 5x2 + 6x - 2 - (...Angel Maliel Limon CaceresNo ratings yet
- Question: A Pattern Needed To Be Designed For The Part Shown in The GDocument3 pagesQuestion: A Pattern Needed To Be Designed For The Part Shown in The GEhtsham AwanNo ratings yet
- Solved - A Prototype Automobile Is Designed To Travel at 65 km2Fh Cheggcom PDFDocument3 pagesSolved - A Prototype Automobile Is Designed To Travel at 65 km2Fh Cheggcom PDFNabihah AzanNo ratings yet
- DY Centralised Distribution at Nike Centralised An...Document3 pagesDY Centralised Distribution at Nike Centralised An...Daniyal AsifNo ratings yet
- Solved During A Subsurface Exploration, An Undisturbed Soil Sa...Document1 pageSolved During A Subsurface Exploration, An Undisturbed Soil Sa...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Fluid Mechanics: (11th Edition)Document3 pagesEngineering Fluid Mechanics: (11th Edition)كرار عبدالحسين قاسمNo ratings yet
- Question: Problem On Accrual E. Gevera Realty Co. Who Owns A BuildingDocument2 pagesQuestion: Problem On Accrual E. Gevera Realty Co. Who Owns A BuildingKen SannNo ratings yet
- Principles of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Document2 pagesPrinciples of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Uzair Ahmed SoomroNo ratings yet
- Principles of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Document2 pagesPrinciples of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Uzair Ahmed SoomroNo ratings yet
- Solved - Tampa Instrument Company Manufactures Gauges For Constr...Document3 pagesSolved - Tampa Instrument Company Manufactures Gauges For Constr...Raaqib KhanNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.41. Given q2 3800 LBFT, x1 18 ...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.41. Given q2 3800 LBFT, x1 18 ...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- TSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 36P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionDocument1 pageTSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 36P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionxomuxNo ratings yet
- Question: 3 Pts D Question 5 Nicanor Left The Following Bank Deposits UDocument2 pagesQuestion: 3 Pts D Question 5 Nicanor Left The Following Bank Deposits UShiela MayNo ratings yet
- TSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 34P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionDocument1 pageTSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 34P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionxomuxNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.47. A Flexible Rectangular Area Is S...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.47. A Flexible Rectangular Area Is S...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- C Lombard Company Is Contemplating The Purchase ODocument5 pagesC Lombard Company Is Contemplating The Purchase OFahmi Ilham AkbarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Financial Management: (12th Edition)Document5 pagesFundamentals of Financial Management: (12th Edition)Usman Ali0% (1)
- Solved Solve Problem 8.10 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Document1 pageSolved Solve Problem 8.10 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Question: in Each of The Following Cases, Draw The Smooth Curve, Mark ItsDocument1 pageQuestion: in Each of The Following Cases, Draw The Smooth Curve, Mark ItsRahayu Rizki PutriNo ratings yet
- Principles of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Document3 pagesPrinciples of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Uzair Ahmed SoomroNo ratings yet
- Principles of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Document3 pagesPrinciples of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Uzair Ahmed SoomroNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.49. For The Linearly Increasing Vert...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.49. For The Linearly Increasing Vert...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Loans Form An Integral Part of Banking Operations....Document3 pagesLoans Form An Integral Part of Banking Operations....Ameer HamzaNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To The Cross Section of The Earth Dam Shown in Fi...Document1 pageSolved Refer To The Cross Section of The Earth Dam Shown in Fi...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Local Media2138585013869044277Document3 pagesLocal Media2138585013869044277panger moooNo ratings yet
- Solved Repeat Problem 8.8 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Document1 pageSolved Repeat Problem 8.8 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Derive The Equation of Motion and Response Equatio Chegg ComDocument1 pageDerive The Equation of Motion and Response Equatio Chegg ComMuhd HarithNo ratings yet
- Solved Draw A Flow Net For The Weir Shown in Figure 8.25. Calc...Document1 pageSolved Draw A Flow Net For The Weir Shown in Figure 8.25. Calc...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Question: Dudster Manufacturing Has 2 Options For Installing Legally ReqDocument3 pagesQuestion: Dudster Manufacturing Has 2 Options For Installing Legally ReqJosh GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 8.23. Given - H1 6 M - H2 1.5 M - D ...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 8.23. Given - H1 6 M - H2 1.5 M - D ...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 9.4a. If H1 3 FT, H2 4.5 FT, H 1....Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 9.4a. If H1 3 FT, H2 4.5 FT, H 1....Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: (7th Edition)Document4 pagesFluid Mechanics: (7th Edition)Asfand Yar QureshiNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Problem 8.4. Using The Flow Net Drawn, Calcula...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Problem 8.4. Using The Flow Net Drawn, Calcula...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved - Which $1,000 Bond Has The Higher Yield To Maturity, A T...Document4 pagesSolved - Which $1,000 Bond Has The Higher Yield To Maturity, A T...Sanjna ChimnaniNo ratings yet
- Consider A Three-Dimensional Differential Fluid El...Document1 pageConsider A Three-Dimensional Differential Fluid El...Mergen KhanNo ratings yet
- Solved - Chapter 3 Problem 77RE Solution - Probability and Statistics For Engineers and Scientists 9th EditionDocument4 pagesSolved - Chapter 3 Problem 77RE Solution - Probability and Statistics For Engineers and Scientists 9th EditionJaleel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Solved - You Have Been Asked by The Head of Marketing To Design ...Document2 pagesSolved - You Have Been Asked by The Head of Marketing To Design ...Clyden Jaile RamirezNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.43. A Strip Load of Q 1450 lbft2 ...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.43. A Strip Load of Q 1450 lbft2 ...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Estimate The Hydraulic Conductivity of A Saturated Clay...Document1 pageSolved Estimate The Hydraulic Conductivity of A Saturated Clay...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Section 4. Asymmetric Shock (24 Points) Consider A...Document4 pagesSection 4. Asymmetric Shock (24 Points) Consider A...Noor FatimaNo ratings yet
- Find Its Acceleration For The First Instant and Se...Document2 pagesFind Its Acceleration For The First Instant and Se...Ionaishi FloresNo ratings yet
- Applied Calculus For Business, Economics, and The Social and Life Sciences, Expanded EditionDocument2 pagesApplied Calculus For Business, Economics, and The Social and Life Sciences, Expanded EditionAsif HossainNo ratings yet
- A Large Refinery and Petrochemical Complex Is Plan...Document4 pagesA Large Refinery and Petrochemical Complex Is Plan...Abdullah QureshiNo ratings yet
- Q#3. A) What Are Various Water Efficiencies When A...Document2 pagesQ#3. A) What Are Various Water Efficiencies When A...Muhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Solved Figure 9.29 Shows The Zone of Capillary Rise Within A C... Chegg - Com 2Document1 pageSolved Figure 9.29 Shows The Zone of Capillary Rise Within A C... Chegg - Com 2Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Question: 11. Incremental Costs Can Be de Ned As A. Costs That Are IrreleDocument2 pagesQuestion: 11. Incremental Costs Can Be de Ned As A. Costs That Are IrreleLayout By nicaNo ratings yet
- Calculus of A Single Variable: (11th Edition)Document1 pageCalculus of A Single Variable: (11th Edition)Noman MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Management, Student Value EditionDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Management, Student Value EditionMalik GNo ratings yet
- Solved - The Fourth-Degree Polynomial F (X) 230x4 + 18x3 + 9x2...Document7 pagesSolved - The Fourth-Degree Polynomial F (X) 230x4 + 18x3 + 9x2...Malik Ijaz Ali AwanNo ratings yet
- Solved The 5-m High Retaining Wall in Figure 13.40c Is Subject...Document1 pageSolved The 5-m High Retaining Wall in Figure 13.40c Is Subject...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved - You Have Data From A Corporation On The Annual Salary O...Document1 pageSolved - You Have Data From A Corporation On The Annual Salary O...Clyden Jaile RamirezNo ratings yet
- 15 KG of Refrigerant-134a (R-1340 Per Minute Flows ...Document3 pages15 KG of Refrigerant-134a (R-1340 Per Minute Flows ...Logendran A/l MurgayaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Corporate Finance: (9th Edition)Document4 pagesPrinciples of Corporate Finance: (9th Edition)Uzair Ahmed SoomroNo ratings yet
- Solved Repeat Problem 10.3 For The Element Shown in Figure 10....Document1 pageSolved Repeat Problem 10.3 For The Element Shown in Figure 10....Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved For A Dynamic Compaction Test, The Weight of The Hammer...Document1 pageSolved For A Dynamic Compaction Test, The Weight of The Hammer...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Ven A 1. Oped The Nase J.S. In. Do You Think That ...Document4 pagesVen A 1. Oped The Nase J.S. In. Do You Think That ...sidra tulmuntahaNo ratings yet
- Pulp and Paper Liquid Waste Treatment Using Electro Coagulation MembraneDocument7 pagesPulp and Paper Liquid Waste Treatment Using Electro Coagulation MembraneRobby KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 11 RP SP Equipment SpecificationDocument39 pages11 RP SP Equipment SpecificationRobby KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Skripsi EtanaDocument13 pagesSkripsi EtanaRobby KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Azeri Light 2005 06Document18 pagesAzeri Light 2005 06Robby KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Ray Crystallography Is The Deployment of X-Ray Diffraction Techniques For TheDocument5 pagesRay Crystallography Is The Deployment of X-Ray Diffraction Techniques For TheRobby KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Final Exam Case StuDocument2 pagesMarketing Management Final Exam Case Stumahmoud sakrNo ratings yet
- Fulfillment Process Presentation Final Team 5Document11 pagesFulfillment Process Presentation Final Team 5Bhargav MehtaNo ratings yet
- Bootcamp Assignment 4 - by Pratap ReddyDocument10 pagesBootcamp Assignment 4 - by Pratap ReddyPratap ReddyNo ratings yet
- Improving Returns On Stock Investment Through Neural Network SelectionDocument7 pagesImproving Returns On Stock Investment Through Neural Network SelectionAakash DebnathNo ratings yet
- Budget Operations Manual For Local Government UnitsDocument247 pagesBudget Operations Manual For Local Government UnitsJean Rema GonjoranNo ratings yet
- Lean 4Document9 pagesLean 4Arun PrasadNo ratings yet
- John F. Kennedy: Bachelor of Science: Major Public AccountingDocument2 pagesJohn F. Kennedy: Bachelor of Science: Major Public AccountingConnor FentonNo ratings yet
- Allowable DeductionsDocument4 pagesAllowable Deductionswind snip3r reojaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Evolution and Fundamental of BusinessDocument211 pagesChapter 1 Evolution and Fundamental of BusinessDr. Nidhi KumariNo ratings yet
- Prospectus - Optimal SA FundDocument45 pagesProspectus - Optimal SA FundMigle BloomNo ratings yet
- MVV Green Gardens FinalDocument10 pagesMVV Green Gardens FinalVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Buletin Mutiara - English/Chinese/Tamil - Mac #1 IssueDocument28 pagesBuletin Mutiara - English/Chinese/Tamil - Mac #1 IssueChan LilianNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Final AccountsDocument13 pagesPreparation of Final AccountsDr Sarbesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary Level: Cambridge Assessment International EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge Ordinary Level: Cambridge Assessment International EducationhbuzdarNo ratings yet
- MR4 - G2 Research ReportDocument66 pagesMR4 - G2 Research Reportngân hà maNo ratings yet
- Bitcoin Mining SurveyDocument7 pagesBitcoin Mining SurveyxxNo ratings yet
- Customised Profit & Loss (Rs - in Crores) Mar 18 17-Mar 16-Mar 15-Mar 14-Mar 5,592.29 5,290.65 5,750.00 5,431.28 4,870.08Document20 pagesCustomised Profit & Loss (Rs - in Crores) Mar 18 17-Mar 16-Mar 15-Mar 14-Mar 5,592.29 5,290.65 5,750.00 5,431.28 4,870.08Akshay Yadav Student, Jaipuria LucknowNo ratings yet
- ProspectusDocument2 pagesProspectusJuliana Mae FradesNo ratings yet
- PratimaMehta May2020Document3 pagesPratimaMehta May2020rajan mishraNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management Quarter 1 Week 2Document19 pagesOrganization and Management Quarter 1 Week 2Rui Isaac Fernando75% (4)
- It Application Tools in Business Chapter 1Document30 pagesIt Application Tools in Business Chapter 1pahatiprincess05No ratings yet
- 700 Transport Gurney: Operations and Maintenance ManualDocument27 pages700 Transport Gurney: Operations and Maintenance Manualsec.ivbNo ratings yet
- Book Building: IPO Price Discovery MechanismDocument35 pagesBook Building: IPO Price Discovery MechanismDevyansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- ICT1006 - ACC1007-CSC1005 Individual Assignment 1Document3 pagesICT1006 - ACC1007-CSC1005 Individual Assignment 1Yong RenNo ratings yet
- CMS Fee Payment ProcedureDocument2 pagesCMS Fee Payment ProceduresrijithspNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - 1 Cash and Marketable SecuritiesDocument15 pagesCHAPTER 6 - 1 Cash and Marketable SecuritiesAhmad Ridhuwan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- PMMSY1Document4 pagesPMMSY1NEC Andaman AccountsNo ratings yet
- Liability Insurance Certificate 2020Document2 pagesLiability Insurance Certificate 2020Majdi BelguithNo ratings yet
Solved Chapter 8 Problem 39P Solution Engineer
Solved Chapter 8 Problem 39P Solution Engineer
Uploaded by
Robby KurniawanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solved Chapter 8 Problem 39P Solution Engineer
Solved Chapter 8 Problem 39P Solution Engineer
Uploaded by
Robby KurniawanCopyright:
Available Formats
!
" Textbook Solutions Expert Q&A Practice #
Find solutions for your homework Search
home / study / business / business statistics / business statistics solutions manuals / engineering economic analysis / 11th edition / chapter 8 / problem 39p
Engineering Economic Analysis (11th Edition) Post a question
Answers from our experts for your tough
homework questions
See this solution in the app
Enter question
Chapter 8, Problem 39P Bookmark Show all steps: ON
ON
Step-by-step solution
Continue to post
12 questions remaining
Step 1 of 6
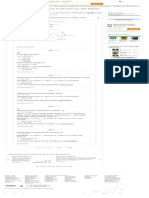
There are two alternatives available to own a car. The cost of car is $9,400. The information is
Snap a photo from your
given as follows: phone to post a question
Lease: We'll send you a one-time
download link
• Monthly lease charge is $267
• Number of monthly payments are 24 888-888-8888 Text me
• After that the car is returned to the company. That means salvage value is zero.
Loan: By providing your phone number, you agree to receive
a one-time automated text message with a link to get
the app. Standard messaging rates may apply.
• Zero down-payment
• Nominal annual interest rate is 12%, and nominal monthly interest rate is 1%
• Number of installments are 24
My Textbook Solutions
• Salvage value at the end of 24 months is $4,700
Calculation of monthly installments:
Here,
Engineering Introduction Introduction
A= the monthly installments = ? Economic... to Chemical... to Chemical...
11th Edition 6th Edition 7th Edition
P= the principal amount = $9,400
View all solutions
i%=the monthly rate of interest = 1%
n= time period = 24months
Substituting these values in the above equation:
…… (See compound interest table)
Therefore, the monthly installment is $442.74.
Comment
Step 2 of 6
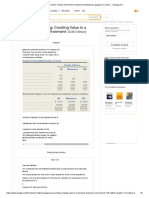
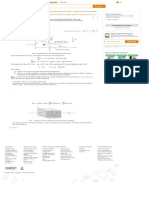
Next step is to calculate the net present worth of the differenced cash flow series and find the
incremental rate of return of this differenced cash flow series. Following table shows the two
alternatives and differenced cash flow series:
Table-1
Months Loan (A) Lease(B) Loan(A)-Lease(B)
1-24 -$442.74 -$267 -$175.74
Salvage value $4,700 0 $4,700
NET PRESENT WORTH OF (ALTERNATIVE A)-(ALTERNATIVE B):
Here,
P= initial costs
A= annual amount that is uniform over the time period
F=future value or salvage value
i= rate of return
n= time period
Comment
Step 3 of 6
In this case, the values are all differenced values and the variables can take the following values:
P= $175.74
A= $175.74
F=$4,700
i= ?
n= 22 for A
23 for F
Comment
Step 4 of 6
Now, substituting the value of variables into the above formula:
…… (1)
Look through the compound interest table and apply trial and error method and find an interest
rate which equalizes equation (1). That is, find an interest rate which equalizes left-hand side and
right-hand side of equation (1).
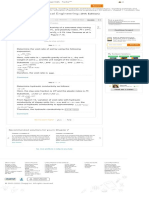
Substituting the tabular values into the right-hand side of equation (1). The table below shows the
two options whose values are closer to left-hand side of equation (1).
Table-2
Interest Rate (P/A,i,22) (P/F,i,23) Value
1.25% 19.131 0.7515 $184.125
1.50% 18.621 0.7100 $78.325
The rate of return, which is between 1.25% and 1.50%, may indeed be computed by linear
interpolation.
…… (2)
Here,
= lower interest rate
= higher interest rate
= factor of lower interest rate
= factor of higher interest rate
Substituting the values in equation (2), the result is as follows:
Therefore, the monthly incremental rate of return is 0.01271 or 1.271% (approx.)
Comment
Step 5 of 6
a)
The Annual incremental rate of return is 15.252% (1.271%*12). This suggests that below the
15.252% rate of return, loan (alternative-A) is preferred alternative and after this percentage,
leasing (Alternative-B) is the preferred alternative.
Therefore, over 15.252%, leasing is the preferred alternative.
Comment
Step 6 of 6
b)
Due to following reasons, leasing is more desirable alternative:
• The most important reason is the cost. It is always less expensive to lease a car than it is to
own the car. The people with less disposable income can afford a car using lease alternative.
• In some cases, Leasing is more attractive than buying or taking a loan. In this case also, if the
return from car is above 15.252%, then leasing is the best alternative.
• Some consumers prefer to have the latest cars but not for a long time. Then leasing is the best
alternative for such consumers.
Comment
Was this solution helpful? 0 0
Recommended solutions for you in Chapter 8
Chapter 8, Solution 34P Chapter 8, Solution 41P
The problem that you have below has to do with There are three options
multiple alternatives that we must decide between. available to buy a new
In this situation, we have a... car: • Pay $15,999 now
(Alternative A). • Take a
See solution 5-year loan at 9%
interest...
See solution
See more problems in subjects you study
COMPANY LEGAL & POLICIES CHEGG PRODUCTS AND SERVICES CHEGG NETWORK CUSTOMER SERVICE
About Chegg Advertising Choices Cheap Textbooks Mobile Apps EasyBib Customer Service
Chegg For Good Cookie Notice Chegg Coupon Sell Textbooks Internships.com Give Us Feedback
College Marketing General Policies Chegg Play Solutions Manual Thinkful Help with eTextbooks
Corporate Development Intellectual Property Rights Chegg Study Help Study 101 Help to use EasyBib Plus
Investor Relations Terms of Use College Textbooks Textbook Rental Manage Chegg Study
Jobs Global Privacy Policy eTextbooks Used Textbooks Subscription
Join Our Affiliate Program DO NOT SELL MY INFO Flashcards Digital Access Codes Return Your Books
Media Center Honor Code Learn Chegg Money Textbook Return Policy
Site Map Honor Shield Chegg Math Solver
© 2003-2021 Chegg Inc. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Mad English TV Celpip 8-9Document95 pagesMad English TV Celpip 8-9john huo100% (6)
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.46. A Flexible Circular Area of Radi...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.46. A Flexible Circular Area of Radi...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow SimulationDocument5 pagesCircular Flow Simulationsamira2702No ratings yet
- Solved For A Given Soil, The Following Are Known Gs 2.74, M...Document1 pageSolved For A Given Soil, The Following Are Known Gs 2.74, M...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Tango's Tamales Is A Small Restaurant On A Busy St...Document1 pageTango's Tamales Is A Small Restaurant On A Busy St...rizqighaniNo ratings yet
- Solved - Determine The Real Root of F (X) 5x3 - 5x2 + 6x - 2 - (...Document6 pagesSolved - Determine The Real Root of F (X) 5x3 - 5x2 + 6x - 2 - (...Angel Maliel Limon CaceresNo ratings yet
- Question: A Pattern Needed To Be Designed For The Part Shown in The GDocument3 pagesQuestion: A Pattern Needed To Be Designed For The Part Shown in The GEhtsham AwanNo ratings yet
- Solved - A Prototype Automobile Is Designed To Travel at 65 km2Fh Cheggcom PDFDocument3 pagesSolved - A Prototype Automobile Is Designed To Travel at 65 km2Fh Cheggcom PDFNabihah AzanNo ratings yet
- DY Centralised Distribution at Nike Centralised An...Document3 pagesDY Centralised Distribution at Nike Centralised An...Daniyal AsifNo ratings yet
- Solved During A Subsurface Exploration, An Undisturbed Soil Sa...Document1 pageSolved During A Subsurface Exploration, An Undisturbed Soil Sa...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Fluid Mechanics: (11th Edition)Document3 pagesEngineering Fluid Mechanics: (11th Edition)كرار عبدالحسين قاسمNo ratings yet
- Question: Problem On Accrual E. Gevera Realty Co. Who Owns A BuildingDocument2 pagesQuestion: Problem On Accrual E. Gevera Realty Co. Who Owns A BuildingKen SannNo ratings yet
- Principles of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Document2 pagesPrinciples of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Uzair Ahmed SoomroNo ratings yet
- Principles of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Document2 pagesPrinciples of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Uzair Ahmed SoomroNo ratings yet
- Solved - Tampa Instrument Company Manufactures Gauges For Constr...Document3 pagesSolved - Tampa Instrument Company Manufactures Gauges For Constr...Raaqib KhanNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.41. Given q2 3800 LBFT, x1 18 ...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.41. Given q2 3800 LBFT, x1 18 ...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- TSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 36P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionDocument1 pageTSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 36P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionxomuxNo ratings yet
- Question: 3 Pts D Question 5 Nicanor Left The Following Bank Deposits UDocument2 pagesQuestion: 3 Pts D Question 5 Nicanor Left The Following Bank Deposits UShiela MayNo ratings yet
- TSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 34P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionDocument1 pageTSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 34P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionxomuxNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.47. A Flexible Rectangular Area Is S...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.47. A Flexible Rectangular Area Is S...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- C Lombard Company Is Contemplating The Purchase ODocument5 pagesC Lombard Company Is Contemplating The Purchase OFahmi Ilham AkbarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Financial Management: (12th Edition)Document5 pagesFundamentals of Financial Management: (12th Edition)Usman Ali0% (1)
- Solved Solve Problem 8.10 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Document1 pageSolved Solve Problem 8.10 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Question: in Each of The Following Cases, Draw The Smooth Curve, Mark ItsDocument1 pageQuestion: in Each of The Following Cases, Draw The Smooth Curve, Mark ItsRahayu Rizki PutriNo ratings yet
- Principles of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Document3 pagesPrinciples of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Uzair Ahmed SoomroNo ratings yet
- Principles of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Document3 pagesPrinciples of Corporate Finance + S&P Market Insight: (10th Edition)Uzair Ahmed SoomroNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.49. For The Linearly Increasing Vert...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.49. For The Linearly Increasing Vert...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Loans Form An Integral Part of Banking Operations....Document3 pagesLoans Form An Integral Part of Banking Operations....Ameer HamzaNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To The Cross Section of The Earth Dam Shown in Fi...Document1 pageSolved Refer To The Cross Section of The Earth Dam Shown in Fi...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Local Media2138585013869044277Document3 pagesLocal Media2138585013869044277panger moooNo ratings yet
- Solved Repeat Problem 8.8 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Document1 pageSolved Repeat Problem 8.8 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Derive The Equation of Motion and Response Equatio Chegg ComDocument1 pageDerive The Equation of Motion and Response Equatio Chegg ComMuhd HarithNo ratings yet
- Solved Draw A Flow Net For The Weir Shown in Figure 8.25. Calc...Document1 pageSolved Draw A Flow Net For The Weir Shown in Figure 8.25. Calc...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Question: Dudster Manufacturing Has 2 Options For Installing Legally ReqDocument3 pagesQuestion: Dudster Manufacturing Has 2 Options For Installing Legally ReqJosh GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 8.23. Given - H1 6 M - H2 1.5 M - D ...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 8.23. Given - H1 6 M - H2 1.5 M - D ...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 9.4a. If H1 3 FT, H2 4.5 FT, H 1....Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 9.4a. If H1 3 FT, H2 4.5 FT, H 1....Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: (7th Edition)Document4 pagesFluid Mechanics: (7th Edition)Asfand Yar QureshiNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Problem 8.4. Using The Flow Net Drawn, Calcula...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Problem 8.4. Using The Flow Net Drawn, Calcula...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved - Which $1,000 Bond Has The Higher Yield To Maturity, A T...Document4 pagesSolved - Which $1,000 Bond Has The Higher Yield To Maturity, A T...Sanjna ChimnaniNo ratings yet
- Consider A Three-Dimensional Differential Fluid El...Document1 pageConsider A Three-Dimensional Differential Fluid El...Mergen KhanNo ratings yet
- Solved - Chapter 3 Problem 77RE Solution - Probability and Statistics For Engineers and Scientists 9th EditionDocument4 pagesSolved - Chapter 3 Problem 77RE Solution - Probability and Statistics For Engineers and Scientists 9th EditionJaleel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Solved - You Have Been Asked by The Head of Marketing To Design ...Document2 pagesSolved - You Have Been Asked by The Head of Marketing To Design ...Clyden Jaile RamirezNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.43. A Strip Load of Q 1450 lbft2 ...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.43. A Strip Load of Q 1450 lbft2 ...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Estimate The Hydraulic Conductivity of A Saturated Clay...Document1 pageSolved Estimate The Hydraulic Conductivity of A Saturated Clay...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Section 4. Asymmetric Shock (24 Points) Consider A...Document4 pagesSection 4. Asymmetric Shock (24 Points) Consider A...Noor FatimaNo ratings yet
- Find Its Acceleration For The First Instant and Se...Document2 pagesFind Its Acceleration For The First Instant and Se...Ionaishi FloresNo ratings yet
- Applied Calculus For Business, Economics, and The Social and Life Sciences, Expanded EditionDocument2 pagesApplied Calculus For Business, Economics, and The Social and Life Sciences, Expanded EditionAsif HossainNo ratings yet
- A Large Refinery and Petrochemical Complex Is Plan...Document4 pagesA Large Refinery and Petrochemical Complex Is Plan...Abdullah QureshiNo ratings yet
- Q#3. A) What Are Various Water Efficiencies When A...Document2 pagesQ#3. A) What Are Various Water Efficiencies When A...Muhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Solved Figure 9.29 Shows The Zone of Capillary Rise Within A C... Chegg - Com 2Document1 pageSolved Figure 9.29 Shows The Zone of Capillary Rise Within A C... Chegg - Com 2Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Question: 11. Incremental Costs Can Be de Ned As A. Costs That Are IrreleDocument2 pagesQuestion: 11. Incremental Costs Can Be de Ned As A. Costs That Are IrreleLayout By nicaNo ratings yet
- Calculus of A Single Variable: (11th Edition)Document1 pageCalculus of A Single Variable: (11th Edition)Noman MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Management, Student Value EditionDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Management, Student Value EditionMalik GNo ratings yet
- Solved - The Fourth-Degree Polynomial F (X) 230x4 + 18x3 + 9x2...Document7 pagesSolved - The Fourth-Degree Polynomial F (X) 230x4 + 18x3 + 9x2...Malik Ijaz Ali AwanNo ratings yet
- Solved The 5-m High Retaining Wall in Figure 13.40c Is Subject...Document1 pageSolved The 5-m High Retaining Wall in Figure 13.40c Is Subject...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved - You Have Data From A Corporation On The Annual Salary O...Document1 pageSolved - You Have Data From A Corporation On The Annual Salary O...Clyden Jaile RamirezNo ratings yet
- 15 KG of Refrigerant-134a (R-1340 Per Minute Flows ...Document3 pages15 KG of Refrigerant-134a (R-1340 Per Minute Flows ...Logendran A/l MurgayaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Corporate Finance: (9th Edition)Document4 pagesPrinciples of Corporate Finance: (9th Edition)Uzair Ahmed SoomroNo ratings yet
- Solved Repeat Problem 10.3 For The Element Shown in Figure 10....Document1 pageSolved Repeat Problem 10.3 For The Element Shown in Figure 10....Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved For A Dynamic Compaction Test, The Weight of The Hammer...Document1 pageSolved For A Dynamic Compaction Test, The Weight of The Hammer...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Ven A 1. Oped The Nase J.S. In. Do You Think That ...Document4 pagesVen A 1. Oped The Nase J.S. In. Do You Think That ...sidra tulmuntahaNo ratings yet
- Pulp and Paper Liquid Waste Treatment Using Electro Coagulation MembraneDocument7 pagesPulp and Paper Liquid Waste Treatment Using Electro Coagulation MembraneRobby KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 11 RP SP Equipment SpecificationDocument39 pages11 RP SP Equipment SpecificationRobby KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Skripsi EtanaDocument13 pagesSkripsi EtanaRobby KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Azeri Light 2005 06Document18 pagesAzeri Light 2005 06Robby KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Ray Crystallography Is The Deployment of X-Ray Diffraction Techniques For TheDocument5 pagesRay Crystallography Is The Deployment of X-Ray Diffraction Techniques For TheRobby KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Final Exam Case StuDocument2 pagesMarketing Management Final Exam Case Stumahmoud sakrNo ratings yet
- Fulfillment Process Presentation Final Team 5Document11 pagesFulfillment Process Presentation Final Team 5Bhargav MehtaNo ratings yet
- Bootcamp Assignment 4 - by Pratap ReddyDocument10 pagesBootcamp Assignment 4 - by Pratap ReddyPratap ReddyNo ratings yet
- Improving Returns On Stock Investment Through Neural Network SelectionDocument7 pagesImproving Returns On Stock Investment Through Neural Network SelectionAakash DebnathNo ratings yet
- Budget Operations Manual For Local Government UnitsDocument247 pagesBudget Operations Manual For Local Government UnitsJean Rema GonjoranNo ratings yet
- Lean 4Document9 pagesLean 4Arun PrasadNo ratings yet
- John F. Kennedy: Bachelor of Science: Major Public AccountingDocument2 pagesJohn F. Kennedy: Bachelor of Science: Major Public AccountingConnor FentonNo ratings yet
- Allowable DeductionsDocument4 pagesAllowable Deductionswind snip3r reojaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Evolution and Fundamental of BusinessDocument211 pagesChapter 1 Evolution and Fundamental of BusinessDr. Nidhi KumariNo ratings yet
- Prospectus - Optimal SA FundDocument45 pagesProspectus - Optimal SA FundMigle BloomNo ratings yet
- MVV Green Gardens FinalDocument10 pagesMVV Green Gardens FinalVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Buletin Mutiara - English/Chinese/Tamil - Mac #1 IssueDocument28 pagesBuletin Mutiara - English/Chinese/Tamil - Mac #1 IssueChan LilianNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Final AccountsDocument13 pagesPreparation of Final AccountsDr Sarbesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary Level: Cambridge Assessment International EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge Ordinary Level: Cambridge Assessment International EducationhbuzdarNo ratings yet
- MR4 - G2 Research ReportDocument66 pagesMR4 - G2 Research Reportngân hà maNo ratings yet
- Bitcoin Mining SurveyDocument7 pagesBitcoin Mining SurveyxxNo ratings yet
- Customised Profit & Loss (Rs - in Crores) Mar 18 17-Mar 16-Mar 15-Mar 14-Mar 5,592.29 5,290.65 5,750.00 5,431.28 4,870.08Document20 pagesCustomised Profit & Loss (Rs - in Crores) Mar 18 17-Mar 16-Mar 15-Mar 14-Mar 5,592.29 5,290.65 5,750.00 5,431.28 4,870.08Akshay Yadav Student, Jaipuria LucknowNo ratings yet
- ProspectusDocument2 pagesProspectusJuliana Mae FradesNo ratings yet
- PratimaMehta May2020Document3 pagesPratimaMehta May2020rajan mishraNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management Quarter 1 Week 2Document19 pagesOrganization and Management Quarter 1 Week 2Rui Isaac Fernando75% (4)
- It Application Tools in Business Chapter 1Document30 pagesIt Application Tools in Business Chapter 1pahatiprincess05No ratings yet
- 700 Transport Gurney: Operations and Maintenance ManualDocument27 pages700 Transport Gurney: Operations and Maintenance Manualsec.ivbNo ratings yet
- Book Building: IPO Price Discovery MechanismDocument35 pagesBook Building: IPO Price Discovery MechanismDevyansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- ICT1006 - ACC1007-CSC1005 Individual Assignment 1Document3 pagesICT1006 - ACC1007-CSC1005 Individual Assignment 1Yong RenNo ratings yet
- CMS Fee Payment ProcedureDocument2 pagesCMS Fee Payment ProceduresrijithspNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - 1 Cash and Marketable SecuritiesDocument15 pagesCHAPTER 6 - 1 Cash and Marketable SecuritiesAhmad Ridhuwan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- PMMSY1Document4 pagesPMMSY1NEC Andaman AccountsNo ratings yet
- Liability Insurance Certificate 2020Document2 pagesLiability Insurance Certificate 2020Majdi BelguithNo ratings yet