Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Verbs Followed by An Infinitive and Geru
Verbs Followed by An Infinitive and Geru
Uploaded by
nestor caroCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Aitchison College Syllabus 2022-23Document18 pagesAitchison College Syllabus 2022-23Salman Jawaid50% (4)
- Gerund and To Infinitive NewDocument15 pagesGerund and To Infinitive NewAlifaisyah BaydillaNo ratings yet
- Reactivate - C1-C2 - 6. Gerunds & Infinitives - 1-4 TheoryDocument4 pagesReactivate - C1-C2 - 6. Gerunds & Infinitives - 1-4 TheoryciorapelaNo ratings yet
- LecturesDocument194 pagesLecturesHuỳnh KiềuNo ratings yet
- Verb Lists - Infinitives and GerundsDocument2 pagesVerb Lists - Infinitives and GerundsAli DoostmohammadiNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed Infinitive and Gerund Ambiental 7Document38 pagesVerbs Followed Infinitive and Gerund Ambiental 7YolandaLupacaCaxiNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument6 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesdindaNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument4 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesThais22 EstudosNo ratings yet
- Gerund and Infinitive ListDocument4 pagesGerund and Infinitive ListVale VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Verb ListsDocument2 pagesVerb ListsCamila ChavezNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument5 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesKatherine JuleNo ratings yet
- Gerunds Infinitives LenteleDocument2 pagesGerunds Infinitives LenteleMarius Ranusas100% (1)
- TenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsDocument11 pagesTenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsHoshi MartinezNo ratings yet
- Verb Lists - Infinitives and GerundsDocument2 pagesVerb Lists - Infinitives and GerundsFederico Asiss González0% (1)
- TenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsDocument11 pagesTenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsCARLOS ANDRES HOSTIA VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Infinitive and GerundsDocument4 pagesInfinitive and GerundsMonica TiriraNo ratings yet
- List of Verbs ReactiuneDocument2 pagesList of Verbs ReactiuneRazvan SebesNo ratings yet
- Verb Lists - Infinitives and GerundsDocument2 pagesVerb Lists - Infinitives and GerundsMohammedAhmed Jubara100% (1)
- Verb ListsInfinIngDocument1 pageVerb ListsInfinIngAdam SmithNo ratings yet
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument1 pageGerund or InfinitiveЕленаNo ratings yet
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument17 pagesGerund or InfinitiveFebriantiKomalasariNo ratings yet
- Gerund and Infinitive FormsDocument5 pagesGerund and Infinitive Formslbn_mobkNo ratings yet
- Grammar Course Lecture Four Infintive PhrasesDocument5 pagesGrammar Course Lecture Four Infintive Phrasesfarawella09No ratings yet
- Verbs That Are Normally Followed by The Gerund Form:-: With No Change in MeaningDocument3 pagesVerbs That Are Normally Followed by The Gerund Form:-: With No Change in MeaningBeatrice FanareanuNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument3 pagesGerunds and InfinitiveshubertNo ratings yet
- Verbs Lists Gerund-InfinitvDocument3 pagesVerbs Lists Gerund-InfinitvNoemi PerezNo ratings yet
- Complete Verb PatternsDocument10 pagesComplete Verb PatternsPAULANo ratings yet
- Verbs That Take Infinitive Objects: Reference ListsDocument2 pagesVerbs That Take Infinitive Objects: Reference ListsKonankovNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument2 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesMarby Palomino100% (2)
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument6 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesMavelyn FelizNo ratings yet
- TenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsDocument11 pagesTenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsLuis Antonio Castañeda TiscareñoNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument5 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesYennNo ratings yet
- Infinitives and GerundsDocument24 pagesInfinitives and GerundsNath BonesiNo ratings yet
- English Grade 10 Ms Thao Nguyen-Kim Lien High School-0902114242Document10 pagesEnglish Grade 10 Ms Thao Nguyen-Kim Lien High School-0902114242Linh Ngọc NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Verb Pattern ListDocument2 pagesVerb Pattern ListHelenNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument8 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesLaura AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Gerunds Infinitives ListDocument5 pagesGerunds Infinitives ListYiğit Kaan ÜnalNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument2 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesRecabreratNo ratings yet
- GerundDocument3 pagesGerundThalia DstnNo ratings yet
- Verbs With Gerund and InfinitiveDocument3 pagesVerbs With Gerund and InfinitiveFitrianingsihNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument3 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesPraery PraeNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Top Notch 2 - Extra MaterialDocument5 pagesUnit 7 - Top Notch 2 - Extra MaterialKathyPazmiñoViteriNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument4 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesHồng Nhung NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitivesDocument24 pagesGerund and InfinitivesSeptiana Dewi AlhabbiyNo ratings yet
- Verb Lists - Infinitives and Gerunds 1Document1 pageVerb Lists - Infinitives and Gerunds 1mohamed abdallahNo ratings yet
- B2 Course: Unit 51 - Infinitive Vs GerundDocument4 pagesB2 Course: Unit 51 - Infinitive Vs GerundEugeniaNo ratings yet
- Gerunds - InfinitivesDocument4 pagesGerunds - InfinitivesMirzal TanrıkuluNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by Gerunds and Infinitives PDFDocument2 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerunds and Infinitives PDFTamer Obeid100% (2)
- English - Gerund, Infinitives and Bare InfinitivesDocument9 pagesEnglish - Gerund, Infinitives and Bare Infinitivesyod3853No ratings yet
- Regunds and InfinitivesDocument18 pagesRegunds and InfinitivesHuong HoangNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and Infinitives ListDocument5 pagesGerunds and Infinitives ListMonica Fernanda Cifuentes100% (1)
- Summary of The Unit - Kamila OrellanaDocument9 pagesSummary of The Unit - Kamila OrellanaKamila OrellanaNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument2 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesmenekshistivenNo ratings yet
- Infinitives and GerundsDocument4 pagesInfinitives and Gerundsاعتدال العبد اللهNo ratings yet
- Infinitives Vs Gerunds ListDocument2 pagesInfinitives Vs Gerunds ListClaudia RiveraNo ratings yet
- Link GrammarBk2 U2 Answer-CheckingDocument11 pagesLink GrammarBk2 U2 Answer-Checkingmiki leeNo ratings yet
- Review Topic 6 and Topic 7Document15 pagesReview Topic 6 and Topic 7Linh ChuNo ratings yet
- Infinitive or GerundDocument3 pagesInfinitive or GerundDiana AgudeloNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and INFINITIVESDocument7 pagesGerunds and INFINITIVESapi-199750620% (1)
- Gerunds N InfınıtıvesDocument21 pagesGerunds N Infınıtıvesİpek İpekogluNo ratings yet
- 118-Consiliere Si Dezvoltare PersonalaDocument2 pages118-Consiliere Si Dezvoltare PersonalaIrma KissNo ratings yet
- .Archivetemp1212 Words You Need To Pass The TOEFLDocument38 pages.Archivetemp1212 Words You Need To Pass The TOEFLfarhad shahryarpoorNo ratings yet
- Verb PatternsDocument4 pagesVerb PatternsOum El GhoulNo ratings yet
- Causative FormDocument2 pagesCausative FormmaiNo ratings yet
- Take-Home (2022)Document15 pagesTake-Home (2022)sofy rodriguezZNo ratings yet
- Simpe Past TenseDocument18 pagesSimpe Past TenseIndri GunawanNo ratings yet
- Catalog RuslangDocument45 pagesCatalog RuslangCristina_spqrNo ratings yet
- Writing A Successful Paragraphan Extended Paragraph and A Five - Paragraph CompositionDocument5 pagesWriting A Successful Paragraphan Extended Paragraph and A Five - Paragraph CompositionJesuv Cristian Clete100% (1)
- Access Spanish: Student Book: A First Language Course (Access Language Series) by María Utrera Cejudo. Hodder & Stoughton (FirstDocument3 pagesAccess Spanish: Student Book: A First Language Course (Access Language Series) by María Utrera Cejudo. Hodder & Stoughton (FirstkarlamoraNo ratings yet
- Оқу бағдарламасы - Ағылшын тілі 1-4 клDocument42 pagesОқу бағдарламасы - Ағылшын тілі 1-4 клзульфираNo ratings yet
- Open ClozeDocument2 pagesOpen Clozeuk idiomasNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect TenseDocument34 pagesPast Perfect TenseChique LabuguenNo ratings yet
- AE Think Starter SBDocument11 pagesAE Think Starter SBCarolina EliamNo ratings yet
- 02 - 05 Answer Papers - 6508369f95b6cDocument24 pages02 - 05 Answer Papers - 6508369f95b6cayeshashaikh3536No ratings yet
- 50 HomophonDocument9 pages50 HomophonAmeeshaNo ratings yet
- Reading Materials - LOW PDFDocument22 pagesReading Materials - LOW PDFFranfie Manalow100% (1)
- Академ Англ 1 Белгтленген (Копия)Document40 pagesАкадем Англ 1 Белгтленген (Копия)Асель СембекNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Ss17 JALAN SS17/1, Subang Jaya English Scheme of Work Form 3Document11 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Ss17 JALAN SS17/1, Subang Jaya English Scheme of Work Form 3Rohana YahyaNo ratings yet
- Disha Publication English SupplementDocument26 pagesDisha Publication English SupplementphysicspalanichamyNo ratings yet
- Ges 102 Lecture NoteDocument18 pagesGes 102 Lecture NoteakokodoubaraNo ratings yet
- Teaching Guide 8 PDFDocument84 pagesTeaching Guide 8 PDFRabi Kumar PatraNo ratings yet
- Students' Worksheet 6 - Present Perfect TenseDocument4 pagesStudents' Worksheet 6 - Present Perfect Tenseask ya bootyNo ratings yet
- Action Nominalization in AkanDocument12 pagesAction Nominalization in AkanGabija PaškevičiūtėNo ratings yet
- English Iv Unit 5: ESL Language CenterDocument35 pagesEnglish Iv Unit 5: ESL Language CenterDaniel QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam EnglishDocument5 pagesMidterm Exam EnglishKelly ChengNo ratings yet
- passive المبني للمجهولDocument3 pagespassive المبني للمجهولSadon B AsyNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal TOEFLDocument42 pagesContoh Soal TOEFLSundari FitriNo ratings yet
- 9.present Continuous IIIDocument4 pages9.present Continuous IIIQuiroz OliveraNo ratings yet
- Use The Past Form of Regular and Irregular Verbs: Elaine T. Arcangel Teacher IIIDocument18 pagesUse The Past Form of Regular and Irregular Verbs: Elaine T. Arcangel Teacher IIIELAINE ARCANGELNo ratings yet
Verbs Followed by An Infinitive and Geru
Verbs Followed by An Infinitive and Geru
Uploaded by
nestor caroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Verbs Followed by An Infinitive and Geru
Verbs Followed by An Infinitive and Geru
Uploaded by
nestor caroCopyright:
Available Formats
EASY FLUENCY
CONVERSATIONAL ENGLISH GRAMMAR
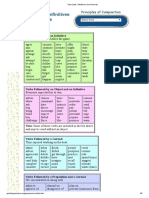
Verbs Followed by an Infinitive
She agreed to speak before the game.
agree choose fail leave prepare strive
aim condescend forget like proceed swear
appear consent get long promise threaten
arrange continue happen love propose try
ask dare have mean refuse use
attempt decide hesitate neglect remember wait
be able deserve hope offer say want
beg detest hurry ought shoot wish
begin dislike intend plan start
care expect leap prefer stop
Verbs Followed by an Object and an Infinitive
Everyone expected her to win.
advise challenge forbid leave permit teach
allow choose force let persuade tell
ask command have like prepare urge
beg dare hire love promise want
bring direct instruct motivate remind warn
build encourage invite order require
buy expect lead pay send
Note: Some of these verbs are included in the list above and may be used without an object.
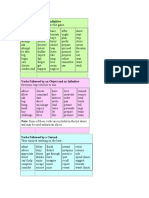
Verbs Followed by a Gerund
They enjoyed working on the boat.
admit consider escape imagine quit risk
advise delay excuse mind recall spend (time)
appreciate deny finish miss report suggest
avoid detest forbid permit resent tolerate
can't help dislike get through postpone resist waste (time)
complete enjoy have practice resume
Verbs Followed by a Preposition and a Gerund
We concentrated on doing well.
admit to care about depend on feel like plan on succeed in
approve of complain about disapprove of forget about prevent talk about
argue about concentrate on discourage from insist on (someone) from think about
believe in confess to dream about object to refrain from worry about
WWW.EASYFLUENCY.ORG ANDERSLIZZ2000@YAHOO.COM ENGLISH WITH ANDERSON
EASY FLUENCY
CONVERSATIONAL ENGLISH GRAMMAR
1. A gerund is a noun made from a verb by adding "-ing." The gerund form of the verb "read" is "reading." You
can use a gerund as the subject, the complement, or the object of a sentence.
Reading helps you learn English. SUBJECT OF SENTENCE
Her favorite hobby is reading. COMPLEMENT OF SENTENCE
I enjoy reading. OBJECT OF SENTENCE
2. Infinitives are the "to" form of the verb. The infinitive form of "learn" is "to learn." You can also use an
infinitive as the subject, the complement, or the object of a sentence.
To learn is important. SUBJECT OF SENTENCE
The most important thing is to learn. COMPLEMENT OF SENTENCE
He wants to learn. OBJECT OF SENTENCE
3. Both gerunds and infinitives can be used as the subject or the complement of a sentence. However, as
subjects or complements, gerunds usually sound more like normal, spoken English, whereas infinitives
sound more abstract. In the following sentences, gerunds sound more natural and would be more common
in everyday English. Infinitives emphasize the possibility or potential for something and sound more
philosophical. If this sounds confusing, just remember that 90% of the time, you will use a gerund as the
subject or complement of a sentence.
Learning is important. NORMAL SUBJECT
To learn is important. ABSTRACT SUBJECT - LESS COMMON
The most important thing is learning. NORMAL COMPLEMENT
The most important thing is to learn. ABSTRACT COMPLEMENT - LESS COMMON
4. As the object of a sentence, it is more difficult to choose between a gerund or an infinitive. In such
situations, gerunds and infinitives are not normally interchangeable. Usually, the main verb in the sentence
determines whether you use a gerund or an infinitive.
He enjoys swimming. "ENJOY" REQUIRES A GERUND.
He wants to swim. "WANT" REQUIRES AN INFINITIVE.
5. Some verbs are followed by infinitives.
agree Tom agreed to help me.
appear His health appeared to be better.
arrange Naomi arranged to stay with her cousin in Miami.
6. Gerunds can often be modified with possessive forms such as his, her, its, your, their, our, John's, Mary's,
the machine's, and so on. This makes it clearer who or what is performing the action.
I enjoyed their singing. THEY WERE SINGING.
She understood his saying no to the offer. HE SAID NO.
Sam resented Debbie's coming late to the dinner. DEBBIE CAME LATE TO THE DINNER.
We discussed the machine's being broken. THE MACHINE IS BROKEN.
7. Some verbs are followed by a noun plus an infinitive. In some situations, the noun is required. In other
situations, the noun is optional.
The police ordered the man to stop. NOUN IS REQUIRED
She asked to leave. NOUN IS OPTIONAL
She asked him to leave. NOUN IS OPTIONAL
8. Gerunds are used after prepositions. Most commonly, these are "verb + preposition" combinations. For
reference, see the Verb + Preposition Dictionary and the Phrasal Verb Dictionary. You don't have to
memorize these resources, you just need to remember that gerunds are used after prepositions!
They admitted to committing the crime.
Leslie made up for forgetting my birthday.
He is thinking about studying abroad.
WWW.EASYFLUENCY.ORG ANDERSLIZZ2000@YAHOO.COM ENGLISH WITH ANDERSON
You might also like
- Aitchison College Syllabus 2022-23Document18 pagesAitchison College Syllabus 2022-23Salman Jawaid50% (4)
- Gerund and To Infinitive NewDocument15 pagesGerund and To Infinitive NewAlifaisyah BaydillaNo ratings yet
- Reactivate - C1-C2 - 6. Gerunds & Infinitives - 1-4 TheoryDocument4 pagesReactivate - C1-C2 - 6. Gerunds & Infinitives - 1-4 TheoryciorapelaNo ratings yet
- LecturesDocument194 pagesLecturesHuỳnh KiềuNo ratings yet
- Verb Lists - Infinitives and GerundsDocument2 pagesVerb Lists - Infinitives and GerundsAli DoostmohammadiNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed Infinitive and Gerund Ambiental 7Document38 pagesVerbs Followed Infinitive and Gerund Ambiental 7YolandaLupacaCaxiNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument6 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesdindaNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument4 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesThais22 EstudosNo ratings yet
- Gerund and Infinitive ListDocument4 pagesGerund and Infinitive ListVale VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Verb ListsDocument2 pagesVerb ListsCamila ChavezNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument5 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesKatherine JuleNo ratings yet
- Gerunds Infinitives LenteleDocument2 pagesGerunds Infinitives LenteleMarius Ranusas100% (1)
- TenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsDocument11 pagesTenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsHoshi MartinezNo ratings yet
- Verb Lists - Infinitives and GerundsDocument2 pagesVerb Lists - Infinitives and GerundsFederico Asiss González0% (1)
- TenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsDocument11 pagesTenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsCARLOS ANDRES HOSTIA VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Infinitive and GerundsDocument4 pagesInfinitive and GerundsMonica TiriraNo ratings yet
- List of Verbs ReactiuneDocument2 pagesList of Verbs ReactiuneRazvan SebesNo ratings yet
- Verb Lists - Infinitives and GerundsDocument2 pagesVerb Lists - Infinitives and GerundsMohammedAhmed Jubara100% (1)
- Verb ListsInfinIngDocument1 pageVerb ListsInfinIngAdam SmithNo ratings yet
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument1 pageGerund or InfinitiveЕленаNo ratings yet
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument17 pagesGerund or InfinitiveFebriantiKomalasariNo ratings yet
- Gerund and Infinitive FormsDocument5 pagesGerund and Infinitive Formslbn_mobkNo ratings yet
- Grammar Course Lecture Four Infintive PhrasesDocument5 pagesGrammar Course Lecture Four Infintive Phrasesfarawella09No ratings yet
- Verbs That Are Normally Followed by The Gerund Form:-: With No Change in MeaningDocument3 pagesVerbs That Are Normally Followed by The Gerund Form:-: With No Change in MeaningBeatrice FanareanuNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument3 pagesGerunds and InfinitiveshubertNo ratings yet
- Verbs Lists Gerund-InfinitvDocument3 pagesVerbs Lists Gerund-InfinitvNoemi PerezNo ratings yet
- Complete Verb PatternsDocument10 pagesComplete Verb PatternsPAULANo ratings yet
- Verbs That Take Infinitive Objects: Reference ListsDocument2 pagesVerbs That Take Infinitive Objects: Reference ListsKonankovNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument2 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesMarby Palomino100% (2)
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument6 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesMavelyn FelizNo ratings yet
- TenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsDocument11 pagesTenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsLuis Antonio Castañeda TiscareñoNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument5 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesYennNo ratings yet
- Infinitives and GerundsDocument24 pagesInfinitives and GerundsNath BonesiNo ratings yet
- English Grade 10 Ms Thao Nguyen-Kim Lien High School-0902114242Document10 pagesEnglish Grade 10 Ms Thao Nguyen-Kim Lien High School-0902114242Linh Ngọc NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Verb Pattern ListDocument2 pagesVerb Pattern ListHelenNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument8 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesLaura AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Gerunds Infinitives ListDocument5 pagesGerunds Infinitives ListYiğit Kaan ÜnalNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument2 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesRecabreratNo ratings yet
- GerundDocument3 pagesGerundThalia DstnNo ratings yet
- Verbs With Gerund and InfinitiveDocument3 pagesVerbs With Gerund and InfinitiveFitrianingsihNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument3 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesPraery PraeNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Top Notch 2 - Extra MaterialDocument5 pagesUnit 7 - Top Notch 2 - Extra MaterialKathyPazmiñoViteriNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument4 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesHồng Nhung NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitivesDocument24 pagesGerund and InfinitivesSeptiana Dewi AlhabbiyNo ratings yet
- Verb Lists - Infinitives and Gerunds 1Document1 pageVerb Lists - Infinitives and Gerunds 1mohamed abdallahNo ratings yet
- B2 Course: Unit 51 - Infinitive Vs GerundDocument4 pagesB2 Course: Unit 51 - Infinitive Vs GerundEugeniaNo ratings yet
- Gerunds - InfinitivesDocument4 pagesGerunds - InfinitivesMirzal TanrıkuluNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by Gerunds and Infinitives PDFDocument2 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerunds and Infinitives PDFTamer Obeid100% (2)
- English - Gerund, Infinitives and Bare InfinitivesDocument9 pagesEnglish - Gerund, Infinitives and Bare Infinitivesyod3853No ratings yet
- Regunds and InfinitivesDocument18 pagesRegunds and InfinitivesHuong HoangNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and Infinitives ListDocument5 pagesGerunds and Infinitives ListMonica Fernanda Cifuentes100% (1)
- Summary of The Unit - Kamila OrellanaDocument9 pagesSummary of The Unit - Kamila OrellanaKamila OrellanaNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument2 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesmenekshistivenNo ratings yet
- Infinitives and GerundsDocument4 pagesInfinitives and Gerundsاعتدال العبد اللهNo ratings yet
- Infinitives Vs Gerunds ListDocument2 pagesInfinitives Vs Gerunds ListClaudia RiveraNo ratings yet
- Link GrammarBk2 U2 Answer-CheckingDocument11 pagesLink GrammarBk2 U2 Answer-Checkingmiki leeNo ratings yet
- Review Topic 6 and Topic 7Document15 pagesReview Topic 6 and Topic 7Linh ChuNo ratings yet
- Infinitive or GerundDocument3 pagesInfinitive or GerundDiana AgudeloNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and INFINITIVESDocument7 pagesGerunds and INFINITIVESapi-199750620% (1)
- Gerunds N InfınıtıvesDocument21 pagesGerunds N Infınıtıvesİpek İpekogluNo ratings yet
- 118-Consiliere Si Dezvoltare PersonalaDocument2 pages118-Consiliere Si Dezvoltare PersonalaIrma KissNo ratings yet
- .Archivetemp1212 Words You Need To Pass The TOEFLDocument38 pages.Archivetemp1212 Words You Need To Pass The TOEFLfarhad shahryarpoorNo ratings yet
- Verb PatternsDocument4 pagesVerb PatternsOum El GhoulNo ratings yet
- Causative FormDocument2 pagesCausative FormmaiNo ratings yet
- Take-Home (2022)Document15 pagesTake-Home (2022)sofy rodriguezZNo ratings yet
- Simpe Past TenseDocument18 pagesSimpe Past TenseIndri GunawanNo ratings yet
- Catalog RuslangDocument45 pagesCatalog RuslangCristina_spqrNo ratings yet
- Writing A Successful Paragraphan Extended Paragraph and A Five - Paragraph CompositionDocument5 pagesWriting A Successful Paragraphan Extended Paragraph and A Five - Paragraph CompositionJesuv Cristian Clete100% (1)
- Access Spanish: Student Book: A First Language Course (Access Language Series) by María Utrera Cejudo. Hodder & Stoughton (FirstDocument3 pagesAccess Spanish: Student Book: A First Language Course (Access Language Series) by María Utrera Cejudo. Hodder & Stoughton (FirstkarlamoraNo ratings yet
- Оқу бағдарламасы - Ағылшын тілі 1-4 клDocument42 pagesОқу бағдарламасы - Ағылшын тілі 1-4 клзульфираNo ratings yet
- Open ClozeDocument2 pagesOpen Clozeuk idiomasNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect TenseDocument34 pagesPast Perfect TenseChique LabuguenNo ratings yet
- AE Think Starter SBDocument11 pagesAE Think Starter SBCarolina EliamNo ratings yet
- 02 - 05 Answer Papers - 6508369f95b6cDocument24 pages02 - 05 Answer Papers - 6508369f95b6cayeshashaikh3536No ratings yet
- 50 HomophonDocument9 pages50 HomophonAmeeshaNo ratings yet
- Reading Materials - LOW PDFDocument22 pagesReading Materials - LOW PDFFranfie Manalow100% (1)
- Академ Англ 1 Белгтленген (Копия)Document40 pagesАкадем Англ 1 Белгтленген (Копия)Асель СембекNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Ss17 JALAN SS17/1, Subang Jaya English Scheme of Work Form 3Document11 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Ss17 JALAN SS17/1, Subang Jaya English Scheme of Work Form 3Rohana YahyaNo ratings yet
- Disha Publication English SupplementDocument26 pagesDisha Publication English SupplementphysicspalanichamyNo ratings yet
- Ges 102 Lecture NoteDocument18 pagesGes 102 Lecture NoteakokodoubaraNo ratings yet
- Teaching Guide 8 PDFDocument84 pagesTeaching Guide 8 PDFRabi Kumar PatraNo ratings yet
- Students' Worksheet 6 - Present Perfect TenseDocument4 pagesStudents' Worksheet 6 - Present Perfect Tenseask ya bootyNo ratings yet
- Action Nominalization in AkanDocument12 pagesAction Nominalization in AkanGabija PaškevičiūtėNo ratings yet
- English Iv Unit 5: ESL Language CenterDocument35 pagesEnglish Iv Unit 5: ESL Language CenterDaniel QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam EnglishDocument5 pagesMidterm Exam EnglishKelly ChengNo ratings yet
- passive المبني للمجهولDocument3 pagespassive المبني للمجهولSadon B AsyNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal TOEFLDocument42 pagesContoh Soal TOEFLSundari FitriNo ratings yet
- 9.present Continuous IIIDocument4 pages9.present Continuous IIIQuiroz OliveraNo ratings yet
- Use The Past Form of Regular and Irregular Verbs: Elaine T. Arcangel Teacher IIIDocument18 pagesUse The Past Form of Regular and Irregular Verbs: Elaine T. Arcangel Teacher IIIELAINE ARCANGELNo ratings yet