Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cells: Biomolecule, The Four Major Types of Biomolecules
Cells: Biomolecule, The Four Major Types of Biomolecules
Uploaded by
AvaricioElPecadoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cells: Biomolecule, The Four Major Types of Biomolecules
Cells: Biomolecule, The Four Major Types of Biomolecules
Uploaded by
AvaricioElPecadoCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: _______________________________________Grade & Section: _______________ Subject: Science 10
Teacher: __________________________________ Score: ____________
Lesson : Quarter 4 Week 3 LAS 2
Activity Title : We are Match!
Learning Target : Describe the structure of biomolecules.
Reference(s) : Science 10 LM, S10MT-IVc-d-22, https://byjus.com/biology/biomolecules/,
https://www.britannica.com/science/biomolecule
LAS Writer : Maria Teresa C. Villamora
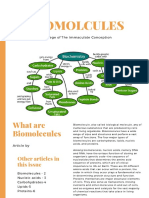
Biomolecule, also called biological molecule, any of numerous substances that are produced by cells and living
organisms. Biomolecules have a wide range of sizes and structures and perform a vast array of functions. The
four major types of biomolecules
Fig.1 Adapted from
https://byjus.com/biology/biomolecules/
1. Carbohydrates - certainly qualifies as the “foundation” element for molecules in living things
which are made up primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, a group of macromolecules that are a vital
energy source for the cell, provide structural support to many organisms, and can be found on the surface of
the cell as receptors or for cell recognition. Carbohydrates are classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides,
and polysaccharides, depending on the number of monomers in the molecule.
2. Lipids - fulfill a variety of roles, including serving as a source of stored energy and acting as chemical
messengers. Major types include fats and oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids.
3. Nucleic acids - namely DNA and RNA, have the unique function of storing an organism’s genetic code—the
sequence of nucleotides that determines the amino acid sequence of proteins, which are of critical importance
to life on Earth.
4. Proteins - are major structural elements of cells. They also serve as transporters, moving nutrients and other
molecules in and out of cells, and as enzymes and catalysts for the vast majority of chemical reactions that
take place in living organisms. Proteins also form antibodies and hormones, and they influence gene activity.
Directions: Fill in the missing words to correctly complete the statement/s. Choose your answer from the box below.
RNA Carbohydrates Protein nucleic acid Biomolecules
DNA energy lipids hydrophobic
The large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules are called 1. ______. That include
large molecules or macromolecules such as 2. ____, 3. _____, 4.____and 5.___. Carbohydrates provide 6. ______ to
the body, particularly through glucose, a simple sugar. Lipids are 7._____, because they are nonpolar molecules. 8.
____are the monomers that make up proteins. Nucleic acids are key macromolecules in the continuity of life. They
carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. 9.____is the genetic material
found in all living organisms, ranging from single-celled bacteria to multicellular mammals and 10. ____, is mostly
involved in protein synthesis.
You might also like
- Week 2 Lab ReportDocument11 pagesWeek 2 Lab ReportTina VargheseNo ratings yet
- Q3 G11 Physical Science Module 7Document19 pagesQ3 G11 Physical Science Module 7Lebz RicaramNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module 2 Combined-1Document14 pagesUnit 2 Module 2 Combined-1api-2930012170% (2)
- Math Curriculum Guide Grades 1-10Document109 pagesMath Curriculum Guide Grades 1-10Ebab Yvi100% (10)
- Concrete Mix Design For M65 Grade ConcreteDocument12 pagesConcrete Mix Design For M65 Grade ConcreteDevendrasinh PadhiyarNo ratings yet
- Q4 Science10 Week3 LAS-2Document1 pageQ4 Science10 Week3 LAS-2Nika NinianNo ratings yet
- Module 27Document23 pagesModule 27Ven Zyndryx De JoyaNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules Extension ActivityDocument4 pagesMacromolecules Extension Activityapi-375285021No ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE Q3 Week 4 - v2Document21 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE Q3 Week 4 - v2Evangelyn Patatag-CatacutanNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Matter and Organic Compounds - WorksheetsDocument9 pages2.1 Matter and Organic Compounds - WorksheetsMahmoud AsmarNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculeDocument16 pagesBio MoleculealialegiliNo ratings yet
- An IntroductionDocument21 pagesAn IntroductionOmar GardiNo ratings yet
- BIOL 307 Biochemistr Y: by Çağdaş D. SonDocument101 pagesBIOL 307 Biochemistr Y: by Çağdaş D. SonMetehan KaraNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument36 pagesBiological MacromoleculesArthur LaurelNo ratings yet
- STUDY GUIDE Week 13 August 1st To 5thDocument6 pagesSTUDY GUIDE Week 13 August 1st To 5thSAM MORANNo ratings yet
- Science AhseyDocument7 pagesScience AhseyWelfredo Jr YuNo ratings yet
- Importance of Biological MoleculeDocument3 pagesImportance of Biological MoleculeMary Antonette LucioNo ratings yet
- LAS Physical Science Week 4Document10 pagesLAS Physical Science Week 4Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument5 pagesBiology ReviewerLykammarvelyn F. MarceloNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument1 pageBiomoleculesCUYOS JellianaNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument6 pagesBiological MacromoleculesTinay escaroNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument26 pagesBio MoleculesSHERRYL PANTANo ratings yet
- Orange Photo College Newsletter2Document6 pagesOrange Photo College Newsletter2CHRISTIAN CUARESMANo ratings yet
- Sci10 Q4 W3-4 Biomolecules Garlejo - FINAL PDFDocument10 pagesSci10 Q4 W3-4 Biomolecules Garlejo - FINAL PDFPd Dapliyan100% (2)
- Bio Molecules ActDocument4 pagesBio Molecules ActMaria Elaine RamosNo ratings yet
- What Is BiochemistryDocument11 pagesWhat Is BiochemistryBalangat Regine L.No ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 MODULE FOURTH QUARTER Week 3 4 BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesSCIENCE 10 MODULE FOURTH QUARTER Week 3 4 Biomoleculesizi iordeinNo ratings yet
- General Biology: First Class Lab 4 & 5 Shahad EmadDocument7 pagesGeneral Biology: First Class Lab 4 & 5 Shahad EmadIraqiNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument7 pagesBio Moleculesmarkkevingonzales1235No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Merged (1) OrganizedDocument13 pagesBiomolecules Merged (1) OrganizedbrrrrrrrrrrrrruNo ratings yet
- SHS Spec Subj STEM Gen Chem1 SIPack W6Document14 pagesSHS Spec Subj STEM Gen Chem1 SIPack W6Glexis TiamsonNo ratings yet
- Shs Module v2020 #m3.2-1Document3 pagesShs Module v2020 #m3.2-1Adrienne ZapantaNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q4 Module-4 Week-4Document4 pagesScience-10 Q4 Module-4 Week-4Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Jose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolDocument8 pagesJose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolEricha SolomonNo ratings yet
- M4 BiomoleculesDocument41 pagesM4 BiomoleculesStephanie TamayuzaNo ratings yet
- Jose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolDocument8 pagesJose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolEricha Solomon0% (1)
- Lesson Plan BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Biomoleculescnjm1104No ratings yet
- Mrs. Tarawally - 045400Document11 pagesMrs. Tarawally - 045400koromamoses235No ratings yet
- A.P. Biology Summer Work: Worksheet: Lesson 1: True or FalseDocument10 pagesA.P. Biology Summer Work: Worksheet: Lesson 1: True or FalseedeceNo ratings yet
- Notes Biological Molecules 3Document8 pagesNotes Biological Molecules 3abdul rehmanNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 General Chemistry 1 m14 v2Document21 pagesQuarter 2 General Chemistry 1 m14 v2Lynette Licsi100% (1)
- With Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2016Document2 pagesWith Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2016Catherine Villaruz100% (1)
- Shivraj Chemistry BiomoleculeDocument15 pagesShivraj Chemistry BiomoleculeRavindra JangidNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument10 pagesCHEMISTRYShyam SundarNo ratings yet
- Physical Science q3 Week 4 v2 RecoveredDocument9 pagesPhysical Science q3 Week 4 v2 Recoveredjensenearl934No ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument4 pagesChemical Basis of LifeAUBREY LISAYENNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 4Document11 pagesPhysical Science Week 4Rona Grace MartinezNo ratings yet
- What Organic Chemicals Are Important To LifeDocument5 pagesWhat Organic Chemicals Are Important To Liferocz dela cruzNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculeDocument22 pagesBiomoleculeAna Carmela MortelNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Submitted By: Group 1 Margielyn Dinglasan Efren Cacao Jr. Jessibel MalaluanDocument6 pagesBiomolecules: Submitted By: Group 1 Margielyn Dinglasan Efren Cacao Jr. Jessibel MalaluanKers CelestialNo ratings yet
- Week 4B Science 7 LasDocument7 pagesWeek 4B Science 7 LasJonah Labine Jabulin-RadazaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument44 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistryFrance Jan First SaplacoNo ratings yet
- Bio Lec.4Document5 pagesBio Lec.4ksoo5118No ratings yet
- Green and Pink Doodle Hand Drawn Science Project PresentationDocument16 pagesGreen and Pink Doodle Hand Drawn Science Project PresentationJatinNo ratings yet
- Cells: The Smallest Unit of LifeDocument13 pagesCells: The Smallest Unit of Liferakhmatov UlanNo ratings yet
- Science7 Q2 WeeK4 LAS1Document2 pagesScience7 Q2 WeeK4 LAS1maeshengNo ratings yet
- Column A A. Biomolecules B. Lipids C. Carbohydrates D. Proteins E. Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesColumn A A. Biomolecules B. Lipids C. Carbohydrates D. Proteins E. Nucleic AcidsAvaricioElPecado100% (1)
- BMS 204 Introduction To Biochemistry: Dr. Reem Arafa Prof. of Biomedical SciencesDocument36 pagesBMS 204 Introduction To Biochemistry: Dr. Reem Arafa Prof. of Biomedical SciencesRamy El-HadadNo ratings yet
- Name: - Section: - Schedule: - Class Number: - DateDocument8 pagesName: - Section: - Schedule: - Class Number: - DateDalrymple Clavo RamosNo ratings yet
- List of Biomolecules ReviewerDocument2 pagesList of Biomolecules Reviewerah1805799No ratings yet
- Q4 Science10 Week1 LAS2Document1 pageQ4 Science10 Week1 LAS2AvaricioElPecadoNo ratings yet
- Medium Anic&Utm - Source Google&Utm - Campaign Iptcurl: Lifted From Ease Module Chem 9 Gas LawDocument1 pageMedium Anic&Utm - Source Google&Utm - Campaign Iptcurl: Lifted From Ease Module Chem 9 Gas LawAvaricioElPecadoNo ratings yet
- Activity: What Is Your Type?Document2 pagesActivity: What Is Your Type?AvaricioElPecado100% (1)
- Column A A. Biomolecules B. Lipids C. Carbohydrates D. Proteins E. Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesColumn A A. Biomolecules B. Lipids C. Carbohydrates D. Proteins E. Nucleic AcidsAvaricioElPecado100% (1)
- 2nd QuantizationDocument41 pages2nd QuantizationAlberto AlbuquerqueNo ratings yet
- CHM 152Ll: Thermodynamics: Pre LabDocument5 pagesCHM 152Ll: Thermodynamics: Pre LabIpshita PathakNo ratings yet
- Introduction - Matter and Measurement 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions AnswerDocument104 pagesIntroduction - Matter and Measurement 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions AnswerNgọc PhụngNo ratings yet
- WMD 4th Gen QuestDocument236 pagesWMD 4th Gen QuestArmstrong Tower100% (1)
- APhO 2016 E2 Presentation FinalDocument22 pagesAPhO 2016 E2 Presentation FinalSiddharth AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Reference Material: Chapter 10.4 (PG 248) of JMH Physics Chapter 8 of MHRDocument19 pagesReference Material: Chapter 10.4 (PG 248) of JMH Physics Chapter 8 of MHRzachariaNo ratings yet
- Infrared SpectrosDocument17 pagesInfrared SpectrosJasper DumalaogNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Trial 2015-2017 ModuleDocument119 pagesSPM Chemistry Trial 2015-2017 Modulekhangsiean8950% (2)
- Alpha-Curcumene - C15H22 - PubChemDocument22 pagesAlpha-Curcumene - C15H22 - PubChemfun factNo ratings yet
- Maha Lift Service ManualDocument30 pagesMaha Lift Service ManualGerard CorcoranNo ratings yet
- MS-06-61 Swagelok SC-01 Ultrahigh-Purity Process SpecificationDocument5 pagesMS-06-61 Swagelok SC-01 Ultrahigh-Purity Process SpecificationLiu YangtzeNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Final PresentationDocument28 pagesMini Project Final Presentationrohan vNo ratings yet
- Https:/suprachem2022.Uni-mainz - de/files/2022/07/SupraChem2022 BookletDocument215 pagesHttps:/suprachem2022.Uni-mainz - de/files/2022/07/SupraChem2022 BookletkaranNo ratings yet
- Xanthan Gum FAO 2Document11 pagesXanthan Gum FAO 2alifia hanifNo ratings yet
- TBRPhysics2 PDFDocument308 pagesTBRPhysics2 PDFNeural Spark Physics CieNo ratings yet
- Phy TST CHP 4 and 5Document2 pagesPhy TST CHP 4 and 5MUhammad Saqib Naveed ShahNo ratings yet
- Amphetamine Leucart ReactionDocument1 pageAmphetamine Leucart Reactionlukasz_wieczorek_praca100% (3)
- Hydrology and Hydraulics: PrecipitationDocument38 pagesHydrology and Hydraulics: PrecipitationMahmoud I. MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Research and Special Programs Admin., DOT 180.209Document5 pagesResearch and Special Programs Admin., DOT 180.209parmindersinNo ratings yet
- Biodegradation of Low Density Polyethylene LDPE by Mesophilic Fungus Penicillium Citrinum Isolated From Soils of Plastic WasteDocument16 pagesBiodegradation of Low Density Polyethylene LDPE by Mesophilic Fungus Penicillium Citrinum Isolated From Soils of Plastic WasteKewin HernandezNo ratings yet
- Biochem 313 Prac 5Document8 pagesBiochem 313 Prac 5Anonymous G8WVOfRqV100% (2)
- Unit - IV - Uv VisibleDocument27 pagesUnit - IV - Uv VisibleM. BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer - A Practical Approach - Yunus A. CengelDocument873 pagesHeat Transfer - A Practical Approach - Yunus A. Cengelvinodkonatham70371% (7)
- 0000 De20 SPC 0018Document36 pages0000 De20 SPC 0018b_m_leeNo ratings yet
- PH102 Course Outline 2023Document9 pagesPH102 Course Outline 2023KAUSHAL KEVINNo ratings yet
- Florida Method of Test For Sulfate in Soil and Water Fm5-553Document3 pagesFlorida Method of Test For Sulfate in Soil and Water Fm5-553Guillermo CegarraNo ratings yet
- Appendix 12B. Liquid-Liquid Distribution (Solvent Extraction)Document21 pagesAppendix 12B. Liquid-Liquid Distribution (Solvent Extraction)rodrigue yanNo ratings yet
- 02 Chemical Periodicity Ques. Final EDocument21 pages02 Chemical Periodicity Ques. Final EanishkadiyalaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Pre Final 1 & 2 PapersDocument12 pagesChemistry Pre Final 1 & 2 PaperskayNo ratings yet