Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 10: Reaching The Age of Adolescence
Chapter 10: Reaching The Age of Adolescence
Uploaded by
Aarti RajanikantOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 10: Reaching The Age of Adolescence
Chapter 10: Reaching The Age of Adolescence
Uploaded by
Aarti RajanikantCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 10: Reaching the Age of Adolescence
Adolescence:
1. It is the period of life, when the body undergoes changes, leading to reproductive
maturity.
2. Adolescents are also called as teenagers. The age group of these teenagers is from 11
years to 18 or 19 years.
Puberty:
1. Marked important change which boys and girls become capable of reproduction is said to
be the onset of puberty.
2. Puberty ends with attainment of reproductive maturity.
Changes at puberty:
1) Increase in Height:
The most noticeable change is the increase in height. It is mainly because of elongation of
the arm and leg bones.
2) Change in body shape:
In girls, the region below the waist becomes wider. In boys, the muscles of the body grow
more prominently than in the girls. Shoulders generally broaden as a result of growth.
Thus, changes occurring in adolescent boys and girls are different.
3) Voice change:
The larynx begins to grow in males. Due to this Boys develop larger voice box which
looks like a protruding part of the throat called Adam’s apple. On the other hand, girls
have a high-pitched voice.
4) Increased Activity of Sweat and Sebaceous Glands:
The secretion of sweat glands and sebaceous glands (oil glands) markedly increases. This
leads to development of acne and pimples on the face.
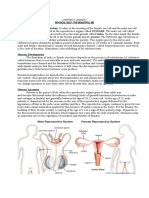
5) Development of Sex Organs:
The male sex organs like the testes and penis develop completely. The testes produce
sperms after attainment of puberty. In girls, the ovaries enlarge and eggs begin to mature.
ovaries start releasing mature eggs.
6) Reaching Mental, Intellectual and Emotional Maturity: It is the period which influences a
person’s way of thinking. A teenager may feel independent, insecure, self-conscious or
even depressed at times while trying to adapt to these body changes.
7) Development of secondary sexual characters:
In girls, breasts development and in boys begin to grow facial hair grows. Features which
distinguish the male from the female they are called secondary sexual characters.
Role of Hormones in Initiating Reproductive Function:
Hormones: Chemical secretions from endocrine glands is called hormones.
The male hormone or testosterone is released by the testes.
Ovaries produce the female hormone or estrogen.
Due to this hormone mammary glands develop inside the breasts.
The production of these hormones is under the control of the pituitary gland.
Target site: A particular body part on which the endocrine hormones act.
The testes and ovaries secrete sex hormones responsible for the male and female
secondary sexual characters.
Pituitary Gland secretes hormones which makes ova mature in the ovaries and sperms
form in the testes
Reproductive Phase of Life in Humans
Adolescents become capable of reproduction when their testes and ovaries begin to
produce gametes.
The capacity for maturation and production of gametes is longer in males.
In females, the reproductive phase of life begins 10 to 12 years of age and lasts till the
age of approximately 45 to 50 years.
The matured ovum is released by one of the ovaries once in about 28 to 30 days.
This period is marked by the development of uterus walls. It becomes thick to receive
the egg in case of fertilization and begins to develop.
This results in pregnancy.
In case if fertilization does not occur, the released egg, thickened lining of the uterus
along with its blood vessels are shed off. This leads to bleeding in women which is
called menstruation.
Initially the menstruation cycle is irregular but it will become regular with time. It is
under the hormonal control.
Menarche: It is the first menstrual flow at onset of puberty.
Menopause: It is the stopping of menstrual cycle in the age between 45 to 50 years.
Sex determination of the Baby:
Zygote has the necessary information for sex determination of babies
Humans have 23 pair of chromosomes.
Chromosomes are thread like structures who store information for sex
determination.
The two chromosomes X and Y are called the sex chromosomes.
A female has two X chromosomes and a male has one X and one Y
chromosome.
The gametes i.e. egg and sperm are haploid having only one set of
chromosomes.
The unfertilized egg always has one X chromosome. Whereas the sperm can
have either X or Y chromosome.
Role of Hormones in Completing the Life History of Insects and Frogs
Metamorphosis: the series of change that take place in life cycle from larva to
adult is called Metamorphosis.
It is controlled by insect hormone and by thyroxine in frogs.
Iodine in water is essential for production of Thyroxine hormone.
Reproductive Health:
1. An Individuals health comprises of both physical and mental wellbeing of the
person.
2. A balanced diet is essential to keep the body healthy at any stage of life.
3. It is very important to have a balanced diet in the Adolescence stage as it is a
stage of rapid growth and development.
4. Chips and packed or tinned snacks, though very tasty can never replace regular
meals as they do not have adequate nutritional value.
Personal Hygiene
1. Have bath once daily to clean body smell as sweat glands are more active during this
period.
2. If cleanliness is not maintained there are chances of catching bacterial infection.
3. Cleanliness during the time of menstrual flow is important. Girls should keep track of
their menstrual cycle and be prepared for the onset of menstruation.
4. One should use sanitary napkin or clean homemade pads. Change pads after every 4–
5 hours as per the requirement.
5. Physical exercise: Walking and playing in fresh air keeps the body fit and healthy.
Hence all young boys and girls should take walks, exercise and play outdoor games.
6. Say “NO” to Drugs: Drugs are addictive and should not be consumed until prescribed
by a doctor.
7. The drugs harm the body and ruin health and happiness
8. AIDS is caused by HIV virus. The virus can pass on to a normal person from an
infected person by sharing the syringes used for injecting drugs.
9. HIV can also be transmitted to an infant from the infected mother through her milk.
10. The virus can also be transmitted through sexual contact with a person infected with
HIV.
You might also like
- CH 10 Class 8th PDF NotesDocument6 pagesCH 10 Class 8th PDF NotesPalak MishraNo ratings yet
- Reaching The Age of Adolescence Class 8 Notes - Chapter 10Document6 pagesReaching The Age of Adolescence Class 8 Notes - Chapter 10anushree ranadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Reaching The Age of Adolescence Adolescence and PubertyDocument4 pagesChapter 10 - Reaching The Age of Adolescence Adolescence and PubertyRehanul IslamNo ratings yet
- Study Material Class 8 (Science) Term IIDocument99 pagesStudy Material Class 8 (Science) Term IIKPOP IS LIFENo ratings yet
- Adolescence: 1. Change in HeightDocument15 pagesAdolescence: 1. Change in HeightVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Revision NotesDocument2 pagesClass 8 Science Chapter 10 Revision NotesAnshul VermaNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Class 8 Science Chapter 10 - Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument2 pagesRevision Notes Class 8 Science Chapter 10 - Reaching The Age of AdolescenceArpit SharmaNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Reaching The Age of Adolescence NotesDocument2 pagesCH 10 Reaching The Age of Adolescence NotesKaz JNo ratings yet
- Understading The Self NotesDocument15 pagesUnderstading The Self NotesdorothyzoeesbietoNo ratings yet
- Reaching To The Age of adoloscensePPTDocument20 pagesReaching To The Age of adoloscensePPTSANGEETA WADHWANo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 10 NotesChahat SanataniNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentSiriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document4 pagesChapter 10senthildevi.namakkalNo ratings yet
- Physical and Sexual SelfDocument88 pagesPhysical and Sexual SelfBrenda EstuyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 UTS RevDocument11 pagesChapter 2 UTS RevYsabel ApostolNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Reaching The Age of Adolescence NotesDocument2 pagesCH 10 Reaching The Age of Adolescence NotesShreyansh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument5 pagesReproduction in Animalsbarnalisharmah586No ratings yet
- (Template) MODULE PART 2 UNPACKING THE SELFDocument14 pages(Template) MODULE PART 2 UNPACKING THE SELFMary Abegail MorandarteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document6 pagesChapter 109871739026saranNo ratings yet
- Ge1-Module 7-The Sexual SelfDocument41 pagesGe1-Module 7-The Sexual SelfCherry Mae CabuangNo ratings yet
- AdolescentDocument9 pagesAdolescentvgautambarcNo ratings yet
- Reaching The Age of Adolescence (Notes) - 2021-22Document6 pagesReaching The Age of Adolescence (Notes) - 2021-22Mohamed Naeem SaifNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument47 pagesLesson 10 Reaching The Age of AdolescenceAvi :DNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Humans CLASS 10Document5 pagesSexual Reproduction in Humans CLASS 10shallowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Gas NgaunDocument27 pagesChapter 2 Gas NgaunGary NavarroNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Human.Document42 pagesSexual Reproduction in Human.wahab.7803No ratings yet
- Module 14Document25 pagesModule 14French Joseph GuiyabNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10: Sexual Aspect of Self: Name: Ramil D Malapo Course: BEEDDocument15 pagesLesson 10: Sexual Aspect of Self: Name: Ramil D Malapo Course: BEEDJOANA MANAOGNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self ReviewerDocument13 pagesUnderstanding The Self ReviewerHani VitalesNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 10Document10 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 10JollyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Sexual Aspect of SelfDocument84 pagesLesson 7 Sexual Aspect of SelfAriel MarcellanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10: Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument11 pagesChapter - 10: Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDestroy YtNo ratings yet
- Module 7 The Sexual SelfDocument21 pagesModule 7 The Sexual SelfJohn Vincent Mina OcampoNo ratings yet
- Sexual SelfDocument13 pagesSexual SelfswitbbgirlNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter - (Reaching The Age of Adolescence) Class 8Document7 pagesScience Chapter - (Reaching The Age of Adolescence) Class 8Khushi Kumari class 9 adm 664No ratings yet
- Class 8th Chapter 10 SolutionDocument6 pagesClass 8th Chapter 10 Solutionvivekg125No ratings yet
- 11 October UTS Complete VersionDocument43 pages11 October UTS Complete VersionMhar BrandonNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument44 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemLilona LilonaNo ratings yet
- GE 1 Understanding The Self MODULE 7Document10 pagesGE 1 Understanding The Self MODULE 7klare montelNo ratings yet
- The Process of ReproductionDocument4 pagesThe Process of ReproductionIvan BixenmanNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Chapter 2: Unpacking The Self Miss KZ Ulboc REFERENCE: Cierva, M Chapter 2: Lesson 1 Physical Self: The Beautiful MeDocument5 pagesUnderstanding The Self Chapter 2: Unpacking The Self Miss KZ Ulboc REFERENCE: Cierva, M Chapter 2: Lesson 1 Physical Self: The Beautiful MeKimNo ratings yet
- A Visit To Cambridge Presentation (By Aishwarya RathiDocument13 pagesA Visit To Cambridge Presentation (By Aishwarya RathiAishwarya RathiNo ratings yet
- Reaching The Age of Adolescence Q and ADocument5 pagesReaching The Age of Adolescence Q and ASuraj PalNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document6 pagesGroup 1alamadadara16No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesReproductive SystemnbcNo ratings yet
- Sexual Self (Understanding The Self)Document25 pagesSexual Self (Understanding The Self)StephRecato100% (1)
- Reaching The Age Od AdolescenceDocument25 pagesReaching The Age Od AdolescenceAyan BordoloiNo ratings yet
- All Document Reader 1709725499579Document4 pagesAll Document Reader 1709725499579Nazia WagleNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Health Reproductive Development - Intrauterine DevelopmentDocument6 pagesReproductive Health Reproductive Development - Intrauterine DevelopmentMabesNo ratings yet
- Edited UTS Module 5 6Document15 pagesEdited UTS Module 5 6elsa galgaoNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Class 8th Answer SheetDocument3 pagesCH 10 Class 8th Answer SheetSvanik DuttaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine and Reproductive SystemsDocument53 pagesEndocrine and Reproductive Systemsapi-287032631No ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 8 March 31 Science Chapter 10 Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument6 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 8 March 31 Science Chapter 10 Reaching The Age of Adolescencekanchansharma7840No ratings yet
- 8th Reaching of The Adolescence Living Science SolutionDocument3 pages8th Reaching of The Adolescence Living Science Solutionabhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- Project in UTSDocument30 pagesProject in UTSLorna Edeza EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument7 pagesReaching The Age of Adolescencesidhantm823No ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemJoseph CristianNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ii: Unpacking The Self A. The Sexual Self: Module OverviewDocument20 pagesChapter Ii: Unpacking The Self A. The Sexual Self: Module OverviewVenus BravoNo ratings yet
- MISOSA S51Quarter 2, Modules 1-3Document27 pagesMISOSA S51Quarter 2, Modules 1-3Di VianNo ratings yet
- 211 Os Mathematics (Set A B C)Document39 pages211 Os Mathematics (Set A B C)Aarti RajanikantNo ratings yet
- 243-S-CARNATIC SangeetDocument7 pages243-S-CARNATIC SangeetAarti RajanikantNo ratings yet
- 250-S-Employ Ablity SkillsDocument8 pages250-S-Employ Ablity SkillsAarti RajanikantNo ratings yet
- 249 EntrepreneurshipDocument8 pages249 EntrepreneurshipAarti RajanikantNo ratings yet
- A Truly Beautiful MindDocument14 pagesA Truly Beautiful MindAarti RajanikantNo ratings yet
- 8th EnglishDocument18 pages8th EnglishAarti RajanikantNo ratings yet
- Masiag National High SchoolDocument6 pagesMasiag National High SchoolJESSAN DE PEDRONo ratings yet
- 017 Muscle PhysiologyDocument62 pages017 Muscle Physiologyapi-23664998867% (3)
- Physiological Changes During Puerperium: Involution of The Uterus Anatomical ConsiderationDocument8 pagesPhysiological Changes During Puerperium: Involution of The Uterus Anatomical Considerationchhayanka RathwaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Embryology (CH 1-7) (KLM) : TrisomyDocument4 pagesClinical Embryology (CH 1-7) (KLM) : Trisomykamran_zarrarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 AnatomyDocument83 pagesChapter 1 Anatomymedic99No ratings yet
- A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Topical Retinol in The Treatment of CelluliteDocument6 pagesA Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Topical Retinol in The Treatment of Cellulitesario indriayaniNo ratings yet
- PathologyDocument36 pagesPathologySayeed KhanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument45 pagesPathophysiology of DMAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- 1184bns 1Document14 pages1184bns 1Daniela GanchasNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument112 pagesHematologyreshadmuktar930No ratings yet
- File - No-1692592096radiology & Medical Imaging Technology I SemDocument31 pagesFile - No-1692592096radiology & Medical Imaging Technology I Sempujasuryawanshi67No ratings yet
- Managing The Difficult Soft Tissue Envelope in Facial and Rhinoplasty SurgeryDocument15 pagesManaging The Difficult Soft Tissue Envelope in Facial and Rhinoplasty SurgeryFabian Camelo OtorrinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 URINARY SYSTEM SeeleysDocument106 pagesChapter 18 URINARY SYSTEM SeeleysAlvinTercianoVitugNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec Session #4 - SASDocument10 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #4 - SASFherry Mae UsmanNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet General Biology 2 (Q4 - Lessons 3 and 4) The Organ Systems of Plants and AnimalsDocument12 pagesLearning Activity Sheet General Biology 2 (Q4 - Lessons 3 and 4) The Organ Systems of Plants and AnimalsJeffrey YumangNo ratings yet
- Coagulation Capillary: BloodDocument5 pagesCoagulation Capillary: BloodSafiyanu IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document4 pagesModule 3Ivan PaulinoNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsRaveena GhodeswarNo ratings yet
- Non Mammalian BarbelsDocument41 pagesNon Mammalian BarbelsDamian HaydenNo ratings yet
- MCQ 1Document4 pagesMCQ 1Maxine foyeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 ReptileDocument5 pagesLecture 21 ReptileLol MdrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 2 AnswersdanielNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Case StudyDocument5 pagesWeek 6 Case StudyElizabeth GithinjiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Presentation - Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid Base BalanceDocument16 pagesLecture Presentation - Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid Base Balancehendra_darmawan_4100% (2)
- Print SGD Ein Fix Gastritis BHDocument21 pagesPrint SGD Ein Fix Gastritis BHSagita Wulan SariNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum SeminarDocument25 pagesCerebellum Seminarprahlad st100% (1)
- References: Points Weight Lecture Actual HoursDocument8 pagesReferences: Points Weight Lecture Actual HoursAlyssa SanchezNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine Proto GihDocument8 pagesCervical Spine Proto GihAndy Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- G6 Lab 4 Basic Food MicrobiologyDocument13 pagesG6 Lab 4 Basic Food MicrobiologyNOR SYUHADA BINTI BAHARUDIN / UPMNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/11Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/11Tamer Ahmed100% (1)