Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modern College of Engineering, Pune-5: Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Question Bank Unit I
Modern College of Engineering, Pune-5: Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Question Bank Unit I
Uploaded by
ratnesh sanklechaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modern College of Engineering, Pune-5: Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Question Bank Unit I
Modern College of Engineering, Pune-5: Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Question Bank Unit I
Uploaded by
ratnesh sanklechaCopyright:
Available Formats
Progressive Education Society's
Modern College of Engineering, Pune-5
Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering
Question Bank
Unit I
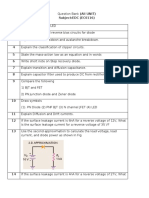
Q1 Explain Evolution of Electronics.
Q2 Explain Impact of electronics in Industry and society.
Q3 Define active and passive components. Explain them with suitable example
Q4 Explain the operation of the Half wave rectifier with a suitable diagram and
waveform.
Q5 Explain the operation of the Center tapped Full wave rectifier with a suitable
diagram and waveform.
Q6 Explain the operation of the Bridge wave rectifier with a suitable diagram
and waveform.
Q7 Explain with V - I characteristics the working of Zener diode as voltage
regulator
Q8 Explain working principle at photodiodes with characteristics.
Q9 Explain the Construction and working principle of LED.
Q 10 Difference between Avalanche Breakdown and Zener Breakdown
Q 11 Compare LED and Photodiode
Progressive Education Society's
Modern College of Engineering, Pune-5
Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering
Q 12 What is Extrinsic semiconductor? Explain P- type and N-Type
Semiconductor
Q 13 For bridge wave rectifier, the RMS Secondary voltage of transformer is 12.7
V. Assume ideal diode and RL= 1 Kohm Find Peak Current Im and Peak
Voltage Vm
Q 14 For Center tapped full wave rectifier circuit voltage across complete
secondary of transformer is 30 ac and if RL= 5.1 Kohm.DC output voltage
and average DC load Current.
Q 15 For zener regulator input voltage varies from 22V to 28V, Vo=18 V. The load
current varies from 200mA to 2 A. Design the suitable zener Regulator.
Assume Izmin = 10% IL max.
Unit II
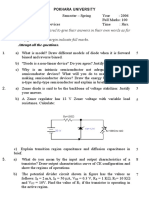
Q1 Draw and explain output characteristic of BJT in Common emitter
configuration.
Q2 Explain working of common base configuration with input and output
characteristic
Q3 Define transistor. Mention its types. for BJT Ib= 20 micro A and Ie= 2 mili
A, Calculate values of Ic and β
Q4 Define α and β in case of transistor and Derive Relationship Between them.
If α =0.98
calculate value of β
Q5 Compare CB CE and CC Configuration.
Progressive Education Society's
Modern College of Engineering, Pune-5
Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering
Q6 Draw and explain BJT used as a amplifies
Q7 Explain CE amplifier with the help of DC Load line.
Q8 Draw and explain N- channel Enhancement MOSFET with characteristics
Q9 Draw and explain MOSFET as switch
Q 10 Draw and explain construction of N- Channel E- MOSFET
Q 11 Draw a neat diagram of Non inverting amplifier using op amp and obtained
the expression output voltage.
Q 12 Draw a neat diagram of inverting amplifier using op amp and obtained the
expression output voltage.
Q 13 Write ideal and practical values of op-amp
Q 14 Define and give typical value of 1) Gain 2) CMRR 3) Slew Rate
Q 15 For inverting op-amp if Rf =100 KΩ , R1=10KΩ, Vcc= +10 V,-10V, Vi= 2 V
dc
I) Calculate output voltage
II) Is the result in part I is practically possible? Justify.
Progressive Education Society's
Modern College of Engineering, Pune-5
Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering
Q 16 Explain following term also give its practical value
I. CMRR
II. PSRR
III. Input offset voltage
IV. Input offset current
V. Input bias current
VI. Slew rate
Q 17 An op-amp is used in non-inverting mode with R1= 1 KΩ, Rf=12 KΩ,
Vcc=+15 V calculate output voltage for 1) Vin 25mV 2) Vin = 3V
Is the result in part1) and 2) is practically possible? Justify
Q 18 Compare BJT and MOSFET
Q 19 Determine Ib, Ic, Ie, Vce, for common emitter configuration. The transistor
has a β= 150, Assume Vbe= 0.7 V, Vbb= 3V, Rc= 1kΩ
Q 20 Draw and explain functional block diagram of operational amplifier
You might also like
- Service Manual (AT) - J Transmission (AT)Document16 pagesService Manual (AT) - J Transmission (AT)Николай КирилловNo ratings yet
- BCWP ManualDocument80 pagesBCWP ManualBottle Mani100% (1)
- Maximo in Oil and GasDocument29 pagesMaximo in Oil and GasDia Putranto Harmay100% (1)
- Basic Electronics Assignmnet 1Document1 pageBasic Electronics Assignmnet 1VinnuhcNo ratings yet
- Eln QBDocument3 pagesEln QBbalakrishnak eceNo ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - AssignmentDocument6 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - AssignmentchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics (BBEE103/BBEE203) - Question Bank - VTUDocument16 pagesBasic Electronics (BBEE103/BBEE203) - Question Bank - VTUShrishail Bhat100% (3)
- Eln QB Ia1Document2 pagesEln QB Ia1balakrishnak eceNo ratings yet
- Electronics AssignmentsDocument7 pagesElectronics AssignmentsSoumyaranjan PandaNo ratings yet
- Question-Bank - Module 1 - Introduction To Electronics and CommunicationDocument1 pageQuestion-Bank - Module 1 - Introduction To Electronics and CommunicationRahul Pokhriyal Rahul PokhriyalNo ratings yet
- AsdaDocument1 pageAsdarrkeerthanaNo ratings yet
- EC Lab Manual (08.407)Document101 pagesEC Lab Manual (08.407)Assini HussainNo ratings yet
- AEC BankDocument9 pagesAEC BankprakashkerurNo ratings yet
- Edc - Assignment Questions - NbaDocument5 pagesEdc - Assignment Questions - Nbagunda manasaNo ratings yet
- Smps UpsDocument1 pageSmps UpsKamaraj V.No ratings yet
- Malariy Teehnologs.: Department FnginceringDocument7 pagesMalariy Teehnologs.: Department FnginceringSmakshi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Subject:EDC (EC0116) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9Document4 pagesSubject:EDC (EC0116) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9Mihir JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 (Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits) UnsolvedDocument9 pagesChapter 14 (Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits) UnsolvedAnanda ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Module-Wise Eln QBDocument5 pagesModule-Wise Eln QBRashmi SamantNo ratings yet
- EC Lec09 Power AmplifierDocument69 pagesEC Lec09 Power Amplifierlê văn tiếnNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument1 pageQuestion BankShailendra SinghNo ratings yet
- G.H.Raisoni College of Engg. Nagpur Department of Information Technology SESSION - 2009-10 Subject: Semester: Iii SemDocument4 pagesG.H.Raisoni College of Engg. Nagpur Department of Information Technology SESSION - 2009-10 Subject: Semester: Iii SembijileeNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For ExaminationDocument4 pagesImportant Questions For ExaminationSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- EDC - Question BankDocument7 pagesEDC - Question BankSwaum KisNo ratings yet
- Ee 352 Ec Ii LabDocument61 pagesEe 352 Ec Ii LabSatya SandeepNo ratings yet
- Analog Expt 1 566Document23 pagesAnalog Expt 1 566Hrivu Dasmunshi (RA1911004010566)No ratings yet
- Mech-I-Basic Electronics Engg AssignmentDocument6 pagesMech-I-Basic Electronics Engg AssignmentArunNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Question Bank 3 PDFDocument3 pagesBasic Electronics Question Bank 3 PDFPRAVEEN YADAWNo ratings yet
- Super 25 BEC I-Scheme V2VDocument3 pagesSuper 25 BEC I-Scheme V2VSanskar NimjeNo ratings yet
- Questions Module 1Document2 pagesQuestions Module 1shashank.hbNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Electrical Engineering Materials & Semiconductor Devices Lab (EC-317-F)Document41 pagesLab Manual: Electrical Engineering Materials & Semiconductor Devices Lab (EC-317-F)Ilavarasan TamizhNo ratings yet
- EEE458 AssI Feb2014 PDFDocument1 pageEEE458 AssI Feb2014 PDFabcdefgNo ratings yet
- Operational AmplifierDocument112 pagesOperational AmplifierEdson TorresNo ratings yet
- Ty PeDocument3 pagesTy Pepankaj mobile zoneNo ratings yet
- Edctutorial BctII IDocument3 pagesEdctutorial BctII INeelesh MrzNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 - Analog Electronics Btech EEE AND CSE 3rd Sem 2021 PDFDocument1 pageAssignment - 1 - Analog Electronics Btech EEE AND CSE 3rd Sem 2021 PDFDr. Binod Kumar ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Edc Question BankDocument6 pagesEdc Question BankManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Edc (PQ)Document28 pagesEdc (PQ)Utsav PoudelNo ratings yet
- BEEE End Term QuesDocument3 pagesBEEE End Term QuesSagar JoonNo ratings yet
- Ec (Ee) 301Document1 pageEc (Ee) 301main2510No ratings yet
- Wh@Ts APP: UniversityDocument6 pagesWh@Ts APP: UniversityYUGI SINGHNo ratings yet
- E-Note 12425 Content Document 20231105014816AMDocument6 pagesE-Note 12425 Content Document 20231105014816AMkartik.doye2005No ratings yet
- Aust/Eee: Ahsanullah University of Science and TechnologyDocument27 pagesAust/Eee: Ahsanullah University of Science and Technologyruhul aminNo ratings yet
- Electronics Model Paper 2nd YearDocument38 pagesElectronics Model Paper 2nd Yearbhaivarun65No ratings yet
- 11 Redução Harmonicos Baixa Frequencia Boost - Metodo Duty RatioDocument8 pages11 Redução Harmonicos Baixa Frequencia Boost - Metodo Duty RatioGleison SilvaNo ratings yet
- LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Question BankDocument17 pagesLINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Question BankDeepak SantNo ratings yet
- Aec AssignmentDocument14 pagesAec AssignmentAnnu YadavNo ratings yet
- Ec-I - Question Bank: Unit I Part - ADocument3 pagesEc-I - Question Bank: Unit I Part - ASuguna Priya0% (1)
- Lap Manual Pspice PDFDocument17 pagesLap Manual Pspice PDFred_heartedNo ratings yet
- 1PUC Electronics Question Papers 2013Document8 pages1PUC Electronics Question Papers 2013masterNo ratings yet
- EDC QuestionDocument5 pagesEDC QuestionSampath KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument41 pagesLab ManualSyaoran7Li80% (5)
- Solid States Final TestDocument7 pagesSolid States Final TestRickel RoweNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document4 pagesLab 3J SarduaNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument3 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksAdhikari SushilNo ratings yet
- SDC Important QuestionsDocument5 pagesSDC Important QuestionsInstagramNo ratings yet
- Applied Electronics Lab 1Document9 pagesApplied Electronics Lab 1Rickel RoweNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 1 Study of Movement of Q-PointDocument4 pagesExperiment - 1 Study of Movement of Q-Pointyasir0% (1)
- 16 131101 Basic ElectronicsDocument2 pages16 131101 Basic Electronicsdhvani5988No ratings yet
- Anallysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits QuestionsDocument5 pagesAnallysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits QuestionsshankarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- CPM5x00 Appendix - High Ton InstallationDocument8 pagesCPM5x00 Appendix - High Ton InstallationtrailNo ratings yet
- Is 11218 1984Document5 pagesIs 11218 1984Ahmed HossamNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manuals (Spanish) Flowbombs-1Document187 pagesInstruction Manuals (Spanish) Flowbombs-1Cristian VegaNo ratings yet
- Arisa Mandir IDocument20 pagesArisa Mandir IAnanda Tis'aNo ratings yet
- DCinv V6 Rev2 CleanDocument38 pagesDCinv V6 Rev2 Cleanyasirarafat91No ratings yet
- The Concrete Norway: Cablewstayed Helgeland Bridge inDocument1 pageThe Concrete Norway: Cablewstayed Helgeland Bridge inArmus MarsNo ratings yet
- Bio-Inspired Imprecise ComputationalDocument13 pagesBio-Inspired Imprecise ComputationalJohn Leons E100% (1)
- Kill Ratio Calculation For in Line Yield PredictionDocument9 pagesKill Ratio Calculation For in Line Yield PredictionMarZiYaNo ratings yet
- ABC2017 065 17 Jessey Lee Design Guidelines For Post Installed and Cast in Anchors in Australia For Safety Critical ApplicationsDocument11 pagesABC2017 065 17 Jessey Lee Design Guidelines For Post Installed and Cast in Anchors in Australia For Safety Critical ApplicationsDuncanNo ratings yet
- Slinky Lam StacksDocument22 pagesSlinky Lam StacksL Mahender ReddyNo ratings yet
- STC1100T6单行本 巴西自动底盘-中英文版20231018Document31 pagesSTC1100T6单行本 巴西自动底盘-中英文版20231018Matheus PiresNo ratings yet
- BS - enDocument14 pagesBS - enTAHER AMMARNo ratings yet
- TeluxDocument85 pagesTeluxMuhammadAnasNo ratings yet
- SSP 208 - Air Conditioner in The Motor VehicleDocument76 pagesSSP 208 - Air Conditioner in The Motor VehicleTajemnicaSlodkaMoja100% (3)
- Operating Instructions Mettler Toledo Viper SW Weighing ScaleDocument24 pagesOperating Instructions Mettler Toledo Viper SW Weighing ScaleDana Iacome CerneaNo ratings yet
- AEE Applied Electricity and Electronics Lab Manual (Revised 2018)Document146 pagesAEE Applied Electricity and Electronics Lab Manual (Revised 2018)hassan100% (1)
- Wood Joists PDFDocument27 pagesWood Joists PDFRicaRDONo ratings yet
- ENCh 11Document43 pagesENCh 11ShyamRathiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Building Utilities 2 - BmusDocument62 pagesLecture 5 - Building Utilities 2 - BmusNicole DizonNo ratings yet
- Sika Rokkon RB: Non Explosive Demolition AgentDocument2 pagesSika Rokkon RB: Non Explosive Demolition AgentIsnan Luthfi100% (1)
- Count IfDocument13 pagesCount IfNoraini Mohd NorNo ratings yet
- SE 095 InstructionsDocument21 pagesSE 095 InstructionsMauricioNo ratings yet
- LED Fittings - Iguzzini - EnglishDocument252 pagesLED Fittings - Iguzzini - EnglishiGuzzini illuminazione SpANo ratings yet
- Process Selection and Facility LayoutDocument38 pagesProcess Selection and Facility LayoutPankaj SahaniNo ratings yet
- Topical Test ElectricityDocument3 pagesTopical Test ElectricityAxien YahyaNo ratings yet
- Iso 08504-1Document12 pagesIso 08504-1Akram DriraNo ratings yet
- Stress in Boiler DrumDocument8 pagesStress in Boiler DrummuhdjusriNo ratings yet