Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unități Interiorale Standard
Unități Interiorale Standard
Uploaded by
Aurelia AlexandraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unități Interiorale Standard
Unități Interiorale Standard
Uploaded by
Aurelia AlexandraCopyright:
Available Formats
02 PHYSICS
51. Standard
international units
The creation of the decimal metric system began during the eighteenth-century French revolution when two
platinum standards, representing the metre and kilogram, were placed in the Archives de la République in Paris.
Eminent scientists like Gauss and Weber then went on to promote the universal application of a standard system
of measurement in the early nineteenth century. By the 1960s, the International System of Units (abbreviated to
SI units from the French Le Système International d’Unités) was developed which incorporated six base units
(the mole was added later) along with rules for the use of derived units and prefixes. The advantage of this unified
system is that equations and calculations will produce answers in the appropriate SI unit. Unfortunately, they are
not used universally.
A question concerning the SI units is a popular opening to the physics SOE and candidates should understand the
relationship between derived and base units and be comfortable in manipulating them from one to the other.
What are the fundamental There are seven base units, which are considered to be dimensionally
(base) units? independent
Table 51.1 Base units
Base unit Name Symbol
Length metre m
Mass kilogram kg
Time second s
Current ampere A
Temperature kelvin K
Amount of substance mole mol
Luminous intensity candela cd
What are the two The plane angle (radian) and solid angle (steradian) were supplementary units
supplementary units? but this category was abolished in 1995. These units are considered named
derived units.
List some of the derived units. Derived units are formed by combination of various base units according to
mathematical relationships which link these quantities.
150
9781785230981_text.indb 150 24/02/16 9:36 pm
STANDARD INTERNATIONAL UNITS
Table 51.2 Derived units
Derived units Name Symbol
Area square metre m2
Volume cubic metre m3
Density kilogram per cubic metre kg/m3
Velocity metre per second m/s
Acceleration metre per second squared m/s2
List some named derived units. These are derived units that have been given specific names.
Table 51.3 Named derived units
Named derived Expression in terms of Expression in terms
unit Name (symbol) other SI units of base SI units
Force newton (N) – kg·m·s–2
Pressure pascal (Pa) N/m2 kg·m–1·s–2
Energy joule (K) N·m kg·m2·s–2
Power watt (W) J/s kg·m2·s–3
Electric charge coulomb (C) – A·s
Electric potential volt (V) W/A kg·m2·s–3·A–1
difference
Capacitance farad (F) C/V kg–1·m–2·s4·A2
Electrical ohm (Ω) V/A kg·m2·s–3·A–2
resistance
Magnetic flux weber (Wb) V·s kg·m2·s–2·A–1
2
Magnetic flux tesla (T) Wb/m kg·s–2·A–1
density
Inductance henry (H) Wb/A kg·m2·s–2·A–2
Temperature degree celsius (°C) – K
What are the common prefixes Prefixes are decimal (base 10) multiples and submultiples of the quantity.
used for SI units?
Table 51.4 Prefixes used for SI units
Prefix name Prefix name
(symbol) Multiple (symbol) Multiple
deca (da) 101 deci (d) 10–1
2
hecto (h) 10 centi (c) 10–2
3
kilo (k) 10 milli (m) 10–3
mega (M) 106 micro (µ) 10–6
9
giga (G) 10 nano (η) 10–9
12
tera (T) 10 pico (p) 10–12
peta (P) 1015 femto (f) 10–15
18
exa (E) 10 atto (a) 10–18
21
zetta (Z) 10 zepto (z) 10–21
24
yotta (Y) 10 yocto (y) 10–24
151
9781785230981_text.indb 151 24/02/16 9:36 pm
You might also like
- The Primary FRCA Structured Oral Examination: Study Guide 1Document13 pagesThe Primary FRCA Structured Oral Examination: Study Guide 1Aurelia Alexandra0% (1)
- The Geometry and Cohomology of Some Simple Shimura Varieties. (AM-151), Volume 151From EverandThe Geometry and Cohomology of Some Simple Shimura Varieties. (AM-151), Volume 151No ratings yet
- Measurement, Quantities and UnitsDocument17 pagesMeasurement, Quantities and UnitsriaNo ratings yet
- SI Units RulesDocument13 pagesSI Units RulesKarthikeyan GNo ratings yet
- 1 - International System of Units (S.I.)Document8 pages1 - International System of Units (S.I.)MisteroNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A FluidDocument16 pagesCharacteristics of A FluidJEMAIMAH BAWALANNo ratings yet
- TyatytyastDocument10 pagesTyatytyastdhaval goswamiNo ratings yet
- Physics First TopicDocument11 pagesPhysics First TopicRj TorresNo ratings yet
- "The True Sign of Intelligence Is Not Knowledge But Imagination." - Albert Einstein (1879-1955)Document49 pages"The True Sign of Intelligence Is Not Knowledge But Imagination." - Albert Einstein (1879-1955)Ivan TNo ratings yet
- International System of UnitsDocument12 pagesInternational System of UnitsVisionateNo ratings yet
- 1.1 & 1.3 Length & Time - Mass & Weight 2Document9 pages1.1 & 1.3 Length & Time - Mass & Weight 2Haniya NadeemNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Intro To Chem CalcDocument9 pagesCH 1 Intro To Chem CalcRose Dane Escobedo DiestaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Tables & Formulas: SI Base UnitsDocument8 pagesPhysical Science: Tables & Formulas: SI Base UnitsNiño AnthonyNo ratings yet
- 4 The Two Classes of SI Units and The SI PrefixesDocument8 pages4 The Two Classes of SI Units and The SI PrefixesJairo EspitiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-Propertiesoffluids Semakan2.1Document35 pagesChapter1-Propertiesoffluids Semakan2.1sufi 3393No ratings yet
- Physical Science Tables Formulas and EquationsDocument10 pagesPhysical Science Tables Formulas and Equationsnpednekar7530No ratings yet
- Intro To Chem CalcDocument9 pagesIntro To Chem CalcPrichebelle Gerona GrafiaNo ratings yet
- Basic & Derived Quantity (SI Units)Document2 pagesBasic & Derived Quantity (SI Units)Muhammad Noman Mughal0% (1)
- SI Unit (Revised)Document32 pagesSI Unit (Revised)t jenNo ratings yet
- Units of MeasurementDocument6 pagesUnits of MeasurementGhazi DallyNo ratings yet
- The International System of Units, Fundamental Constants, and Conversion FactorsDocument4 pagesThe International System of Units, Fundamental Constants, and Conversion FactorsSamir ZaghloolNo ratings yet
- M T L T N I I: Physical Quantity Unit SymbolDocument3 pagesM T L T N I I: Physical Quantity Unit SymbolMark ArceNo ratings yet
- Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction by William D. Callister, JR., David G. Rethwish (Z-Lib - Org) - 896-975Document80 pagesMaterials Science and Engineering An Introduction by William D. Callister, JR., David G. Rethwish (Z-Lib - Org) - 896-975skatod9410No ratings yet
- UnitsDocument16 pagesUnitsVinayChowdaryNo ratings yet
- SI SystemDocument19 pagesSI SystemmyscribdzoneNo ratings yet
- AS Physics Summer ProjectDocument22 pagesAS Physics Summer ProjectBrandon LarmondNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and Measurements (5 Hours) : PhysicsDocument67 pagesPhysical Quantities and Measurements (5 Hours) : PhysicsSaiful NizamNo ratings yet
- Units and MeasurementsDocument16 pagesUnits and MeasurementsKajol HNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and Measurements (3 Hours)Document55 pagesPhysical Quantities and Measurements (3 Hours)Ahmad IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Philippine Agricultural Engineering Standard Paes 020: 2005 General - Metrication GuidelinesDocument22 pagesPhilippine Agricultural Engineering Standard Paes 020: 2005 General - Metrication GuidelinesKayra Myke VelascoNo ratings yet
- NOTES As MechanicsDocument72 pagesNOTES As Mechanicssultan tipuNo ratings yet
- Engineering Units: Block 2 Steam Engineering Principles and Heat TransferDocument12 pagesEngineering Units: Block 2 Steam Engineering Principles and Heat TransferHaiderNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Book-1Document291 pagesClass 11 Book-1jindalipad10No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document10 pagesLecture 2am1998jedNo ratings yet
- Unidades para Formato ApaDocument4 pagesUnidades para Formato ApaJaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-ADocument1 pageChapter 1-AJoshuaNo ratings yet
- ME3351 - Engineering Mechanics - 02 - by WWW - Notesfree.inDocument161 pagesME3351 - Engineering Mechanics - 02 - by WWW - Notesfree.inMd. Zishanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Physical Quantities An UnitDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Physical Quantities An UnitNorhazli IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities, Unit AND VectorsDocument44 pagesPhysical Quantities, Unit AND VectorsJoanne SohNo ratings yet
- Astm 02Document623 pagesAstm 02Bilel RebaiNo ratings yet
- Si Units PDFDocument4 pagesSi Units PDFசெல்வ குமார்No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Physical Quantities, Units & Dimensions 1.1 Physical QuantitiesDocument5 pagesChapter 1: Physical Quantities, Units & Dimensions 1.1 Physical QuantitiesAAAANo ratings yet
- Bansal Units and MeasurementsDocument24 pagesBansal Units and MeasurementsAmbition Study Centre ButiboriNo ratings yet
- Physics Module 2Document153 pagesPhysics Module 2SK93% (29)
- Base Si UnitsDocument10 pagesBase Si UnitsJehana NaolNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations, Constants, and Conversion Factors: Section 11Document15 pagesAbbreviations, Constants, and Conversion Factors: Section 11princeowusuafriyie20No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 StudentDocument38 pagesChapter 1 StudentM HisyamNo ratings yet
- Power and Energy Measurement Units and Techniques: 2.1 The SI System and Conversion FactorsDocument19 pagesPower and Energy Measurement Units and Techniques: 2.1 The SI System and Conversion FactorsSatyam SankhuaNo ratings yet
- Appendices: Appendix A (Tables, ,, And)Document6 pagesAppendices: Appendix A (Tables, ,, And)brendonsithole6No ratings yet
- Sec 9 SiunitsDocument4 pagesSec 9 SiunitsEmilse GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Material Balance NotesDocument102 pagesMaterial Balance Noteshammad100% (1)
- FLUID MECHANICS (MEE 414) LECTURE NOTE (New)Document46 pagesFLUID MECHANICS (MEE 414) LECTURE NOTE (New)Sampson UsangNo ratings yet
- CH - 1 Fundamentals of PhysicsDocument41 pagesCH - 1 Fundamentals of PhysicsNeeraj AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Moduls Math. For ChemistryDocument107 pagesModuls Math. For ChemistryRamli BtgNo ratings yet
- Sec Ii D Si UnitsDocument5 pagesSec Ii D Si UnitssilvanopipeNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Units For Measurement: Chapter - 1 Fundamentals of PhysicsDocument41 pages1.1 Units For Measurement: Chapter - 1 Fundamentals of PhysicsPonmuthu ManikandanNo ratings yet
- Sroc A4Document2 pagesSroc A4Putu Indy GardianNo ratings yet
- Physics Teacher's Copy VI Screening Material 2023-24Document45 pagesPhysics Teacher's Copy VI Screening Material 2023-24govind_galamNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Fundamentals of PhysicsDocument29 pagesCHAPTER 1 Fundamentals of Physicsn0b0dyexx1stshereNo ratings yet
- International UnitsDocument10 pagesInternational Unitspilas_nikolaNo ratings yet
- 29 The Impact of Epidural On Bowel FunctionDocument4 pages29 The Impact of Epidural On Bowel FunctionAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Severe Tracheal StenosisDocument5 pagesSevere Tracheal StenosisAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Importance, Scope of AnestheziaDocument4 pagesImportance, Scope of AnestheziaAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Hypotermia and HipertermiaDocument9 pagesHypotermia and HipertermiaAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Hemodinamyc MonitoringDocument2 pagesHemodinamyc MonitoringAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Anti Fribrinolitic DrugsDocument15 pagesAnti Fribrinolitic DrugsAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Și DopplerDocument3 pagesUltrasound Și DopplerAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Anestezic Intracranial AnevrysmDocument4 pagesAnestezic Intracranial AnevrysmAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- 22 The Application of Farmacodynamics in The Optimization of Antibiotic Therapy PDFDocument2 pages22 The Application of Farmacodynamics in The Optimization of Antibiotic Therapy PDFAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- ADâncimea de Anestezie MOnITORINGDocument3 pagesADâncimea de Anestezie MOnITORINGAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- CT Și RMNDocument3 pagesCT Și RMNAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Pulse OximetryDocument3 pagesPulse OximetryAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- venTILATORIDocument3 pagesvenTILATORIAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Poluare Și ScavengingDocument3 pagesPoluare Și ScavengingAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Cursuri de Revisitare Și ValveDocument4 pagesCursuri de Revisitare Și ValveAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Sisteme de BreathingDocument5 pagesSisteme de BreathingAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Monitori de DiscnecțieDocument2 pagesMonitori de DiscnecțieAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Blockade MonitoringDocument7 pagesNeuromuscular Blockade MonitoringAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Presiune Arterială WaveformDocument3 pagesPresiune Arterială WaveformAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Temperature MeasurementDocument4 pagesTemperature MeasurementAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Lasers: What Do You Understand by The Term Laser'?Document3 pagesLasers: What Do You Understand by The Term Laser'?Aurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Featuri de Siguranță A Machinelor AnesteziceDocument3 pagesFeaturi de Siguranță A Machinelor AnesteziceAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- PH MeasurementDocument2 pagesPH MeasurementAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Presiune de Sânge MeasurementDocument3 pagesPresiune de Sânge MeasurementAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
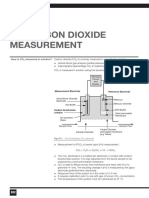
- Carbon Dioxide MeasurementDocument2 pagesCarbon Dioxide MeasurementAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Utput MonitoringDocument7 pagesCardiac Utput MonitoringAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Oxygen MeasurementDocument4 pagesOxygen MeasurementAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- SIGURANȚĂ eLeCTRICĂDocument3 pagesSIGURANȚĂ eLeCTRICĂAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- States of Matter, Heat Capacity and Latent Heat: PhysicsDocument7 pagesStates of Matter, Heat Capacity and Latent Heat: PhysicsAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- LU1 Lecture NotesDocument117 pagesLU1 Lecture NotesMysarah ShukorNo ratings yet
- NIST HB 105-2e2021Document19 pagesNIST HB 105-2e2021PaulNo ratings yet
- San Carlos University of GuatemalaDocument11 pagesSan Carlos University of Guatemalajeday2No ratings yet
- Brass Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar: Standard Specification ForDocument6 pagesBrass Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar: Standard Specification ForOscar OriasNo ratings yet
- NOTA ONE PAGE (Sukatan Membulat 2021)Document1 pageNOTA ONE PAGE (Sukatan Membulat 2021)humaira najehahNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Department of Natural Science University of Cebu - Main Senior High SchoolDocument41 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Department of Natural Science University of Cebu - Main Senior High SchoolJay GeeNo ratings yet
- 20200915-XI-Physics-Unit and Measurement-1 of 4Document13 pages20200915-XI-Physics-Unit and Measurement-1 of 4Omkar DatkhileNo ratings yet
- Of Procedure 1A: Packaged-Products 150 LB (68 KG) or LessDocument8 pagesOf Procedure 1A: Packaged-Products 150 LB (68 KG) or LessTruong Huy HoangNo ratings yet
- B 43 PDFDocument7 pagesB 43 PDFmanuel floresNo ratings yet
- Servicio Health o Meter 553klDocument1 pageServicio Health o Meter 553klDANIEL SANDINONo ratings yet
- Column ComputationDocument5 pagesColumn ComputationPoppy MooreNo ratings yet
- Titrasi Asam Lemah Dengan Basa KuatDocument13 pagesTitrasi Asam Lemah Dengan Basa KuatBarry Tryhadi Putra SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Template Extended Abstract 1 PageDocument1 pageTemplate Extended Abstract 1 PageAhmad KurniawanNo ratings yet
- ch1 ch2Document6 pagesch1 ch2MohammadKazaalNo ratings yet
- First Principles: LengthDocument10 pagesFirst Principles: LengthKarin Setia MuktiNo ratings yet
- Units of Measurement InfographicDocument1 pageUnits of Measurement InfographicDanny WidyNo ratings yet
- Physics: OxfordDocument224 pagesPhysics: OxfordMusic Life100% (1)
- Aluminum-Bronze Sand Castings: Standard Specification ForDocument6 pagesAluminum-Bronze Sand Castings: Standard Specification ForjmquinonesNo ratings yet
- DLL WITH TMDI Metric SystemDocument14 pagesDLL WITH TMDI Metric SystemMaila AsimNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulla BookletDocument5 pagesPhysics Formulla BooklettmsgNo ratings yet
- PERHITUNGAN Hantaran ListrikDocument7 pagesPERHITUNGAN Hantaran ListrikReyhandi RachmadNo ratings yet
- Dr-Id600ru 06eDocument332 pagesDr-Id600ru 06ejesuslugoveNo ratings yet
- Saep 119Document12 pagesSaep 119brecht1980No ratings yet
- Physics 1Document10 pagesPhysics 1Krizel SalidoNo ratings yet
- Standard Conversion FactorsDocument4 pagesStandard Conversion FactorsSuryasis DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Q4 IA Carpentry 7 8 Week4Document4 pagesQ4 IA Carpentry 7 8 Week4Maria Shiela Aniel SeguiNo ratings yet
- General Organic and Biological Chemistry 6th Edition Stoker Test BankDocument12 pagesGeneral Organic and Biological Chemistry 6th Edition Stoker Test BankJenniferCookabdqk100% (14)
- SYN Physical Quantities and Units and Measurement TechniquesDocument42 pagesSYN Physical Quantities and Units and Measurement Techniquessathvikpranavaug28No ratings yet
- Sol-Manual (9-Chap's) Thomas - L.floyd - Principles of Electric Circuits (2013)Document98 pagesSol-Manual (9-Chap's) Thomas - L.floyd - Principles of Electric Circuits (2013)Sarmad AsadNo ratings yet
- NCM7 TRCD Rev3 050215Document98 pagesNCM7 TRCD Rev3 050215Dionel RizoNo ratings yet