Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Are They Stimulated?
How Are They Stimulated?
Uploaded by
Shwe Eain Lin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views6 pagesThis document provides an overview of the human skeletal system, muscles, and joints. It discusses the main functions of bones including support, protection, movement, and storage of minerals. It describes the two types of skeletal systems - axial and appendicular. It also explains the structure of bones including the outer compact bone and inner spongy bone, and bone cells. Additionally, it covers cartilage, joints, ligaments, skeletal muscles, and the anatomy and function of teeth.
Original Description:
Original Title
7.bones[Hbio]
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of the human skeletal system, muscles, and joints. It discusses the main functions of bones including support, protection, movement, and storage of minerals. It describes the two types of skeletal systems - axial and appendicular. It also explains the structure of bones including the outer compact bone and inner spongy bone, and bone cells. Additionally, it covers cartilage, joints, ligaments, skeletal muscles, and the anatomy and function of teeth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views6 pagesHow Are They Stimulated?
How Are They Stimulated?
Uploaded by
Shwe Eain LinThis document provides an overview of the human skeletal system, muscles, and joints. It discusses the main functions of bones including support, protection, movement, and storage of minerals. It describes the two types of skeletal systems - axial and appendicular. It also explains the structure of bones including the outer compact bone and inner spongy bone, and bone cells. Additionally, it covers cartilage, joints, ligaments, skeletal muscles, and the anatomy and function of teeth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Hbio
Chapter 7: Bones, muscles and joints
1. What are humans?
2. How are they supported/built?
3. What is attached to bones? How are they stimulated?
4. What is the function of human skeleton?
5. Give examples of each function.
6. What compromises the axial skeleton?
7. What forms the appendicular skeleton?
8. How many kinds of girdle?
9. Why do we need girdle?
1. What does bone marrow contain? What do they do?
2. Why is bone a hard substance?
3. Why is bone a living organ?
4. What do these cells do?
5. Why can they repair themselves if they are broken?
6. What are tiny bones called?
7. Give example of long bone and tiny bones.
8. What does the presence of blood vessels and living cells in the
bone means?
9. What happens if a long bone is left in a beaker of acid?
1. What does the middle of bone consist of?
2. What do they contain? Describe.
3. What do some larger bones have?
4. What does marrow do?
5. Why are large bones lighter?
6. What is the outside of bone made of?
7. What is ossification?
8. How are osteocytes arranged?
9. What is the function of osteocytes?
1. Where is cartilage present?
2. What is the function of cartilage?
3. What is cartilage? What do they contain?
4. What do chondrocytes do?
5. What is the periosteum?
6. When does the long bone stop growing?
7. What is essential for bone growth? Expand.
8. What is in the bone matrix?
9. What does lack of vitamin D cause?
1. What happens although bone stops growing in length? How?
2. How do bones grow? Fig 7.5
3. Why can the bone resist compression?
4. What can the bone do instead?
5. Fig 7.3
6. Fig 7.1
7. What is osteoporosis?
8. What happens to bones during osteoporosis?
9. Who is affected by this? 70 yrs old >?
1. Who are particularly vulnerable to this? Why?
2. Is there cure for this? How?
3. What happens if bone is affected by osteoporosis?
4. What is a joint?
5. What is articulate?
6. What does the movable joint need to be?
7. What are movable joints called?
8. What do they contain?
9. Why is there synovial fluid in movable joints?
1. Describe synovial fluid.
2. What does the end of each bone has?
3. What does cartilage do?
4. What is the joint surrounded by?
5. How is it held together?
6. What do ligaments have?
7. Why are ligaments tough?
8. What do they do?
9. What is the scientific definition of elastic material?
1. Fig 7.7
2. How many kinds of joints?
3. What does freely movable joint include? Explain. Give example.
4. What does ball and socket joint allow? How?
5. What does partially movable joint allow? Give example.
6. What does fixed joint allow? Give example.
7. How many bones does the cranium consist?
8. What do both ligaments and tendons have?
9. Give differences between them?
1. What is inelastic?
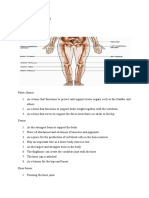
2. What are skeletal muscles?
3. How do they move?
4. Where are tendons?
5. What do tendons have?
6. What can muscle only do?
7. What happens when muscles gets longer?
8. What are antagonistic pairs?
9. Why does muscle contract while the other relaxes?
1. Give example of antagonistic pairs.
2. Fig 7.9 Explain abt it.
3. What is the origin?
4. What is the insertion?
5. What happens when a muscle contract?
6. What are other antagonistic muscles in the body?
7. When are antagonistic muscles used?
8. What muscles is used in running or walking?
9. Write about the muscle of knee.
1. Fig 7.11 Label.
2. In which movements do we need to bend the spine?
3. What happens when we bend spine?
4. What is spine made of?
5. How are these bones joined?
6. Give difference between joint in arm and spine.
7. How can the whole spine bend?
8. What is the main muscle responsible for moving side to side?
9. Fig 7.12
1. How are their shape and size related? How do they differ?
2. Fig 7.13
3. What is skeletal muscle made up of?
4. What are muscle fibres adapted for?
5. What is muscle fibre composed of?
6. How many types of filaments?
7. What happens when muscle contracts?
8. How many types of muscle in the body? Describe.
9. What does contraction of muscle fibre need? Where does it come
from?
1. How does it respire?
2. What happens when we carry out strenuous exercise?
3. What changes happen when we carry out exercises?
4. What is muscle tone?
5. What does muscle tone do?
6. When does it help and how?
7. What are muscles made of?
8. What kind of diet is needed for muscle? Why?
9. Fig 7.14
1. Which jaw is movable in humans?
2. How is chewing done?
3. How many types of teeth do human have?
4. What is dentition?
5. Where are incisors? Shape? What is it for?
6. Where are canines? Shape? Function?
7. Where are premolars and molars? What are they called?
8. What do cheek teeth have?
9. Function of cheek teeth? How?
1. Types of food humans are dealt with?
2. What is crown of tooth covered with?
3. Write about figure of teeth. Fig 4.11
4. Where are cytoplasmic strands and how are they kept alive?
5. What are the first set of teeth called?
6. What happens when baby is a few months old?
7. When will the milk teeth be pushed out? How?
8. How many set of adult teeth is formed?
9. How is tooth decay formed?
1. Another word for tooth decay?
2. Process of tooth decay?
3. When do we feel the pain?
4. What is periodontal disease? What can it lead to?
5. What do bacteria form?
6. How can we prevent tooth decay?
7. How many hours does it take for plaque t form? How many times
to brush?
8. What kind of toothbrush is recommended?
9. What do electric toothbrush has?
1. What happens if plaque is left on teeth?
2. What does fluoride do?
3. How is fluorine added to now? What can we use?
4. What is needed for the teeth to grow healthy?
You might also like
- Skeleton-Worksheet KEY ANSWERDocument4 pagesSkeleton-Worksheet KEY ANSWERjustine alina50% (2)
- Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesSkeletal Systemapi-273443252No ratings yet
- Skeleton WorksheetDocument4 pagesSkeleton Worksheetsmbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- A&P Midterm Exam Review Sheet - 07Document2 pagesA&P Midterm Exam Review Sheet - 07Marckenson Mondelus0% (1)
- Skeletal System-2Document13 pagesSkeletal System-2CHARLES HARYONO TEGUH HS STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Test 0710Document4 pagesAnatomy Test 0710OsteoCarrieNo ratings yet
- Science q2 Week 1Document30 pagesScience q2 Week 1BerMat100% (1)
- Skeletal Phys. ReviewDocument1 pageSkeletal Phys. ReviewMarilynn SpringerNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument2 pagesMusclesPatrickNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science Handout No. 7 The Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesIntegrated Science Handout No. 7 The Skeletal SystemTianna LivanNo ratings yet
- HBS Eoc ReviewDocument5 pagesHBS Eoc ReviewSophie MarinNo ratings yet
- (Template) EXERCISE 6 - SKELETAL SYSTEMDocument4 pages(Template) EXERCISE 6 - SKELETAL SYSTEMBai Putri Rohaina S. MalangNo ratings yet
- Based On The Provided Document On SkeletonsDocument8 pagesBased On The Provided Document On SkeletonsPoppy SiskaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Semester Exam - Part I - Study Guide JANUARY 2007Document6 pagesSkeletal System: Semester Exam - Part I - Study Guide JANUARY 2007api-3698353No ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Answer The Following QuestionsDocument2 pagesThe Skeletal System: Answer The Following QuestionsAnca GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- SkeletonDocument1 pageSkeletonPrish AnandNo ratings yet
- SkeletalDocument29 pagesSkeletalROMNICK NILMAO100% (1)
- P.7 Best Science Notes Term One - Teacher - AcDocument105 pagesP.7 Best Science Notes Term One - Teacher - AcMonydit SantinoNo ratings yet
- Biology M10 Musculo-Skeletal SystemDocument25 pagesBiology M10 Musculo-Skeletal SystemMark Nathaniel100% (2)
- Cuadernillo Biology 2024Document51 pagesCuadernillo Biology 2024Fiorella Panizza (Miss Fiore)No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology Study QuestionsDocument4 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology Study QuestionsLinet Huchu100% (1)
- ORTHOPAEDICS Test QuestionDocument3 pagesORTHOPAEDICS Test QuestionSujitha .VNo ratings yet
- Science LPDocument2 pagesScience LPBizmates WenaNo ratings yet
- Bill Nye Bones MusclesDocument1 pageBill Nye Bones MusclesJoseeNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument12 pagesHistologyulhaqmuhammadjawadNo ratings yet
- He & PeDocument1 pageHe & PeAdrianNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document4 pagesUnit 2Cosmina CorbeanuNo ratings yet
- P - 7 Science Lesson NotesDocument104 pagesP - 7 Science Lesson Notesmichaelopi63No ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Skeletal SystemDocument25 pagesChapter 7: Skeletal SystemZakiyah MahfudhoNo ratings yet
- HSB Skeletal NotesDocument2 pagesHSB Skeletal NotesArvin SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 4 SKELETAL SYSTEMDocument23 pagesModule 4 SKELETAL SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Muscu SkeletalDocument28 pagesWeek 5 Muscu SkeletalKatrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- Skeleton WorksheetDocument4 pagesSkeleton WorksheetNalendra UjiNo ratings yet
- Skeleton Worksheet: Name The Bones in The Body Using The Words at The Bottom of The PageDocument4 pagesSkeleton Worksheet: Name The Bones in The Body Using The Words at The Bottom of The Pagedr.zahid MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Skeleton WorksheetDocument4 pagesSkeleton Worksheetmonica albornozNo ratings yet
- Mascular Skeletal System p7Document17 pagesMascular Skeletal System p7joseph kunikinaNo ratings yet
- Ch07 Answer Key 11editionDocument23 pagesCh07 Answer Key 11editionMike Jj100% (1)
- T1 Chapter 1 JointsDocument6 pagesT1 Chapter 1 JointsShannenNo ratings yet
- Skeleton WorksheetDocument4 pagesSkeleton WorksheetIt's Book O ClockNo ratings yet
- Skeleton Worksheet 3Document4 pagesSkeleton Worksheet 3Tendo ArivyantoNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 PPT - Science - Q2 - Lesson 14Document26 pagesGrade 4 PPT - Science - Q2 - Lesson 14John Benedict CruzNo ratings yet
- June Nean Science LessonDocument18 pagesJune Nean Science Lessonapi-267946111No ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument9 pagesThe Skeletal SystemLili PredescuNo ratings yet
- The Body in Sport - LearnerDocument31 pagesThe Body in Sport - Learnerplumbs23No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 8 - Body Movements Important Questions 2024-25Document5 pagesCBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 8 - Body Movements Important Questions 2024-25S JNo ratings yet
- Learn CBSE: Body Movements Class 6 Extra Questions Science Chapter 8Document5 pagesLearn CBSE: Body Movements Class 6 Extra Questions Science Chapter 8Naresh world SinghNo ratings yet
- 3major Organs of The Human BodyDocument13 pages3major Organs of The Human BodyRosemarie Mascual IndocNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Body Systems ConceptsDocument2 pagesTissues, Body Systems Conceptsapi-422975473No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Study GuideDocument1 pageChapter 14 Study Guideapi-330077886No ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue QuizDocument2 pagesMuscle Tissue QuizPIOZRNo ratings yet
- Biology M10 Musculo-Skeletal SystemDocument24 pagesBiology M10 Musculo-Skeletal SystemDiana Dealino-Sabandal100% (1)
- 19 BIOL 220 SG CH 6Document3 pages19 BIOL 220 SG CH 6Shirley PinedaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document5 pagesActivity 1Mark-Christopher Roi Pelobello MontemayorNo ratings yet
- CXC Human and Social Biology Past Paper Question and Answer (Skeleton System)Document2 pagesCXC Human and Social Biology Past Paper Question and Answer (Skeleton System)marlon fosterNo ratings yet
- Name: Citra Puspita Sari NIM:18301083Document2 pagesName: Citra Puspita Sari NIM:18301083Citra Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- St. Xavier's High School: Sector 49, GurgaonDocument4 pagesSt. Xavier's High School: Sector 49, GurgaonJsjn NNo ratings yet
- Biology HomeworkDocument5 pagesBiology HomeworkAndrew AndersonNo ratings yet
- Skeletal WorksheetDocument2 pagesSkeletal WorksheetWarren Leonardo BelgaNo ratings yet
- Are Bones Bendy? Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandAre Bones Bendy? Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Bone Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandBone Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Children of Blood and Bone by Tomi Adeyemi Novel Study NoteDocument3 pagesChildren of Blood and Bone by Tomi Adeyemi Novel Study NoteShwe Eain LinNo ratings yet
- Ca Carb Protein Fats Eng 06 2021 RDocument2 pagesCa Carb Protein Fats Eng 06 2021 RShwe Eain LinNo ratings yet
- Tests of Short Messages About COVID-19 2021 - 04 - 13Document23 pagesTests of Short Messages About COVID-19 2021 - 04 - 13Shwe Eain LinNo ratings yet
- W73146 International GCSE Pakistan Studies 4PA1 AN Accessible VersionDocument12 pagesW73146 International GCSE Pakistan Studies 4PA1 AN Accessible VersionShwe Eain LinNo ratings yet
- W73153 International GCSE Science (Single Award) 4SS0 AN Accessible VersionDocument4 pagesW73153 International GCSE Science (Single Award) 4SS0 AN Accessible VersionShwe Eain LinNo ratings yet
- Further Pure Mathematics: Pearson Edexcel International GCSEDocument15 pagesFurther Pure Mathematics: Pearson Edexcel International GCSEShwe Eain LinNo ratings yet
- Mathematics B: Pearson Edexcel International GCSEDocument32 pagesMathematics B: Pearson Edexcel International GCSEShwe Eain LinNo ratings yet
- Mathematics B: Pearson Edexcel International GCSEDocument32 pagesMathematics B: Pearson Edexcel International GCSEShwe Eain LinNo ratings yet
- Foundation Semester 1 Phonics and HFWs School Version Home Version 4Document4 pagesFoundation Semester 1 Phonics and HFWs School Version Home Version 4Sum Soo PinNo ratings yet
- Hardtop F15 PDFDocument4 pagesHardtop F15 PDFBiju_PottayilNo ratings yet
- SATIP S 070 02 Irrigation PipingDocument2 pagesSATIP S 070 02 Irrigation PipingMuhammad Farukh ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Bank QusDocument45 pagesBank Qusreveen2010No ratings yet
- David Sm13 PPT 10Document27 pagesDavid Sm13 PPT 10Ahmed Yousufzai100% (1)
- Reu Poster IDocument1 pageReu Poster Iapi-355836337No ratings yet
- Account Opening - QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesAccount Opening - QuestionnaireThembile MohlonyaneNo ratings yet
- IB Membrane Diffusion Lab - Practical #2 - Osmolality of Potato CellsDocument4 pagesIB Membrane Diffusion Lab - Practical #2 - Osmolality of Potato CellsPia Van den ende solisNo ratings yet
- Solutions Chapter6 PDFDocument21 pagesSolutions Chapter6 PDFAnonymous LNtXoE9fgu0% (1)
- Method Statement For The Installation and Recovery of Temporary RoadwaysDocument15 pagesMethod Statement For The Installation and Recovery of Temporary Roadwaysandreipopa84No ratings yet
- Fuelling Active Kids Fuelling Active Kids: Junior Soccer PlayerDocument23 pagesFuelling Active Kids Fuelling Active Kids: Junior Soccer PlayerAdhith PhysioNo ratings yet
- 2010 Calgary Census ResultsDocument124 pages2010 Calgary Census ResultsCalgary HeraldNo ratings yet
- Ed Q 01.00 I 02Document22 pagesEd Q 01.00 I 02joseellargoNo ratings yet
- The Journal of Supercritical FluidsDocument11 pagesThe Journal of Supercritical FluidsẢfnì Ădrỉànâ SịnãgăNo ratings yet
- Max 487 Max 485 IcsDocument19 pagesMax 487 Max 485 IcsPra100% (1)
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractHery Apha'sNo ratings yet
- Tajuk Eksperimen Ebb 325 0809Document1 pageTajuk Eksperimen Ebb 325 0809fred5181No ratings yet
- V. Daftar PustakaDocument5 pagesV. Daftar PustakaDwi Putri GultomNo ratings yet
- MasterDocument20 pagesMasterAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- Wargames Illustrated #017Document60 pagesWargames Illustrated #017Анатолий Золотухин100% (3)
- Artikel RuntinahDocument7 pagesArtikel RuntinahVini VerdinahNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Angiography: IndicationsDocument2 pagesPeripheral Angiography: IndicationsjyothiNo ratings yet
- Ai MLDocument2 pagesAi MLJEBAMALAR LEAVLINE EPIPHANYNo ratings yet
- LKS 160Document10 pagesLKS 160SamulaNo ratings yet
- Directors Report To The Shareholders of Idlc Finance Limited 2019 944529Document9 pagesDirectors Report To The Shareholders of Idlc Finance Limited 2019 944529sajibarafatsiddiquiNo ratings yet
- 4th Unit Test Grade 8Document30 pages4th Unit Test Grade 8Ella Mae CabungcalNo ratings yet
- 2009-09-22 Memo in Support of Motion For Adjournment of Fairness HearingDocument4 pages2009-09-22 Memo in Support of Motion For Adjournment of Fairness HearingPeter Brantley100% (1)
- Past Simple of Regular Verbs ActivitiesDocument1 pagePast Simple of Regular Verbs ActivitiesRafa100% (1)
- Env LabDocument19 pagesEnv LabEJ KooNo ratings yet
- Lms - Question Bank Unit 3Document6 pagesLms - Question Bank Unit 3JAYAPRAKASH SNo ratings yet