Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dilation and Curetage FINAL
Dilation and Curetage FINAL
Uploaded by
Czarina Mae Quinones TadeoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dilation and Curetage FINAL
Dilation and Curetage FINAL
Uploaded by
Czarina Mae Quinones TadeoCopyright:
Available Formats
Dilation and
Curettage
D&C Risks and Complications
Your physician has recommended you have a D&C D&C rarely causes complications. However, as with any
(dilation and curettage). This common procedure helps procedure, D&C has some risks. Before your D&C, your
your physician learn more about problems inside your physician will discuss these with you. You may be asked to
uterus. During a D&C, the cervix (opening of the uterus) sign a consent form.
is widened or dilated. Tissue samples are then removed
Risks may include:
from the endometrium (lining of the uterus) with an
instrument called a curette. In many cases, D&C is done ■■ Infection
to find the cause of abnormal vaginal bleeding, or as a
■■ Heavy bleeding
form of treatment.
■■ Perforation of the uterine wall or damage to
Preparing for D&C nearby organs
■■ Arrange for an adult family member or friend to ■■ The need for additional tests or procedures
drive you home. ■■ Risks associated with anesthesia
■■ Don’t eat or drink anything after the midnight
before your D&C (unless told otherwise by your
physician).
During Your D&C
Just before your D&C, you’ll receive medication to
prevent pain. You may be awake but relaxed during the
procedure, or you may be completely asleep.
■■ Instruments are used to hold the vagina open and
to steady the uterus. The cervical canal is widened
using tapered instruments called dilators.
■■ A hysteroscope (thin, flexible telescope) may be
inserted into the vagina. This allows your health-
After the cervical canal is dilated, a curette is inserted
care provider to see into the uterus. into the uterus to take tissue samples
■■ The curette is inserted into the uterus. Tissue
samples are taken from several areas. These
samples are sent to a lab to be studied.
When to Call Your Doctor
After Your D&C Call your doctor immediately if you have any
■■ You can expect some cramping for a few hours of the following after surgery:
after a D&C. This can be controlled with an over-
the-counter pain reliever. ■■ Heavy bleeding (more than 1 pad an hour)
■■ A fever over 100.4°F
■■ You may have some light bleeding for a few weeks.
Use pads instead of tampons. ■■ Increasing abdominal pain, tenderness
or cramping
■■ Take showers instead of baths for about a week.
Ask your physicians if you should avoid exercising ■■ Foul-smelling discharge
or having sex for a period of time.
You might also like
- Book of Erotic FantasyDocument194 pagesBook of Erotic FantasyBloodshed01288% (130)
- Administering An IntradermalDocument7 pagesAdministering An IntradermalCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Dilation and CurettageDocument8 pagesDilation and CurettageMelody B. Miguel100% (1)
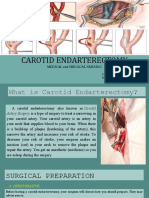
- Carotid Endarterectomy: Medical and Surgical NursingDocument17 pagesCarotid Endarterectomy: Medical and Surgical NursingMonette Abalos MendovaNo ratings yet
- Sop - ObgynDocument5 pagesSop - ObgynanalourdesbonitaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cerclage: About The Cervix in PregnancyDocument2 pagesCervical Cerclage: About The Cervix in Pregnancyamarendra Wardhana100% (1)
- Lap Tubal Sterilization FINALDocument2 pagesLap Tubal Sterilization FINALHidden TruthNo ratings yet
- DILATATION and CURETTAGEDocument31 pagesDILATATION and CURETTAGEEsvinch EsvinchNo ratings yet
- Dilation and CurettageDocument2 pagesDilation and CurettageElisse GarciaNo ratings yet
- Dilatation & Curettage (D & C)Document50 pagesDilatation & Curettage (D & C)Charlene de CastroNo ratings yet
- Dilation and Curettage - Health TeachingDocument4 pagesDilation and Curettage - Health TeachingGol D. RogerNo ratings yet
- Dilation and Curettage: The American College of Obstetricians and GynecologistsDocument2 pagesDilation and Curettage: The American College of Obstetricians and GynecologistsDellaNo ratings yet
- D&C GoniaDocument2 pagesD&C GoniaJustin AlejoNo ratings yet
- Abdominal HysterectomyDocument12 pagesAbdominal Hysterectomytaufique1123No ratings yet
- Rectal ProlapseDocument2 pagesRectal ProlapseSalem ZoghbyNo ratings yet
- Special Lecture 3. Dilatation and CurretageDocument70 pagesSpecial Lecture 3. Dilatation and CurretageMarcus RamosNo ratings yet
- What Is An Abdominal Surgery?Document7 pagesWhat Is An Abdominal Surgery?Sad100% (1)
- What Is Laparoscopy?Document8 pagesWhat Is Laparoscopy?Kamran AfzalNo ratings yet
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C) : COVID 19: Advice, Updates and Vaccine OptionsDocument8 pagesDilation and Curettage (D&C) : COVID 19: Advice, Updates and Vaccine OptionsInokNo ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW Med Umich edu1librGynBSO PDFDocument8 pagesHTTPSWWW Med Umich edu1librGynBSO PDFxfkhwd8mxqNo ratings yet
- Esarean Ction: Cadalin, Fremelen Rose Cedamon, CarloDocument18 pagesEsarean Ction: Cadalin, Fremelen Rose Cedamon, CarloMonette Abalos MendovaNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Hysterectomy and Vaginal Repair: Women's ServiceDocument16 pagesVaginal Hysterectomy and Vaginal Repair: Women's Serviceintan yulia safarinaNo ratings yet
- C P C P P CP P CPDocument7 pagesC P C P P CP P CPLalah Joy MussaNo ratings yet
- HysterosDocument7 pagesHysterosiridadajtiNo ratings yet
- Pilonidal Sinus: Information For PatientsDocument12 pagesPilonidal Sinus: Information For PatientsAliyah Tofani PawelloiNo ratings yet
- Evacuation of Retained Products of Conception ERPC GHPI0131!08!16Document4 pagesEvacuation of Retained Products of Conception ERPC GHPI0131!08!16Shrikant KrNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Abortion: Surgical: Prior To ProcedureDocument3 pagesTherapeutic Abortion: Surgical: Prior To ProcedureMaureen Joy Cascayan EspirituNo ratings yet
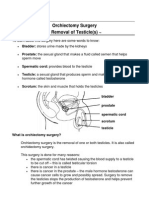
- PD 6660 Orchiectomy SurgeryDocument4 pagesPD 6660 Orchiectomy SurgeryIndra WibawaNo ratings yet
- Branchial Cleft Cyst Is A Condition That Has Its BeginningDocument2 pagesBranchial Cleft Cyst Is A Condition That Has Its BeginningrizzqqNo ratings yet
- "Types of Abortion": A Reading ONDocument3 pages"Types of Abortion": A Reading ONJannine BensiNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy SurgeryDocument2 pagesLaparoscopic Appendectomy SurgeryNycoNo ratings yet
- Private Laparoscopy Information MR Philip Kaloo. The Gynaecology GroupDocument4 pagesPrivate Laparoscopy Information MR Philip Kaloo. The Gynaecology Groupthe gynaecology groupNo ratings yet
- Abdominal HysterectomyDocument7 pagesAbdominal HysterectomyIcicNo ratings yet
- Induced Abortion and STDDocument15 pagesInduced Abortion and STDSummer LoveNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Post-Surgery Instructions ForDocument4 pagesLaparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Post-Surgery Instructions ForAshish DongreNo ratings yet
- MedicinesDocument6 pagesMedicinesTriciaNo ratings yet
- Dilation and Evacuation (D&E)Document1 pageDilation and Evacuation (D&E)Rachel SissonNo ratings yet
- Hysteroscopy, Dilation and Curettage, Polypectomy and Cervical Cautery Under General AnaestheticDocument1 pageHysteroscopy, Dilation and Curettage, Polypectomy and Cervical Cautery Under General AnaestheticMathew ThankachanNo ratings yet
- Colonoscopy Overview 2125Document2 pagesColonoscopy Overview 2125robinmilton1998No ratings yet
- Indication: Dilation & Curettage (D&C)Document1 pageIndication: Dilation & Curettage (D&C)anon_720827871No ratings yet
- Incompetentcervix PDFDocument1 pageIncompetentcervix PDFNita WidjayaNo ratings yet
- Dilation and Curettage PreparationDocument2 pagesDilation and Curettage PreparationKaren ValdezNo ratings yet
- What Is A Total Abdominal Hysterectomy?Document8 pagesWhat Is A Total Abdominal Hysterectomy?Iuthisam HassanNo ratings yet
- Mater Health Preparing For Your Colonoscopy A5 Booklet Mar2021 V5 WEBDocument12 pagesMater Health Preparing For Your Colonoscopy A5 Booklet Mar2021 V5 WEB25hdf89v57No ratings yet
- 99 11 Laparoscopy Sterilisations 2011Document12 pages99 11 Laparoscopy Sterilisations 2011Vivien KrajczNo ratings yet
- CholecystectomyDocument2 pagesCholecystectomyJj Cor-BanoNo ratings yet
- Dilation and Curettage (: Page 359 On Manual) Objectives Fractional D&C Dilation and Vacuum ExtractionDocument37 pagesDilation and Curettage (: Page 359 On Manual) Objectives Fractional D&C Dilation and Vacuum ExtractionAmber De la CernaNo ratings yet
- Branchial Cleft CystDocument2 pagesBranchial Cleft CystMeliNo ratings yet
- Files 100628herniarepairDocument12 pagesFiles 100628herniarepairDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- MGH Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery 5 26 12 - v2Document24 pagesMGH Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery 5 26 12 - v2Deanna WadeNo ratings yet
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C)Document13 pagesDilation and Curettage (D&C)KADIZA ARABINo ratings yet
- Epigastric Hernia Repair: Error! Bookmark Not DefinedDocument6 pagesEpigastric Hernia Repair: Error! Bookmark Not DefineddrpaviNo ratings yet
- Cholecystectomyedited Reporting 2Document13 pagesCholecystectomyedited Reporting 2Chareigna Ramac MagallanesNo ratings yet
- BiopsyzasaDocument2 pagesBiopsyzasapsarunprintNo ratings yet
- Dilation and CurettageDocument4 pagesDilation and CurettageFernand Son Dela Cruz100% (1)
- LSCSDocument10 pagesLSCSkailash chand atalNo ratings yet
- Management of Miscarriage 2016 PDFDocument16 pagesManagement of Miscarriage 2016 PDFJLan JoNo ratings yet
- Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (TLH) : Patient Information Patient InformationDocument7 pagesTotal Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (TLH) : Patient Information Patient InformationMUKUL SAXENANo ratings yet
- Cesarian SectionDocument20 pagesCesarian SectionQurbanovlarNo ratings yet
- Abces SubfrenicDocument2 pagesAbces SubfrenicAdrian NiţuNo ratings yet
- Ob Activity (Cesarean Section)Document3 pagesOb Activity (Cesarean Section)alexander abasNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular AngioplastyDocument4 pagesPeripheral Vascular AngioplastyFatma TahaNo ratings yet
- Written Report (Global Migration)Document3 pagesWritten Report (Global Migration)Czarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- GLOBAL DEMOGRAP-WPS Office2Document2 pagesGLOBAL DEMOGRAP-WPS Office2Czarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Global CitiesDocument7 pagesGlobal CitiesCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Microbio ReviewerDocument2 pagesMicrobio ReviewerCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Global CitiesDocument2 pagesGlobal CitiesCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- APPLICATIONDocument8 pagesAPPLICATIONCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- KhrainzellDocument2 pagesKhrainzellCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Website: EmailDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Website: EmailCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Ap MPSDocument2 pagesAp MPSCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- PhilisophyDocument5 pagesPhilisophyCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Biochem ReviewerDocument5 pagesChapter 5 Biochem ReviewerCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Uep - Edu.ph: Nursing AssessmentDocument9 pagesUep - Edu.ph: Nursing AssessmentCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Able To Perform Able To Perform With Assistance Not Able To PerformDocument2 pagesAble To Perform Able To Perform With Assistance Not Able To PerformCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biochemistry Name: - Date: - Course & Year: - ScoreDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Biochemistry Name: - Date: - Course & Year: - ScoreCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- LateeeDocument4 pagesLateeeCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Request Letter FormatDocument1 pageRequest Letter FormatCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - AADocument17 pagesModule 4 - AACzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Website: EmailDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Website: EmailCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Administering Eye MedicationDocument6 pagesAdministering Eye MedicationCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- My Family'S Genogram: Republic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Web: Http://uep - Edu.ph EmailDocument2 pagesMy Family'S Genogram: Republic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Web: Http://uep - Edu.ph EmailCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- University of Eastern Philippines: Uep - Edu.phDocument4 pagesUniversity of Eastern Philippines: Uep - Edu.phCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- University of Eastern Philippines: Uep - Edu.phDocument6 pagesUniversity of Eastern Philippines: Uep - Edu.phCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Bs NursingDocument11 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Bs NursingCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Web: .PH EmailDocument13 pagesRepublic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Web: .PH EmailCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Administering An IntramascularDocument6 pagesAdministering An IntramascularCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz NCM 101Document11 pagesLong Quiz NCM 101Czarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Mosby's Guide To Physical Examination, 7th Edition: EquipmentDocument7 pagesMosby's Guide To Physical Examination, 7th Edition: EquipmentCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- A. Matching Type: M: Atch The Terms in The Left Column With The Correct Descriptions in The Right ColumnDocument9 pagesA. Matching Type: M: Atch The Terms in The Left Column With The Correct Descriptions in The Right ColumnCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Micropara HomeworkDocument4 pagesMicropara HomeworkCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- STI Module 1Document29 pagesSTI Module 1Mike GesmundoNo ratings yet
- M NewbornDocument13 pagesM NewbornDonaJeanNo ratings yet
- Basic Maternity ConceptsDocument14 pagesBasic Maternity ConceptsDivine Grace Arreglo AbingNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument1 pageArgumentative EssayJonabelle SeraficaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Due DatesDocument16 pagesCalculating Due DatesRobert WayNo ratings yet
- Data Health Record Questionnaire - LectureDocument68 pagesData Health Record Questionnaire - LectureJessie Marie DelivaNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy: 2 Trimester 1 Trimester 3 TrimesterDocument2 pagesPregnancy: 2 Trimester 1 Trimester 3 TrimesterJulia Andreigna LAGCAONo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive CycleDocument4 pagesFemale Reproductive CycleTRASH MAILNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument8 pagesArgumentative Essayapi-272949288No ratings yet
- Blood RelationsDocument11 pagesBlood RelationsradhikaNo ratings yet
- Manual of Obstetrics and GynecologyDocument183 pagesManual of Obstetrics and GynecologyMiraf MesfinNo ratings yet
- Hiv/Aids in Pregnancy: Hassan I.N, Mmed 4Document44 pagesHiv/Aids in Pregnancy: Hassan I.N, Mmed 4HAMIS MASOUDNo ratings yet
- MAR.1,2024 Teaching Guide Catchup Template Health Grade8.Document2 pagesMAR.1,2024 Teaching Guide Catchup Template Health Grade8.jerome.mateNo ratings yet
- Aspek Medikolegal Abortus Flo22 BaruDocument21 pagesAspek Medikolegal Abortus Flo22 BaruPusparasmi Mas Ayu SuprabhaNo ratings yet
- Postpartum SimulationDocument2 pagesPostpartum SimulationEarly SaribaNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Insemination: The ESHRE Capri Workshop GroupDocument13 pagesIntrauterine Insemination: The ESHRE Capri Workshop Groupintan syabinaNo ratings yet
- Labour Chart: Intranatal Case Record - 9Document4 pagesLabour Chart: Intranatal Case Record - 9Mrinmoy MaitiNo ratings yet
- Family Chapter Revision GuideDocument9 pagesFamily Chapter Revision GuidePuss BootNo ratings yet
- Herbs For Womb Health 2Document14 pagesHerbs For Womb Health 2Maggie WoodNo ratings yet
- Womens Knowledge Regarding Symptoms of Menopause in Al Najaf CityDocument9 pagesWomens Knowledge Regarding Symptoms of Menopause in Al Najaf CityakankshaNo ratings yet
- SNJune2009 SfinalDocument109 pagesSNJune2009 SfinalrickkolluriNo ratings yet
- IUGRDocument6 pagesIUGRabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Management of Prolonged Second Stage of Labor: Sanjay Singh, Uttara Aiyer Kohli, Shakti VardhanDocument5 pagesManagement of Prolonged Second Stage of Labor: Sanjay Singh, Uttara Aiyer Kohli, Shakti VardhansheilaNo ratings yet
- Talk ShowDocument3 pagesTalk ShowChristineNo ratings yet
- Erinyes Submission To Australian Human Rights CommissionDocument52 pagesErinyes Submission To Australian Human Rights CommissionZoe Ellen BrainNo ratings yet
- Destructive Delivery Craniotomy - Kano 2017Document6 pagesDestructive Delivery Craniotomy - Kano 2017sauwalsuraiyaNo ratings yet
- Atosiban Improves The Outcome of Embryo TransferDocument15 pagesAtosiban Improves The Outcome of Embryo TransferMeliana JayasaputraNo ratings yet
- Who HerpesDocument56 pagesWho HerpesYanna RizkiaNo ratings yet