Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Production D'energie - Formula SHEET
Production D'energie - Formula SHEET
Uploaded by
hasan bishOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Production D'energie - Formula SHEET
Production D'energie - Formula SHEET
Uploaded by
hasan bishCopyright:
Available Formats
Heat rate (Η ) and thermal efficiency (ηth ):
KJ / KW . h Btu/ KW .h K cal/ KW .h
3600 3 412 860
ηth = ηth = ηth =
Η Η Η
Fuel rate (ṁ fuel ) in kg/s
Pth
ṁfuel =
( HHV )fuel−as burned
- Pth :Thermal Power (Watt th)
Pe
Pth =
ηth
Pe : Electrical Power (Watt e)
- To determine the as-burned HHV: As burned HHV =( 1−M − A ) × Dry ash free HHV
Theoretical (stoichiometric) gravimetric (m) dry (d) Air-Fuel ratio for COAL:
( AF ) theoretical m , d
=
1
0.232
( 2.66 × C+8 × H 2+ S−O2 )
- ( AF )
theoretical m ,d
: Kg air / Kg fuel (coal)
- To determine the as-burned mass fraction of each component of the coal:
As burned mass fraction=( 1−M −A ) × Dry ash free mass fraction
- Theoretical value – Using Dulong’s formula:
Dulong’s formula for HHV (O 2 <10 %) based on as-burned mass fraction of elements in the fuel:
HHV theoretical =33950 ×C+ 144200× H 2 – ( O2
8 )
+9400 × S
Theoretical (stoichiometric) molar (mol) dry (d) Air-Fuel ratio for LIQUID & GASEOUS fuel:
( AF )
theoretical mol,d
=
1
0.21
( Z ( C )+ 0.25× Z ( H )+ Z ( S)−0.5 × Z (O) )
- ( )
A
F theoretical
: Kmol air / Kmol fuel
mol, d
- Z : nb of atoms of a given element in a mole of fuel.
Relation between Theoretical gravimetric and molar Air-Fuel ratio:
( AF ) ( AF )
M air
= ×
theoretical m ,d theoreticalmol ,d M fuel
- M air =29 kg /kmol: Molar mass
- M fuel : Molar mass of Fuel
Actual gravimetric (m) dry (d) Air-Fuel ratio for COAL:
( )
A
F actual m ,d
=
[
1 % N 2 ×28
0.768 12 ( % CO 2 +%CO )
×C b−N f
]
- ( AF )
actual m , d
: Kg air / Kg fuel (coal)
- C b=C −C r: Burned Carbon : Kg burned carbon / kg fuel (coal)
C : As burned mass fraction of Carbon
- N f : Nitrogen in fuel
- % N 2=100−( % CO 2+%CO+% O2) :ORSAT analysis
From the refuse analysis:
Cr ( HHV )refuse
=
R ( HHV )carbon
- C r: mass of unburned Carbon per unit mass of fuel in the refuse (for Coals): Kg unburned carbon/ kg fuel
(refuse)
- (HHV )refuse: Given Kj/Kg
- R=A +Cr : Refuse (mass fraction): kg refuse in Kg coal
A : Ashmass fraction
- (HHV )carbon=32778 Kj / Kg
Actual molar (mol) dry (d) Air-Fuel ratio for LIQUID & GASEOUS fuel:
( AF ) actual mol , d
=
1
0.79
¿
- ( AF )
actual mol,d
: Kmol air / Kmol fuel
- % N 2=100−( % CO 2+%CO+% O2) :ORSAT analysis
Relation between Actual gravimetric and molar Air-Fuel ratio:
( ) ( )
A A M air
= ×
F actual m ,d F actualmol ,d M fuel
Dilution Coefficient:
DC=
( F)
A
actual m ,d
>1
( AF ) theoreticalm ,d
Percentage of excess air:
% Excess air=100 × ( DC−1 )
Required Power for FANS (Horse Power)
∆P
HP=Q̇ ×
η
- HP : Power in Watts
- Q̇ : flow rate volumetric m3 /s
- η : efficiency of the fan
- ∆ P : Variation of pressure across the fan – fan static pressure (Pa)
(¿ . wg) Psf Psi 3 ¿ . wg× 249.9
HP=CFM × HP=CFM × HP=CFM × HP=m /s ×
6343 ×η 33000 ×η 229 ×η η
CFM= f t 3/min
For FD fans:
- Mass flow rate of air:
ṁair =1.2 × ṁfuel × ( FA ) actualm ,d
× ( 1+w )
ṁ air : Kg/s
( electrical power /thermal efficiency )
ṁ fuel =
( HHV )fuel−asburned
Specific humidity w : (kg water/ kg air)
m water P water
w= =0.622
mair Pair
- P
Partial pressure of water: water =P v =φ × P g
Pg =Ps : Saturation pressure of water
φ : relative humidity in % Given
- Pair =P atm−P water=Patm −φ× Pg
φ × Ps
w=0.622
P atm−φ × Ps
- Volumetric flow rate of air:
ṁair
Q̇ air = 3
ρair =1 kg / m
Required mechanical power to drive FD-Fan:
∆P
HP=Q̇air ×
ηfan
For ID fans:
- Mass flow rate of Flue gas:
ṁgas =1.2 × ṁfuel ×
[( A
F ) actualm ,w
+1−Rfuel gas
]
ṁgas : Kg/s
R fuel gas=R air : Refuse (mass fraction)
Actual gravimetric (m) wet air basis (w) Air-Fuel ratio: (Kg wet air/Kg fuel
( AF )
actual m ,w
= ( AF ) actualm ,d
× (1+ w )
- Volumetric flow rate of air:
ṁgas Rgas ×T gas
Q̇ gas= =ṁ gas
ρgas P gas
R gas=R air =287 J / Kg . K ; T gas (K ) ; Pgas (Pa) given
Required mechanical power to drive ID-Fan:
∆P
HP=Q̇ gas ×
ηfan
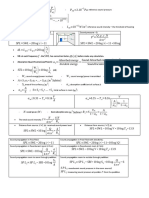
Indirect Method by ASME power test codes; to estimate Performance of a Boiler:
1. Heat lost with the dry flue gases (Dry gas loss) DGL: KJ/Kg fuel
q 1=DGL=wg C p ¿
- wg= ( AF )
actual m ,d
+1−R−M −9 H 2 , kg dry flue gas/ kg fuel
- C p=1005 J / Kg. K : Specific heat of flue gas=Specific heat of air
- T g , out : Outlet flue-gas temperature (℃ /K )
- T g ,∈¿ ¿: Inlet air temperature (℃ /K )
- R=A +Cr : Refuse (mass fraction) A : Ash mass fraction
- M : Moisture mass fraction H 2: hydrogen mass fraction as-burned ultimate analyses
2. Heat lost with the water in flue gases (Moisture loss) ML: KJ/Kg fuel
q 2=ML= ( M + 9 H 2) ( hs−hw )
- h s: Specific enthalpy of superheated steam at T g , out and a pressure of 1 psia (7 KPa): KJ/Kg
- h w: Specific enthalpy of water at T g ,∈¿ ¿: KJ/Kg
- If T g , out > 300℃ : h s−h w =2442+2.1× T g ,out −4.2 ×T g ,∈¿ ¿
- If T g , out ≤ 300 ℃: h s−h w =2492.6+1.93 ×T g , out −4.2× T g ,∈¿¿
T g , out ; T g ,∈¿ ¿ in ℃
3. Moisture in combustion air loss MCAL: KJ/Kg fuel
q 3=MCAL= ( FA )
actualm ,d
× w ×C p ,w ׿
- w : humidity ratio of the entering air, Kg water/Kg dry air
φ × Ps
w=0.622
P atm−φ × Ps
Ps : saturation pressure of water vapor at T g ,∈¿ ¿
- C p ,w =1926 J / Kg . K : Specific heat of water vapor.
4. Losses in incombustible in Ash (Unburned-Carbon Loss) UCL: KJ/Kg fuel
q 4=UCL=( HHV )carbon ×C r =32778× Cr
- C r: mass of unburned Carbon per unit mass of fuel in the refuse (for Coals): Kg unburned carbon/ kg fuel (refuse)
5. Losses in incombustible in flue gases (Incomplete combustion) ICL: KJ/Kg fuel
q 5=
28
[ %CO
12 % CO2 +%CO
×C b × ( HHV )CO
]
- C b: mass of carbon burned per mass of fuel
- ( HHV )CO =10 127 KJ / Kg
- %CO and % CO 2: value directly from ORSAT analysis
6. Radiation and combustion losses RL: KJ/Kg fuel
q 6=RL=( HHV )fuel ×ζ
- ζ : radiation factor
Energy balance:
- Total Losses: KJ/Kg fuel
Q L=q1 +q 2+ q3 +q 4 +q 5+ q6
- Useful heat transfer to the steam: KJ/Kg fuel
Quseful =( HHV )fuel −Q L
- Steam generator efficiency:
Quseful
η= ×100
QL
Feed water system FWP
Total efficiency of FWP:
ηtotal− FWP=ηhydraulic × ηvolumetric × ηmechanical
Hydraulic (Useful) Power of FWP: Watts
Phydraulic =Q̇ steam × ( P out , FWP−P¿, FWP )
- Q̇steam : m / s
3
- Pout , FWP ; P ¿, FWP: Pa
Mechanical Power of FWP: Watts
Phydraulic
Pmechanical −FWP=
ηtotal− FWP
Mechanical Power of BP: Watts
Q̇steam × ( Pout , BP−P¿ ,BP )
Pmechanical−BP=
ηtotal−BP
System K coefficient of resistance:
H pump =H s + K Q̇steam 2 ⇛ ( ρw g ) H pump =( ρ w g ) H s+ ( ρw g ) K Q̇ steam2 ⇛ P out , FWP=Psteam(boiler ) + ( ρ w g ) K Q̇ steam2
4 3
- ρw g=10 N /m
L
- K=0.08 λ 5 : L: Length of pipe (m) / D: Diameter of pipe (m) / λ : friction coefficient
D
Number of FWP stages (n )
Pout ,FWP −P ¿, FWP
n=
Pressure developped by each stage
Specific speed ( N ¿¿ s)¿
nMP × √Q̇steam
Ns=
H each stage
- n MP : Main pump rotational speed (RPM)
3
- Q̇ steam : m / h
Pressure developped by each stage
- H each stage: Pump head for each stage ¿
ρw g=104 N /m 3
Gear Box Design:
- BP: Boost pump
- EM: Electrical motor n EM : Speed of rotation (RPM)
- VSG: Variable speed turbo-gear
n MP
Gear ratio: r GB =¿
n EM
- MP: Main Pump
- Type: Simple cylindrical gear box with 2 gears (ratio of diameter = r GB )
- Torque on the pump shaft: (N.m)
Pmechanical −FWP ×60
T pump=
2 π × nMP
- Torque on the motor shaft: (N.m)
T pump ×r GB
T motor =
ηGB
- Calculation of shaft diameter:
When the shaft is subjected to twisting moment (or torque); the maximum stress is given by the torsion equation:
T τ 16 1 σ yield
= ⟹ τ d = 3 ×T = [ σ ] =
J ρ ρ=
2 πd 2 2 × FS
where;
- T : Twisting moment acting on the shaft
π 4
- J= × d : Polar moment of inertia of the shaft about the axis of rotation
32
- τ : Torsional shear stress
d
- ρ= : Distance from neutral axis to the radius where d is the diameter of the shaft
2
Power plant condensers - Condenser Design
From steam table – Saturated water pressure entry – at P:
T sat ; hfg : Latent enthalpy in KJ/Kg
Heat load (Heat flow rate) : (watt)
Qsteam =ṁsteam × h fg ×quality steam
- ṁsteam: mass flow rate kg /s
Log mean temperature difference in the condenser: ∆ T m in K
- LMTD Formula:
∆ T i−∆T 0
∆ T m=
ln
( )
∆ Ti
∆T 0
∆Ti
∆ T 0=TTD : Terminal Temperature difference in K
5 5
∆ T 0 in K = ∆ T 0 ( F)× ; ℃=( ℉−32 ) ×
9 9
∆ T i=T sat −T cooling water in K
Overall heat transfer coefficient: U in W /m 2 . K
- Heat exchange institute method
U =C1 C2 C3 C 4 √ V
- Tube outer diameter: … C 1
- Fresh water temperature: … C 2
- Tube material: … C 3
- Clean tube C 4=0.85
- V : Velocity of water at inlet of tube in m/ s 1 ft / s=0.3048 m/s
Heat exchange area A (m2 ¿
Q steam
Q Heat exhanger =U × A ×∆ T m ⇛ A=
U × ∆T m
- Q Heat exhanger =Q steam =Q water Heat balance
Number of tubes for one pass n:
A
A=n × π × D outer × L⇛ n=
π × D outer × L
- A : Heat echange area (m 2 ¿
- Douter : Outer diameter of tube (m ) 1∈¿ 0.0254 m
- L: Length of tubes (m ) 1 ft =0.3048 m
Total number of tubes: n × nb of passes
Required cooling water flow rate ṁwater in kg/s
Qwater
ṁwater =
C p , water ×∆ T water
- C p ,w ater =4186 J / Kg . K : Specific heat of water.
- ∆ T water =T out ,water −T ¿, water in K
T out ,water =T sat −TTD ; T ¿, water=T cooling water
ṁ water
Volumetric flow rate of water: m 3 /s Q̇ water = 3
ρwater =1000 kg/ m
Cooling Pump Mechanical Power
Q̇ water ×∆ Ptotal
Pmechanical , pump =
ηtotal− pump
- ∆ Ptotal =¿Pressure drop of condenser + Suction lines + discharge line =1.2 ×∆ Pcondenser : System Pressure drop
∆ Pcondenser =∆ Pwater box +∆ Ptubes
∆ P water box in ft
∆ Ptubes =¿ tube friction losses ×length of tubes in ft
⟹ ∆ Pcondenser =( ∆ Pwater box +∆ Ptubes ) × 0.3048 in m
⟹ ρwater × g × ∆ Pcondenser =10 4 × ∆ Pcondenser in Pa
⟹ ∆ Ptotal=1.2 × ∆ P condenser in Pa
Maximum suction height of circulating Pumps
( H suction) max= (P −P v
atm
γ )−( NPSH )r−¿ suctionlosses
- Pv : Saturation Vapor pressure
You might also like
- ch08 41 85Document52 pagesch08 41 85Giuseppe TestarossaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Double-V-Weld Consumption Formula in Excel SheetDocument6 pagesDouble-V-Weld Consumption Formula in Excel SheetvinothNo ratings yet
- Process Design and Optimization: University of Punjab LahoreDocument7 pagesProcess Design and Optimization: University of Punjab LahoreAbubakr KhanNo ratings yet
- Combustion ExamplesDocument5 pagesCombustion ExamplesSameen QaisarNo ratings yet
- 360equipartition PDFDocument2 pages360equipartition PDFkurakidNo ratings yet
- 360 Equi PartitionDocument2 pages360 Equi PartitionMeisy RadhistaNo ratings yet
- Products of CombustionDocument5 pagesProducts of CombustionAJ SiosonNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument48 pagesChemical Kineticsvikash kumarNo ratings yet
- Departure FunctionsDocument7 pagesDeparture Functionsharekrishnaiitkanpur2004No ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Limitations in A PFRDocument7 pagesMass Transfer Limitations in A PFRFreddy QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Part 2.C: Introduction To ThermochemistryDocument12 pagesPart 2.C: Introduction To Thermochemistrymahmudul adilNo ratings yet
- Combustion of Methanol-Air MixtureDocument3 pagesCombustion of Methanol-Air MixturemrpcuNo ratings yet
- 05 - Energy BalanceDocument28 pages05 - Energy BalanceNoman AslamNo ratings yet
- Handouts PPE Day 5Document5 pagesHandouts PPE Day 5Reinzo GallegoNo ratings yet
- Adiab FL Temp v2Document8 pagesAdiab FL Temp v2Fares JawadNo ratings yet
- 2 Combustion and ThermochemistryDocument111 pages2 Combustion and ThermochemistryAjin SajeevanNo ratings yet
- Equations You Need To KnowDocument2 pagesEquations You Need To KnowAjab MookhtiarNo ratings yet
- Funtions Mathcad For Energy Systems CourseDocument5 pagesFuntions Mathcad For Energy Systems CourseRahul VaswaniNo ratings yet
- Vol-1, Issue-5Document6 pagesVol-1, Issue-5Ijrei JournalNo ratings yet
- ICE Lecture 2Document6 pagesICE Lecture 2Roger MontepioNo ratings yet
- Lampiran: 1. Data Pada Tanggal 28 Oktober 2019Document42 pagesLampiran: 1. Data Pada Tanggal 28 Oktober 2019Rizki OctaNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Furnace FullDocument6 pagesPerhitungan Furnace FullRizki OctaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Biodiesel Fuel On EthanolDocument11 pagesThe Impact of Biodiesel Fuel On EthanolLetso JamesNo ratings yet
- First Law (Contd.)Document6 pagesFirst Law (Contd.)ashish44571No ratings yet
- CH 1-P23 PDFDocument1 pageCH 1-P23 PDFA.HassanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 10Document6 pagesTutorial 10karl davidNo ratings yet
- Heat Capacity RatioDocument8 pagesHeat Capacity RatioCharmaine ColetaNo ratings yet
- On The Performance of Absorption Heat Pump-TransformesDocument6 pagesOn The Performance of Absorption Heat Pump-TransformesRedees RedeesNo ratings yet
- SMD 1 2020 Z SNF HS CAL 0001 02 Safety Relief Valve Load Calculations (AutoRecovered)Document4 pagesSMD 1 2020 Z SNF HS CAL 0001 02 Safety Relief Valve Load Calculations (AutoRecovered)Amr TarekNo ratings yet
- 3.E First Law of Thermodynamics (Exercises)Document3 pages3.E First Law of Thermodynamics (Exercises)Aicha DahmaniNo ratings yet
- Carrizales PresDocument17 pagesCarrizales Presnde90No ratings yet
- M150ahw3 s18Document1 pageM150ahw3 s18art180No ratings yet
- Bautista, Joanna Marie Z. Ganelo, Jethro B. Gaulit, Carlo J. Bsme 3B APRIL 19,2021 Combustion EngineeringDocument8 pagesBautista, Joanna Marie Z. Ganelo, Jethro B. Gaulit, Carlo J. Bsme 3B APRIL 19,2021 Combustion Engineeringjethro ganeloNo ratings yet
- Gibbs Phase Rule Iron-Iron Carbide Phase DiagramDocument6 pagesGibbs Phase Rule Iron-Iron Carbide Phase DiagramTarekNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic Flame Temperature Example ProblemDocument2 pagesAdiabatic Flame Temperature Example ProblemdarthmaniNo ratings yet
- Reactor ModelDocument32 pagesReactor ModelMohaiminNo ratings yet
- Compressors Efficiency Calculations5Document11 pagesCompressors Efficiency Calculations5Ahmed HassanNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionsDocument7 pagesFuels and CombustionsRica ArellagaNo ratings yet
- Ognition PSV Sizing Calculation SpreadsheetDocument2 pagesOgnition PSV Sizing Calculation SpreadsheetJoseph Paul IlaganNo ratings yet
- TMK Lecture 4Document8 pagesTMK Lecture 4Andre SusandyNo ratings yet
- ASEN 4013 - Exam 1: Section 3: Compressible FlowDocument2 pagesASEN 4013 - Exam 1: Section 3: Compressible FlowJacob WeinerNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Combustion and CalcinationDocument6 pagesModelling of Combustion and Calcinationmahendra senNo ratings yet
- Vent ForceDocument1 pageVent ForceAnjani PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Ognition PSV Sizing Calculation SpreadsheetDocument2 pagesOgnition PSV Sizing Calculation Spreadsheetrisqi ilham zulfahmiNo ratings yet
- ME201 CombustionDocument4 pagesME201 Combustioniftekher khanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 SolutionsDocument7 pagesAssignment 4 SolutionsEllie AustinNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap15 P068Document21 pagesThermo 5th Chap15 P068IENCSNo ratings yet
- Chem 111 Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesChem 111 Cheat Sheet: by ViaWalid EbaiedNo ratings yet
- Bullecer MECC486 M3-ASSIGNMENTDocument30 pagesBullecer MECC486 M3-ASSIGNMENTJane BullecerNo ratings yet
- David Knezevic PDFDocument89 pagesDavid Knezevic PDFYuxiang WangNo ratings yet
- Multipasos Heat ExchangersDocument8 pagesMultipasos Heat ExchangersYesid Tapiero MartínezNo ratings yet
- Zetao Wang, Yujiao Gong, Xuedong Jing: A Method For Calculating Thermal Efficiency of The Solid Fuel Fired BoilerDocument7 pagesZetao Wang, Yujiao Gong, Xuedong Jing: A Method For Calculating Thermal Efficiency of The Solid Fuel Fired BoilerAmr AbdeinNo ratings yet
- CHEM-Year 2 Chemistry Cheat Sheet For EDEXCELDocument12 pagesCHEM-Year 2 Chemistry Cheat Sheet For EDEXCELraiabhijith586No ratings yet
- Saleem Bahi Software SimulationDocument5 pagesSaleem Bahi Software SimulationUsama ArifNo ratings yet
- 7.thermo Ideal and Real Gases Objective by RajputDocument3 pages7.thermo Ideal and Real Gases Objective by RajputMuruganantham MajesticNo ratings yet
- Individual Equipment Design: Ammonia ConverterDocument26 pagesIndividual Equipment Design: Ammonia ConverterMohaiminNo ratings yet
- Solution Combustion Ra CompressDocument39 pagesSolution Combustion Ra CompressJuanNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger DesignDocument74 pagesHeat Exchanger DesignChisom ChubaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: ME 760: Name: Anuj Agrawal Roll: 180110012Document6 pagesAssignment 1: ME 760: Name: Anuj Agrawal Roll: 180110012Hriday MittalNo ratings yet
- Drying Tower & Sulphur BurnerDocument18 pagesDrying Tower & Sulphur BurnerAhmed Qutb AkmalNo ratings yet
- AcousticDocument3 pagesAcoustichasan bishNo ratings yet
- StructureDocument43 pagesStructurehasan bishNo ratings yet
- Principles of DrawingDocument55 pagesPrinciples of Drawinghasan bishNo ratings yet
- V H H CT T CT T T: 6 May 2019 5-1 The Laval Nozzle Choked Nozzle (Col Amorcé)Document12 pagesV H H CT T CT T T: 6 May 2019 5-1 The Laval Nozzle Choked Nozzle (Col Amorcé)hasan bishNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument3 pagesSummaryhasan bishNo ratings yet
- RickiDocument1 pageRickihasan bishNo ratings yet
- Pertes Dans Les TurbinesDocument17 pagesPertes Dans Les Turbineshasan bishNo ratings yet
- WTP-cog-floc-sed (Autosaved)Document45 pagesWTP-cog-floc-sed (Autosaved)hasan bishNo ratings yet
- ThermDocument14 pagesThermhasan bishNo ratings yet
- CDM I-Chapter 4 - DeflectionDocument27 pagesCDM I-Chapter 4 - Deflectionhasan bishNo ratings yet
- Technology IDocument6 pagesTechnology Ihasan bishNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machines Chapter 8 Cam Design: Dr. Jaafar HallalDocument75 pagesKinematics of Machines Chapter 8 Cam Design: Dr. Jaafar Hallalhasan bishNo ratings yet
- 5-2 The Laval Nozzle Choked Nozzle (Col Amorcé) : (Tuyère de Laval)Document8 pages5-2 The Laval Nozzle Choked Nozzle (Col Amorcé) : (Tuyère de Laval)hasan bishNo ratings yet
- DissertacaoDocument110 pagesDissertacaohasan bishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document7 pagesChapter 8hasan bishNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram and StabilityDocument101 pagesBlock Diagram and Stabilityhasan bishNo ratings yet
- Energy: Ali Azam, Ammar Ahmed, Nasir Hayat, Shoukat Ali, Abdul Shakoor Khan, Ghulam Murtaza, Touqeer AslamDocument18 pagesEnergy: Ali Azam, Ammar Ahmed, Nasir Hayat, Shoukat Ali, Abdul Shakoor Khan, Ghulam Murtaza, Touqeer Aslamhasan bishNo ratings yet
- Applied Hydraulics: Hydraulic PumpsDocument136 pagesApplied Hydraulics: Hydraulic Pumpshasan bishNo ratings yet
- Block Diagrams and The Stability of Linear Feedback SystemsDocument26 pagesBlock Diagrams and The Stability of Linear Feedback Systemshasan bishNo ratings yet
- Applied Hydraulics: Circuit Analysis and DesignDocument92 pagesApplied Hydraulics: Circuit Analysis and Designhasan bishNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control - ExercisesDocument140 pagesAutomatic Control - Exerciseshasan bishNo ratings yet
- Applied Hydraulics: Hydraulic ValvesDocument219 pagesApplied Hydraulics: Hydraulic Valveshasan bishNo ratings yet
- FMO LectureDocument14 pagesFMO Lecturebooks4free23No ratings yet
- TechCare TCCDocument6 pagesTechCare TCCironiteNo ratings yet
- CV Ana Ventura en 23.05.2023Document13 pagesCV Ana Ventura en 23.05.2023Ana Cristina VenturaNo ratings yet
- Construction ContractsDocument3 pagesConstruction Contractskat kaleNo ratings yet
- 0500 s04 QP 2Document8 pages0500 s04 QP 2bluehorse99No ratings yet
- Sweet Little Lauren 5bDocument6 pagesSweet Little Lauren 5bnoneNo ratings yet
- Ingles III - Advantages and Disadvantages of Rapid Development in The Province of TeteDocument6 pagesIngles III - Advantages and Disadvantages of Rapid Development in The Province of TeteVercinio Teodoro VtbNo ratings yet
- Virtual Flight Planning SolutionsDocument1 pageVirtual Flight Planning SolutionsBruno GasperinNo ratings yet
- Asymmetric Dual N-Channel Trench MOSFET 30V: General Description FeaturesDocument9 pagesAsymmetric Dual N-Channel Trench MOSFET 30V: General Description Featureschristian romoNo ratings yet
- MCO - Available - KiosksDocument3 pagesMCO - Available - KiosksSobanah ChandranNo ratings yet
- Fruits Washing & SanitationDocument43 pagesFruits Washing & SanitationMuhammad RamzanNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Myofunctional Therapy in Ankyloglossia: A Systematic ReviewDocument18 pagesEffectiveness of Myofunctional Therapy in Ankyloglossia: A Systematic Reviewmistic0No ratings yet
- Knitjoy ManufacturingDocument2 pagesKnitjoy ManufacturingVenti S. GoNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsDocument7 pagesActivity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsAryan Jovic DomingoNo ratings yet
- Valvulas XT PDFDocument4 pagesValvulas XT PDFIsidro Gomez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Model Element Table - LOD MATRIX INSTRUCTIONSDocument6 pagesModel Element Table - LOD MATRIX INSTRUCTIONSMark ChuoNo ratings yet
- Epidural Intraspinal Anticoagulation Guidelines - UKDocument9 pagesEpidural Intraspinal Anticoagulation Guidelines - UKjoshNo ratings yet
- 8008 MSDSDocument5 pages8008 MSDSAhmed Emad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Hubungan Kebisingan Dengan Tingkat Stress PekerjaDocument12 pagesJurnal Hubungan Kebisingan Dengan Tingkat Stress PekerjaKafi MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Effects of Grape Seed Oil Nanoemulsion On Physicochemical and Antibacterial Properties of Gelatin Sodium Alginate Film BlendsDocument12 pagesEffects of Grape Seed Oil Nanoemulsion On Physicochemical and Antibacterial Properties of Gelatin Sodium Alginate Film BlendsMohammad Hamayoon Norri100% (1)
- Cii-Sorabji Green Business CentreDocument46 pagesCii-Sorabji Green Business CentremadhuNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy TestDocument2 pagesPregnancy TestOsinachi WilsonNo ratings yet
- PMS - Data TTM Return Till May16bDocument15 pagesPMS - Data TTM Return Till May16bMoneylife FoundationNo ratings yet
- Product Overview: Ethylene Oxide Handling SafetyDocument3 pagesProduct Overview: Ethylene Oxide Handling Safetymanojkp33No ratings yet
- Red Beryl - Article - InColor Magazine-2Document2 pagesRed Beryl - Article - InColor Magazine-2JeremyNo ratings yet
- Notes On How To Fill in The Medical Certificate of Cause of DeathDocument10 pagesNotes On How To Fill in The Medical Certificate of Cause of DeathSayantan BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Dutch Compaies in IndiaDocument28 pagesDutch Compaies in IndiaSourabh GargNo ratings yet
- Campbell - Walsh-Wein UROLOGY 12th Ed (Dragged) 2Document24 pagesCampbell - Walsh-Wein UROLOGY 12th Ed (Dragged) 2revanth kallaNo ratings yet
- Sharp+LC-32A47L-ADocument32 pagesSharp+LC-32A47L-Aalexnder gallegoNo ratings yet