Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Radiation Worksheet
Types of Radiation Worksheet
Uploaded by
juana130 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views1 pageThe document discusses basic information about radioactivity including the three types of radiation (alpha, beta, gamma), their properties, how they are emitted from unstable atomic nuclei in a random process, and how they can ionize atoms. It also discusses using radiation detectors and completing sentences about radioactive decay. Tables are included showing radiation penetration and the charges of different types of radiation. Images of particle trails in a cloud chamber are analyzed to distinguish alpha and beta particles and explain their properties and interactions. The use of lead shielding for radioactive sources and its limitations are also covered.
Original Description:
Original Title
types-of-radiation-worksheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses basic information about radioactivity including the three types of radiation (alpha, beta, gamma), their properties, how they are emitted from unstable atomic nuclei in a random process, and how they can ionize atoms. It also discusses using radiation detectors and completing sentences about radioactive decay. Tables are included showing radiation penetration and the charges of different types of radiation. Images of particle trails in a cloud chamber are analyzed to distinguish alpha and beta particles and explain their properties and interactions. The use of lead shielding for radioactive sources and its limitations are also covered.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views1 pageTypes of Radiation Worksheet
Types of Radiation Worksheet
Uploaded by
juana13The document discusses basic information about radioactivity including the three types of radiation (alpha, beta, gamma), their properties, how they are emitted from unstable atomic nuclei in a random process, and how they can ionize atoms. It also discusses using radiation detectors and completing sentences about radioactive decay. Tables are included showing radiation penetration and the charges of different types of radiation. Images of particle trails in a cloud chamber are analyzed to distinguish alpha and beta particles and explain their properties and interactions. The use of lead shielding for radioactive sources and its limitations are also covered.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Basic
1. What are the three types of radiation?
2. What are alpha particles made of?
3. What are beta particles made of?
4. What is gamma radiation made of?
5. What is ionisation?
6. Why is radiation dangerous?
7. What do we use to detect radiation?
8. Complete the following sentences.
Gains ions unstable decay random loses
Use the words in the box.
Ionising radiation is emitted from ___________ nuclei. The process is __________. This means you cannot predict
when the nucleus will ___________ and emit radiation. This radiation can cause atoms to become __________.
Ionisation occurs when an atom _________ or __________ electrons.
Medium
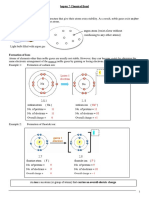
9. Complete the table of radioactive penetration using the
diagram. For the last two columns use the words
“strongly”, “partly” or “weakly”.
10. Which of the three types of radiation:
a) Has the greatest mass?
b) Has the greatest charge?
c) Does not have any mass?
d) Has the same mass as an electron?
e) Is equivalent to a helium nucleus.
f) Is a type of electromagnetic radiation.
11. What are the charges of alpha, beta and gamma radiation?
Hard
12. Look at the diagram, which shows trails in a cloud chamber. The
radioactive source is emitting both alpha and beta particles.
a) Which trails are caused by alpha particles?
b) Which trails are caused by beta particles?
c) Explain how you can tell.
d) Can you predict when alpha or beta particles will be emitted? Explain
your answer?
e) What happens when the alpha particles collide with the particles in the cloud chamber?
13. When radioactive sources are stored in boxes in schools, the boxes are always lined with lead on the inside.
Why is this necessary?
14. A student said: “If I were to wear a lead suit, I would be completely protected from radiation!” Explain why
this statement is not true.
You might also like
- Exercise 13 Worksheet: FaisanDocument4 pagesExercise 13 Worksheet: FaisanFrancesca FaisanNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules Webquest - Arya SoniDocument7 pagesAtoms and Molecules Webquest - Arya SoniArya SoniNo ratings yet
- Bill Nye Energy WorksheetDocument2 pagesBill Nye Energy Worksheetapi-55809756100% (1)
- Light Sound Wave Simulations AnswersDocument9 pagesLight Sound Wave Simulations Answersapi-233194737No ratings yet
- Accuracy Precision Mini POGIL, LabDocument6 pagesAccuracy Precision Mini POGIL, LabAlistair Morgan100% (1)
- 5 Isotope Practice WorksheetDocument1 page5 Isotope Practice Worksheetapi-369690183No ratings yet
- What is Charge? – The Redefinition of Atom - Energy to Matter ConversionFrom EverandWhat is Charge? – The Redefinition of Atom - Energy to Matter ConversionNo ratings yet
- Everything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandEverything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Licensure Examination For Teachers Practice TestDocument29 pagesLicensure Examination For Teachers Practice Testapi-286466377100% (1)
- Rs1088 - Final Optional Science Grade 9Document378 pagesRs1088 - Final Optional Science Grade 9deepak subediNo ratings yet
- How Cells Harvest Chemical EnergyDocument75 pagesHow Cells Harvest Chemical EnergylinNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Life QuizDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of Life QuizRuth Danielle GasconNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Forces PDFDocument2 pagesFundamental Forces PDFemNo ratings yet
- G Science PDFDocument177 pagesG Science PDFTaslima TabassumNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis ProcessDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis ProcessAgus Dian PratamaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Water Notes: Honors BiologyDocument15 pagesProperties of Water Notes: Honors BiologyPavanNo ratings yet
- POGIL Stoichiometry SheetsDocument9 pagesPOGIL Stoichiometry SheetsForced MemesNo ratings yet
- Name - Date - ScoreDocument11 pagesName - Date - ScoreSheena Mae Pegate TresmanioNo ratings yet
- EcologyguidednotesDocument6 pagesEcologyguidednotesapi-251568608No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Document4 pagesChemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Lama DebanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Microscopic World 1 S3AC Answers 220811 175227Document10 pagesUnit 7 Microscopic World 1 S3AC Answers 220811 1752274A10 HUI OI YU KATRINANo ratings yet
- 5 Water LectureDocument37 pages5 Water Lecturevanessa biliyaNo ratings yet
- Activity 8 Ionic BondingDocument3 pagesActivity 8 Ionic BondingLuis Michael MiradoraNo ratings yet
- Power, Work, and Force IDocument4 pagesPower, Work, and Force Ichpwalker100% (4)
- AP Biology - Ecological Pyramids - Worksheet PDFDocument6 pagesAP Biology - Ecological Pyramids - Worksheet PDFVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- 2-Revision Atomic Structure & Periodic TableDocument14 pages2-Revision Atomic Structure & Periodic TableMohamudNo ratings yet
- Power, Work and Force IIDocument4 pagesPower, Work and Force IIchpwalkerNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument24 pagesOhms LawSaad MajeedNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions WorksheetDocument10 pagesChemical Reactions WorksheetJoel VillegasNo ratings yet
- Biological Science Major - Part 1Document9 pagesBiological Science Major - Part 1Willington CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- 13 Cellular Respiration KEYDocument6 pages13 Cellular Respiration KEYLilOgLemon 101No ratings yet
- Ap18 FRQ Environmental Science PDFDocument6 pagesAp18 FRQ Environmental Science PDFadolecente venezolanoNo ratings yet
- g485 5 3 4 Fission and FusionDocument14 pagesg485 5 3 4 Fission and Fusionapi-236179294No ratings yet
- Molar Mass: Avogadro's Number and The MoleDocument5 pagesMolar Mass: Avogadro's Number and The MoleMegan CabahugNo ratings yet
- 21 Types of Chemical Reactions-SDocument6 pages21 Types of Chemical Reactions-SMichael BensonNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Questions Energy and Work With AnswersDocument14 pagesElectrostatics Questions Energy and Work With Answersmicheal_cksNo ratings yet
- CH 14-VP-Stoichiometry - 2020Document37 pagesCH 14-VP-Stoichiometry - 2020Mlamuli MlarhNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of PopulationsDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of PopulationsAnn Marilette100% (2)
- GB Atoms Pogil 2014-2015Document2 pagesGB Atoms Pogil 2014-2015api-261277442No ratings yet
- Intro To Light: Electromagnetic Waves: Warm Up - What Is The Main Difference BetweenDocument17 pagesIntro To Light: Electromagnetic Waves: Warm Up - What Is The Main Difference BetweenAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Physics Republic of The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesPhysics Republic of The PhilippinesGlenda AstodilloNo ratings yet
- Bonding QuizDocument7 pagesBonding Quiz卜一斐No ratings yet
- Frequency, Energy, Wavelength Activity C12!2!01Document7 pagesFrequency, Energy, Wavelength Activity C12!2!01Niko BrocesNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionDocument3 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionLyrah ManioNo ratings yet
- Module 4.1Document16 pagesModule 4.1RainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Friction) PDFDocument72 pagesChapter 4 (Friction) PDFRa Note A/l Som TebNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Test ReviewDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding Test ReviewAlakh Jagtap100% (1)
- Structure of AtomDocument5 pagesStructure of AtomSaurabh DhyaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 What Is BiologyDocument23 pagesUnit 1 What Is BiologySela Siti DeliantiNo ratings yet
- Show All Work - Multiple Choice Answers "MUST Be Proven" For Full Credit! (Show Your Solution!!!)Document2 pagesShow All Work - Multiple Choice Answers "MUST Be Proven" For Full Credit! (Show Your Solution!!!)Yzelle SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Biome Poster RubricDocument1 pageBiome Poster Rubricapi-359626316No ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Worksheet: Name: - Period: - DateDocument2 pagesIonic Bonding Worksheet: Name: - Period: - DateAly MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To SolubilityDocument47 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To SolubilityshiraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Periodic Trends ActivityDocument6 pagesChemistry Periodic Trends ActivityocNo ratings yet
- First Grading G8 Summative 3 and 4Document3 pagesFirst Grading G8 Summative 3 and 4Ederzon IlustricimoNo ratings yet
- Six Types of Chemical Reaction WorksheetDocument0 pagesSix Types of Chemical Reaction WorksheetMax SaubermanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: The Periodic Table and PeriodicityDocument7 pagesChemistry: The Periodic Table and PeriodicityAiden100% (1)
- Biological Science - Midterm ModuleDocument81 pagesBiological Science - Midterm Moduleoliver buenaobraNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration WorksheetDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration WorksheetKlit MejanNo ratings yet