Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scenario NCP
Scenario NCP
Uploaded by
Zanie Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views3 pagesMat was admitted due to symptoms of angina. The nursing diagnosis was decreased cardiac output related to coronary artery disease. The plan was for the patient to report reduced angina episodes after 8 hours of nursing intervention. Interventions included establishing rapport, instructing the patient on medications and symptoms, and monitoring the patient's condition. The goal of reducing angina symptoms was met after 8 hours.
Original Description:
Original Title
scenario-ncp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMat was admitted due to symptoms of angina. The nursing diagnosis was decreased cardiac output related to coronary artery disease. The plan was for the patient to report reduced angina episodes after 8 hours of nursing intervention. Interventions included establishing rapport, instructing the patient on medications and symptoms, and monitoring the patient's condition. The goal of reducing angina symptoms was met after 8 hours.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views3 pagesScenario NCP
Scenario NCP
Uploaded by
Zanie CruzMat was admitted due to symptoms of angina. The nursing diagnosis was decreased cardiac output related to coronary artery disease. The plan was for the patient to report reduced angina episodes after 8 hours of nursing intervention. Interventions included establishing rapport, instructing the patient on medications and symptoms, and monitoring the patient's condition. The goal of reducing angina symptoms was met after 8 hours.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
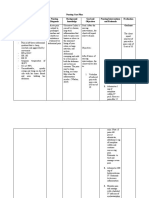
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION EVALUATION
S: Decrease cardiac After 8 hours of Goal met
Mat was awakened output related to nursing intervention Establish rapport After 8 hours of
due to shortness of disease process the patient will be Encourage the patient to take nursing intervention
breath, noticed chest of coronary able to: medicine on time. the patient was able to
discomfort and artery disease Report Instruct patient to notify nurse
weakness in both (CAD) as anginal immediately when chest pain report reduce
upper and lower evidenced by episodes occurs. the frequency
extremities, and general weakness decreased in Assess and document patient and severity of
increase in blood and dizziness frequency, response to medication. angina
pressure. duration, and Provides information about The patient
severity. disease progression. will be able to
O: Demonstrate Identify precipitating event, if verbalize
(2/8/11) relief of pain any: frequency, duration, understanding
BP 160/120 as evidenced intensity, and location of pain. of the disease
Cholesterol: 234 by stable vital Helps differentiate this chest process and
Triglyceride: 123 signs, absence pain, and aids in evaluating treatment
HDL: 26 of muscle possible progression to regimen.
LDL: 83.4 tension and unstable angina.
CHEST PAL: restlessness Observe for associated
Negative for symptoms:
pneumohemothorax. dyspnea, nausea and vomiting,
Heart is not enlarged. dizziness, palpitations, desire
Atherosclerotic aorta. to micturate. Decreased
Bones are cardiac output stimulates
unremarkable sympathetic and
parasympathetic nervous
(2/19/11) system.
Troponin T: 0.03-0.1
Evaluate reports of pain in
ECG CONCLUSION:
jaw, neck, shoulder, arm, or
Thickened hand. Pain is often referred to
anterior mitral more superficial sites served
valve leaflet by the same spinal cord nerve
with trivial level.
mitral Place patient at complete rest
regurgitation. during anginal episodes.
Aortic Reduces myocardial oxygen
sclerosis with demand to minimize risk of
trivial aortic tissue injury.
regurgitation. Elevate head of bed if patient
Trivial is short of breath. Facilitates
tricuspid gas exchange to decrease
regurgitation hypoxia and resultant
CT SCAN REPORT: shortness of breath.
Monitor heart rate and
Chronic small vessel rhythm. Patients with
ischemic changes unstable angina have an
increased risk of acute life-
threatening dysrhythmias.
Monitor vital signs every 5
min during initial anginal
attack. Blood pressure may
initially rise because of
sympathetic stimulation.
Maintain quiet, comfortable
environment. Restrict visitors
as necessary.
Mental/emotional stress
increases myocardial
workload.
Provide light meals. Have
patient rest for 1 hr after
meals. Decreases myocardial
workload associated with
work of digestion, reducing
risk of anginal attack.
Administer Prescribed
medications. Aspirin to
reduce ability of blood clot so
that the blood flows easier;
Nitrates to relax blood
vessels; Statis to reduce
deposit on the arterial walls;
Beta blockers to decrease
cardiac demand for oxygen
Provide supplemental oxygen
as indicated. Increases oxygen
available for myocardial
uptake and reversal of
ischemia.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Paediatrics Cardiology MCQDocument9 pagesPaediatrics Cardiology MCQJOYANTA ROY100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 100 Case Histories in Clinical Medicine For MRCP by Jypee (PART 1) PDFDocument352 pages100 Case Histories in Clinical Medicine For MRCP by Jypee (PART 1) PDFmuntaser67% (3)
- NSG 6001 Week 1 DiscussionDocument4 pagesNSG 6001 Week 1 DiscussionrachaelNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Document 29Document23 pagesDocument 29Zanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Funda 3Document3 pagesFunda 3Zanie CruzNo ratings yet
- NCM 118Document8 pagesNCM 118Zanie CruzNo ratings yet
- 300 Items NLE Reviewer-2Document51 pages300 Items NLE Reviewer-2Zanie CruzNo ratings yet
- PnleDocument118 pagesPnleZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- EmergencyDocument8 pagesEmergencyZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Functional HealthassessmentDocument74 pagesFunctional HealthassessmentZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Health HistoryDocument19 pagesHealth HistoryZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument34 pagesNursing DiagnosisZanie Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Goal MetDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Goal MetZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument30 pagesPhysical AssessmentZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Health Challenges of Nurses With Existing Health Conditions at CVMC During COVID 19 Pandemic DEFENSEDocument17 pagesHealth Challenges of Nurses With Existing Health Conditions at CVMC During COVID 19 Pandemic DEFENSEZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Richest Berry Source of Anthocyanin: Bilberry Angina Atherosclerosis Circulatory Retinopathy Varicose VeinsDocument5 pagesRichest Berry Source of Anthocyanin: Bilberry Angina Atherosclerosis Circulatory Retinopathy Varicose VeinsZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Theories On AgingDocument5 pagesTheories On AgingZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument26 pagesLipidsZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Cruz, Chriszanie - Activity-Geriatric Functional AssessmentDocument2 pagesCruz, Chriszanie - Activity-Geriatric Functional AssessmentZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesPathophysiologyZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Also Called Public Health Nursing or Community NursingDocument2 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Also Called Public Health Nursing or Community NursingZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- The Life Ang Conversion of PaulDocument10 pagesThe Life Ang Conversion of PaulZanie Cruz100% (1)
- Cardiac Disease in PregnancyDocument5 pagesCardiac Disease in PregnancyArely GomezNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction With ST Segment ElevationDocument27 pagesMyocardial Infarction With ST Segment ElevationRika Yulizah GobelNo ratings yet
- Arritmias VentricularesDocument11 pagesArritmias VentricularesJesusIsmaelCoronaNo ratings yet
- Chandak Myocardial PDFDocument12 pagesChandak Myocardial PDFAugustusNo ratings yet
- XXX. MCQ Cardiovascular System Book 315-336Document19 pagesXXX. MCQ Cardiovascular System Book 315-336Maria OnofreiNo ratings yet
- Transposition of Great ArteriesDocument18 pagesTransposition of Great Arteriesparmeshori100% (2)
- State of Philippine Jail CongestionDocument11 pagesState of Philippine Jail CongestionZamaeSanchezNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain ProtocolDocument7 pagesChest Pain Protocolomar kmr97No ratings yet
- Chest Pain Questionnaire - Attending PhysicianDocument2 pagesChest Pain Questionnaire - Attending PhysicianVia B. BorrezNo ratings yet
- Acute STEMI With Multiple Culprit Vessels in Young MaleDocument24 pagesAcute STEMI With Multiple Culprit Vessels in Young MaleVickry WahidjiNo ratings yet
- The Abdominojugular Reflux Sign: Jeff Wiese, MDDocument3 pagesThe Abdominojugular Reflux Sign: Jeff Wiese, MDRed RubyNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction (Stemi) - Tennessee: Statpearls PublishingDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction (Stemi) - Tennessee: Statpearls PublishingMery AlizaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology ErDocument3 pagesPathophysiology ErAlexa A. AldayNo ratings yet
- Cvs2-k1 (JP-PJB Pada Dewasa)Document81 pagesCvs2-k1 (JP-PJB Pada Dewasa)32 sebastian Josia N.No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Table - Docx - StudentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Table - Docx - StudentLuigi LauNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 L 3rd ExamDocument3 pagesNCM 118 L 3rd Examj UNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia CBLDocument7 pagesArrhythmia CBLRyuuzakiDNNo ratings yet
- LV Systolic FunctionDocument36 pagesLV Systolic Functionsruthimeena6891No ratings yet
- DR Mervat Aboulmaaty Nabih Professor of Cardiology Ain Shams UniversityDocument51 pagesDR Mervat Aboulmaaty Nabih Professor of Cardiology Ain Shams UniversitySaud ShirwanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Valve Replacement SurgeryDocument25 pagesCardiac Valve Replacement SurgeryJamalul AdilNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Ischemic Stroke - VinaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Ischemic Stroke - VinaDevi Astri KusumawardaniNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument47 pagesIschemic Heart DiseaseAbood SamoudiNo ratings yet
- Impact of High Sensitivity Troponins For 6nov Cardiac ForumDocument39 pagesImpact of High Sensitivity Troponins For 6nov Cardiac Forummouna6685No ratings yet
- Grsmu - Byfilesfileuniversitycafedrynevrologiifileslfklin Protokol PDFDocument197 pagesGrsmu - Byfilesfileuniversitycafedrynevrologiifileslfklin Protokol PDFАнна ФоменкоNo ratings yet
- Cardiology OSCEsDocument85 pagesCardiology OSCEsMed StudentNo ratings yet
- ECG Normal Values and InterpretationsDocument6 pagesECG Normal Values and InterpretationsAlexandryaHaleNo ratings yet
- Cardiology 2012 MrcppassDocument127 pagesCardiology 2012 MrcppassRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNo ratings yet