Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ME8491 IQ 02 - by LearnEngineering - in
ME8491 IQ 02 - by LearnEngineering - in
Uploaded by
Dr.A.Maniram KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Question Bank Subject: Materials Science and EngineeringDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank Subject: Materials Science and Engineeringsharma05031989No ratings yet
- Unit 1: 13 Marks Questions: Anna University QuestionsDocument4 pagesUnit 1: 13 Marks Questions: Anna University Questions10BShalini.B IgmmNo ratings yet
- Me6403 Engineering Materials and Metallurgy: Unit 1.alloys and Phase Diagram Part ADocument6 pagesMe6403 Engineering Materials and Metallurgy: Unit 1.alloys and Phase Diagram Part Ajamunaa83No ratings yet
- Emm Question BankDocument6 pagesEmm Question BankMurugesan JeevaNo ratings yet
- ME2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy QBDocument3 pagesME2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy QBVasantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Industrial Metallurgy Part A - 2 MarksDocument8 pagesQuestion Bank - Industrial Metallurgy Part A - 2 Marks17TUME212 ROHITH.MNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument11 pagesEngineering Materials and Metallurgyabdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I (Constitution of Alloys and Phase Diagrams) Part-ADocument7 pagesUNIT-I (Constitution of Alloys and Phase Diagrams) Part-AkarthisanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials & Metallurgy Question BankDocument7 pagesEngineering Materials & Metallurgy Question BankJOHN PAUL V67% (3)
- Emm Lab QuestionsDocument9 pagesEmm Lab QuestionsVijai KaladadNo ratings yet
- Principles of Material Selection Question BankDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Material Selection Question BankGurpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 &4 Question BankDocument4 pagesUnit 3 &4 Question BankcprabhakaranNo ratings yet
- Unit-I - Alloys and Phase Diagrams Part-A (2 Marks) : Question BankDocument10 pagesUnit-I - Alloys and Phase Diagrams Part-A (2 Marks) : Question BankDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy Question Bank - Questions OnlyDocument6 pagesMetallurgy Question Bank - Questions OnlyMANYAM. HARI KRISHNA MECHANICAL ENGINEERINGNo ratings yet
- Question Papers - Heat TreatmentDocument9 pagesQuestion Papers - Heat TreatmentSrilakshmi Shunmugaraj100% (3)
- Engineering Metallurgy Part.A Unit - IDocument4 pagesEngineering Metallurgy Part.A Unit - Ijamunaa83No ratings yet
- Engineering Material AssignmentDocument3 pagesEngineering Material AssignmentSharjeel Faisal100% (1)
- Department of Chemistry: Question Bank Unit 1 Electrochemistry Part ADocument4 pagesDepartment of Chemistry: Question Bank Unit 1 Electrochemistry Part AJahith HussainNo ratings yet
- ME6403-Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument12 pagesME6403-Engineering Materials and Metallurgysanthanam102No ratings yet
- Emm 3Document4 pagesEmm 3mdinoco95No ratings yet
- ME3393 IQ 02 - by LearnEngineering - inDocument10 pagesME3393 IQ 02 - by LearnEngineering - inUrbhi SahaNo ratings yet
- ME-8491 EM QB For UT1Document2 pagesME-8491 EM QB For UT1ajaymNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document1 pageAssignment 4kaushikNo ratings yet
- CH 6604 Materials Science and Technology Part B Questions Unit IDocument3 pagesCH 6604 Materials Science and Technology Part B Questions Unit Ichitra123No ratings yet
- Material Science Important Questions For AMIE Section-ADocument8 pagesMaterial Science Important Questions For AMIE Section-AThota Sai Swaroop67% (3)
- Me8491-Engineering MetallurgyDocument10 pagesMe8491-Engineering MetallurgyMadhanRavNo ratings yet
- Mfe QBDocument4 pagesMfe QBV VikasNo ratings yet
- Previous Question Papers of Metallurgy and Material SciencesDocument10 pagesPrevious Question Papers of Metallurgy and Material SciencesRajeev SaiNo ratings yet
- BF1113 Assignment 2Document2 pagesBF1113 Assignment 2sanasieNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Material ScienceDocument3 pagesImportant Questions Material Sciencetheamg7272No ratings yet
- 9 - Phase DiagramsDocument13 pages9 - Phase DiagramsJohny SkNo ratings yet
- ME1253-Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument0 pagesME1253-Engineering Materials and MetallurgybalajimeieNo ratings yet
- Mse21 MergedDocument16 pagesMse21 Mergedkuldeep thakorNo ratings yet
- Rr411809 Light Metals and AlloysDocument4 pagesRr411809 Light Metals and AlloysSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Question Paper - Material Technology May - 2012 (Mumbai University) - Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageQuestion Paper - Material Technology May - 2012 (Mumbai University) - Mechanical Engineeringlearning.aatNo ratings yet
- MP Question BankDocument10 pagesMP Question Bankazhagan.mecNo ratings yet
- G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur: Mechanical Engineering Department Question BankDocument12 pagesG. H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur: Mechanical Engineering Department Question BankRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- 1616403463914-Subjective Questions On Material Science MET-09Document3 pages1616403463914-Subjective Questions On Material Science MET-09praiselovesscienceNo ratings yet
- Closed-Book Practice-Ch 11 (2015!03!16)Document17 pagesClosed-Book Practice-Ch 11 (2015!03!16)Juan100% (1)
- Unit - I Engineering MaterialsDocument6 pagesUnit - I Engineering MaterialsLohanathan VkNo ratings yet
- 07a81803 SuperalloysDocument4 pages07a81803 SuperalloysSharanya ThirichinapalliNo ratings yet
- ST010 503-Material ScienceDocument2 pagesST010 503-Material SciencepramodNo ratings yet
- My339 Special Steels and Non-Ferrous AlloysDocument2 pagesMy339 Special Steels and Non-Ferrous AlloysHari HaranNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For MFT (Two Mark Questions With Answers and PARTB Questions)Document4 pagesQuestion Bank For MFT (Two Mark Questions With Answers and PARTB Questions)Senthil Kumar Periyasamy100% (1)
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)P MithunNo ratings yet
- 금속재료 중간고사 기출문제 (2006-2016)Document10 pages금속재료 중간고사 기출문제 (2006-2016)Li Ken LokNo ratings yet
- Material Science and Engineering Ch. 11 SolDocument56 pagesMaterial Science and Engineering Ch. 11 SolPatrick Gibson100% (1)
- سنوات سابقة خواصDocument64 pagesسنوات سابقة خواصmechanical depNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument14 pagesEngineering Materials and Metallurgyashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Subject: Material Science & Metallurgy (3131904) Semester: B.E. (ME) Sem. - 3Document4 pagesQuestion Bank Subject: Material Science & Metallurgy (3131904) Semester: B.E. (ME) Sem. - 3Jay SathwaraNo ratings yet
- MS 206Document2 pagesMS 206Muzaffar AlamNo ratings yet
- Me 2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy April - May 2011Document3 pagesMe 2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy April - May 2011imamuddeenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - BasicsDocument1 pageTutorial 2 - BasicsTwinkelsNo ratings yet
- MT I Question BankDocument10 pagesMT I Question BankAnonymous ZB6qyhD6No ratings yet
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsFrom EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsNo ratings yet
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusFrom EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusNo ratings yet
- Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics: Materials for Extreme Environment ApplicationsFrom EverandUltra-High Temperature Ceramics: Materials for Extreme Environment ApplicationsWilliam G. FahrenholtzNo ratings yet
- Deep Earth: Physics and Chemistry of the Lower Mantle and CoreFrom EverandDeep Earth: Physics and Chemistry of the Lower Mantle and CoreHidenori TerasakiNo ratings yet
- Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandTitanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and ApplicationsChristoph LeyensNo ratings yet
- Fea HandoutsDocument51 pagesFea HandoutsDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- FEA Periodical - IIDocument4 pagesFEA Periodical - IIDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Overall Summary & Review: Chapter 1: What Is The 10X Rule?Document14 pagesOverall Summary & Review: Chapter 1: What Is The 10X Rule?Dr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Designing and Evaluating A Workstation in Real and Virtual EnvironmentDocument16 pagesDesigning and Evaluating A Workstation in Real and Virtual EnvironmentDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Emm Unit NotesDocument101 pagesEmm Unit NotesDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Free Virtual Guest Lecture On Research Funding Opportunities and Proposal Writing - CAMPUZINEDocument6 pagesFree Virtual Guest Lecture On Research Funding Opportunities and Proposal Writing - CAMPUZINEDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Emm HandoutsDocument58 pagesEmm HandoutsDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- ME8491 IQ 01 - by LearnEngineering - inDocument9 pagesME8491 IQ 01 - by LearnEngineering - inDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Me8491 QB 03Document20 pagesMe8491 QB 03Dr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- MM Question BankDocument22 pagesMM Question BankDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Me8491 QB 02Document30 pagesMe8491 QB 02Dr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- WWW - Learnengineering.In: Me8491 - Engineering Metallurgy Question BankDocument21 pagesWWW - Learnengineering.In: Me8491 - Engineering Metallurgy Question BankDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING GRAPHICS Lab ManualDocument52 pagesENGINEERING GRAPHICS Lab ManualDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-I - Alloys and Phase Diagrams Part-A (2 Marks) : Question BankDocument10 pagesUnit-I - Alloys and Phase Diagrams Part-A (2 Marks) : Question BankDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Sof-10 E-BookDocument313 pagesSof-10 E-BookDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- HW8 Solution KeyDocument3 pagesHW8 Solution KeyHerlina PebrianiNo ratings yet
- State of Matter of Matter 2Document65 pagesState of Matter of Matter 2Fritzel Pallon SusbillaNo ratings yet
- Metallic GlassDocument19 pagesMetallic GlassHarmish BhattNo ratings yet
- Poster Template LQFDocument1 pagePoster Template LQFvestuario17.1No ratings yet
- Module 2 Physical MetallurgyDocument12 pagesModule 2 Physical Metallurgytejasteja9148No ratings yet
- Classification of Materials NotesDocument9 pagesClassification of Materials NotesJohn K KikwaiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers Question Bank With AnswerDocument72 pagesChemistry For Engineers Question Bank With AnswerVIGNESH L RNo ratings yet
- Stainless SteelDocument81 pagesStainless SteelRockey ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Metal-Casting Processes and Equipment Heat TreatmentDocument55 pagesChapter 5. Metal-Casting Processes and Equipment Heat TreatmentBassel AlshamiNo ratings yet
- 9 6Document5 pages9 6이수연No ratings yet
- TDF Q - Assignment Week2Document10 pagesTDF Q - Assignment Week2Ayu Sekar TunjungNo ratings yet
- Iron CastingDocument23 pagesIron CastingDiego MoralesNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of Ceramic and Composite MaterialsDocument407 pagesCorrosion of Ceramic and Composite MaterialsKhin Aung ShweNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0196890422012109 MainDocument27 pages1 s2.0 S0196890422012109 MainPranav OmkarNo ratings yet
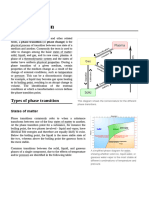
- Phase TransitionDocument16 pagesPhase Transitionyehtt0212No ratings yet
- Balmer Exp 6Document6 pagesBalmer Exp 6Collin ChuNo ratings yet
- (Battezzati - L., - Pozzovivo - S., - Rizzi - P.) Nanocrystalline Aluminum Alloys PDFDocument24 pages(Battezzati - L., - Pozzovivo - S., - Rizzi - P.) Nanocrystalline Aluminum Alloys PDFPhung Tuan AnhNo ratings yet
- MMS Unit 2 Phase DiagramsDocument35 pagesMMS Unit 2 Phase DiagramsPraveen KolukulaNo ratings yet
- Al Alaşim Elementleri̇ h1-13Document13 pagesAl Alaşim Elementleri̇ h1-13KaanMertNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagrams Study NotesDocument13 pagesPhase Diagrams Study NotesSushilNo ratings yet
- Characterizing Metallic Microstructure Cu-Based AlloysDocument51 pagesCharacterizing Metallic Microstructure Cu-Based AlloysjuegyiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Bookmatter MetallographyInArchaeologyAndADocument29 pages2019 Bookmatter MetallographyInArchaeologyAndAMorneNo ratings yet
- Production EngineeringDocument110 pagesProduction EngineeringmuthuramprodNo ratings yet
- Platinum Alloys For Shape Memory ApplicationsDocument15 pagesPlatinum Alloys For Shape Memory ApplicationsKursalNo ratings yet
- Lec-8 - Metallurgy PDFDocument16 pagesLec-8 - Metallurgy PDFGhaith MdljNo ratings yet
- Incipient Melting of Al5Mg8Si6Cu2 XDocument15 pagesIncipient Melting of Al5Mg8Si6Cu2 Xmiramirjafari2No ratings yet
- 1980 The Phase Diagram of NaNO3-KNO3 PDFDocument12 pages1980 The Phase Diagram of NaNO3-KNO3 PDFAdrian CaraballoNo ratings yet
- Ch09 Diagrama de FasesDocument13 pagesCh09 Diagrama de FasesFERNANDO JOSE NOVAESNo ratings yet
- Tensile Properties of Directionally Solidified AI-4 WT PCT Cu Alloys With Columnar and Equiaxed GrainsDocument10 pagesTensile Properties of Directionally Solidified AI-4 WT PCT Cu Alloys With Columnar and Equiaxed GrainspaolaNo ratings yet
- Georgia Southern University Foundry Education IntroductionDocument20 pagesGeorgia Southern University Foundry Education IntroductionXantos YulianNo ratings yet
ME8491 IQ 02 - by LearnEngineering - in
ME8491 IQ 02 - by LearnEngineering - in
Uploaded by
Dr.A.Maniram KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ME8491 IQ 02 - by LearnEngineering - in
ME8491 IQ 02 - by LearnEngineering - in
Uploaded by
Dr.A.Maniram KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.
in
Department of Mechanical Engineering
ME8491 - Engineering Metallurgy
Question Bank
n
g .i
Unit-1- Constitution of Alloys and Phase Diagrams
Part-A
rin
1. When will interstitial solid solution occur?
2. What is isomorphous?
3. How is plain carbon steels classified? Define an alloy?
ee
4. Classify the alloys.
5. What are solid solutions?
6. Differentiate substitutional and interstitial solid solutions with examples.
gin
7. What are intermediate phases?
8. Define the term phase.
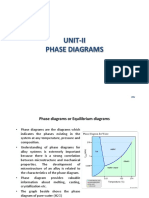
9. What is an equilibrium phase diagram?
En
10.Define eutectic reactions?
11.Define peritectic reactions?
12.Define eutectoid reactions?
arn
13.Define peritectoid reactions?
14.Distinguish eutectic and eutectoid transformations.
15.Distinguish peritectic and peritectoid transformations.
16.What are the uses of grey cast iron?
Le
17.What are chilled cast irons?
18.Why nodular cast iron is called ductile cast iron?
19.What are the advantages of alloy steels over plain carbon steels?
w.
20.What is the effect of additions of chromium on the characteristics of steel?
ww
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Part-B
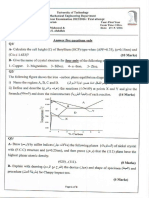
1. Show the different steel and cast iron region in the iron carbon diagram with
its microstructure and write down its composition, mechanical properties and
application.
2. Draw a neat sketch and explain TTT diagram.
3. Draw Iron carbon diagram and label all fields?
4. Draw a typical equilibrium diagram for an isomorphous system and explain
n
the equilibrium cooling of any one alloy from the above diagram.
g .i
5. Draw a typical equilibrium diagram for a eutectic type of system with limited
solid solubility and explain its important features.
6. Explain the Peritectic temperature using a binary equilibrium peritectic phase
rin
diagram
7. What is the effect of small quantities of
(a) Sulphur
ee
(b) manganese
(c) phosphorus
gin
(d) Silicon upon the properties of steel?
8. Explain the method of plotting an equilibrium diagram and derive the lever
rule as applied to equilibrium diagram.
En
9. Discuss the effect of Silicon, Manganese elements in cast iron.
10.Describe the composition, microstructure, properties and applications of grey
cast iron.
arn
Le
w.
ww
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Unit-II HEAT TREATMENT
Part-A
1. Name various methods of heat treatment of steel.
2. When the annealing process is preferred?
3. Define full annealing.
4. Define heat treatment.
5. What is martensite and for eutectoid steel in what temperature range it is
n
generally formed?
g .i
6. What is the purpose of spheroidising annealing?
7. Define normalizing.
8. What is the purpose of normalizing?
rin
9. What are the factors affecting the hardening process?
10.What is austempering process and what is the microstructure produced after
austempering?
ee
11.What is martempering process and what is the purpose of this treatment?
12.Distinguish between hardness and hardenability.
gin
13.Define carburizing.
14.What are the three methods of carburizing commonly employed?
15.What is the purpose of flame hardening and induction hardening of steel?
16.Name the four different methods used for flame hardening.
En
17.what steels are commonly used for nitriding?
18.What is the process of nitriding?
19.Define cyaniding.
arn
20.What is the process of carbonitriding?
Le
w.
ww
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Part-B
1. Describe the method of plotting isothermal transformation or TTT diagram?
2. Draw an IT diagram or TTT diagram for an eutectoid steel .Indicate the
various decomposition products on it and explain?
3. Draw a schematic CCT diagram for a carbon steel containing 0.8% C .Using
this diagram explain how different cooling curves lead to the
(a)Annealing heat treatment
n
(b) Normalizing heat treatment
g .i
(c) Hardening heat treatment
4. Explain how Jominy end quench test is used for determining the harden ability
rin
of steels.
5. Describe the heat treatment cycle following carburizing.
6. Describe the process of carbonitriding. Differentiate between carburizing and
ee
carbonitriding.
7. Explain flame hardening.
gin
8. Explain Induction hardening.
9. Give a detailed account on
(a) Annealing (b) Normalizing (c) Austempering
En
(d) Case hardening.
10.Explain how surface hardening is achieved using flame hardening.
arn
Le
w.
ww
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Unit-III Ferrous and Non Ferrous Metals
Part-A
1. What is the effect of chromium alloying element on the properties of steel?
2. What is cast iron?
3. What is HSLA?
4. What are advantages of alloy steels over plain carbon steels?
5. Discuss the general effects of alloying elements in steel.
n
6. Specify the effect of nickel on the properties of steel.
g .i
7. What advantages are derived by using a combination of nickel and chromium
in steel?
8. What are the principal alloying elements in triple alloy steel?
rin
9. How is silicon useful as an alloying element in steel?
10.For what purpose is tungsten used in steel?
11.What are stainless steels? Why are these steels stainless?
ee
12.What type of stainless steels is referred to as ferritic stainless steels?
13.What are tool steels? Classify them.
14.List the bearing materials that are commonly used?
gin
15.What is meant by precipitation hardening?
16.What is duralumin?
17.Give composition and applications of duralumin?
En
18.List at least four types of brasses used.
19.List some bronze alloys.
20.How can you classify tool steels?
arn
Le
w.
ww
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Part-B
1. Write short note on compositions and properties of the following stainless
steels,
(a) Ferritic stainless steel
(b) Austenitic stainless steel
(c) Martensitic stainless steel
n
(d) Precipitation hardening stainless steel
g .i
2. State the types, compositions and properties of high speed steel.
3. Discuss Hadfield and Mar aging steels on the following lines
rin
(a) Chemical composition
(b) Heat treatment
ee
(c) Mechanical properties
(d) Applications
gin
4. Explain the various methods to achieve high strength in HSLA steels.
5. Explain Bearing alloys.
6. Explain Tool steels.
7. Name different alloys of copper. Give its composition, properties and uses.
En
8. Explain Mar aging steels.
9. Explain Stainless steels, High speed steels.
10.Explain, bearing metals, Explain brasses
arn
Le
w.
ww
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Unit-IV NON METALLIC MATERILS
Part-A
1. What is PTFE?
2. What is PE?
3. What is PS?
4. Define the degree of polymerization.
5. What is PVC?
n
6. What is copolymerization?
g .i
7. What is PMMA?
8. What is PET?
9. What is ABS?
rin
10.What is PI?
11.What is PAI?
12.What is PPO?
ee
13.What is PPS?
14.What is PEEK?
15.What is PTFE?
gin
16.What is PA?
17.What is PP?
18.What are acrylics? Mention their application.
En
19.Distinguish between hard and soft glasses.
20.How is alumina ceramics produced?
arn
Le
w.
ww
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Part-B
1. Explain the properties and application of the PVC,PE, PTFE, ABS
2. Give the detailed account on:
(a) Urea formaldehydes
(b) Fibre reinforced plastics
(c) Cellulose nitrate.
3. Explain PMMA.
n
4. What is polymerization? Describe addition polymerization and condensation
g .i
polymerization.
5. How plastic materials are classified? Explain each classification.
6. Write brief notes on following traditional ceramics
rin
(a) Clay products
(b) Glasses
(c) Cements
ee
(d) Refractory's
7. Describe the properties and applications of following structural ceramics
gin
(a) Alumina
(b) Partially stabilized zirconia
(c) Silicon carbide (d) Silicon nitride (e) Sialon
8. Describe the structures, properties and applications of following commodity thermoplastic
En
polymers
(a) Polyethylene
(b) Polyvinylchloride
arn
(c) Polystyrene
9. Describe the strictures, properties and applications of the following commodity
thermoplastic polymers
Le
(a) Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
(b) Polytetrafluoroethylene
(c) Nylons
w.
(d) Polycarbonates
(e) Polyethylene terephthalate
ww
10. Describe the structures, properties and applications of the following thermoset polymers
(a) Phenol formaldehyde
(b) Urea formaldehyde
(c) Epoxies
(d) Unsaturated polyesters
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Unit-V MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND TESTING
Part-A
1. Name the slip plane and slip direction for FCC crystal.
2. What is creep?
3. Define slip.
4. Name different types of facture.
5. What properties are determined from tensile testing of metallic products?
n
6. Distinguish between resilience and toughness.
g .i
7. Draw typical engineering stress strain curves for the following materials: (a)
Aluminum (b) Mild steel (c) Cast iron (d) Polymer
8. What do you mean by ‘double shear’ test?
rin
9. Define the hardness of a material.
10.State the advantage and limitation of Rockwell hardness test over the Brinell
and Vickers hardness test.
ee
11.Differentiate between Charpy and Izod test results not useful in design?
12.What is fatigue test S-N curve?
gin
13.Define endurance limit in fatigue test.
14.Define fatigue strength in fatigue test.
15.Differentiate between elasticity and plasticity.
16.Differentiate between ductility and malleability.
En
17.Define the terms brittleness and hardness.
18.How can you prevent the brittle fracture?
19.What is meant by creep fracture?
arn
20.Sketch a creep curve explaining different stages of it.
Le
w.
ww
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Part-B
1. Describe with neat sketch fatigue test.
2. Describe with neat sketch creep test.
3. Explain the mechanism of plastic deformation by slip and twinning with neat
sketch.
4. Describe how the torsion test is conducted and what are the properties deter
from this test?
n
5. Explain the testing procedure for Vickers hardness test and mention the
g .i
advantages and limitations.
6. Describe the procedure of Charpy impact testing and the properties obtained
from it.
rin
7. Explain the method of testing the materials for fatigue and how is the fatigue
data presented.
8. Draw a typical creep curve and explain the various stages of creep.
ee
9. What is meant by ductile fracture? Explain the mechanism of it.
10.Compare and contrast the Brinell, Vickers and Rockwell hardness tests.
gin
En
arn
Le
w.
ww
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
You might also like
- Question Bank Subject: Materials Science and EngineeringDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank Subject: Materials Science and Engineeringsharma05031989No ratings yet
- Unit 1: 13 Marks Questions: Anna University QuestionsDocument4 pagesUnit 1: 13 Marks Questions: Anna University Questions10BShalini.B IgmmNo ratings yet
- Me6403 Engineering Materials and Metallurgy: Unit 1.alloys and Phase Diagram Part ADocument6 pagesMe6403 Engineering Materials and Metallurgy: Unit 1.alloys and Phase Diagram Part Ajamunaa83No ratings yet
- Emm Question BankDocument6 pagesEmm Question BankMurugesan JeevaNo ratings yet
- ME2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy QBDocument3 pagesME2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy QBVasantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Industrial Metallurgy Part A - 2 MarksDocument8 pagesQuestion Bank - Industrial Metallurgy Part A - 2 Marks17TUME212 ROHITH.MNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument11 pagesEngineering Materials and Metallurgyabdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I (Constitution of Alloys and Phase Diagrams) Part-ADocument7 pagesUNIT-I (Constitution of Alloys and Phase Diagrams) Part-AkarthisanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials & Metallurgy Question BankDocument7 pagesEngineering Materials & Metallurgy Question BankJOHN PAUL V67% (3)
- Emm Lab QuestionsDocument9 pagesEmm Lab QuestionsVijai KaladadNo ratings yet
- Principles of Material Selection Question BankDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Material Selection Question BankGurpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 &4 Question BankDocument4 pagesUnit 3 &4 Question BankcprabhakaranNo ratings yet
- Unit-I - Alloys and Phase Diagrams Part-A (2 Marks) : Question BankDocument10 pagesUnit-I - Alloys and Phase Diagrams Part-A (2 Marks) : Question BankDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy Question Bank - Questions OnlyDocument6 pagesMetallurgy Question Bank - Questions OnlyMANYAM. HARI KRISHNA MECHANICAL ENGINEERINGNo ratings yet
- Question Papers - Heat TreatmentDocument9 pagesQuestion Papers - Heat TreatmentSrilakshmi Shunmugaraj100% (3)
- Engineering Metallurgy Part.A Unit - IDocument4 pagesEngineering Metallurgy Part.A Unit - Ijamunaa83No ratings yet
- Engineering Material AssignmentDocument3 pagesEngineering Material AssignmentSharjeel Faisal100% (1)
- Department of Chemistry: Question Bank Unit 1 Electrochemistry Part ADocument4 pagesDepartment of Chemistry: Question Bank Unit 1 Electrochemistry Part AJahith HussainNo ratings yet
- ME6403-Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument12 pagesME6403-Engineering Materials and Metallurgysanthanam102No ratings yet
- Emm 3Document4 pagesEmm 3mdinoco95No ratings yet
- ME3393 IQ 02 - by LearnEngineering - inDocument10 pagesME3393 IQ 02 - by LearnEngineering - inUrbhi SahaNo ratings yet
- ME-8491 EM QB For UT1Document2 pagesME-8491 EM QB For UT1ajaymNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document1 pageAssignment 4kaushikNo ratings yet
- CH 6604 Materials Science and Technology Part B Questions Unit IDocument3 pagesCH 6604 Materials Science and Technology Part B Questions Unit Ichitra123No ratings yet
- Material Science Important Questions For AMIE Section-ADocument8 pagesMaterial Science Important Questions For AMIE Section-AThota Sai Swaroop67% (3)
- Me8491-Engineering MetallurgyDocument10 pagesMe8491-Engineering MetallurgyMadhanRavNo ratings yet
- Mfe QBDocument4 pagesMfe QBV VikasNo ratings yet
- Previous Question Papers of Metallurgy and Material SciencesDocument10 pagesPrevious Question Papers of Metallurgy and Material SciencesRajeev SaiNo ratings yet
- BF1113 Assignment 2Document2 pagesBF1113 Assignment 2sanasieNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Material ScienceDocument3 pagesImportant Questions Material Sciencetheamg7272No ratings yet
- 9 - Phase DiagramsDocument13 pages9 - Phase DiagramsJohny SkNo ratings yet
- ME1253-Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument0 pagesME1253-Engineering Materials and MetallurgybalajimeieNo ratings yet
- Mse21 MergedDocument16 pagesMse21 Mergedkuldeep thakorNo ratings yet
- Rr411809 Light Metals and AlloysDocument4 pagesRr411809 Light Metals and AlloysSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Question Paper - Material Technology May - 2012 (Mumbai University) - Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageQuestion Paper - Material Technology May - 2012 (Mumbai University) - Mechanical Engineeringlearning.aatNo ratings yet
- MP Question BankDocument10 pagesMP Question Bankazhagan.mecNo ratings yet
- G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur: Mechanical Engineering Department Question BankDocument12 pagesG. H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur: Mechanical Engineering Department Question BankRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- 1616403463914-Subjective Questions On Material Science MET-09Document3 pages1616403463914-Subjective Questions On Material Science MET-09praiselovesscienceNo ratings yet
- Closed-Book Practice-Ch 11 (2015!03!16)Document17 pagesClosed-Book Practice-Ch 11 (2015!03!16)Juan100% (1)
- Unit - I Engineering MaterialsDocument6 pagesUnit - I Engineering MaterialsLohanathan VkNo ratings yet
- 07a81803 SuperalloysDocument4 pages07a81803 SuperalloysSharanya ThirichinapalliNo ratings yet
- ST010 503-Material ScienceDocument2 pagesST010 503-Material SciencepramodNo ratings yet
- My339 Special Steels and Non-Ferrous AlloysDocument2 pagesMy339 Special Steels and Non-Ferrous AlloysHari HaranNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For MFT (Two Mark Questions With Answers and PARTB Questions)Document4 pagesQuestion Bank For MFT (Two Mark Questions With Answers and PARTB Questions)Senthil Kumar Periyasamy100% (1)
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)P MithunNo ratings yet
- 금속재료 중간고사 기출문제 (2006-2016)Document10 pages금속재료 중간고사 기출문제 (2006-2016)Li Ken LokNo ratings yet
- Material Science and Engineering Ch. 11 SolDocument56 pagesMaterial Science and Engineering Ch. 11 SolPatrick Gibson100% (1)
- سنوات سابقة خواصDocument64 pagesسنوات سابقة خواصmechanical depNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument14 pagesEngineering Materials and Metallurgyashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Subject: Material Science & Metallurgy (3131904) Semester: B.E. (ME) Sem. - 3Document4 pagesQuestion Bank Subject: Material Science & Metallurgy (3131904) Semester: B.E. (ME) Sem. - 3Jay SathwaraNo ratings yet
- MS 206Document2 pagesMS 206Muzaffar AlamNo ratings yet
- Me 2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy April - May 2011Document3 pagesMe 2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy April - May 2011imamuddeenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - BasicsDocument1 pageTutorial 2 - BasicsTwinkelsNo ratings yet
- MT I Question BankDocument10 pagesMT I Question BankAnonymous ZB6qyhD6No ratings yet
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsFrom EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsNo ratings yet
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusFrom EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusNo ratings yet
- Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics: Materials for Extreme Environment ApplicationsFrom EverandUltra-High Temperature Ceramics: Materials for Extreme Environment ApplicationsWilliam G. FahrenholtzNo ratings yet
- Deep Earth: Physics and Chemistry of the Lower Mantle and CoreFrom EverandDeep Earth: Physics and Chemistry of the Lower Mantle and CoreHidenori TerasakiNo ratings yet
- Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandTitanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and ApplicationsChristoph LeyensNo ratings yet
- Fea HandoutsDocument51 pagesFea HandoutsDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- FEA Periodical - IIDocument4 pagesFEA Periodical - IIDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Overall Summary & Review: Chapter 1: What Is The 10X Rule?Document14 pagesOverall Summary & Review: Chapter 1: What Is The 10X Rule?Dr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Designing and Evaluating A Workstation in Real and Virtual EnvironmentDocument16 pagesDesigning and Evaluating A Workstation in Real and Virtual EnvironmentDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Emm Unit NotesDocument101 pagesEmm Unit NotesDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Free Virtual Guest Lecture On Research Funding Opportunities and Proposal Writing - CAMPUZINEDocument6 pagesFree Virtual Guest Lecture On Research Funding Opportunities and Proposal Writing - CAMPUZINEDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Emm HandoutsDocument58 pagesEmm HandoutsDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- ME8491 IQ 01 - by LearnEngineering - inDocument9 pagesME8491 IQ 01 - by LearnEngineering - inDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Me8491 QB 03Document20 pagesMe8491 QB 03Dr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- MM Question BankDocument22 pagesMM Question BankDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Me8491 QB 02Document30 pagesMe8491 QB 02Dr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- WWW - Learnengineering.In: Me8491 - Engineering Metallurgy Question BankDocument21 pagesWWW - Learnengineering.In: Me8491 - Engineering Metallurgy Question BankDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING GRAPHICS Lab ManualDocument52 pagesENGINEERING GRAPHICS Lab ManualDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-I - Alloys and Phase Diagrams Part-A (2 Marks) : Question BankDocument10 pagesUnit-I - Alloys and Phase Diagrams Part-A (2 Marks) : Question BankDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Sof-10 E-BookDocument313 pagesSof-10 E-BookDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- HW8 Solution KeyDocument3 pagesHW8 Solution KeyHerlina PebrianiNo ratings yet
- State of Matter of Matter 2Document65 pagesState of Matter of Matter 2Fritzel Pallon SusbillaNo ratings yet
- Metallic GlassDocument19 pagesMetallic GlassHarmish BhattNo ratings yet
- Poster Template LQFDocument1 pagePoster Template LQFvestuario17.1No ratings yet
- Module 2 Physical MetallurgyDocument12 pagesModule 2 Physical Metallurgytejasteja9148No ratings yet
- Classification of Materials NotesDocument9 pagesClassification of Materials NotesJohn K KikwaiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers Question Bank With AnswerDocument72 pagesChemistry For Engineers Question Bank With AnswerVIGNESH L RNo ratings yet
- Stainless SteelDocument81 pagesStainless SteelRockey ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Metal-Casting Processes and Equipment Heat TreatmentDocument55 pagesChapter 5. Metal-Casting Processes and Equipment Heat TreatmentBassel AlshamiNo ratings yet
- 9 6Document5 pages9 6이수연No ratings yet
- TDF Q - Assignment Week2Document10 pagesTDF Q - Assignment Week2Ayu Sekar TunjungNo ratings yet
- Iron CastingDocument23 pagesIron CastingDiego MoralesNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of Ceramic and Composite MaterialsDocument407 pagesCorrosion of Ceramic and Composite MaterialsKhin Aung ShweNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0196890422012109 MainDocument27 pages1 s2.0 S0196890422012109 MainPranav OmkarNo ratings yet
- Phase TransitionDocument16 pagesPhase Transitionyehtt0212No ratings yet
- Balmer Exp 6Document6 pagesBalmer Exp 6Collin ChuNo ratings yet
- (Battezzati - L., - Pozzovivo - S., - Rizzi - P.) Nanocrystalline Aluminum Alloys PDFDocument24 pages(Battezzati - L., - Pozzovivo - S., - Rizzi - P.) Nanocrystalline Aluminum Alloys PDFPhung Tuan AnhNo ratings yet
- MMS Unit 2 Phase DiagramsDocument35 pagesMMS Unit 2 Phase DiagramsPraveen KolukulaNo ratings yet
- Al Alaşim Elementleri̇ h1-13Document13 pagesAl Alaşim Elementleri̇ h1-13KaanMertNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagrams Study NotesDocument13 pagesPhase Diagrams Study NotesSushilNo ratings yet
- Characterizing Metallic Microstructure Cu-Based AlloysDocument51 pagesCharacterizing Metallic Microstructure Cu-Based AlloysjuegyiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Bookmatter MetallographyInArchaeologyAndADocument29 pages2019 Bookmatter MetallographyInArchaeologyAndAMorneNo ratings yet
- Production EngineeringDocument110 pagesProduction EngineeringmuthuramprodNo ratings yet
- Platinum Alloys For Shape Memory ApplicationsDocument15 pagesPlatinum Alloys For Shape Memory ApplicationsKursalNo ratings yet
- Lec-8 - Metallurgy PDFDocument16 pagesLec-8 - Metallurgy PDFGhaith MdljNo ratings yet
- Incipient Melting of Al5Mg8Si6Cu2 XDocument15 pagesIncipient Melting of Al5Mg8Si6Cu2 Xmiramirjafari2No ratings yet
- 1980 The Phase Diagram of NaNO3-KNO3 PDFDocument12 pages1980 The Phase Diagram of NaNO3-KNO3 PDFAdrian CaraballoNo ratings yet
- Ch09 Diagrama de FasesDocument13 pagesCh09 Diagrama de FasesFERNANDO JOSE NOVAESNo ratings yet
- Tensile Properties of Directionally Solidified AI-4 WT PCT Cu Alloys With Columnar and Equiaxed GrainsDocument10 pagesTensile Properties of Directionally Solidified AI-4 WT PCT Cu Alloys With Columnar and Equiaxed GrainspaolaNo ratings yet
- Georgia Southern University Foundry Education IntroductionDocument20 pagesGeorgia Southern University Foundry Education IntroductionXantos YulianNo ratings yet