Professional Documents
Culture Documents
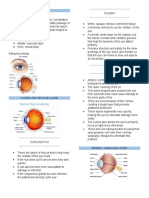
Biology - Structure of Eye
Biology - Structure of Eye
Uploaded by
Leung Bibi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesThe document summarizes the internal structures of the eye in 3 layers - outer, middle, and inner layers. It describes the key structures in each layer including the sclera and cornea in the outer layer, choroid, ciliary body and iris in the middle layer, and retina in the inner layer. It also notes the two chambers of the eye - anterior and posterior chambers, separated by the lens.
Original Description:
My own Biology revision note about the structure of an eye
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the internal structures of the eye in 3 layers - outer, middle, and inner layers. It describes the key structures in each layer including the sclera and cornea in the outer layer, choroid, ciliary body and iris in the middle layer, and retina in the inner layer. It also notes the two chambers of the eye - anterior and posterior chambers, separated by the lens.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesBiology - Structure of Eye
Biology - Structure of Eye
Uploaded by
Leung BibiThe document summarizes the internal structures of the eye in 3 layers - outer, middle, and inner layers. It describes the key structures in each layer including the sclera and cornea in the outer layer, choroid, ciliary body and iris in the middle layer, and retina in the inner layer. It also notes the two chambers of the eye - anterior and posterior chambers, separated by the lens.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
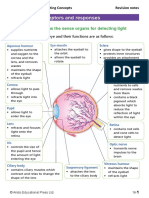
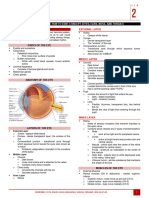
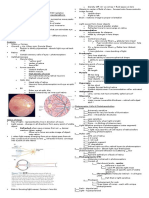
Internal structures of eye
the 3 layers include:
outer layer:sclera and cornea
middle layer:choroid, ciliary body and iris
inner layer:retina
-the eye is divided into 2 chambers, which are the (anterior) and (posterior ) chambers, by
the (lens)
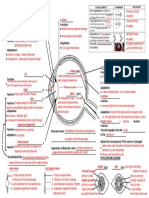
letter name appearance functions
A lens -transparent -refract and focus
-elastic light onto the retina
-biconvex
-living cells that
have lost their nuclei
B anterior chamber space between Aqueous humour as
filled with aqueous cornea & lens a clear, watery
humour solution secreted by
the ciliary body
supplies the cornea
& lens with oxygen
& nutrients, which
have no blood
vessels
C cornea -front layer of the -curved surface
eye refracts light
-continuous to
sclera
-curved surface
-transparent for light
to pass through
D pupil -central hole /
E iris -connected to the -muscles controls
ciliary body, lying in the size of the pupil
front of the lens -adjusts the amount
-contains pigment of light entering the
that gives the color eye
of the eye
-consists of radial
muscles and circular
muscles
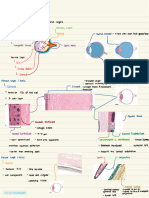
F suspensory ligament / /
G ciliary muscle / contracts and
relaxes to change
the tension in the
suspensory ligament
, hence the shape of
the lens, to focus
light from object at
different distances
H ciliary body -forward /
continuation of
choroid
-a ring of muscular
tissue surrounding
the edge of the lens
-attached to the lens
by suspensory
ligaments
I posterior chamber -spaces between The fluid keeps the
filled with vitreous lens & retina shape of the
humour -filled with vitreous eyeball, help refract
humour, which is a & focus light onto
clear jelly-like fluid the retina
also secreted by
ciliary body
J eye muscles / -contract and relax
to allow the eyeball
to rotate
K sclera -white -gives the shape of
-opaque the eyeball
-fibrous -protects the
-tough structure inside
-surface for eye
muscles to attach on
L choroid -middle layer of the reduces internal
eye reflection of light in
-dark in color due to the eye, contributes
presence of black to sharp vision
pigment
-with blood vessels
M retina -inner layer of the -photoreceptors
eye stimulated by lights
- contains -> generate nerve
photoreceptors impulses
connected to
neurones
N yellow spot -central region of the /
retina with cone
cells only
O blind spot where the optic fibre /
leaves the eye,
contains no
photoreceptors
P blood vessels / supply the cells in
the retina with
oxygen & nutrients,
and remove wastes.
Q optic nerve bundles of nerve transmit nerve
fibres from neurones impulses to the
in retina brain
You might also like
- MCQ of Review of OphthalmologyDocument78 pagesMCQ of Review of Ophthalmologyحلو المذاق100% (3)
- Special SensesDocument29 pagesSpecial Sensesmawel100% (2)
- The Eye Is Made Up of THREE LayersDocument2 pagesThe Eye Is Made Up of THREE LayersMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- 5 Special SensesDocument8 pages5 Special SensesEdel GapasinNo ratings yet
- EENTDocument21 pagesEENTMary Beth AbelidoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyecarminaduriasNo ratings yet
- NeuroSensory - Eye Part 2Document38 pagesNeuroSensory - Eye Part 2Zed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument9 pagesThe Human Eyegiana 4e100% (1)
- Eye LectureDocument38 pagesEye LectureAMR WALIDNo ratings yet
- External Layer: The Fibrous Tunic: Structure S Characteristics FunctionDocument23 pagesExternal Layer: The Fibrous Tunic: Structure S Characteristics FunctionTheodora IonescuNo ratings yet
- C1 F3 BiodiversityDocument112 pagesC1 F3 BiodiversityNurul Shafiah Mustafa KamalNo ratings yet
- Opto Reviewe2Document8 pagesOpto Reviewe2isseylimboNo ratings yet
- Our Sense of Sight and LightDocument6 pagesOur Sense of Sight and LightnorafaizalNo ratings yet
- Eent MidtermsDocument7 pagesEent MidtermsDavid Dwane Art SilorioNo ratings yet
- Eye AnatomyDocument4 pagesEye AnatomyILAH REANNIE ENRIQUEZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 f3Document113 pagesChapter 1 f3FAthiyah Abdul RahimNo ratings yet
- MataaaaDocument109 pagesMataaaaFelecia ChristyNo ratings yet
- Ha Eyes and Ears 1Document7 pagesHa Eyes and Ears 1SICAT, Keeshan KeithNo ratings yet
- External Eye: Internal EyeDocument2 pagesExternal Eye: Internal EyeJustin John NavarroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeMargaretha AdhiningrumNo ratings yet
- Trans Sa MHSBDocument6 pagesTrans Sa MHSBanthea AllamNo ratings yet
- Special Senses 1Document14 pagesSpecial Senses 1Juan Miguel TevesNo ratings yet
- Gross Eye AnatomyDocument48 pagesGross Eye AnatomyAzizan Hanny100% (2)
- Subject: Physiology Topic: Vision Physiology 1 Lecturer: Dr. Vic Mendoza DATE: MARCH, 2011Document7 pagesSubject: Physiology Topic: Vision Physiology 1 Lecturer: Dr. Vic Mendoza DATE: MARCH, 2011Std DlshsiNo ratings yet
- Ch16 Notes eDocument5 pagesCh16 Notes eJulius CruelNo ratings yet
- Structure and FunctionDocument15 pagesStructure and FunctionGOODWIN GALVANNo ratings yet
- Finals - Eyes and EarsDocument4 pagesFinals - Eyes and EarsCrisanta Grace OpondaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Sense Organs Eyes Skin and TongueDocument33 pagesUnit 2 Sense Organs Eyes Skin and TongueBONGISIPHO HLOPHENo ratings yet
- A. Eye Balls D. Lacrimal Glands: 1. External Structures of The EyeDocument7 pagesA. Eye Balls D. Lacrimal Glands: 1. External Structures of The EyebeayapNo ratings yet
- Workbook Activity #22: Special Sense Organ: The Eye: Tissue Structure Function DrawingDocument3 pagesWorkbook Activity #22: Special Sense Organ: The Eye: Tissue Structure Function DrawingAmbaw PutiiNo ratings yet
- Vision in ArthropodaDocument4 pagesVision in Arthropodasurbhisaini0904No ratings yet
- Eye and Ear 2.1 Human EyeDocument12 pagesEye and Ear 2.1 Human Eyechakshana kannangaraNo ratings yet
- Iris Muscle - (Most Anterior Extension: EyeballDocument8 pagesIris Muscle - (Most Anterior Extension: EyeballBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Special Senses NotesDocument3 pagesSpecial Senses NotesChelsa LeyritanaNo ratings yet
- EENT NotesDocument12 pagesEENT NotesMhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Eent CompiledDocument15 pagesEent CompiledAlthea Franz DuoNo ratings yet
- 27 Physiology of Visual AnalyzerDocument39 pages27 Physiology of Visual Analyzersiwap34656No ratings yet
- Eyes Health AssessmenttDocument34 pagesEyes Health AssessmenttMhiaBuenafeNo ratings yet
- Eyes Lecture 1Document4 pagesEyes Lecture 1Rue Cheng MaNo ratings yet
- Week 15Document2 pagesWeek 15Diana MontaosNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument16 pagesSpecial SensesAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Windows of KnowledgeDocument9 pagesUnit 2 Windows of Knowledgesajith kumar VariathNo ratings yet
- Science - Part of The Eye - RUPHAADocument7 pagesScience - Part of The Eye - RUPHAAIsmail ZueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World NoteDocument13 pagesChapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World NoteJay MakiNo ratings yet
- Eg9 TB Sci Chap2Document22 pagesEg9 TB Sci Chap2JAYDEN JANSZNo ratings yet
- Structure of The EyeDocument2 pagesStructure of The EyeminaNo ratings yet
- Brightness - Amplitude of Wave High Wave-Brighter, Low Have - DullDocument3 pagesBrightness - Amplitude of Wave High Wave-Brighter, Low Have - Dullpreetirajput2412No ratings yet
- Ophthalmology 1st SessionDocument26 pagesOphthalmology 1st SessionWais samarNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-08 at 8.34.09 PMDocument61 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-08 at 8.34.09 PM08-Akshay BoraNo ratings yet
- Eye & EarDocument15 pagesEye & EarfatimasulaimanishereNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Biology The EyeDocument5 pagesGrade 11 Biology The EyeDexter TorringtonNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument3 pagesHuman Eyeupadhyayula srikrishnaNo ratings yet
- The Sensory Organs: Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityDocument117 pagesThe Sensory Organs: Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityamiraNo ratings yet
- Kevt 101Document7 pagesKevt 101Donald HrangkholNo ratings yet
- Kevt 101Document7 pagesKevt 101RajinderKumarNo ratings yet
- 400-750 NM AccommodationDocument2 pages400-750 NM AccommodationTeves AdrianNo ratings yet
- ED II Lens Camerae Bulbivitrous Body Accomodation TZSDocument25 pagesED II Lens Camerae Bulbivitrous Body Accomodation TZSBojanaNo ratings yet
- 2 2 Sensory OrgansDocument27 pages2 2 Sensory OrgansKeashi VelzyNo ratings yet
- Eye and VisionDocument20 pagesEye and VisionshyanNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of RetinaDocument18 pagesAnatomy of RetinaNuman QayyumNo ratings yet
- 02 Trauma Oculi - Dr. Tutuk Wibowo Chamidy, SP.MDocument60 pages02 Trauma Oculi - Dr. Tutuk Wibowo Chamidy, SP.MDissa Yulianita SuryaniNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Lectures PDFDocument88 pagesOphthalmology Lectures PDFsharenNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Set 5Document5 pagesOphthalmology Set 5ajay khadeNo ratings yet
- Cap 18 Raices Sist SensorialDocument2 pagesCap 18 Raices Sist SensorialSandra OrtizNo ratings yet
- Parts of The EyeDocument15 pagesParts of The EyeShayan SushilNo ratings yet
- Subluksasi LensaDocument12 pagesSubluksasi LensaDede GunawanNo ratings yet
- Iris Anatomy MmeDocument4 pagesIris Anatomy MmeSatyam ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- What Makes Up An EyeDocument3 pagesWhat Makes Up An EyenandhantammisettyNo ratings yet
- 2014's MataPedia For OphthalmologistDocument191 pages2014's MataPedia For OphthalmologistGede PardiantoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 Student Handout2023-IDocument12 pagesUNIT 6 Student Handout2023-IPaola Mercedes Matos OrtegaNo ratings yet
- 12-2 - Fri - vision-hearing-EQDocument13 pages12-2 - Fri - vision-hearing-EQTyler DeanNo ratings yet
- 2.eyes HistologyDocument23 pages2.eyes Histologyqty9jgkpnzNo ratings yet
- TM3 - P17410211020 - Nisa Amanda Diva P - 1A - TUGAS KODEFIKASI 3Document4 pagesTM3 - P17410211020 - Nisa Amanda Diva P - 1A - TUGAS KODEFIKASI 3NisaadivaNo ratings yet
- Eyes RETDEMDocument2 pagesEyes RETDEMRenz Kier L. ComaNo ratings yet
- Kode Icd MataDocument5 pagesKode Icd Mataindah ramadhaniNo ratings yet
- Week 18 - SDL Preview QuestionsDocument3 pagesWeek 18 - SDL Preview QuestionsAAMNA HAROONNo ratings yet
- Biology - Structure of EyeDocument3 pagesBiology - Structure of EyeLeung BibiNo ratings yet
- Peaphy Week 3 - Activity 1 - Group 2Document3 pagesPeaphy Week 3 - Activity 1 - Group 2John Paul DioneoNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of Netra Sharir of Ayurveda in The Modern PerspectiveDocument10 pagesA Critical Review of Netra Sharir of Ayurveda in The Modern PerspectiveSambamurthi Punninnair NarayanNo ratings yet
- DR Gargi Singh - 2 Page Notes - NeuralDocument9 pagesDR Gargi Singh - 2 Page Notes - NeuralSuccessfactors TrainerNo ratings yet
- 4.1 One Pager Eye - MEMO PDFDocument1 page4.1 One Pager Eye - MEMO PDFRudzi Udzi100% (1)
- The Human Eye and The Colourful World PPT-Mod-1 (10TH)Document12 pagesThe Human Eye and The Colourful World PPT-Mod-1 (10TH)chanskeyan100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Eye - Dr. Lim-Cecilio (2022)Document3 pagesAnatomy of The Eye - Dr. Lim-Cecilio (2022)Patricia ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Plantilla Powerpoint Del Sistema MuscularDocument48 pagesPlantilla Powerpoint Del Sistema MuscularLimberg ArhuataNo ratings yet
- Ocular Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesOcular Anatomy and Physiologylaibanisar227No ratings yet
- Notas OjoDocument1 pageNotas Ojodaniela.garciagarciaNo ratings yet
- Science - Part of The Eye - RUPHAADocument7 pagesScience - Part of The Eye - RUPHAAIsmail ZueNo ratings yet
- Hicks AnteriorChamberAngle HandoutsDocument16 pagesHicks AnteriorChamberAngle HandoutsAbegail IbañezNo ratings yet