Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adobe Scan Jun 12, 2022
Adobe Scan Jun 12, 2022
Uploaded by
Subrat BarikOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adobe Scan Jun 12, 2022
Adobe Scan Jun 12, 2022
Uploaded by
Subrat BarikCopyright:
Available Formats
-sin o 0
sin a
2af1+)2a(1+#)
Or n?= 1
sides and
using
both
Squaring
sin'a(1+
4u'(1+)
p=2a(1+Pcosec'a
tptana =
#2a(1+r2 coseca seca
Again o =
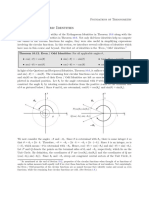
Example - 10
is normal to the cylinder th
der, binoTmai m the
helix, the principalnormal
Show that in any cylindrical to torsion is constant
constant angle with the axisand the ratio of curvature
a
the cylinder, then the position vector r of any point on te
Solution. Ifa is the radius of
is given by.
r={acos8,asin 6, a®tan a)
Where a is the angle of helix.
d6
1=r=(-acos, asin , atan a ds
Take module
1=(a+dtan a ds
d6 COSa
Or
ds a
.I =
cosa(-sin6,cos 6, tan a
= kn=
a -cos0,-sin 0,0)
Or
n=- cos6,-sin ,0)
Where k= COS a
.d.s.'sof the n6, 0.
Vector
equation ofprincipal normal to the helix are prop s
to cos,
the proportional
cylinder is
r=(acos,a
Where and
sin 0,z)
6 z as
Let
suffixes land 2parameters.
denote partial deriuntiu unertivcly, then
You might also like
- Elements of Strength of Material Timoshenko Young 5th EditionDocument194 pagesElements of Strength of Material Timoshenko Young 5th EditionShipali Parjapat100% (2)
- Lecture Notes - Week 2Document28 pagesLecture Notes - Week 2Nawin RaNo ratings yet
- 15 462 Fall03 WrAssign1 AnswerDocument5 pages15 462 Fall03 WrAssign1 AnswerBayu Yudha PratamaNo ratings yet
- Space Curves - 1: Differential Geometry III, Solutions 4 (Week 4)Document3 pagesSpace Curves - 1: Differential Geometry III, Solutions 4 (Week 4)Gag PafNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document29 pagesCH 2Yahya AlmolikiNo ratings yet
- A4 SolDocument7 pagesA4 SolMeyssa SmiraniNo ratings yet
- The Magnetic Dipole: Flux Density IsDocument8 pagesThe Magnetic Dipole: Flux Density IsPalashNo ratings yet
- Euler S DiskDocument4 pagesEuler S Disksanhthanh24091994No ratings yet
- DU MCA - 2017: 18, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319 - 1Document4 pagesDU MCA - 2017: 18, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319 - 1Soumik KarmakarNo ratings yet
- S&Z 10.4 PDFDocument20 pagesS&Z 10.4 PDFHarold de ChavezNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions: 7.1 AnglesDocument11 pagesTrigonometric Functions: 7.1 AnglesGlorilie Perez PazNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field Theory: A Problem Solving ApproachDocument283 pagesElectromagnetic Field Theory: A Problem Solving ApproachEkSlzrNo ratings yet
- The 74th William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Saturday, December 7, 2013Document2 pagesThe 74th William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Saturday, December 7, 2013Ignacio MartinezNo ratings yet
- Tutorial v1Document5 pagesTutorial v1Ram KumarNo ratings yet
- Robotics1 Test 09.11.10Document5 pagesRobotics1 Test 09.11.10asalifew belachewNo ratings yet
- Root LocusDocument5 pagesRoot LocusADVAITANo ratings yet
- FPM Formula Sheet 2Document13 pagesFPM Formula Sheet 2Yolo Gamer DudeNo ratings yet
- 6 TopologyDocument4 pages6 TopologyFrancisco CruzNo ratings yet
- Slide 01 - 3D Coordinate SystemDocument49 pagesSlide 01 - 3D Coordinate SystemOmor FarukNo ratings yet
- MTHS2007 Formula SheetwithtablescorrectedDocument3 pagesMTHS2007 Formula SheetwithtablescorrectedBenjamin OpokuNo ratings yet
- A5 SolutionDocument8 pagesA5 SolutionRaja KumarNo ratings yet
- "Just The Maths" Unit Number 11.4 Differentiation Applications 4 (Circle, Radius & Centre of Curvature) by A.J.HobsonDocument6 pages"Just The Maths" Unit Number 11.4 Differentiation Applications 4 (Circle, Radius & Centre of Curvature) by A.J.Hobsonelias pappasNo ratings yet
- PageNo 7 20 7 21 Atullah PathanDocument5 pagesPageNo 7 20 7 21 Atullah PathanManas HiremathNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field Theory - A Problem Solving Approach (PDFDrive)Document753 pagesElectromagnetic Field Theory - A Problem Solving Approach (PDFDrive)cachojrNo ratings yet
- Linearna AlgebraDocument70 pagesLinearna AlgebraKatarinaNo ratings yet
- Maths Shift 1 Nest 2023Document6 pagesMaths Shift 1 Nest 2023Hardik JoshiNo ratings yet
- Wang, KaixinDocument13 pagesWang, KaixinsergenNo ratings yet
- S (U, V) (U V, U + V, U: Chapter 6: Surface IntegralsDocument18 pagesS (U, V) (U V, U + V, U: Chapter 6: Surface IntegralsMariveluswamyNo ratings yet
- MATH3968 Lecture 3: DR Emma Carberry 30 July 2009Document3 pagesMATH3968 Lecture 3: DR Emma Carberry 30 July 2009TOM DAVISNo ratings yet
- CS 103X: Discrete Structures Homework Assignment 5 - SolutionsDocument3 pagesCS 103X: Discrete Structures Homework Assignment 5 - SolutionsMichel MagnaNo ratings yet
- Math Cumulative 2 ReviewDocument5 pagesMath Cumulative 2 ReviewJNo ratings yet
- 06.drawing ToolsDocument7 pages06.drawing ToolsYang CaoNo ratings yet
- MATH3968 Lecture 2: DR Emma Carberry 29 July 2009Document5 pagesMATH3968 Lecture 2: DR Emma Carberry 29 July 2009TOM DAVISNo ratings yet
- Robotics1 13.01.09Document5 pagesRobotics1 13.01.09asalifew belachewNo ratings yet
- 18 Final Exercises and Problems in CalculusDocument34 pages18 Final Exercises and Problems in Calculuslucia lopez lopezNo ratings yet
- 442 2019HW2solDocument7 pages442 2019HW2solAllenNo ratings yet
- PHYS 253 Final Exam: Name Student IDDocument3 pagesPHYS 253 Final Exam: Name Student IDaikfirkiNo ratings yet
- Parte 10Document7 pagesParte 10Elohim Ortiz CaballeroNo ratings yet
- D 08 Poly Hedra TextDocument264 pagesD 08 Poly Hedra Texteluucee81No ratings yet
- Circular FunctionsDocument2 pagesCircular FunctionsPanizales, Anne Gella CatesNo ratings yet
- Complex Variables and Partial Differential Equations 2019 Apr (2015 Ad)Document2 pagesComplex Variables and Partial Differential Equations 2019 Apr (2015 Ad)Aswin AswinNo ratings yet
- Banco Imo 1996 Sem SoluçõesDocument6 pagesBanco Imo 1996 Sem SoluçõesIsrael DouradoNo ratings yet
- Trigo ReviewDocument4 pagesTrigo ReviewDaniel VargasNo ratings yet
- MATH3968 Lecture 4: DR Emma Carberry 4 August 2009Document4 pagesMATH3968 Lecture 4: DR Emma Carberry 4 August 2009TOM DAVISNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment - 2 PDFJayesh NarayanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Complex Exponential SignalsDocument44 pagesLecture 3 Complex Exponential SignalsÖmer Yağız ÜskesNo ratings yet
- Ib Math HL Differentiation Past Exam QuestionDocument19 pagesIb Math HL Differentiation Past Exam QuestionNguyen Quynh VyNo ratings yet
- Assign 0 PDFDocument7 pagesAssign 0 PDFghukato awomiNo ratings yet
- UMANG Class 11th - Trigonometric Functions - 1 - VMathDocument74 pagesUMANG Class 11th - Trigonometric Functions - 1 - VMathnabhijain9No ratings yet
- Lecture 21 NotesDocument4 pagesLecture 21 NotesDaniel VargasNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 3Document2 pagesAnalytic Geometry 3ggomo15100% (1)
- Text (Vector Space)Document15 pagesText (Vector Space)colindanielblassingameNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Paper - Rainbow - FINALDocument6 pagesAstronomy Paper - Rainbow - FINALargyNo ratings yet
- DiffGeo and Planetary MotionDocument99 pagesDiffGeo and Planetary MotionJanusz SiodaNo ratings yet
- Mitres 18 001 f17 Guide ch09Document14 pagesMitres 18 001 f17 Guide ch09ClaptrapjackNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Sol 1 Series and Matrices IitmDocument3 pagesAssignment 3 Sol 1 Series and Matrices IitmRam Lakhan MeenaNo ratings yet
- Trig1 - Compound Angles - TN - FDocument20 pagesTrig1 - Compound Angles - TN - FSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Random Fourier Series with Applications to Harmonic Analysis. (AM-101), Volume 101From EverandRandom Fourier Series with Applications to Harmonic Analysis. (AM-101), Volume 101No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- 5603H19018 CC6 MathDocument12 pages5603H19018 CC6 MathSubrat BarikNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jun 12, 2022 (4) SubraDocument1 pageAdobe Scan Jun 12, 2022 (4) SubraSubrat BarikNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jun 12, 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan Jun 12, 2022Subrat BarikNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07 Mar 2022Document15 pagesAdobe Scan 07 Mar 2022Subrat BarikNo ratings yet
- 8 K4 Exercise 6 (D) : So, JX+) D DyDocument8 pages8 K4 Exercise 6 (D) : So, JX+) D DySubrat BarikNo ratings yet
- 5603H19019 CC VIII MathDocument4 pages5603H19019 CC VIII MathSubrat BarikNo ratings yet
- 203H19002 Dsc-A Physics P-1Document12 pages203H19002 Dsc-A Physics P-1Subrat BarikNo ratings yet
- Review of Vector Algebra (Ch-7) Multivariate CalculusDocument14 pagesReview of Vector Algebra (Ch-7) Multivariate CalculusSubrat BarikNo ratings yet
- 5603H19018 CC Viii MathDocument4 pages5603H19018 CC Viii MathSubrat BarikNo ratings yet
- 5703H19027 - Physics - CC 5Document12 pages5703H19027 - Physics - CC 5Subrat BarikNo ratings yet
- 5603H19018 - Reeh - Sec-1Document11 pages5603H19018 - Reeh - Sec-1Subrat BarikNo ratings yet
- 5603H19007 - GE-1 - ChemistryDocument11 pages5603H19007 - GE-1 - ChemistrySubrat BarikNo ratings yet
- Begaj Introduction To Metaphysics in Contemporanea FísicaDocument16 pagesBegaj Introduction To Metaphysics in Contemporanea FísicakkadilsonNo ratings yet
- Cuadrivectores en ElectromagnetismoDocument27 pagesCuadrivectores en ElectromagnetismoDennis Diaz Trujillo100% (1)
- Case Studies On Nonlinear Control Theory of The Inverted PendulumDocument28 pagesCase Studies On Nonlinear Control Theory of The Inverted PendulumDragan ErcegNo ratings yet
- Mth166:Differential Equations and Vector Calculus: Session 2021-22 Page:1/1Document1 pageMth166:Differential Equations and Vector Calculus: Session 2021-22 Page:1/1Mohit RajNo ratings yet
- Thomas Valone Zero Point Energy PDFDocument184 pagesThomas Valone Zero Point Energy PDFPeter MossNo ratings yet
- Resonant X-Ray Scattering Studies of Charge Order in CupratesDocument39 pagesResonant X-Ray Scattering Studies of Charge Order in Cupratesthomas abramsNo ratings yet
- Application of 1st Order de in Drainage of A Water TankDocument5 pagesApplication of 1st Order de in Drainage of A Water TankIrsyad Sony100% (1)
- M.SC PhyscisDocument11 pagesM.SC Physcis4utiktehpNo ratings yet
- Sarachik and SchappertDocument16 pagesSarachik and Schappertrc85948No ratings yet
- Gnphys+2+ +worktext+ +week+6+ +unit+6Document10 pagesGnphys+2+ +worktext+ +week+6+ +unit+6Nad dlanyer LatigidadNo ratings yet
- Pauli Matrices: 1 Algebraic PropertiesDocument6 pagesPauli Matrices: 1 Algebraic PropertiesAnthony RogersNo ratings yet
- Finite Element AnalysisDocument1 pageFinite Element AnalysisnawinerdNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 PHY1701 ETH VL2019201005729 Reference Material I 29-Jul-2019 04u-QUANTUM MECHANICSDocument22 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 PHY1701 ETH VL2019201005729 Reference Material I 29-Jul-2019 04u-QUANTUM MECHANICSMajety S LskshmiNo ratings yet
- Black Holes, Gravitational Waves and Fundamental Physics: A RoadmapDocument216 pagesBlack Holes, Gravitational Waves and Fundamental Physics: A RoadmapDiogo MesquitaNo ratings yet
- Wavelet - A Tutorial On Wavelets and Their ApplicationsDocument29 pagesWavelet - A Tutorial On Wavelets and Their Applicationsbashar_asaadNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics KAS101TDocument3 pagesEngineering Physics KAS101TNeelam SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Moment and CouplesDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Moment and CouplesMihir Kumar MechNo ratings yet
- Today's Objectives: In-Class ActivitiesDocument23 pagesToday's Objectives: In-Class ActivitiesAtef NazNo ratings yet
- School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocument6 pagesSchool Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterAutumnNo ratings yet
- Tensors - 1mary L. Boas - Mathematical Methods in The PhyDocument21 pagesTensors - 1mary L. Boas - Mathematical Methods in The PhyRaza Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- Della Pietra S 1Document28 pagesDella Pietra S 1123chessNo ratings yet
- Tut12ans 01 PDFDocument7 pagesTut12ans 01 PDFأحمدآلزهوNo ratings yet
- Stability of A Charged Interface Between A Magnetoradiative Dusty Plasma and VacuumDocument5 pagesStability of A Charged Interface Between A Magnetoradiative Dusty Plasma and VacuumRUBY REHANNo ratings yet
- Y20 Phy102 EsDocument28 pagesY20 Phy102 EsSAURAV kumarNo ratings yet
- Hill CH 5Document158 pagesHill CH 5Shahriar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Online Homework 8Document5 pagesOnline Homework 8Hoang PhuonghaNo ratings yet
- Order Parameters, Broken Symmetry, and Topology: PACS Numbers: KeywordsDocument10 pagesOrder Parameters, Broken Symmetry, and Topology: PACS Numbers: KeywordsgoogleNo ratings yet
- OSE5312 Slides Class 12 - Optical Properties of Semiconductors 1Document22 pagesOSE5312 Slides Class 12 - Optical Properties of Semiconductors 1Mastering Zinc OxideNo ratings yet