Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ARC-3080 Town Planning
ARC-3080 Town Planning
Uploaded by
TARIQ TANSEEF0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views23 pagesThe document discusses the evolution of town planning concepts over time. It describes early proposals for self-sufficient planned industrial towns with communal buildings and housing surrounded by gardens. Later concepts included concentric designs with public buildings in the center and different land uses in surrounding circles. The document also outlines Garden City proposals and new town developments in the UK, as well as modern high-density city proposals with underground connections between tall buildings.
Original Description:
Detailed study on utopians architecture.
Original Title
UTOPIANS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the evolution of town planning concepts over time. It describes early proposals for self-sufficient planned industrial towns with communal buildings and housing surrounded by gardens. Later concepts included concentric designs with public buildings in the center and different land uses in surrounding circles. The document also outlines Garden City proposals and new town developments in the UK, as well as modern high-density city proposals with underground connections between tall buildings.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views23 pagesARC-3080 Town Planning
ARC-3080 Town Planning
Uploaded by
TARIQ TANSEEFThe document discusses the evolution of town planning concepts over time. It describes early proposals for self-sufficient planned industrial towns with communal buildings and housing surrounded by gardens. Later concepts included concentric designs with public buildings in the center and different land uses in surrounding circles. The document also outlines Garden City proposals and new town developments in the UK, as well as modern high-density city proposals with underground connections between tall buildings.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 23
ARC-3080 Town Planning
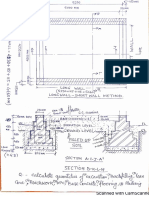
In 1816 he proposed a self-supporting
industrial town.
Communal buildings were located in the
broad common situated in the center.
The central broad common was surrounded
by dwellings which were surrounded by
large gardens.
A road surrounded the community abutted
the factories and workshops.
Designed for 1200 population it had 1000-
1500 acres of land for agricultural activity.
An Architect he proposed concentric town
plan with a large central square surrounded
by mansions.
This central court is surrounded by public
buildings and churches.
Then the concentric surrounding by various
category of housing, commercial belt,
workshop belt, school and dining places
etc.
Industries were proposed 1.5 miles away
from the town.
Came to India in 1915.
Gave his expert advice on 18 Indian cities.
Diagnostic approach: Survey before Plan.
Geddesian triad: Folk (social aspect), place
(physical aspect) and work (economic aspect).
City looked upon as organisms governed by
definite laws of growth where people live, work
and play.
His foresight shook up town planning of
contemporary world and later on gave way to
modern day regional planning.
He published his idea for a Garden City in his book titled
Tomorrow.
Combining the goods of city and country life he
proposed a community living for 30,000 people in an
area of 1000 acres.
Surrounding the city would be a green belt of 5000
acres.
The public buildings would be located in the centre
surrounded by the residential area.
The shopping centre would be on the edge of the town
and the industries on the ourskirts.
Letchworth city was started in 1903 with an area of 4500
acres and population of 35000.
Permanent Green belt of 3000 acres is reserved.
The city dwellers receive a 5% dividend on their
stocks annually and the profit above this goes for
public welfare.
Another city Welwyn started with a land area of
2400 acres population of 40000.
Mixed use is totally absent.
Green belt serves as protection instead of urban
expansion space.
Over crowding of city centre and under
development of outskirts is prevented.
He was influenced by Sir Patrick Geddes.
He believed in human ability for building a better future
using technology.
But later on he criticized the extensive use of machines.
Modern technology—which he calls 'megatechnics'—
evades producing lasting, quality products by using
devices such as consumer credit, installment buying, non-
functioning and defective designs, built-in fragility, and
frequent superficial fashion changes.
Polytechnics vs monotechnics
Biotechnics
He emphasized relationship of organisms and their living
spaces in urban planning.
He blamed modern day urban sprawl for many of the
social problems.
He proposed La ville contemporaine.
A city of skyscrpaers with huge gardens.
At the hub was tranport centre, rail and airfield.
Surrounding this were 60 storey office buildings with a
density of 1200 persons per acre.
These buildings are linked to each other underground
by shopping area and civic centre.
8-storey residential buildings surrounded this were
arranged in a zigzag row with 5% ground coverage
with a density of 120 persons per acre.
On the outskirts were the city gardens.
The city had a population of 30,00,000.
(Image Credit: Artists Rights Society
(ARS), New York / ADAGP, Paris / F.L.C.)
(Image Credit: Google Maps)
He considered the city as an organism.
The Administrative buildings are the
head
The commercial buildings are the heart.
Industries and education buildings the
limb
Parks and playgrounds are the lungs
The roads and walkways are the arteries.
International Congress of Modern
Architects.
It subjected the city to re-examination
and posed four basic elements of urban
biology:
Sun
Space
Vegetation
Steel and Concrete.
Le Corbusier palyed a leading role in
CIAM and organised Assembly of
Constructors for Architectural
Renovation (ASCORAL) to investigate
the character of the city
ASCORAL setforth the “Three Human
Establishmnets”:
The farming community
The radiocentric city
The industrial city
Gallion,Eisner, 1986, The Urban Pattern: City
planning and Design, Van Nostrand
Reinhold; Subsequent edition (1 February
1986).
Gallion. B., Urban Pattern and Growth
Hiraskar. G. K., Fundamentals of Town
Planning
Rangawala S. C., Town Planning
https://www.citylab.com/design/2012/11/e
volution-urban-planning-10-diagrams/3851/
You might also like
- Industrial Revolution and Town PlanningDocument24 pagesIndustrial Revolution and Town PlanningAnupamaTirkey33% (3)
- Intro To Plastic Injection Molding EbookDocument43 pagesIntro To Plastic Injection Molding EbookJames Farrugia78% (9)
- Duke XC SL Race ServiceDocument10 pagesDuke XC SL Race ServicesilverapeNo ratings yet
- What Was Garden City Movement by Sir Ebenezer Howard ?Document6 pagesWhat Was Garden City Movement by Sir Ebenezer Howard ?Aisha MalikNo ratings yet
- Ebenezer Howard FinalDocument13 pagesEbenezer Howard FinalsanamNo ratings yet
- Different Types of City ModelsDocument56 pagesDifferent Types of City ModelsManpreet Kaur100% (1)
- INTRODUCTION To Town PlanningDocument21 pagesINTRODUCTION To Town PlanningPrabhat Jadli100% (3)
- Ebenezer HowardDocument29 pagesEbenezer HowardSadia Husain0% (1)
- 13.a. Explain The Planning Concepts and Their Relevance To Indian Planning Practice As Per Ebenezer HowardDocument10 pages13.a. Explain The Planning Concepts and Their Relevance To Indian Planning Practice As Per Ebenezer HowardMadhu VanthiNo ratings yet
- Town Plannin G: Module - 2Document15 pagesTown Plannin G: Module - 2Amita MaddhesiyaNo ratings yet
- Ebenezer Howard (Garden City)Document39 pagesEbenezer Howard (Garden City)megha madhuNo ratings yet
- That Could Be Used To Improve The World Through The Design of Buildings and Through Urban PlanningDocument6 pagesThat Could Be Used To Improve The World Through The Design of Buildings and Through Urban PlanningKRISHNA SUPRADEEPNo ratings yet
- Utopian CitiesDocument9 pagesUtopian CitiesMichaela ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 2Document64 pagesChapter 2 2Amul ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Ebenzer Howard: Assignment: Eminent Town PlannerDocument5 pagesEbenzer Howard: Assignment: Eminent Town PlannerAmit PatelNo ratings yet
- Howard ResourseDocument12 pagesHoward Resoursefitsum tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Ebenezer Howard and Soria y MataDocument10 pagesEbenezer Howard and Soria y MataVandana RagothamanNo ratings yet
- Planning TheoriesDocument26 pagesPlanning TheoriesMiti AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Topic 2A - Theories of Urban GrowthDocument79 pagesTopic 2A - Theories of Urban GrowthAizat kamarudinNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Town PlanningDocument28 pages1.introduction To Town PlanningChekha0% (1)
- Planning TheoriesDocument34 pagesPlanning TheoriesNoven Amaller100% (1)
- History-Theories and Movements2-20160315-095449910Document16 pagesHistory-Theories and Movements2-20160315-095449910Shashank SinhaNo ratings yet
- Urban Design Methods and TechniquesDocument9 pagesUrban Design Methods and TechniquesShraddha BahiratNo ratings yet
- Garden CityDocument12 pagesGarden CityElang Shullai0% (1)
- Smart CityDocument7 pagesSmart CityalakshendraNo ratings yet
- Case Study On ChandigarhDocument16 pagesCase Study On Chandigarharchitects100% (1)
- 3 Vertical NCDocument13 pages3 Vertical NCAdil A S 191006No ratings yet
- INDUSTRIAL ERA ReportDocument38 pagesINDUSTRIAL ERA ReportJay SuNo ratings yet
- Utopians-II: ARC-3080 Town PlanningDocument18 pagesUtopians-II: ARC-3080 Town PlanningTARIQ TANSEEFNo ratings yet
- Synthesis PaperDocument4 pagesSynthesis PaperBermelyn grace BorneaNo ratings yet
- Planningconcepts 120318075647 Phpapp02Document40 pagesPlanningconcepts 120318075647 Phpapp02Viral AggarwalNo ratings yet
- City PlanningDocument35 pagesCity PlanningnimeshpillaNo ratings yet
- Review Mats22Document21 pagesReview Mats22Donvar Abarcar DiamanteNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document32 pagesLecture 5jabranalamNo ratings yet
- Urban Theorist & Brief History PDFDocument10 pagesUrban Theorist & Brief History PDFNerissa SantiagoNo ratings yet
- How Urban Planning Works TextDocument5 pagesHow Urban Planning Works TextAdam BeymNo ratings yet
- Garden City MovementDocument9 pagesGarden City MovementIsmail Omer100% (1)
- Le Corbusier Forays Into UrbanismDocument22 pagesLe Corbusier Forays Into UrbanismHarleen SehgalNo ratings yet
- CLA - 3 Answer Key HSTPDocument18 pagesCLA - 3 Answer Key HSTPVaidehi EPNo ratings yet
- Urban Planning ConceptsDocument5 pagesUrban Planning ConceptsGlenn Paul GalanoNo ratings yet
- American CitiesDocument24 pagesAmerican CitiesBRUSLIN ABISHEKNo ratings yet
- GARDEN CITIES OF TO-MORROW by Ebenezer Howard: Arturo Soria y MataDocument4 pagesGARDEN CITIES OF TO-MORROW by Ebenezer Howard: Arturo Soria y MataBrylle De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Urban Planning TheoriesDocument20 pagesUrban Planning TheoriesAlyssa Harriet MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document14 pagesLec 4Fayaz JerovNo ratings yet
- The MA ArchitectureDocument5 pagesThe MA ArchitectureKarabo ThokoziLe SetholeNo ratings yet
- Patrick Geddes - Sanan VermaDocument22 pagesPatrick Geddes - Sanan VermaKhalida ParveenNo ratings yet
- What Is Urban and Regional PlanningDocument12 pagesWhat Is Urban and Regional PlanningMayowa Zacchaeus100% (1)
- Chandigarh: Urban Planning ConceptsDocument10 pagesChandigarh: Urban Planning ConceptsAbhishek ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Emergence of Urban Design As A DisciplineDocument13 pagesEmergence of Urban Design As A DisciplinesuryasooriyamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document166 pagesUnit 2IswaryaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - Town PlanningDocument9 pagesAssignment 2 - Town PlanningJayesh JainNo ratings yet
- Own Planning and ArchitectureDocument40 pagesOwn Planning and ArchitectureKavan PathakNo ratings yet
- The Urban PatternDocument14 pagesThe Urban PatternAyushmaan RaiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Global CitiesDocument6 pagesModule 4 Global CitiesRosalyn BacolongNo ratings yet
- Cities in Nature by Lam Khee Poh and Khoo Teng ChyeDocument29 pagesCities in Nature by Lam Khee Poh and Khoo Teng ChyeAvelyn LaiNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Town PlanningDocument5 pagesDefinitions of Town PlanningShane RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Classic Urban Theories: Ebenezer Howard (Three Magnets Concept)Document19 pagesClassic Urban Theories: Ebenezer Howard (Three Magnets Concept)Fritz BechaydaNo ratings yet
- LEC 4 - Planning Concepts PART 2Document61 pagesLEC 4 - Planning Concepts PART 2Aayush KumarNo ratings yet
- Mughal Architecture: Arc 3110 - Islamic Architecture - B.Arch. V Sem. - Ar. Nawab AhmadDocument33 pagesMughal Architecture: Arc 3110 - Islamic Architecture - B.Arch. V Sem. - Ar. Nawab AhmadTARIQ TANSEEFNo ratings yet
- Arabian and MoorishDocument46 pagesArabian and MoorishTARIQ TANSEEFNo ratings yet
- Utopians-II: ARC-3080 Town PlanningDocument18 pagesUtopians-II: ARC-3080 Town PlanningTARIQ TANSEEFNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rates - L-1Document18 pagesAnalysis of Rates - L-1TARIQ TANSEEFNo ratings yet
- Methods of EstimationDocument1 pageMethods of EstimationTARIQ TANSEEFNo ratings yet
- Traffic Problems and RemediesDocument11 pagesTraffic Problems and RemediesTARIQ TANSEEFNo ratings yet
- Road Network and Heirarchy of RoadsDocument16 pagesRoad Network and Heirarchy of RoadsTARIQ TANSEEFNo ratings yet
- House Guest: Litereture Study + Case StudyDocument32 pagesHouse Guest: Litereture Study + Case StudyTARIQ TANSEEFNo ratings yet
- Accessible Guesthouses For Disable PersonDocument10 pagesAccessible Guesthouses For Disable PersonTARIQ TANSEEFNo ratings yet
- Tariq Assignment Unit 4Document8 pagesTariq Assignment Unit 4TARIQ TANSEEFNo ratings yet
- Equipment and Technology & TrendsDocument4 pagesEquipment and Technology & TrendsTARIQ TANSEEFNo ratings yet
- Exercise Oracle Forms 6i TrainingDocument5 pagesExercise Oracle Forms 6i TrainingFarooq Shahid100% (1)
- Let's Celebrate Diversity! : English: Level A2+Document10 pagesLet's Celebrate Diversity! : English: Level A2+JAIR DIEGO VIDAURRE QUISPENo ratings yet
- Psychosocial Support Activity Sheet No. 2Document2 pagesPsychosocial Support Activity Sheet No. 2Rizza De MesaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S096098221730708X MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S096098221730708X Mainrotinda bilekNo ratings yet
- Sspc-Ab 2Document3 pagesSspc-Ab 2HafidzManafNo ratings yet
- Kansas Academy of Science: Info/about/policies/terms - JSPDocument6 pagesKansas Academy of Science: Info/about/policies/terms - JSPKeily VilcarromeroNo ratings yet
- Parts List: JTR-MOL254/LBADocument74 pagesParts List: JTR-MOL254/LBAJoseNo ratings yet
- Lab6 Phase Locked LoopsDocument20 pagesLab6 Phase Locked Loopsuitce2011No ratings yet
- THE Cost OF Delay IN ConstructionDocument3 pagesTHE Cost OF Delay IN ConstructionJonathan WallaceNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Cable Lugs Crimping ToolsDocument6 pagesHydraulic Cable Lugs Crimping ToolsbaolifengNo ratings yet
- UPS Technical Data Sheet (MS-DD-SAP01-ELE-DS-0015 - Rev2)Document6 pagesUPS Technical Data Sheet (MS-DD-SAP01-ELE-DS-0015 - Rev2)Muhammad YusufNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 1.3Document38 pagesLesson Plan in Science 1.3Heidi Dalyagan DulnagonNo ratings yet
- Resistances, Voltages and Current in CircuitsDocument21 pagesResistances, Voltages and Current in CircuitsHisyamAl-MuhammadiNo ratings yet
- Dibrugarh AirportDocument30 pagesDibrugarh AirportRafikul RahemanNo ratings yet
- Pearl Brochure SinglePageScroll A4 New Claim Final 10 05.ENDocument8 pagesPearl Brochure SinglePageScroll A4 New Claim Final 10 05.ENlassanac85No ratings yet
- William James - PsychologistDocument5 pagesWilliam James - PsychologistCecilia SusaiNo ratings yet
- Ultra Dense NetworkDocument27 pagesUltra Dense NetworkYounesNo ratings yet
- 3 Generations of Human RightsDocument1 page3 Generations of Human RightsDzenan HakalovicNo ratings yet
- Creating A Sample BI Report in Oracle Cloud With Excel Template - TrinamixDocument1 pageCreating A Sample BI Report in Oracle Cloud With Excel Template - TrinamixIshaq Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- HR304Document3 pagesHR304Tanmoy MondalNo ratings yet
- Forex Survival GuideDocument22 pagesForex Survival Guidevikki2810No ratings yet
- Delayed Hospital Discharges of Older Patients A Systematic Review On Prevalence and CostsDocument12 pagesDelayed Hospital Discharges of Older Patients A Systematic Review On Prevalence and CostsGabriela ObonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management ScienceDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Management ScienceVenice Marie Arroyo100% (1)
- Power Quality Enhancement Using Custom Power DevicesDocument1 pagePower Quality Enhancement Using Custom Power DevicesankitNo ratings yet
- Yellow Illustrative Digital Education For Children InfographicDocument1 pageYellow Illustrative Digital Education For Children InfographicNur Azimah AzibNo ratings yet
- Zen and The ArtDocument3 pagesZen and The ArtMaria GonzálezNo ratings yet
- rx330 Gasoline 106Document2 pagesrx330 Gasoline 106Андрей СилаевNo ratings yet
- Volume AdministrationDocument264 pagesVolume AdministrationeviyipyipNo ratings yet