Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DBMS Lab Exam
DBMS Lab Exam
Uploaded by
Komal nadakuditiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- SQL Queries: 200+ Queries to Challenge you.From EverandSQL Queries: 200+ Queries to Challenge you.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- SQL Class NotesDocument54 pagesSQL Class Notesranjithgottimukkala100% (2)
- Cheat SheetDocument29 pagesCheat SheetRithihas ReddyNo ratings yet
- Rdbms Writing and PrintDocument115 pagesRdbms Writing and PrintsornammalchennappanNo ratings yet
- 2014 Batch GR DBMS LAB RECORDDocument76 pages2014 Batch GR DBMS LAB RECORDlalithaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Number - Experiment TitleDocument14 pagesExperiment Number - Experiment TitleApoorv AgrawalNo ratings yet
- CommandsDocument10 pagesCommands166CMYashvardhan ShindeNo ratings yet
- Day1 - Commands PL SQLDocument13 pagesDay1 - Commands PL SQLAmarender MattepallyNo ratings yet
- Forgotten T-SQL Cheat Sheet: L P O Select XML T: L DDocument1 pageForgotten T-SQL Cheat Sheet: L P O Select XML T: L DJivan Goyal100% (1)
- MySQL CheatsheetDocument4 pagesMySQL CheatsheetGiova RossiNo ratings yet
- Oracle QuestionsDocument87 pagesOracle QuestionsSatheessh KonthalaNo ratings yet
- Program 1Document13 pagesProgram 1Engineer of India [TIMELINE]No ratings yet
- Oracle 11gDocument3 pagesOracle 11gMatthew CoxNo ratings yet
- Delete:It's An DML Command Which Is Used For Deleting Particular Table in TheDocument6 pagesDelete:It's An DML Command Which Is Used For Deleting Particular Table in TheArya SumeetNo ratings yet
- SQL SyntaxDocument11 pagesSQL SyntaxBhargav BattinaNo ratings yet
- SQL PracticalDocument13 pagesSQL PracticalabhiroopnigoteNo ratings yet
- The CREATE TABLE Statement Is Used To Create A Table in A DatabaseDocument17 pagesThe CREATE TABLE Statement Is Used To Create A Table in A DatabaseRitu KapurNo ratings yet
- Complex SQLDocument127 pagesComplex SQLlokeshscribd186100% (6)
- SQL StatementsDocument11 pagesSQL StatementsVijji VijayNo ratings yet
- Create Table: Performing Operation On Table DataDocument6 pagesCreate Table: Performing Operation On Table DataQueen StyleNo ratings yet
- Types of SQL CommandsDocument56 pagesTypes of SQL CommandsAnant MoreNo ratings yet
- RDBMSDocument49 pagesRDBMSRameswar ReddyNo ratings yet
- It Is Object Level CommandDocument7 pagesIt Is Object Level CommandDileepNo ratings yet
- SQL LessonDocument56 pagesSQL LessonMusammat Samina100% (1)
- Complex SQL QueriesDocument127 pagesComplex SQL Queriessahu.aashish03No ratings yet
- Complex SQL QueriesDocument127 pagesComplex SQL QueriessachinyarNo ratings yet
- ?SQL Commands ?Document32 pages?SQL Commands ?Sanchit Kumar SNo ratings yet
- 10-Table Creation and Its Operations in Mysql: 1. Create CommandDocument2 pages10-Table Creation and Its Operations in Mysql: 1. Create CommandnaveenNo ratings yet
- DB2Document6 pagesDB2Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- CRUD - Fundamentals of SQL OperationDocument13 pagesCRUD - Fundamentals of SQL OperationtestuserNo ratings yet
- Adbms Front TRDocument40 pagesAdbms Front TRaamirmansoori9870No ratings yet
- sql1 StudentsDocument83 pagessql1 Studentsim cryptowala786No ratings yet
- EX - NO:1a Data Definition Languages (DDL) Commands of Base Tables and ViewsDocument44 pagesEX - NO:1a Data Definition Languages (DDL) Commands of Base Tables and Viewslalit thakur100% (1)
- SQL SyntaxDocument4 pagesSQL SyntaxmahasayrajeshNo ratings yet
- The SELECT TOP Clause Is Used To Specify The Number of Records To ReturnDocument5 pagesThe SELECT TOP Clause Is Used To Specify The Number of Records To ReturnManoharNo ratings yet
- SQL PLSQL Queries VasuDocument126 pagesSQL PLSQL Queries Vasuvasu.ind9255No ratings yet
- SQL BasicsDocument9 pagesSQL BasicsJose Antonio Diaz DiazNo ratings yet
- Dbms Lab ManualDocument58 pagesDbms Lab ManualmanjariteshNo ratings yet
- It DBMS RecDocument77 pagesIt DBMS RecLokeshkumar Ramasamy100% (1)
- SQLDocument19 pagesSQLramuNo ratings yet
- Find The Minimum or Maximum Value Across Several Columns?: Case When Col1 Col2 Then Col1 Else Col2 End As NewcolDocument9 pagesFind The Minimum or Maximum Value Across Several Columns?: Case When Col1 Col2 Then Col1 Else Col2 End As Newcolbalakrishna6No ratings yet
- Find The Minimum or Maximum Value Across Several Columns?: Case When Col1 Col2 Then Col1 Else Col2 End As NewcolDocument9 pagesFind The Minimum or Maximum Value Across Several Columns?: Case When Col1 Col2 Then Col1 Else Col2 End As Newcolgopal_amara6820No ratings yet
- Institute of Engineering and ManagementDocument30 pagesInstitute of Engineering and ManagementAbhishek DasNo ratings yet
- CS2258 DBMS ManualDocument57 pagesCS2258 DBMS ManualRaj Bharath RajuNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 & 5 - SQL Aggregate Fns - Joins - PLSQLDocument37 pagesUnit 4 & 5 - SQL Aggregate Fns - Joins - PLSQLSathish BabuNo ratings yet
- Data Base RevisionDocument1 pageData Base RevisionhectorvalinciNo ratings yet
- DBMS Lab Manual 2017Document69 pagesDBMS Lab Manual 2017Monica GaneshNo ratings yet
- Structured Query Language (SQL) : DatabaseDocument72 pagesStructured Query Language (SQL) : DatabaseM. Thirumala ReddyNo ratings yet
- Select Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - SQL ServerDocument3 pagesSelect Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - SQL ServerTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- Sqlite SummaryDocument3 pagesSqlite SummaryMalin ChhanNo ratings yet
- Rdbms Basic ProgramDocument56 pagesRdbms Basic Program19bca12 R.ANANDNo ratings yet
- D LabDocument153 pagesD LabManikandan MNo ratings yet
- 10 - Oracle PracticalDocument5 pages10 - Oracle PracticalAditya GogoiNo ratings yet
- Select Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - PostgresqlDocument3 pagesSelect Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - PostgresqlTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- SQL - Quick ReferenceDocument3 pagesSQL - Quick ReferenceBCONo ratings yet
- SQL Tips - DB2Document10 pagesSQL Tips - DB2anbucheliyanNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Logistics Flows 3: Discrete and Continuous Flows in 2D/3DFrom EverandModeling and Simulation of Logistics Flows 3: Discrete and Continuous Flows in 2D/3DNo ratings yet
- Qos Command Reference, Cisco Ios Release 15.2 (2) E (Catalyst 2960-X Switch)Document120 pagesQos Command Reference, Cisco Ios Release 15.2 (2) E (Catalyst 2960-X Switch)AHOUALAKOUNNo ratings yet
- First Boot LogDocument47 pagesFirst Boot LogAndreea NistorNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Queue Data Structure Using Array: 20CS2013 L-Data Structures and Algorithms LabDocument3 pagesImplementation of Queue Data Structure Using Array: 20CS2013 L-Data Structures and Algorithms LabELIZAROSHAN D URK20CS1116No ratings yet
- SoC SyllabusDocument2 pagesSoC SyllabuslokeshNo ratings yet
- Gava - (Lab-04) Time Complexity Analysis Using Big-OhDocument5 pagesGava - (Lab-04) Time Complexity Analysis Using Big-OhCh Salman AhsanNo ratings yet
- Sample Doc FATP Complete V - 1.6 EID MW Indosat ProjectDocument33 pagesSample Doc FATP Complete V - 1.6 EID MW Indosat ProjectMuh ramli RamliNo ratings yet
- Security of Hash Functions and MacsDocument9 pagesSecurity of Hash Functions and MacsKirti singh sikarwarNo ratings yet
- Smart GridsDocument2 pagesSmart GridsJaideep BollapragadaNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Zero Dynamics in Control SystemsDocument12 pagesNonlinear Zero Dynamics in Control SystemsAshik AhmedNo ratings yet
- SoftReqAnalysis OLDocument4 pagesSoftReqAnalysis OLFahim Hasan AlifNo ratings yet
- Rewrite 3d S Vs Sketchup - April 15thDocument3 pagesRewrite 3d S Vs Sketchup - April 15thDhyan AcademyNo ratings yet
- Apj Abdul Kalam Technological University: Answer All Questions, Each Carries 3 MarksDocument3 pagesApj Abdul Kalam Technological University: Answer All Questions, Each Carries 3 MarksJunaid M FaisalNo ratings yet
- Head First Mobile Web (100-277)Document178 pagesHead First Mobile Web (100-277)Plug InNo ratings yet
- Amd S1G2 Cpu: Vramx4 Gddr3 512MBDocument56 pagesAmd S1G2 Cpu: Vramx4 Gddr3 512MBحسن علي نوفلNo ratings yet
- Week6 Technical Support and Fundamentals WeekDocument6 pagesWeek6 Technical Support and Fundamentals WeekSakuntala AmpoluNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lesson 2Document7 pagesModule 2 Lesson 2Kobe DecenaNo ratings yet
- 3.1.2.6 Lab - Working With Text Files in The CLIDocument10 pages3.1.2.6 Lab - Working With Text Files in The CLIEkka XakraNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Summit HandbookDocument170 pagesEnhanced Summit HandbookOm Sai AyyappaNo ratings yet
- Critical Section Problem: CIS 450 Winter 2003Document26 pagesCritical Section Problem: CIS 450 Winter 2003rahul cNo ratings yet
- Distributed Computing - 2Document7 pagesDistributed Computing - 2Rahmat HidayatNo ratings yet
- APPLEDocument8 pagesAPPLEIsrael Sodium JobNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2020-1 - Ryan Absar - 1806187581Document2 pagesAssignment 2020-1 - Ryan Absar - 1806187581Ryan AbsarNo ratings yet
- COMPUTING FUNDAMENTALS Lab ManualsDocument42 pagesCOMPUTING FUNDAMENTALS Lab ManualsWajiha JavedNo ratings yet
- Data Sheets CC 2 3 0 3 - G - 0 1 A: Yanbu Strategic TanksDocument3 pagesData Sheets CC 2 3 0 3 - G - 0 1 A: Yanbu Strategic TanksBhavanishankar ShettyNo ratings yet
- Net Communication From Ie To PB Via Routing enDocument22 pagesNet Communication From Ie To PB Via Routing enarmazemdociso04No ratings yet
- Goal11 Casino 17Document3 pagesGoal11 Casino 17goal11phNo ratings yet
- Topic 4:the Art of Assembly Language Programming (08 Marks)Document9 pagesTopic 4:the Art of Assembly Language Programming (08 Marks)cwipediaNo ratings yet
- Data Structures CWDocument4 pagesData Structures CWamone nNo ratings yet
- Capstone 2 Module 2, Lesson 1Document5 pagesCapstone 2 Module 2, Lesson 1Rachelle NobsNo ratings yet
- Students List With Schedule For Elitmus Test On 2nd & 3rd March'2020Document35 pagesStudents List With Schedule For Elitmus Test On 2nd & 3rd March'2020SACHIN SINGHNo ratings yet
DBMS Lab Exam
DBMS Lab Exam
Uploaded by
Komal nadakuditiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DBMS Lab Exam
DBMS Lab Exam
Uploaded by
Komal nadakuditiCopyright:
Available Formats
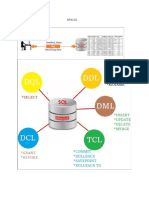
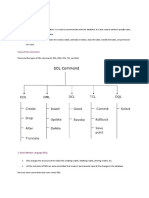
DDL(DATA DEFINITION LANGUAGE)
1) Create
create table tablename(col1 datatype(size) , col2
datatype(size)...);
2)ALter ADD
alter table tablename ADD columnname datatype(size); to
chech whether the col is add or not : Desc tablename ;
....ALTER DROP
alter table tablename drop column columnname ;
....ALTER RENAME
alter table tablename rename col oldname to new col name ;
....ALTER MODIFY
alter table tablename modify address varchar2(15) ;
3)RENAME
Rename old tablename to new_tablename ;
4)DROP
Drop table tablename ;
5) TRUNCATE
truncate table tablename ;
DML(DATA MANIPULATION LANGUAGE)
1) INSERT
Insert into tablename values(eno,'ename',sal);
2) DELETE
Delete from tablename where columnname='value'; AND Delete table
tablename ;
example:Delete from emp where eno=2;
3) UPDATE
Update tablename set columnname=value;
example:Update emp set salary=6000 where eno=3;
4) SELECT
* indicates all the records in the table
Example: Select * from emp where sal>3000 ;
TCL(TRANSACTION CONTROL LANGUAGE)
1) COMMIT : IT PERMANENTLY STORES THE DATA IN A DATABASE
syntax : commit
2) SAVEPOINT :
syntax : savepoint savepoint name ;
3) ROLLBACK :
syntax : Rollback
DCL(DATA CONTROL LANGUAGE)
CREATING A USER IN DATABASE
.....user created.....
Grant access priviliges to username ;
...... Grant succeded......
1) GRANT
Grant insert , delete privilege to username ;
Grant all access privileges to username ;
2) REVOKE
Revoke delete privileges ;
Revoke username ;
SET OPERATORS
1)ARTHEMETIC OPERATORS : + , - , * , % , / . syntax : select 2 + 3 ;
2)LOGICAL OPERATORS : AND , NOT , OR . syntax : select eno , dept from emp
where sal > 3000 whose dept = 'CSE' AND/OR/NOT 'ECE' ;
3)CONDITIONAL OPERATORS: > , < , >= , <= , == , != , = . syntax : select
eno , dept from emp where sal > 3000 whose dept = 'CSE' >/</>=/<=/==/!=/= 'ECE' ;
4)BITWISE OPERATRS: & , ! , && , !! , ^ . syntax : select a & b ;
5)BOOLEAN OPERATORS: TRUE , FALSE .
SQL OPERATORS
1) UNION select * from emp union select * from emp1;
2) UNION ALL select * from emp union all select * from emp1 ;
3) INTERSECT select * from emp intersect selct * from emp1 ;
4) MINUS select * from emp minus select * from emp 1 ;
JOINS
1) INNER JOIN select table1.col1 , table2.col1,.....
from table1
inner join table2 on table1.matching_col=table2.matching_col ;
2) LEFT JOIN select table1.col1 , table2.col1,.....
from table1
left join table2 on table1.matching_col=table2.matching_col ;
3) RIGHT JOIN select table1.col1 , table2.col1,.....
from table1
right join table2 on table1.matching_col=table2.matching_col ;
4) FULL JOIN select table1.col1 , table2.col1,.....
from table1
full join table2 on table1.matching_col=table2.matching_col ;
VIEWS
1) CREATING VIEW FOR ONE TABLE create view viewname as
select col1 , col1 from tablename
where condition ;
2) CREATING VIEW FOR TWO TABLES create view viewname as
select tablename1.col1 , tablename1.col2,......
tablename2.col1 , tablename2.col2,.....
from tablename1 , tablename2
where condition ;
You might also like
- SQL Queries: 200+ Queries to Challenge you.From EverandSQL Queries: 200+ Queries to Challenge you.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- SQL Class NotesDocument54 pagesSQL Class Notesranjithgottimukkala100% (2)
- Cheat SheetDocument29 pagesCheat SheetRithihas ReddyNo ratings yet
- Rdbms Writing and PrintDocument115 pagesRdbms Writing and PrintsornammalchennappanNo ratings yet
- 2014 Batch GR DBMS LAB RECORDDocument76 pages2014 Batch GR DBMS LAB RECORDlalithaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Number - Experiment TitleDocument14 pagesExperiment Number - Experiment TitleApoorv AgrawalNo ratings yet
- CommandsDocument10 pagesCommands166CMYashvardhan ShindeNo ratings yet
- Day1 - Commands PL SQLDocument13 pagesDay1 - Commands PL SQLAmarender MattepallyNo ratings yet
- Forgotten T-SQL Cheat Sheet: L P O Select XML T: L DDocument1 pageForgotten T-SQL Cheat Sheet: L P O Select XML T: L DJivan Goyal100% (1)
- MySQL CheatsheetDocument4 pagesMySQL CheatsheetGiova RossiNo ratings yet
- Oracle QuestionsDocument87 pagesOracle QuestionsSatheessh KonthalaNo ratings yet
- Program 1Document13 pagesProgram 1Engineer of India [TIMELINE]No ratings yet
- Oracle 11gDocument3 pagesOracle 11gMatthew CoxNo ratings yet
- Delete:It's An DML Command Which Is Used For Deleting Particular Table in TheDocument6 pagesDelete:It's An DML Command Which Is Used For Deleting Particular Table in TheArya SumeetNo ratings yet
- SQL SyntaxDocument11 pagesSQL SyntaxBhargav BattinaNo ratings yet
- SQL PracticalDocument13 pagesSQL PracticalabhiroopnigoteNo ratings yet
- The CREATE TABLE Statement Is Used To Create A Table in A DatabaseDocument17 pagesThe CREATE TABLE Statement Is Used To Create A Table in A DatabaseRitu KapurNo ratings yet
- Complex SQLDocument127 pagesComplex SQLlokeshscribd186100% (6)
- SQL StatementsDocument11 pagesSQL StatementsVijji VijayNo ratings yet
- Create Table: Performing Operation On Table DataDocument6 pagesCreate Table: Performing Operation On Table DataQueen StyleNo ratings yet
- Types of SQL CommandsDocument56 pagesTypes of SQL CommandsAnant MoreNo ratings yet
- RDBMSDocument49 pagesRDBMSRameswar ReddyNo ratings yet
- It Is Object Level CommandDocument7 pagesIt Is Object Level CommandDileepNo ratings yet
- SQL LessonDocument56 pagesSQL LessonMusammat Samina100% (1)
- Complex SQL QueriesDocument127 pagesComplex SQL Queriessahu.aashish03No ratings yet
- Complex SQL QueriesDocument127 pagesComplex SQL QueriessachinyarNo ratings yet
- ?SQL Commands ?Document32 pages?SQL Commands ?Sanchit Kumar SNo ratings yet
- 10-Table Creation and Its Operations in Mysql: 1. Create CommandDocument2 pages10-Table Creation and Its Operations in Mysql: 1. Create CommandnaveenNo ratings yet
- DB2Document6 pagesDB2Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- CRUD - Fundamentals of SQL OperationDocument13 pagesCRUD - Fundamentals of SQL OperationtestuserNo ratings yet
- Adbms Front TRDocument40 pagesAdbms Front TRaamirmansoori9870No ratings yet
- sql1 StudentsDocument83 pagessql1 Studentsim cryptowala786No ratings yet
- EX - NO:1a Data Definition Languages (DDL) Commands of Base Tables and ViewsDocument44 pagesEX - NO:1a Data Definition Languages (DDL) Commands of Base Tables and Viewslalit thakur100% (1)
- SQL SyntaxDocument4 pagesSQL SyntaxmahasayrajeshNo ratings yet
- The SELECT TOP Clause Is Used To Specify The Number of Records To ReturnDocument5 pagesThe SELECT TOP Clause Is Used To Specify The Number of Records To ReturnManoharNo ratings yet
- SQL PLSQL Queries VasuDocument126 pagesSQL PLSQL Queries Vasuvasu.ind9255No ratings yet
- SQL BasicsDocument9 pagesSQL BasicsJose Antonio Diaz DiazNo ratings yet
- Dbms Lab ManualDocument58 pagesDbms Lab ManualmanjariteshNo ratings yet
- It DBMS RecDocument77 pagesIt DBMS RecLokeshkumar Ramasamy100% (1)
- SQLDocument19 pagesSQLramuNo ratings yet
- Find The Minimum or Maximum Value Across Several Columns?: Case When Col1 Col2 Then Col1 Else Col2 End As NewcolDocument9 pagesFind The Minimum or Maximum Value Across Several Columns?: Case When Col1 Col2 Then Col1 Else Col2 End As Newcolbalakrishna6No ratings yet
- Find The Minimum or Maximum Value Across Several Columns?: Case When Col1 Col2 Then Col1 Else Col2 End As NewcolDocument9 pagesFind The Minimum or Maximum Value Across Several Columns?: Case When Col1 Col2 Then Col1 Else Col2 End As Newcolgopal_amara6820No ratings yet
- Institute of Engineering and ManagementDocument30 pagesInstitute of Engineering and ManagementAbhishek DasNo ratings yet
- CS2258 DBMS ManualDocument57 pagesCS2258 DBMS ManualRaj Bharath RajuNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 & 5 - SQL Aggregate Fns - Joins - PLSQLDocument37 pagesUnit 4 & 5 - SQL Aggregate Fns - Joins - PLSQLSathish BabuNo ratings yet
- Data Base RevisionDocument1 pageData Base RevisionhectorvalinciNo ratings yet
- DBMS Lab Manual 2017Document69 pagesDBMS Lab Manual 2017Monica GaneshNo ratings yet
- Structured Query Language (SQL) : DatabaseDocument72 pagesStructured Query Language (SQL) : DatabaseM. Thirumala ReddyNo ratings yet
- Select Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - SQL ServerDocument3 pagesSelect Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - SQL ServerTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- Sqlite SummaryDocument3 pagesSqlite SummaryMalin ChhanNo ratings yet
- Rdbms Basic ProgramDocument56 pagesRdbms Basic Program19bca12 R.ANANDNo ratings yet
- D LabDocument153 pagesD LabManikandan MNo ratings yet
- 10 - Oracle PracticalDocument5 pages10 - Oracle PracticalAditya GogoiNo ratings yet
- Select Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - PostgresqlDocument3 pagesSelect Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - PostgresqlTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- SQL - Quick ReferenceDocument3 pagesSQL - Quick ReferenceBCONo ratings yet
- SQL Tips - DB2Document10 pagesSQL Tips - DB2anbucheliyanNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Logistics Flows 3: Discrete and Continuous Flows in 2D/3DFrom EverandModeling and Simulation of Logistics Flows 3: Discrete and Continuous Flows in 2D/3DNo ratings yet
- Qos Command Reference, Cisco Ios Release 15.2 (2) E (Catalyst 2960-X Switch)Document120 pagesQos Command Reference, Cisco Ios Release 15.2 (2) E (Catalyst 2960-X Switch)AHOUALAKOUNNo ratings yet
- First Boot LogDocument47 pagesFirst Boot LogAndreea NistorNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Queue Data Structure Using Array: 20CS2013 L-Data Structures and Algorithms LabDocument3 pagesImplementation of Queue Data Structure Using Array: 20CS2013 L-Data Structures and Algorithms LabELIZAROSHAN D URK20CS1116No ratings yet
- SoC SyllabusDocument2 pagesSoC SyllabuslokeshNo ratings yet
- Gava - (Lab-04) Time Complexity Analysis Using Big-OhDocument5 pagesGava - (Lab-04) Time Complexity Analysis Using Big-OhCh Salman AhsanNo ratings yet
- Sample Doc FATP Complete V - 1.6 EID MW Indosat ProjectDocument33 pagesSample Doc FATP Complete V - 1.6 EID MW Indosat ProjectMuh ramli RamliNo ratings yet
- Security of Hash Functions and MacsDocument9 pagesSecurity of Hash Functions and MacsKirti singh sikarwarNo ratings yet
- Smart GridsDocument2 pagesSmart GridsJaideep BollapragadaNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Zero Dynamics in Control SystemsDocument12 pagesNonlinear Zero Dynamics in Control SystemsAshik AhmedNo ratings yet
- SoftReqAnalysis OLDocument4 pagesSoftReqAnalysis OLFahim Hasan AlifNo ratings yet
- Rewrite 3d S Vs Sketchup - April 15thDocument3 pagesRewrite 3d S Vs Sketchup - April 15thDhyan AcademyNo ratings yet
- Apj Abdul Kalam Technological University: Answer All Questions, Each Carries 3 MarksDocument3 pagesApj Abdul Kalam Technological University: Answer All Questions, Each Carries 3 MarksJunaid M FaisalNo ratings yet
- Head First Mobile Web (100-277)Document178 pagesHead First Mobile Web (100-277)Plug InNo ratings yet
- Amd S1G2 Cpu: Vramx4 Gddr3 512MBDocument56 pagesAmd S1G2 Cpu: Vramx4 Gddr3 512MBحسن علي نوفلNo ratings yet
- Week6 Technical Support and Fundamentals WeekDocument6 pagesWeek6 Technical Support and Fundamentals WeekSakuntala AmpoluNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lesson 2Document7 pagesModule 2 Lesson 2Kobe DecenaNo ratings yet
- 3.1.2.6 Lab - Working With Text Files in The CLIDocument10 pages3.1.2.6 Lab - Working With Text Files in The CLIEkka XakraNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Summit HandbookDocument170 pagesEnhanced Summit HandbookOm Sai AyyappaNo ratings yet
- Critical Section Problem: CIS 450 Winter 2003Document26 pagesCritical Section Problem: CIS 450 Winter 2003rahul cNo ratings yet
- Distributed Computing - 2Document7 pagesDistributed Computing - 2Rahmat HidayatNo ratings yet
- APPLEDocument8 pagesAPPLEIsrael Sodium JobNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2020-1 - Ryan Absar - 1806187581Document2 pagesAssignment 2020-1 - Ryan Absar - 1806187581Ryan AbsarNo ratings yet
- COMPUTING FUNDAMENTALS Lab ManualsDocument42 pagesCOMPUTING FUNDAMENTALS Lab ManualsWajiha JavedNo ratings yet
- Data Sheets CC 2 3 0 3 - G - 0 1 A: Yanbu Strategic TanksDocument3 pagesData Sheets CC 2 3 0 3 - G - 0 1 A: Yanbu Strategic TanksBhavanishankar ShettyNo ratings yet
- Net Communication From Ie To PB Via Routing enDocument22 pagesNet Communication From Ie To PB Via Routing enarmazemdociso04No ratings yet
- Goal11 Casino 17Document3 pagesGoal11 Casino 17goal11phNo ratings yet
- Topic 4:the Art of Assembly Language Programming (08 Marks)Document9 pagesTopic 4:the Art of Assembly Language Programming (08 Marks)cwipediaNo ratings yet
- Data Structures CWDocument4 pagesData Structures CWamone nNo ratings yet
- Capstone 2 Module 2, Lesson 1Document5 pagesCapstone 2 Module 2, Lesson 1Rachelle NobsNo ratings yet
- Students List With Schedule For Elitmus Test On 2nd & 3rd March'2020Document35 pagesStudents List With Schedule For Elitmus Test On 2nd & 3rd March'2020SACHIN SINGHNo ratings yet