Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Measures of Dispersion: Chapter 2 / Example 3
Measures of Dispersion: Chapter 2 / Example 3
Uploaded by
Naif MeshaalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Measures of Dispersion: Chapter 2 / Example 3
Measures of Dispersion: Chapter 2 / Example 3
Uploaded by
Naif MeshaalCopyright:
Available Formats
GDC skills: TI-84 Plus C
Chapter 2 / Example 3
Measures of dispersion
The number of days of precipitation in January in London for 2008–2017 is given in the
table:
Year 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
Days of
19 16 21 21 13 21 30 26 21 15
precipitation
(data from weatherline.co.uk)
a Write down the range of the number of days of precipitation in January in London
for these years.
b Calculate the interquartile range of the number of days of precipitation in January
in London for these years.
c Find the standard deviation of the number of days of precipitation in January in
London for these years.
d Find whether the 30 cm precipitation in January 2014 is an outlier.
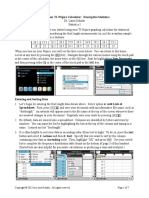
Press … 1:Edit and press Í
Type 19, 16, 21, … 15 in the first column.
Press Í or † after each number to move to the next cell.
Note: If the list contains other numbers, you can clear it by pressing
… 4:ClrList and press Í. The home screen displays ClrList. Press
y À d and press Í. Press … 1:Edit and press Í to return
to the table.
To calculate a statistical summary of the data
Press … and ~ to access the CALC menu.
Select 1:1-Var Stats and press Í.
Leave FreqList empty.
Navigate to Calculate and press Í.
Scroll down using †.
The table of statistics shows that the minimum is 13 and the
maximum is 30.
© Oxford University Press 2019 1
GDC skills: TI-84 Plus C
Chapter 2 / Example 3
Measures of dispersion
Press y 5 to enter the home screen.
Press ½ 5:Statistics…
The statistics that you calculated earlier are all stored as
variables.
To calculate the range Use Range = maxX − minX.
Select 8:maxX and 9:minX from the list to enter the calculation.
The range is 17.
Press ½ 5:Statistics… and use ~ to navigate to PTS.
The statistics that you calculated earlier are all stored as
variables.
To calculate the interquartile range Use IQR = Q3 − Q1.
Select 9:Q3 and 7:Q1 from the list to enter the calculation.
The inter quartile range is 5.
Press ½ 5:Statistics… and select 4:σx, the standard
deviation, from the list of stored variables.
The standard deviation is 4.80 days.
To determine whether 30 is an outlier use Q3 + 1.5(IQR)
Select Q3 and Q1 from the list to enter the calculation
Q3 Ã 1.5 ( Q₃ j Q₁ ).
30 < 28.5, so 30 is an outlier.
© Oxford University Press 2019 2
You might also like
- AP Psych Review Videos Unit 1Document12 pagesAP Psych Review Videos Unit 1ajahn50% (2)
- Measures of Dispersion: Chapter 2 / Example 3Document3 pagesMeasures of Dispersion: Chapter 2 / Example 3Anoop SreedharNo ratings yet
- Bks MaaHL 0502 gdc05 Xxti84Document4 pagesBks MaaHL 0502 gdc05 Xxti845546152rishabh9No ratings yet
- Learning Intentions:: by The End of This Chapter I Will Be Able ToDocument45 pagesLearning Intentions:: by The End of This Chapter I Will Be Able ToValeriaNo ratings yet
- Using The TI 84 For StatisticsDocument2 pagesUsing The TI 84 For StatisticsreshamegaNo ratings yet
- Casio Classpad ManualDocument57 pagesCasio Classpad ManualZhiyong HuangNo ratings yet
- Document For IELTS WritingDocument28 pagesDocument For IELTS WritingtranNo ratings yet
- Scientific Graphing LabDocument13 pagesScientific Graphing LabAndreaNo ratings yet
- Document For IELTS WritingDocument17 pagesDocument For IELTS WritingtranNo ratings yet
- Cima Online Calculator ManualDocument44 pagesCima Online Calculator ManualWalakulage Dilan Urban PereraNo ratings yet
- Basics Stats Ti NspireDocument7 pagesBasics Stats Ti NspirePanagiotis SotiropoulosNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 1 SimonDocument31 pagesIELTS Writing Task 1 SimonDat Nguyen ThanhNo ratings yet
- GC Skills For H2 StatisticsDocument33 pagesGC Skills For H2 StatisticsjuliaongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Time Series Analysis - LecturerDocument38 pagesLecture 3 - Time Series Analysis - LecturerSubmission Portal100% (1)
- Daa2cntns 014 02 PDFDocument3 pagesDaa2cntns 014 02 PDFValine Cysteine MethionineNo ratings yet
- Regress 83 ADocument5 pagesRegress 83 AkNo ratings yet
- It Lab ReportDocument37 pagesIt Lab Reportsharawatchhaya27No ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency: Chapter 2 / Example 2Document2 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency: Chapter 2 / Example 2Anoop SreedharNo ratings yet
- Ti 84 Help Manual: Index Topic Page NumberDocument33 pagesTi 84 Help Manual: Index Topic Page Numberjoshua0047No ratings yet
- Using SDAM in Regional Analysis: Figure 1: Insertion of A New ColumnDocument3 pagesUsing SDAM in Regional Analysis: Figure 1: Insertion of A New ColumnMas Inoenk Nurdin SulistiyonoNo ratings yet
- Investigation07 Task enDocument5 pagesInvestigation07 Task enreshamegaNo ratings yet
- Circumference and DiameterDocument2 pagesCircumference and Diameterapi-256464200No ratings yet
- Quick Reference Sheeta2Document1 pageQuick Reference Sheeta2api-265200443No ratings yet
- Instructions For Using Your Calculator TI 82, 83 and 84: Max Q Med Q Min S XDocument1 pageInstructions For Using Your Calculator TI 82, 83 and 84: Max Q Med Q Min S Xbeachgirl123No ratings yet
- File 001Document27 pagesFile 001saifsaad106226No ratings yet
- De Kiem Tra 11 Lan 2Document25 pagesDe Kiem Tra 11 Lan 2Quỳnh NhiNo ratings yet
- Stats Project Tech InstructionsDocument9 pagesStats Project Tech Instructionsk8nowakNo ratings yet
- Deciles and PercentilesDocument52 pagesDeciles and PercentilesShaik Mujeeb RahamanNo ratings yet
- Guide For Texas Instruments TI-83, TI-83 Plus, or TI-84 Plus Graphing CalculatorDocument114 pagesGuide For Texas Instruments TI-83, TI-83 Plus, or TI-84 Plus Graphing CalculatorRicky KingNo ratings yet
- Measure of Central TendencyDocument18 pagesMeasure of Central Tendencyanonymous 009No ratings yet
- Tutorial 8Document1 pageTutorial 8priyasivagsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Data Visualisation - LecturerDocument43 pagesLecture 7 - Data Visualisation - LecturerSubmission PortalNo ratings yet
- Econ3150 v12 Note01 PDFDocument6 pagesEcon3150 v12 Note01 PDFRitaSilabanNo ratings yet
- Essential Spreadsheets Exercises PDFDocument31 pagesEssential Spreadsheets Exercises PDFUlii PntNo ratings yet
- Quantitative TechniqueDocument23 pagesQuantitative Techniqueapi-3805289No ratings yet
- Unemployment RateDocument11 pagesUnemployment RateLuis LeeNo ratings yet
- Scatter Plot - Correlation - and Regression On The TI-83-84Document5 pagesScatter Plot - Correlation - and Regression On The TI-83-84AlexNo ratings yet
- ESTADISTICADocument115 pagesESTADISTICAVerónica NaviaNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Plotting Data, Statistical Variables, and Matrix EditorDocument8 pagesExercises: Plotting Data, Statistical Variables, and Matrix Editorapi-297287463No ratings yet
- Technical Note On Growth AccountingDocument4 pagesTechnical Note On Growth Accountingapi-358990925No ratings yet
- Using Excel To Create An X-Bar & R ChartDocument1 pageUsing Excel To Create An X-Bar & R Chartankur panwarNo ratings yet
- Regression and CorrelationDocument8 pagesRegression and CorrelationdmosleyNo ratings yet
- BFF3121 Lecture 5 Assignment 3 Benchmarks Student WorkDocument3 pagesBFF3121 Lecture 5 Assignment 3 Benchmarks Student WorkAshton LeeNo ratings yet
- Anscombe S Quartet: HP Prime Graphing CalculatorDocument3 pagesAnscombe S Quartet: HP Prime Graphing Calculatorjcbp9No ratings yet
- Agric CalculationsDocument16 pagesAgric CalculationsPortia ShilengeNo ratings yet
- Population ChangeDocument19 pagesPopulation ChangeAlya Putri KhairaniNo ratings yet
- TI30XProMultiView Guidebook EN PDFDocument79 pagesTI30XProMultiView Guidebook EN PDFSteven NotosNo ratings yet
- TI30XMVS Guidebook Texas InstrumentsDocument44 pagesTI30XMVS Guidebook Texas InstrumentsLizeth Paola Lopez PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Calc Lesson Instruct v7Document5 pagesCalc Lesson Instruct v7jiashengroxNo ratings yet
- IELTS Task 1 (Promi)Document34 pagesIELTS Task 1 (Promi)MD Sheikh SadiNo ratings yet
- Representing DataDocument5 pagesRepresenting DataLove BordamonteNo ratings yet
- Excel ClimatogramDocument3 pagesExcel ClimatogramAnonymous ZADhuLzS4No ratings yet
- 05 Casio Quickstartguide Fx-991ex Fx-570ex StatisticsDocument5 pages05 Casio Quickstartguide Fx-991ex Fx-570ex StatisticsAdrian ToribioNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 1 SimonDocument28 pagesIELTS Writing Task 1 SimonCarol Tường ViNo ratings yet
- Statek 1Document31 pagesStatek 1MiftaNo ratings yet
- Time Series Practice HWDocument3 pagesTime Series Practice HWLuisSanchezNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics: A Simplified Detailed Edition for Students Understanding Fundamentals of MacroeconomicsFrom EverandMacro Economics: A Simplified Detailed Edition for Students Understanding Fundamentals of MacroeconomicsNo ratings yet
- The Practically Cheating Statistics Handbook TI-83 Companion GuideFrom EverandThe Practically Cheating Statistics Handbook TI-83 Companion GuideRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Climate Finance as an Instrument to Promote the Green Growth in Developing CountriesFrom EverandClimate Finance as an Instrument to Promote the Green Growth in Developing CountriesNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Acid BaseDocument4 pagesLab Report Acid Basexuni34No ratings yet
- College of St. John - Roxas: de La Salle SupervisedDocument3 pagesCollege of St. John - Roxas: de La Salle SupervisedLina Marie BesaNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment - AS GRP 5 PDFDocument37 pagesGroup Assignment - AS GRP 5 PDFprabu2125No ratings yet
- Reflections ChaptersDocument10 pagesReflections ChaptersRia LopezNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Khat Chewing by TelakeDocument43 pagesThesis On Khat Chewing by TelakeTelake Azale83% (6)
- ANOVADocument57 pagesANOVAMegha OmshreeNo ratings yet
- Project On Student SatisfactionDocument71 pagesProject On Student SatisfactionAngel RituNo ratings yet
- Leveling Worked ExamplesDocument2 pagesLeveling Worked ExamplesKalasekar M SwamyNo ratings yet
- Dykstra Steinbrenner 2015 StudentengagementpreprintDocument51 pagesDykstra Steinbrenner 2015 StudentengagementpreprintHannah EnanodNo ratings yet
- AnnexDocument340 pagesAnnexChittaranjan BhoiNo ratings yet
- Edinburgh University Dissertation GuidelinesDocument8 pagesEdinburgh University Dissertation GuidelinesWhereToBuyPapersLittleRock100% (1)
- Mei Structured MathematicsDocument4 pagesMei Structured Mathematicskaran79No ratings yet
- Teen Stress - ExercisesDocument4 pagesTeen Stress - ExercisesYến PhạmNo ratings yet
- Fully Corrected Chapters 4 & 5Document21 pagesFully Corrected Chapters 4 & 5Iyobosa OmoregieNo ratings yet
- AR3a Data Mining Applications in Accounting ADocument27 pagesAR3a Data Mining Applications in Accounting AAyuu RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- MBA - Project Report GuidelinesDocument11 pagesMBA - Project Report GuidelinesAkansha SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3 Is Module 7Document8 pages3 Is Module 7Hiezeyl Ymana GuntangNo ratings yet
- Practice Tests (1-4) and Final Exams - Introductory StatisticsDocument111 pagesPractice Tests (1-4) and Final Exams - Introductory StatisticsQuỳnh Như Trần100% (1)
- Methods and Tools of Data CollectionDocument25 pagesMethods and Tools of Data CollectionPravedNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Having A Relationship To The Academic Performance of CFAD StudentsDocument4 pagesThe Effects of Having A Relationship To The Academic Performance of CFAD StudentsAnonymous THm8WD6No ratings yet
- How Do Customers Respond To The Hotel - 2019 - IntDocument11 pagesHow Do Customers Respond To The Hotel - 2019 - Intjohanes purbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3Dañella Jane Baisa0% (1)
- DOC-20240425-WA0000. NewDocument29 pagesDOC-20240425-WA0000. NewMayank SainiNo ratings yet
- AKS Arch CV 092413Document4 pagesAKS Arch CV 092413Angel StueweNo ratings yet
- Performance Measurement of Cooperative UnionDocument5 pagesPerformance Measurement of Cooperative UnionMBA SAWLACAMPUS2014No ratings yet
- Metrics and Operators On (1,1) Tensor Bundle 25 Some Notes On Lifts of The Modified Riemannian Extension Cotangent Bundle 26 Some Notes On Metalic PDFDocument300 pagesMetrics and Operators On (1,1) Tensor Bundle 25 Some Notes On Lifts of The Modified Riemannian Extension Cotangent Bundle 26 Some Notes On Metalic PDFOzgun KosanerNo ratings yet
- Unit V (MBA 206)Document45 pagesUnit V (MBA 206)Gunjan AwalNo ratings yet
- M - 1.6 - Training EvaluationDocument15 pagesM - 1.6 - Training EvaluationLGED ManikganjNo ratings yet
- Impact of Covid On Tourism - Factors Impacting The Tourism Industry in IndiaDocument25 pagesImpact of Covid On Tourism - Factors Impacting The Tourism Industry in IndiaHari ShankarNo ratings yet