Professional Documents
Culture Documents
101 DNS+Policy
101 DNS+Policy
Uploaded by
Ashraf SaeedCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 27-Security Policy ConceptsDocument12 pages27-Security Policy Conceptssatyam sumanNo ratings yet
- Cisco ASA V Palo Alto ComparisonDocument1 pageCisco ASA V Palo Alto ComparisonProdec_Networks100% (1)
- Big Data Demystified - How To Use Big Data, Data Science and AI To Make Better Business Decisions and Gain Competitive AdvantageDocument196 pagesBig Data Demystified - How To Use Big Data, Data Science and AI To Make Better Business Decisions and Gain Competitive AdvantageAshfaque Reza100% (4)
- FirewallDocument10 pagesFirewallAris SuryatnoNo ratings yet
- Genband Q21 SBC: High Performance, High Density Session Border ControllerDocument4 pagesGenband Q21 SBC: High Performance, High Density Session Border Controllerkaz7878No ratings yet
- John Wiley & SonsDocument168 pagesJohn Wiley & SonsMohammed Nasser20% (10)
- Palo Alto NetworksDocument28 pagesPalo Alto NetworksLavi Chhabra100% (3)
- Network Security1Document7 pagesNetwork Security1upadhyay kulbhushanNo ratings yet
- Fortigate Firewall Policies:: Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail:, Mobile: 056 430 3717Document9 pagesFortigate Firewall Policies:: Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail:, Mobile: 056 430 3717AyanNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuestionsSrinivas Naidu T SNo ratings yet
- Sophos - Considerations For Deploying Sophos Firewall in Common ScenariosDocument22 pagesSophos - Considerations For Deploying Sophos Firewall in Common ScenariosMiguel António ManuelNo ratings yet
- Alteon ITM TrainingDocument39 pagesAlteon ITM Training李謝揚No ratings yet
- How Information Flows On NetworksDocument3 pagesHow Information Flows On NetworksAdi SuryaNo ratings yet
- Palo Alto Networks 101 - App-ID and User-ID Best PracticesDocument5 pagesPalo Alto Networks 101 - App-ID and User-ID Best PracticesRyanb378No ratings yet
- FirewallDocument2 pagesFirewallsanamanand3300No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Firewalls and The Firewall Selection ProcessDocument10 pagesAn Introduction To Firewalls and The Firewall Selection ProcessS SagarNo ratings yet
- Integrated URL Filtering: Content-IDDocument2 pagesIntegrated URL Filtering: Content-IDErivelton SouzaNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument161 pagesDownloadSarayut SineninetyNo ratings yet
- Firewall Rulebase Analysis ToolDocument8 pagesFirewall Rulebase Analysis ToolShubham MittalNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv:: Security Measurement StrategiesDocument43 pagesUnit Iv:: Security Measurement Strategiesarnav_mailboxNo ratings yet
- What Is FirewallDocument4 pagesWhat Is Firewallahmedtehseem0062No ratings yet
- Abstract On Network Security and CryptographyDocument13 pagesAbstract On Network Security and Cryptographytharun89% (9)
- FW2030 19.0v1 Configuring TLS Decryption On Sophos FirewallDocument14 pagesFW2030 19.0v1 Configuring TLS Decryption On Sophos FirewallVanderwaal PromolykoNo ratings yet
- FW2030 19.0v1 Configuring TLS Decryption On Sophos FirewallDocument14 pagesFW2030 19.0v1 Configuring TLS Decryption On Sophos FirewallAndré MouraNo ratings yet
- Secure Wireless Firewall Integration: Role of The FirewallDocument54 pagesSecure Wireless Firewall Integration: Role of The FirewallFlavio MirandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Security PolicyDocument32 pagesChapter 5 - Security PolicyJosé Miguel Melgar RojasNo ratings yet
- Cap9 Access Control ListsDocument87 pagesCap9 Access Control ListsDobre DanielNo ratings yet
- App-Id:: Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail:, Mobile: 056 430 3717Document16 pagesApp-Id:: Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail:, Mobile: 056 430 3717Crypto DudeNo ratings yet
- Tut04-Access Control UpdatedDocument16 pagesTut04-Access Control UpdatedGiang Trần ThịNo ratings yet
- Network ACLsDocument99 pagesNetwork ACLsjanerie71No ratings yet
- INformation Security 5Document11 pagesINformation Security 5Shantanu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Securing Networks: Access Control List (ACL) ConceptsDocument4 pagesSecuring Networks: Access Control List (ACL) ConceptsAbdul Sami MohammedNo ratings yet
- Faq FirewallDocument13 pagesFaq FirewallTaoufic Ben HcineNo ratings yet
- Case Study On "Firewall"Document8 pagesCase Study On "Firewall"Lokesh ShindeNo ratings yet
- Howto Config FW Policies Ruleshowto Config FW Policies RulesDocument6 pagesHowto Config FW Policies Ruleshowto Config FW Policies RulesBaBu BiNo ratings yet
- Ofcom Site Blocking Report With Redactions RemovedDocument56 pagesOfcom Site Blocking Report With Redactions RemovedTJ McIntyreNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Firewall Types: National Security AgencyDocument2 pagesEnterprise Firewall Types: National Security AgencyFelipe Ramirez HerreraNo ratings yet
- Basic Firewall PolicyDocument6 pagesBasic Firewall PolicyhenriquecongoNo ratings yet
- Untitled 2Document13 pagesUntitled 2sheraz salimNo ratings yet
- Hillario Zidan - 00000050745 - IF673 - A - UTSDocument4 pagesHillario Zidan - 00000050745 - IF673 - A - UTSHillario ZidanNo ratings yet
- SL Assignment No 1 - AY2023-24Document5 pagesSL Assignment No 1 - AY2023-24only.moviewebseries123No ratings yet
- Access Controls Tutorial: Hoang Thi Kieu Hoa Faculty of Information Technology, Hanoi UniversityDocument14 pagesAccess Controls Tutorial: Hoang Thi Kieu Hoa Faculty of Information Technology, Hanoi UniversityOanh Đoàn ThịNo ratings yet
- Blocking TOR BrowserDocument8 pagesBlocking TOR BrowserpoojaNo ratings yet
- App IDsection 8Document26 pagesApp IDsection 8satya28No ratings yet
- Firewall: Name: Sumit Sharma Register no.:RA1611003010777Document9 pagesFirewall: Name: Sumit Sharma Register no.:RA1611003010777Sumit SharmaNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument3 pagesDocxMOUMITA BHATTACHARJEE0% (1)
- Best Practices DecryptionDocument5 pagesBest Practices DecryptionPartha DashNo ratings yet
- A Firewall Is A Set of Related ProgramsDocument11 pagesA Firewall Is A Set of Related ProgramsDeep RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Networking Basics and TerminologyDocument25 pagesNetworking Basics and Terminologyنكت مضحكةNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint FirewallDocument14 pagesCheckpoint FirewallJonnalagadda Harshavardhan100% (2)
- Interview Preparation For Cyber SecurityDocument114 pagesInterview Preparation For Cyber SecurityAhmed Ajmal100% (2)
- Network Defense 14gDocument36 pagesNetwork Defense 14gBolaji WilliamsNo ratings yet
- NP000421-Sushil Poudel Question 1 (30 Marks) : System & Network Administration 1 of 4Document4 pagesNP000421-Sushil Poudel Question 1 (30 Marks) : System & Network Administration 1 of 4Sushil PaudelNo ratings yet
- 12 - LAS - WEEk8 Access Control ListsDocument3 pages12 - LAS - WEEk8 Access Control ListsJenelyn RusianaNo ratings yet
- FGT1 03 Firewall Policies PDFDocument69 pagesFGT1 03 Firewall Policies PDFhola amigoNo ratings yet
- 2 Firewall+TechnologiesDocument7 pages2 Firewall+TechnologiesCrypto DudeNo ratings yet
- Isaaa Review 2Document25 pagesIsaaa Review 2Azisz PaudelNo ratings yet
- 20 MonitoringDocument5 pages20 Monitoringshahrukh khanNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik - Zone Based FirewallDocument15 pagesMikrotik - Zone Based Firewalljwtven100% (1)
- Securing Communication of Legacy Applications with IPSec: Step-by-Step Guide to Protecting “Data in Transit” without Changes in Your Existing SoftwareFrom EverandSecuring Communication of Legacy Applications with IPSec: Step-by-Step Guide to Protecting “Data in Transit” without Changes in Your Existing SoftwareNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeFrom EverandCryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Enforcement and Monitoring Solutions: Enhanced Wireless, Mobile and Cloud Security DeploymentFrom EverandCybersecurity Enforcement and Monitoring Solutions: Enhanced Wireless, Mobile and Cloud Security DeploymentNo ratings yet
- F5 FSA Integrationv1.0Document15 pagesF5 FSA Integrationv1.0Ashraf SaeedNo ratings yet
- 103 Introduction+to+IPSDocument5 pages103 Introduction+to+IPSAshraf SaeedNo ratings yet
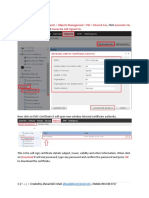
- SSL Policy:: Objects Objects Management PKI Internal Cas Generate CA Generate Self-Signed CADocument12 pagesSSL Policy:: Objects Objects Management PKI Internal Cas Generate CA Generate Self-Signed CAAshraf SaeedNo ratings yet
- Cv1000 Tim WinDocument202 pagesCv1000 Tim WinAshraf SaeedNo ratings yet
- 350 701 2Document43 pages350 701 2Ashraf SaeedNo ratings yet
- v5.1.0.ERN - External v0.5Document44 pagesv5.1.0.ERN - External v0.5Ashraf SaeedNo ratings yet
- Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum 2.0 HelpDocument34 pagesKaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum 2.0 HelpAshraf SaeedNo ratings yet
- ns3 Tut3Document38 pagesns3 Tut3Mariam Mamdouh Mohamed Mohamed GhoniemNo ratings yet
- Overuse of Digital DevicesDocument3 pagesOveruse of Digital DevicesSagar paulNo ratings yet
- Global Wireless Telecommunications Carriers PDFDocument35 pagesGlobal Wireless Telecommunications Carriers PDFEmille Martin Crisostomo Munsayac IINo ratings yet
- Domain Name SystemDocument18 pagesDomain Name Systemvishnu haridasNo ratings yet
- 10 Minute MailDocument2 pages10 Minute MailasdfaNo ratings yet
- Essay Writing Guide-SPM 2016Document5 pagesEssay Writing Guide-SPM 2016Shariffah Nur FarhatunNo ratings yet
- Service Flow Diameter To OCSDocument5 pagesService Flow Diameter To OCSLiren AnNo ratings yet
- Voip in Atm - FrequentisDocument37 pagesVoip in Atm - FrequentisRoberto Vianu100% (1)
- Switch Dell Powerconnect (LCWIKI)Document7 pagesSwitch Dell Powerconnect (LCWIKI)HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Heidelberg, Honeywell, and Eaton: Using Information Technology To Build Smart Products and ServicesDocument2 pagesHeidelberg, Honeywell, and Eaton: Using Information Technology To Build Smart Products and ServicesBùi Danh NhânNo ratings yet
- Module 3 THE DIGITAL AND SOCIAL WORLDS ECONOMY, ENTERPRISES, AND SOCIETYDocument33 pagesModule 3 THE DIGITAL AND SOCIAL WORLDS ECONOMY, ENTERPRISES, AND SOCIETYLeighann MeerNo ratings yet
- Zap FiDocument6 pagesZap FiIonut DanifeldNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming EnvironmentDocument4 pagesComputer Programming Environmentf bhavaniNo ratings yet
- Lab 04Document33 pagesLab 04senthil kumarNo ratings yet
- Sim Swapping, Mobile Phone Fraud and RICA 70 of 2002Document16 pagesSim Swapping, Mobile Phone Fraud and RICA 70 of 2002mpho7967No ratings yet
- Impact Ict SchoolsDocument93 pagesImpact Ict SchoolsMax BauerNo ratings yet
- IPT Chapter 2Document10 pagesIPT Chapter 2Dagim Fekadu AmenuNo ratings yet
- MP3 GENDHING JAWA - Alangalangkumitir PDFDocument15 pagesMP3 GENDHING JAWA - Alangalangkumitir PDFagusrisNo ratings yet
- Presentation Concept Css DiagramDocument31 pagesPresentation Concept Css DiagramRivanza EmirmullahNo ratings yet
- CS 640: Introduction To Computer Networks: Aditya Akella Lecture 25 - Network SecurityDocument39 pagesCS 640: Introduction To Computer Networks: Aditya Akella Lecture 25 - Network SecurityXozanNo ratings yet
- IPv6Security SlidesDocument191 pagesIPv6Security SlidesConcha SolerNo ratings yet
- Information Technology: Scheme of Work Unit 1Document23 pagesInformation Technology: Scheme of Work Unit 1new yearNo ratings yet
- F 36543632Document2 pagesF 36543632Nick LuftNo ratings yet
- M-Commerce Unit VDocument20 pagesM-Commerce Unit VmsksaranNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledRENIER ACE ABORDONo ratings yet
- Identify Different Channels of Communications Used by VIACK. Which According To You Is The Most Effective Channel and Why? AnswerDocument5 pagesIdentify Different Channels of Communications Used by VIACK. Which According To You Is The Most Effective Channel and Why? AnswerHaris MunirNo ratings yet
- 025.37 - Lab Guide Kata 3.7, Kedr 1.7Document168 pages025.37 - Lab Guide Kata 3.7, Kedr 1.7Nizar Hajji karwiNo ratings yet
101 DNS+Policy
101 DNS+Policy
Uploaded by
Ashraf SaeedOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
101 DNS+Policy
101 DNS+Policy
Uploaded by
Ashraf SaeedCopyright:
Available Formats
Access Control Policies:
o Access Control Policies, or ACP’s, are the Firepower rules that allow, deny & log traffic.
o Access Policies are where you define your Firewall rule base and associated actions.
o It is also the component that glues together most of the other policies we will look at.
o The Firewall rules add in Firepower are more advanced than the old port-based rules.
o Can include applications, user identity, zones, URLs and many other things in your rules.
o In some ways, Access Control Policy rules are like traditional or Cisco ASA firewall rules.
o They can match the traffic based on source or destination IP, as well as port number.
o ACP’s evaluate info, includes application, user, URL, traffic payload, business relevance.
o The Access Control Policies (ACP) evaluate information this include, risk, and reputation.
o ACP (Access Control Policies) tie many other policies together as well such as SSL policy.
o Prefilter, SSL, Identity policies, Intrusion policies, and File policies are all used by the ACP.
o ACP allows a hierarchy, with a base policy at the bottom, and child policies on the top.
o Access Control Policy is a policy that pulls together rule sets for L3/L4,L7(Application).
o ACP pulls together rule URL filtering, IPS/IDS, File/AMP (Advanced Malware Protection).
o When evaluating conditions WITHIN a tab, multiple selections are treated as an OR.
o When evaluating conditions BETWEEN tabs in Firepower it is considered as an AND.
o Policies match IP prefixes, IP ports, the protocols TCP, UDP, and ICMP, and applications.
o Nonmatching flows are dropped by default. Matching applications can only be denied.
1 | P a g e Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail: ahmadalimsc@gmail.com , Mobile: 056 430 3717
ACP’s can be found at Policies -> Access Control -> Access Control. Click New Policy and enter a
Name and Description. If you have a base policy that you want to use as a parent, select it here.
The Default Action applies when traffic does not match any rules. The action depends on what
you’re trying to achieve in your network. For example, an edge firewall will likely need to Block
All Traffic. An internal device between networks may be use Intrusion Protection as the default.
Prefilter Policy:
o An Access Control List (ACL) check that runs before the Access Control Policy evaluation.
o This allows or denies traffic without deep packet inspection, may improve performance.
o ACL/Prefilter basic dictionary, block=deny, Fastpath=permit and Analyze=permit go to next.
o Prefiltering is applied before Access Control in traffic flow, it operates at layer 4 like ACLs.
o Prefiltering allows less control on how want to identify traffic and the actions to perform.
2 | P a g e Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail: ahmadalimsc@gmail.com , Mobile: 056 430 3717
SSL Policy:
o SSL Policy tells the Access Control Policy (ACP) how to handle the encrypted traffic.
o This decrypt traffic for inspection, block encrypted traffic, or allow encrypted traffic.
o Cisco Firepower has the ability to decrypt SSL traffic (or to be more accurate – TLS).
o Depending on platform you are running this could significantly impact performance.
Identity Policy:
o The Identify Policy used along with Realms to associate traffic with the users & Groups.
o Cisco Firepower has the ability to integrate with user identities (Users/Groups AD etc).
o Useful if want usernames in logs or if want to tie certain rules to specific users/groups.
o In general, there are two ways of obtaining user identity in Firepower Passively, Actively.
o Passively in Cisco Firepower learns the IP to user mappings from an external source.
o This is typically either via a special agent which is running on a domain server AD Server.
o Actively in Firepower can actively provide a login page to users to enter their credentials.
Intrusion Policies:
o Intrusion Policy is where setup and configure your Intrusion Prevention/Detection policies.
o It is based on Snort & like other similar systems it is signature-based protection mechanism.
o Out of the box the Cisco FTD Firepower comes with a number of pre-defined base policies.
Malware and File Policies:
o In Cisco firepower FTD the Malware and File policies allow you to perform two main tasks.
o Firstly, through Malware and File polices can control the flow of files through the network.
o secondly can check these for malware using Cisco’s Advanced Malware Protection feature.
o In Cisco Firepower FTD the File control can be based on the file type, protocol and direction.
o wanted to prevent users downloading exe files, then this can be achieved with a file policy.
o Advanced Malware Protection checks files for malware before passing files through firewall.
DNS Policy:
o DNS-based Security Intelligence allows to whitelist, or blacklist traffic based on domain.
o Cisco provides the domain name (FQDN) intelligence you can use to filter your traffic.
o Can also configure custom lists and feeds of domain names tailored to your deployment.
o Traffic blacklisted by DNS policy is blocked and not subject to any further inspection.
o Also, not for intrusions, exploits, malware, and so on, but also not for network discovery.
o Firewall sits between internal & external networks; it is well placed to inspect DNS traffic.
o Basically, DNS Polices will drop any requests for known malicious domains included list.
o DNS policies allow to statically whitelist and blacklist FQDNs as well as dynamically Cisco.
3 | P a g e Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail: ahmadalimsc@gmail.com , Mobile: 056 430 3717
Mandatory and Default Rule:
There are two sections for rules; Mandatory and Default. These sections affect the evaluation
of child policies. Child policies go between the two sections. Mandatory rules are evaluated
first, then the child policy rules. Finally, the default rules.
Access Policy Action:
There are seven different actions which a rule can use in Access Policy in Cisco FTD.
Action Description
Allow Allows the traffic, there may yet be more inspections, such as Intrusion
and File policies.
Trust Sends traffic straight to the egress interface, without any extra
inspections. Identity policies and rate limiting still apply.
Monitor Logs traffic and continues to the rest of the rules.
Block Drops traffic silently, causing the connection to timeout.
Block with reset Drops traffic and sends a TCP FIN message to client so the connection
closes rather than times out.
Interactive Displays a web page with conditions that users may accept. This is where
Block the Interactive Block Response Page comes into play.
Interactive Block Combination of interactive block, with a TCP FIN message to client so the
with Reset connection is close rather than times out.
Zones The Zones tab allows Firepower to match traffic based on the source or
destination zone. Zones are objects that contain one or more interfaces.
Networks The Networks tab uses IP addresses, much like a common ACL.
Geolocation This can match traffic from a particular country or region.
VLAN The VLAN tab matches traffic based on VLAN.
Applications The Applications tab allows traffic matching based on the application.
Ports It’s where you can match traffic based on source and destination ports.
URL On the URL tab, we can match traffic to URL. This may use a list of specific
URL’s, or category of URL’s.
SGT/ISE The SGT/ISE Attributes tab can match traffic based on the users Security
Attributes Group Tag (SGT).
Inspection The Inspection tab is where to assign the Intrusion and File policies. If
traffic matches rule & action is allow, then firepower evaluates these.
Logging Each connection can log data to the event viewer. This is how we get
information into the Dashboard and Analysis sections.
4 | P a g e Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail: ahmadalimsc@gmail.com , Mobile: 056 430 3717
You might also like
- 27-Security Policy ConceptsDocument12 pages27-Security Policy Conceptssatyam sumanNo ratings yet
- Cisco ASA V Palo Alto ComparisonDocument1 pageCisco ASA V Palo Alto ComparisonProdec_Networks100% (1)
- Big Data Demystified - How To Use Big Data, Data Science and AI To Make Better Business Decisions and Gain Competitive AdvantageDocument196 pagesBig Data Demystified - How To Use Big Data, Data Science and AI To Make Better Business Decisions and Gain Competitive AdvantageAshfaque Reza100% (4)
- FirewallDocument10 pagesFirewallAris SuryatnoNo ratings yet
- Genband Q21 SBC: High Performance, High Density Session Border ControllerDocument4 pagesGenband Q21 SBC: High Performance, High Density Session Border Controllerkaz7878No ratings yet
- John Wiley & SonsDocument168 pagesJohn Wiley & SonsMohammed Nasser20% (10)
- Palo Alto NetworksDocument28 pagesPalo Alto NetworksLavi Chhabra100% (3)
- Network Security1Document7 pagesNetwork Security1upadhyay kulbhushanNo ratings yet
- Fortigate Firewall Policies:: Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail:, Mobile: 056 430 3717Document9 pagesFortigate Firewall Policies:: Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail:, Mobile: 056 430 3717AyanNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuestionsSrinivas Naidu T SNo ratings yet
- Sophos - Considerations For Deploying Sophos Firewall in Common ScenariosDocument22 pagesSophos - Considerations For Deploying Sophos Firewall in Common ScenariosMiguel António ManuelNo ratings yet
- Alteon ITM TrainingDocument39 pagesAlteon ITM Training李謝揚No ratings yet
- How Information Flows On NetworksDocument3 pagesHow Information Flows On NetworksAdi SuryaNo ratings yet
- Palo Alto Networks 101 - App-ID and User-ID Best PracticesDocument5 pagesPalo Alto Networks 101 - App-ID and User-ID Best PracticesRyanb378No ratings yet
- FirewallDocument2 pagesFirewallsanamanand3300No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Firewalls and The Firewall Selection ProcessDocument10 pagesAn Introduction To Firewalls and The Firewall Selection ProcessS SagarNo ratings yet
- Integrated URL Filtering: Content-IDDocument2 pagesIntegrated URL Filtering: Content-IDErivelton SouzaNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument161 pagesDownloadSarayut SineninetyNo ratings yet
- Firewall Rulebase Analysis ToolDocument8 pagesFirewall Rulebase Analysis ToolShubham MittalNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv:: Security Measurement StrategiesDocument43 pagesUnit Iv:: Security Measurement Strategiesarnav_mailboxNo ratings yet
- What Is FirewallDocument4 pagesWhat Is Firewallahmedtehseem0062No ratings yet
- Abstract On Network Security and CryptographyDocument13 pagesAbstract On Network Security and Cryptographytharun89% (9)
- FW2030 19.0v1 Configuring TLS Decryption On Sophos FirewallDocument14 pagesFW2030 19.0v1 Configuring TLS Decryption On Sophos FirewallVanderwaal PromolykoNo ratings yet
- FW2030 19.0v1 Configuring TLS Decryption On Sophos FirewallDocument14 pagesFW2030 19.0v1 Configuring TLS Decryption On Sophos FirewallAndré MouraNo ratings yet
- Secure Wireless Firewall Integration: Role of The FirewallDocument54 pagesSecure Wireless Firewall Integration: Role of The FirewallFlavio MirandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Security PolicyDocument32 pagesChapter 5 - Security PolicyJosé Miguel Melgar RojasNo ratings yet
- Cap9 Access Control ListsDocument87 pagesCap9 Access Control ListsDobre DanielNo ratings yet
- App-Id:: Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail:, Mobile: 056 430 3717Document16 pagesApp-Id:: Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail:, Mobile: 056 430 3717Crypto DudeNo ratings yet
- Tut04-Access Control UpdatedDocument16 pagesTut04-Access Control UpdatedGiang Trần ThịNo ratings yet
- Network ACLsDocument99 pagesNetwork ACLsjanerie71No ratings yet
- INformation Security 5Document11 pagesINformation Security 5Shantanu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Securing Networks: Access Control List (ACL) ConceptsDocument4 pagesSecuring Networks: Access Control List (ACL) ConceptsAbdul Sami MohammedNo ratings yet
- Faq FirewallDocument13 pagesFaq FirewallTaoufic Ben HcineNo ratings yet
- Case Study On "Firewall"Document8 pagesCase Study On "Firewall"Lokesh ShindeNo ratings yet
- Howto Config FW Policies Ruleshowto Config FW Policies RulesDocument6 pagesHowto Config FW Policies Ruleshowto Config FW Policies RulesBaBu BiNo ratings yet
- Ofcom Site Blocking Report With Redactions RemovedDocument56 pagesOfcom Site Blocking Report With Redactions RemovedTJ McIntyreNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Firewall Types: National Security AgencyDocument2 pagesEnterprise Firewall Types: National Security AgencyFelipe Ramirez HerreraNo ratings yet
- Basic Firewall PolicyDocument6 pagesBasic Firewall PolicyhenriquecongoNo ratings yet
- Untitled 2Document13 pagesUntitled 2sheraz salimNo ratings yet
- Hillario Zidan - 00000050745 - IF673 - A - UTSDocument4 pagesHillario Zidan - 00000050745 - IF673 - A - UTSHillario ZidanNo ratings yet
- SL Assignment No 1 - AY2023-24Document5 pagesSL Assignment No 1 - AY2023-24only.moviewebseries123No ratings yet
- Access Controls Tutorial: Hoang Thi Kieu Hoa Faculty of Information Technology, Hanoi UniversityDocument14 pagesAccess Controls Tutorial: Hoang Thi Kieu Hoa Faculty of Information Technology, Hanoi UniversityOanh Đoàn ThịNo ratings yet
- Blocking TOR BrowserDocument8 pagesBlocking TOR BrowserpoojaNo ratings yet
- App IDsection 8Document26 pagesApp IDsection 8satya28No ratings yet
- Firewall: Name: Sumit Sharma Register no.:RA1611003010777Document9 pagesFirewall: Name: Sumit Sharma Register no.:RA1611003010777Sumit SharmaNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument3 pagesDocxMOUMITA BHATTACHARJEE0% (1)
- Best Practices DecryptionDocument5 pagesBest Practices DecryptionPartha DashNo ratings yet
- A Firewall Is A Set of Related ProgramsDocument11 pagesA Firewall Is A Set of Related ProgramsDeep RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Networking Basics and TerminologyDocument25 pagesNetworking Basics and Terminologyنكت مضحكةNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint FirewallDocument14 pagesCheckpoint FirewallJonnalagadda Harshavardhan100% (2)
- Interview Preparation For Cyber SecurityDocument114 pagesInterview Preparation For Cyber SecurityAhmed Ajmal100% (2)
- Network Defense 14gDocument36 pagesNetwork Defense 14gBolaji WilliamsNo ratings yet
- NP000421-Sushil Poudel Question 1 (30 Marks) : System & Network Administration 1 of 4Document4 pagesNP000421-Sushil Poudel Question 1 (30 Marks) : System & Network Administration 1 of 4Sushil PaudelNo ratings yet
- 12 - LAS - WEEk8 Access Control ListsDocument3 pages12 - LAS - WEEk8 Access Control ListsJenelyn RusianaNo ratings yet
- FGT1 03 Firewall Policies PDFDocument69 pagesFGT1 03 Firewall Policies PDFhola amigoNo ratings yet
- 2 Firewall+TechnologiesDocument7 pages2 Firewall+TechnologiesCrypto DudeNo ratings yet
- Isaaa Review 2Document25 pagesIsaaa Review 2Azisz PaudelNo ratings yet
- 20 MonitoringDocument5 pages20 Monitoringshahrukh khanNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik - Zone Based FirewallDocument15 pagesMikrotik - Zone Based Firewalljwtven100% (1)
- Securing Communication of Legacy Applications with IPSec: Step-by-Step Guide to Protecting “Data in Transit” without Changes in Your Existing SoftwareFrom EverandSecuring Communication of Legacy Applications with IPSec: Step-by-Step Guide to Protecting “Data in Transit” without Changes in Your Existing SoftwareNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeFrom EverandCryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Enforcement and Monitoring Solutions: Enhanced Wireless, Mobile and Cloud Security DeploymentFrom EverandCybersecurity Enforcement and Monitoring Solutions: Enhanced Wireless, Mobile and Cloud Security DeploymentNo ratings yet
- F5 FSA Integrationv1.0Document15 pagesF5 FSA Integrationv1.0Ashraf SaeedNo ratings yet
- 103 Introduction+to+IPSDocument5 pages103 Introduction+to+IPSAshraf SaeedNo ratings yet
- SSL Policy:: Objects Objects Management PKI Internal Cas Generate CA Generate Self-Signed CADocument12 pagesSSL Policy:: Objects Objects Management PKI Internal Cas Generate CA Generate Self-Signed CAAshraf SaeedNo ratings yet
- Cv1000 Tim WinDocument202 pagesCv1000 Tim WinAshraf SaeedNo ratings yet
- 350 701 2Document43 pages350 701 2Ashraf SaeedNo ratings yet
- v5.1.0.ERN - External v0.5Document44 pagesv5.1.0.ERN - External v0.5Ashraf SaeedNo ratings yet
- Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum 2.0 HelpDocument34 pagesKaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum 2.0 HelpAshraf SaeedNo ratings yet
- ns3 Tut3Document38 pagesns3 Tut3Mariam Mamdouh Mohamed Mohamed GhoniemNo ratings yet
- Overuse of Digital DevicesDocument3 pagesOveruse of Digital DevicesSagar paulNo ratings yet
- Global Wireless Telecommunications Carriers PDFDocument35 pagesGlobal Wireless Telecommunications Carriers PDFEmille Martin Crisostomo Munsayac IINo ratings yet
- Domain Name SystemDocument18 pagesDomain Name Systemvishnu haridasNo ratings yet
- 10 Minute MailDocument2 pages10 Minute MailasdfaNo ratings yet
- Essay Writing Guide-SPM 2016Document5 pagesEssay Writing Guide-SPM 2016Shariffah Nur FarhatunNo ratings yet
- Service Flow Diameter To OCSDocument5 pagesService Flow Diameter To OCSLiren AnNo ratings yet
- Voip in Atm - FrequentisDocument37 pagesVoip in Atm - FrequentisRoberto Vianu100% (1)
- Switch Dell Powerconnect (LCWIKI)Document7 pagesSwitch Dell Powerconnect (LCWIKI)HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Heidelberg, Honeywell, and Eaton: Using Information Technology To Build Smart Products and ServicesDocument2 pagesHeidelberg, Honeywell, and Eaton: Using Information Technology To Build Smart Products and ServicesBùi Danh NhânNo ratings yet
- Module 3 THE DIGITAL AND SOCIAL WORLDS ECONOMY, ENTERPRISES, AND SOCIETYDocument33 pagesModule 3 THE DIGITAL AND SOCIAL WORLDS ECONOMY, ENTERPRISES, AND SOCIETYLeighann MeerNo ratings yet
- Zap FiDocument6 pagesZap FiIonut DanifeldNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming EnvironmentDocument4 pagesComputer Programming Environmentf bhavaniNo ratings yet
- Lab 04Document33 pagesLab 04senthil kumarNo ratings yet
- Sim Swapping, Mobile Phone Fraud and RICA 70 of 2002Document16 pagesSim Swapping, Mobile Phone Fraud and RICA 70 of 2002mpho7967No ratings yet
- Impact Ict SchoolsDocument93 pagesImpact Ict SchoolsMax BauerNo ratings yet
- IPT Chapter 2Document10 pagesIPT Chapter 2Dagim Fekadu AmenuNo ratings yet
- MP3 GENDHING JAWA - Alangalangkumitir PDFDocument15 pagesMP3 GENDHING JAWA - Alangalangkumitir PDFagusrisNo ratings yet
- Presentation Concept Css DiagramDocument31 pagesPresentation Concept Css DiagramRivanza EmirmullahNo ratings yet
- CS 640: Introduction To Computer Networks: Aditya Akella Lecture 25 - Network SecurityDocument39 pagesCS 640: Introduction To Computer Networks: Aditya Akella Lecture 25 - Network SecurityXozanNo ratings yet
- IPv6Security SlidesDocument191 pagesIPv6Security SlidesConcha SolerNo ratings yet
- Information Technology: Scheme of Work Unit 1Document23 pagesInformation Technology: Scheme of Work Unit 1new yearNo ratings yet
- F 36543632Document2 pagesF 36543632Nick LuftNo ratings yet
- M-Commerce Unit VDocument20 pagesM-Commerce Unit VmsksaranNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledRENIER ACE ABORDONo ratings yet
- Identify Different Channels of Communications Used by VIACK. Which According To You Is The Most Effective Channel and Why? AnswerDocument5 pagesIdentify Different Channels of Communications Used by VIACK. Which According To You Is The Most Effective Channel and Why? AnswerHaris MunirNo ratings yet
- 025.37 - Lab Guide Kata 3.7, Kedr 1.7Document168 pages025.37 - Lab Guide Kata 3.7, Kedr 1.7Nizar Hajji karwiNo ratings yet