Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Breathing and Respiration
Breathing and Respiration
Uploaded by
jenn78Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Breathing and Respiration
Breathing and Respiration
Uploaded by
jenn78Copyright:
Available Formats
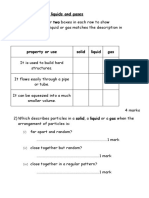
8Cb-1 The gas exchange system
Name Class Date
1 Draw lines from the labels to the correct part of the diagram.
trachea bronchus
diaphragm lung
rib muscle between rib
2 Draw lines to match the words with their meanings.
breathing air moving into and out of the lungs
ventilation a chemical process that happens in cells
respiration oxygen and carbon dioxide diffusing in the lungs
alveolus using muscles to expand and deflate the lungs
gas exchange a small pocket in the lungs
3 The drawing shows a model used to explain how the lungs
expand and fill with air. Number the phrases to put them in
the correct order.
air enters the balloon, and so
the pressure in the jar is
less than atmospheric pressure, and so ...
the balloon inflates.
the stretched balloon is pulled downwards, and so
The air in the jar is at the same pressure as atmospheric
pressure. Then
4 Why can particles diffuse?
5 Why do lungs have a large surface area?
I can
recall the functions of the organs in the gas exchange system
explain how the structure of the lungs allows efficient gas exchange.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2014. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. 8
8Cb-6
Breathing, ventilation
and respiration
Name Class Date
1 Air flows into and out of the lungs.
a What is this called? Circle one.
breathing contraction ventilation wind
b In order, list the organs through which air travels as it goes into the body.
2 What is the process that uses up oxygen and produces carbon dioxide?
3 Complete this table to show what happens when you breathe.
Do the ribs move Does the diaphragm Does air in the trachea contain
in or out? move up or down? more or less carbon dioxide?
Inhaling
Exhaling
4 The drawing shows a model that can be used to explain how the lungs
expand and deflate. Explain what will happen when the cord is pulled
downwards.
5 Inside the lungs the breathing tubes divide and get smaller and smaller until they end in an air
sac. What are air sacs made of? Circle one.
air alveoli blood bronchi cilia avioli
6 Inside the lungs there is an overall movement of oxygen from the air into the blood. At the
same time there is an overall movement of carbon dioxide from the blood into the air.
a What is this swapping of gases called?
b How does it occur? Tick ( ) the best explanation.
You breathe out more carbon dioxide than is in the air that you breathe in.
Small hairs in the lungs push oxygen into the blood and remove carbon dioxide.
Red blood cells enter the lungs and pump oxygen into them and let carbon dioxide out.
Particles are always moving, so naturally move into places where there are fewer of them.
Oxygen particles swim to red blood cells; carbon dioxide particles swim away from them.
I can
recall the functions of the organs in the gas exchange system
explain how the structure of the lungs allows efficient gas exchange.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2014. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. 13
You might also like
- 9a Mark SchemesDocument6 pages9a Mark Schemesobomar2010No ratings yet
- 7ge Air PressureDocument25 pages7ge Air PressureSapphire BlueNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument17 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (4)
- Name Class Date: G - N/KGDocument4 pagesName Class Date: G - N/KGDelosh TNo ratings yet
- 7g Quick Quiz - pdf-4Document2 pages7g Quick Quiz - pdf-4Ondra KlimšaNo ratings yet
- Algae Water Flea Stickleback: ProtoctistsDocument2 pagesAlgae Water Flea Stickleback: Protoctistsghadeer alkhayatNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: Cells and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesSummary Sheets: Cells and Their FunctionsLola Smith0% (1)
- RN Fundamentals Online Practice 2016 A Study Online at QuizletDocument14 pagesRN Fundamentals Online Practice 2016 A Study Online at QuizletDerek Scott Tripp100% (1)
- CRRT Self Learning PKT 5 - 2015Document25 pagesCRRT Self Learning PKT 5 - 2015pamoralesNo ratings yet
- 8ca - Aerobic Respiration: Word SheetsDocument3 pages8ca - Aerobic Respiration: Word SheetsOanaEmmNo ratings yet
- Homework T1 WK5 Science YR 7Document2 pagesHomework T1 WK5 Science YR 7Siyamala NagarajuNo ratings yet
- 7d-Word SheetDocument6 pages7d-Word SheetKwan Ye LinNo ratings yet
- Types of Reproduction: I CanDocument1 pageTypes of Reproduction: I CanazharNo ratings yet
- Book and Work Sheet Answers Year 7Document100 pagesBook and Work Sheet Answers Year 7reetiNo ratings yet
- AP Chem MC Practice ProblemsKeyDocument20 pagesAP Chem MC Practice ProblemsKeyJenniferChenNo ratings yet
- Es Int 9e QQ AspDocument3 pagesEs Int 9e QQ AspRifaa WidasmaraNo ratings yet
- Electricity RevisionDocument2 pagesElectricity RevisionThe PassionNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDocument50 pagesQuick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionAmeera Hashim0% (1)
- Grade 7 ChemDocument19 pagesGrade 7 ChemAnand Kumar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Unit of Work - Summative Information - Science Unit 7G - Year 7Document4 pagesUnit of Work - Summative Information - Science Unit 7G - Year 7Amir AminiNo ratings yet
- Force & Pressure PPT-4Document12 pagesForce & Pressure PPT-4ARNAB GHOSH CLASS VNo ratings yet
- 7h Summary Sheets PDFDocument3 pages7h Summary Sheets PDFAghaanaa JaiganeshNo ratings yet
- 8fa5 Modelling MatterDocument1 page8fa5 Modelling MatterameemaNo ratings yet
- Decomposers and Carbon: Name Ghadeer Hussain Al-Khayat Class 9gg Date 25-9-2020Document2 pagesDecomposers and Carbon: Name Ghadeer Hussain Al-Khayat Class 9gg Date 25-9-2020ghadeer alkhayatNo ratings yet
- 8B RespirationDocument8 pages8B RespirationMaoga2013No ratings yet
- 8F Quick Check Quiz AnswersDocument1 page8F Quick Check Quiz AnswersClaire LNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05Document7 pagesIGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05María Eugenia MolteniNo ratings yet
- 8A B C D Summary SheetsDocument13 pages8A B C D Summary SheetsFaheem BhaimedNo ratings yet
- Year 8end TestDocument26 pagesYear 8end TestFrancisNo ratings yet
- Energy From Food Resources 2023-10-20 07 - 26 - 20Document4 pagesEnergy From Food Resources 2023-10-20 07 - 26 - 20steckova.lindaNo ratings yet
- 7ba - Escaped Zoo Animals: Word SheetsDocument6 pages7ba - Escaped Zoo Animals: Word Sheetsnelly hammoudaNo ratings yet
- 8I Fluids Revision - Worksheet - Answers 660Document1 page8I Fluids Revision - Worksheet - Answers 660gbqwzy56fzNo ratings yet
- Term Test QP 1Document9 pagesTerm Test QP 1sollu786_889163149No ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument50 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesRumaisa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Energy Revision Answer KeyDocument5 pagesEnergy Revision Answer KeyariaNo ratings yet
- Science 8G Metals and Their UsesDocument2 pagesScience 8G Metals and Their UsesHeba AwadNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets For Unit 7JDocument2 pagesSummary Sheets For Unit 7JJohn Osborne100% (1)
- Force Field Questions: Name Ghadeer Hussain Al-Khayat Class Date 1Document2 pagesForce Field Questions: Name Ghadeer Hussain Al-Khayat Class Date 1ghadeer alkhayatNo ratings yet
- 7G Particles: Solids, Liquids and GasesDocument3 pages7G Particles: Solids, Liquids and GasesBen PassmoreNo ratings yet
- 8c Summary SheetsDocument2 pages8c Summary SheetsSelena Alsrouri100% (1)
- Summary Sheets: Going For Gold!Document2 pagesSummary Sheets: Going For Gold!chan myae100% (1)
- Activity Pack &student Book Answers - 8Document86 pagesActivity Pack &student Book Answers - 8Eliana FalahatNo ratings yet
- 9 BCDocument21 pages9 BCAnonymous RuslwNZZlNo ratings yet
- 8D-Unicellular-organisms - Summary SheetDocument2 pages8D-Unicellular-organisms - Summary Sheetzasad1499100% (1)
- 9f Word SheetsDocument2 pages9f Word SheetsbanaliaNo ratings yet
- Int Esws at 7e Unit TTPPDocument30 pagesInt Esws at 7e Unit TTPPHisokagenNo ratings yet
- 7ga - Sorting Rubbish: Word SheetsDocument2 pages7ga - Sorting Rubbish: Word SheetsAmir AminiNo ratings yet
- Science Book Chemistry PDFDocument11 pagesScience Book Chemistry PDFyenumi nethayaNo ratings yet
- 8Cc Getting Oxygen EPSDocument44 pages8Cc Getting Oxygen EPSZak Remtulla100% (1)
- Types of Energy and ChangersDocument2 pagesTypes of Energy and ChangersDanielGuimarãesCostaNo ratings yet
- Practical 2Document2 pagesPractical 2Dr.CharinNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Biology IGCSE: 2.12: Enzymes and TemperatureDocument3 pagesEdexcel Biology IGCSE: 2.12: Enzymes and TemperatureahmedNo ratings yet
- Dalton's Atomic ModelDocument16 pagesDalton's Atomic ModelHadeel IbrahemNo ratings yet
- States of Matter QuizDocument2 pagesStates of Matter Quizroy.chuaNo ratings yet
- 8c Summary SheetsDocument2 pages8c Summary SheetslNo ratings yet
- Summary 7KDocument2 pagesSummary 7KTHJNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: 9ba 9BbDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: 9ba 9BbOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- 1st Mid Exam Science 9.1Document4 pages1st Mid Exam Science 9.1Jass AllasNo ratings yet
- Energy in Food Worksheet - InteractiveDocument2 pagesEnergy in Food Worksheet - Interactivecf4b2sp6p4No ratings yet
- ESWS - Teacher Guide 2014Document32 pagesESWS - Teacher Guide 2014Vikrant ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Enzymes 2Document26 pagesChemical Reactions and Enzymes 2api-240096234100% (1)
- Module 2 Respiratory System DinDocument13 pagesModule 2 Respiratory System DinAhmad NajmuddinNo ratings yet
- 8Cb Gas Exchange (Part 1)Document19 pages8Cb Gas Exchange (Part 1)maryamNo ratings yet
- Simple Pendulums Investigate ItDocument2 pagesSimple Pendulums Investigate Itjenn78No ratings yet
- Does The Sun Move Across The SkyDocument2 pagesDoes The Sun Move Across The Skyjenn78No ratings yet
- My Experiment PlanDocument2 pagesMy Experiment Planjenn78No ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument1 pagePeriodic Tablejenn78No ratings yet
- The Scientific MethodDocument3 pagesThe Scientific Methodjenn78No ratings yet
- Sunrise and Sunset Patterns Interpret ItDocument1 pageSunrise and Sunset Patterns Interpret Itjenn78No ratings yet
- What Shape Is The MoonDocument2 pagesWhat Shape Is The Moonjenn78No ratings yet
- Rocket Testing Investigate ItDocument2 pagesRocket Testing Investigate Itjenn78No ratings yet
- Our Orbiting Spinning EarthDocument2 pagesOur Orbiting Spinning Earthjenn78No ratings yet
- Energy Transfers 1 (A) An Electric Drill, A Radio and A Torch All Convert Electrical Energy Into Other FormsDocument2 pagesEnergy Transfers 1 (A) An Electric Drill, A Radio and A Torch All Convert Electrical Energy Into Other Formsjenn78No ratings yet
- 6.14 Series and ParallelDocument18 pages6.14 Series and Paralleljenn78No ratings yet
- Extraction of IronDocument3 pagesExtraction of Ironjenn78No ratings yet
- Density, Mass and WeightDocument15 pagesDensity, Mass and Weightjenn78No ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument4 pagesSolar Energyjenn78No ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument1 pageLife Processesjenn78No ratings yet
- Extraction and Uses of Metals: Section 2: Inorganic ChemistryDocument8 pagesExtraction and Uses of Metals: Section 2: Inorganic Chemistryjenn78No ratings yet
- Human Impact On The EnvironmentDocument2 pagesHuman Impact On The Environmentjenn78No ratings yet
- WelcomeDocument1 pageWelcomejenn78No ratings yet
- Description of The DrugDocument1 pageDescription of The Drugjenn78No ratings yet
- Cell InjuryDocument92 pagesCell InjuryMariam AlavidzeNo ratings yet
- (Health) Breathing Better With A COPD DiagnosisDocument4 pages(Health) Breathing Better With A COPD DiagnosisgenierozeNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biochemistry A Short Course 2nd Edition John L Tymoczko Isbn 10 1429283602 Isbn 13 9781429283601Document13 pagesTest Bank For Biochemistry A Short Course 2nd Edition John L Tymoczko Isbn 10 1429283602 Isbn 13 9781429283601Angela Roberts100% (39)
- Chapter 1 RespirationDocument15 pagesChapter 1 Respirationcik_wana100% (1)
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesRepublic of The PhilippinesTroy JcNo ratings yet
- 2012 Effect of AmoxicillinClavulanate On Gastrointestinal Motility in ChildrenDocument5 pages2012 Effect of AmoxicillinClavulanate On Gastrointestinal Motility in Children陳偉燾No ratings yet
- Ekstraksi Anggur Merah - CyntiaDocument11 pagesEkstraksi Anggur Merah - CyntiaAdilah AthtahirahNo ratings yet
- KHUMBAKHAbandhasDocument2 pagesKHUMBAKHAbandhasAlejandro LomeNo ratings yet
- Neurophysiology Learning ObjectivesDocument88 pagesNeurophysiology Learning ObjectivesBad BunnyNo ratings yet
- 8B RespirationDocument8 pages8B RespirationMaoga2013No ratings yet
- Case of DM Type 2 UTIDocument38 pagesCase of DM Type 2 UTIMicheleNo ratings yet
- Fitness Training Program-MiaFDocument5 pagesFitness Training Program-MiaFMiaFernstrom100% (1)
- An Essential Role of The Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain in Cell Proliferation Is To Enable Aspartate SynthesisDocument13 pagesAn Essential Role of The Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain in Cell Proliferation Is To Enable Aspartate Synthesisyylf2016No ratings yet
- Protein MetabolismDocument78 pagesProtein MetabolismU2002862 STUDENTNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Natural Product Plant Secondary MetabolitesDocument9 pagesThe Chemistry of Natural Product Plant Secondary MetabolitesImdad HussainNo ratings yet
- VomitingDocument29 pagesVomitinganusrisaranganNo ratings yet
- Approach To Cyanosis in NewbornDocument28 pagesApproach To Cyanosis in NewbornbidisNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients Undergoing Valvular Heart SurgerryDocument62 pagesCare of Patients Undergoing Valvular Heart SurgerryanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Esophagus: Lamina Propria-Muscularis Mucosae SubmucosaDocument6 pagesEsophagus: Lamina Propria-Muscularis Mucosae SubmucosaMa. Mil Adrianne PamaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland PresentationDocument10 pagesThyroid Gland PresentationDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument5 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionNIKKI GRACE SANTILLANNo ratings yet
- Evolution and The Fossil RecordDocument79 pagesEvolution and The Fossil Recordpopayonutz22No ratings yet
- SclerotherapyDocument92 pagesSclerotherapysamuelebenezer100% (1)
- Incision Sites 2Document4 pagesIncision Sites 2Angel Garcia CarbajalNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document67 pagesCase Study 1Herbie SoNo ratings yet
- Mra CRDocument87 pagesMra CRyailetc3796No ratings yet
- Lipid Profile in ChildrenDocument8 pagesLipid Profile in Childrenheema valeraNo ratings yet