Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Book Based Pathophysiology - Hemorrhagic Stroke
Book Based Pathophysiology - Hemorrhagic Stroke
Uploaded by
ZAY EMCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Rehab Cheat SheetDocument18 pagesRehab Cheat SheetZ A100% (3)
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Pathophysiologynursing concept maps40% (5)
- Neurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IIFrom EverandNeurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeAqeel Al-Mahdaly0% (1)
- Stroke RehabilitationDocument57 pagesStroke RehabilitationWahyu FajarNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology PDFMohd Amir Bin Bashir0% (1)
- Schematic Diagram On The 4 Types of ShockDocument5 pagesSchematic Diagram On The 4 Types of Shockgodgiven25100% (5)
- Pathophysiology Total Anterior Circulation Infarction Left Middle Cerebral Artery (TACILMCA)Document2 pagesPathophysiology Total Anterior Circulation Infarction Left Middle Cerebral Artery (TACILMCA)PATHOSHOPPE100% (1)
- 2 Social Political and Cultural Behavior and PhenomenaDocument4 pages2 Social Political and Cultural Behavior and PhenomenaKeano Christian MacrohonNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Lesson Plan 5Document2 pagesMental Health Lesson Plan 5api-143975079No ratings yet
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument2 pagesSubarachnoid HemorrhageJethro Bacayo Zamora100% (1)
- Pathophysiology ErDocument3 pagesPathophysiology ErAlexa A. AldayNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJet Ray-Ann GaringanNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology StrokeDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology StrokeknazaretaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Disorders of Consciousness and Language I (Coma and Confusional States) LectureDocument119 pages10 - Disorders of Consciousness and Language I (Coma and Confusional States) LectureRanjit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Iskemia Kerusakan Membran Nekrosis Sel Gangguan Sel Ca InflukDocument12 pagesIskemia Kerusakan Membran Nekrosis Sel Gangguan Sel Ca Influkmuhammad_aulia_5No ratings yet
- Stroke Pathophysiology 1Document5 pagesStroke Pathophysiology 1Jeco ValdezNo ratings yet
- Stroke PathoDocument1 pageStroke PathograsyaNo ratings yet
- TBI PathophysioClinicalManifestationsDocument7 pagesTBI PathophysioClinicalManifestationsJan Philippe BelandoNo ratings yet
- Pendukung StrokeDocument202 pagesPendukung StrokeNovita DuffNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: P A R A L Y S I SDocument1 pagePathophysiology: P A R A L Y S I SJordan Garcia AguilarNo ratings yet
- Strokeppt 170720174010Document95 pagesStrokeppt 170720174010Venosha GunasekaranNo ratings yet
- PathophysioDocument2 pagesPathophysioceyieNo ratings yet
- Bab IiDocument13 pagesBab IiNanda SusiloNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Cerebrovascular Accident Hemorrhagic Right Lobe)Document4 pagesPathophysiology (Cerebrovascular Accident Hemorrhagic Right Lobe)jhonkivenNo ratings yet
- 1 - Rehabilitasi Medik Pada Penderita StrokeDocument55 pages1 - Rehabilitasi Medik Pada Penderita StrokeKrisma susantiNo ratings yet
- Definition and Etiology: Back To TopDocument9 pagesDefinition and Etiology: Back To TopMark Earlmafrey SaguiboNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Stroke: The Normal Blood Supply To The Brain Is DisruptedDocument5 pagesIschemic Stroke: The Normal Blood Supply To The Brain Is DisruptedMelchora Lea Castro SorianoNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: Darpen Subhashbhai Mori Group 2, MD 3BDocument13 pagesHemorrhagic Stroke: Darpen Subhashbhai Mori Group 2, MD 3BDarpen MoriNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGYJeroham CoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Stroke - NewDocument4 pagesNursing Care of Stroke - Newninda saputriNo ratings yet
- Stroke Syndromes and Localization 2007Document56 pagesStroke Syndromes and Localization 2007SaintPaul Univ100% (1)
- Geriatric SyndromeDocument49 pagesGeriatric Syndromewita prabawatiNo ratings yet
- Overview of Stroke - Knowledge at AMBOSSDocument19 pagesOverview of Stroke - Knowledge at AMBOSSandimija16No ratings yet
- StrokeDocument28 pagesStrokeBEA RADANo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology MSDocument3 pagesPathophysiology MSLord Allen B. GomezNo ratings yet
- NonmodifiableDocument4 pagesNonmodifiableAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.No ratings yet
- Case Study CvaDocument6 pagesCase Study Cvajing_elizabethNo ratings yet
- Neurology (Cerebrovascular Disease)Document69 pagesNeurology (Cerebrovascular Disease)Mahadhir AkmalNo ratings yet
- KUL 8 Stroke Nursing ManagementDocument45 pagesKUL 8 Stroke Nursing ManagementErina NopiyantiNo ratings yet
- Special Neurology - Second Edition RevisedDocument115 pagesSpecial Neurology - Second Edition RevisedAimee100% (1)
- Special NeurologyDocument115 pagesSpecial NeurologyUbaidillah Romadlon AlfairuziNo ratings yet
- Notes On SyncopeDocument8 pagesNotes On SyncopeViswa Giri100% (1)
- Cva (Npte)Document16 pagesCva (Npte)papermannerNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi Dan Penyimpangan KDM StrokeDocument1 pagePatofisiologi Dan Penyimpangan KDM StrokeNur Fadyla PeluNo ratings yet
- FINALe ISCHEMIC STROKES NEUROSURGDocument13 pagesFINALe ISCHEMIC STROKES NEUROSURGadrian kristopher dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive ICHDocument49 pagesHypertensive ICHmingchuan chuNo ratings yet
- Penilaian Awal Pasien SyokDocument33 pagesPenilaian Awal Pasien SyokatikaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Disease Lipincott 24 10 2012 FinalDocument10 pagesCerebrovascular Disease Lipincott 24 10 2012 Finalرافت العواضيNo ratings yet
- Subdural Woc IchaDocument1 pageSubdural Woc IchaNajla KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Refreshing Shock: Pembimbing: Dr. Fauzi Abdillah Susman, SP - An, MSC Disusun Oleh: Achmad Reza SyamsuladeDocument14 pagesRefreshing Shock: Pembimbing: Dr. Fauzi Abdillah Susman, SP - An, MSC Disusun Oleh: Achmad Reza SyamsuladeSam.No ratings yet
- Seminar On Management of StrokeDocument54 pagesSeminar On Management of Stroke7762n9qsntNo ratings yet
- Stroke PathoDocument15 pagesStroke PathoWiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Pathopyshiology-w-Risk-Factors - DTDocument3 pagesPathopyshiology-w-Risk-Factors - DTDivynne MadeloNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Cva... by Mizzy BaylonDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Cva... by Mizzy BaylonmizzybaylonNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Cardiac ArrestDocument1 pagePathophysiology Cardiac ArrestPATHOSHOPPE100% (2)
- PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPathophysiologyDimple BlancoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - Tia VS CvaDocument6 pagesPathophysiology - Tia VS CvaZeo Zafaralla100% (1)
- Pathways Hypertension On ElderlyDocument1 pagePathways Hypertension On ElderlyFuzna DahliaNo ratings yet
- Compendium on Cardiomyopathies - Basics, Therapeutics, and PerspectivesFrom EverandCompendium on Cardiomyopathies - Basics, Therapeutics, and PerspectivesNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic/Laborator Y Procedures Indication/Purpose S Result Analysis and Interpretation of Results Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDiagnostic/Laborator Y Procedures Indication/Purpose S Result Analysis and Interpretation of Results Nursing ResponsibilitiesZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Area Assessment Description of Findings & Interpretation General Appearance PostureDocument6 pagesArea Assessment Description of Findings & Interpretation General Appearance PostureZAY EMNo ratings yet
- FFFFDocument2 pagesFFFFZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: Is Used To Dissolve (Cholesterol) Gallstones and PDocument9 pagesGeneric Name:: Is Used To Dissolve (Cholesterol) Gallstones and PZAY EMNo ratings yet
- PREECLAMPSIADocument9 pagesPREECLAMPSIAZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Gestational DiabetesDocument6 pagesGestational DiabetesZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument5 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Viral GastroenteritisDocument1 pageViral GastroenteritisZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument2 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Viral GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesViral GastroenteritisZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Gestational DiabetesDocument1 pageGestational DiabetesZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Simplifying Numerical Expressions: Rules For The Order of ExpressionDocument4 pagesSimplifying Numerical Expressions: Rules For The Order of ExpressionZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Florence Nightingale'S Environmental TheoryDocument16 pagesFlorence Nightingale'S Environmental TheoryZAY EMNo ratings yet
- BasketballDocument11 pagesBasketballZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Hildegard Peplau: Interpersonal Relations TheoryDocument4 pagesHildegard Peplau: Interpersonal Relations TheoryZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Hildegard Peplau: Interpersonal Relations TheoryDocument5 pagesHildegard Peplau: Interpersonal Relations TheoryZAY EMNo ratings yet
- InfographicDocument1 pageInfographicZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Speech BullyingDocument1 pageSpeech BullyingZAY EMNo ratings yet
- What Is HallucinogensDocument3 pagesWhat Is HallucinogenskerenNo ratings yet
- Ion Channels PDFDocument7 pagesIon Channels PDFHyunji KimNo ratings yet
- Agggression ScaleDocument4 pagesAgggression ScaleDixha BaggaNo ratings yet
- On Consciousness - Science and Subjectivity - A Q&A With Bernard Baars - Scientific American Blog NetworkDocument16 pagesOn Consciousness - Science and Subjectivity - A Q&A With Bernard Baars - Scientific American Blog NetworkFred MeyerNo ratings yet
- Lab 4: Finger Reaction Time To Visual, Auditory and Combined StimulusDocument7 pagesLab 4: Finger Reaction Time To Visual, Auditory and Combined Stimulusapi-318013724No ratings yet
- Intro To QeegDocument19 pagesIntro To Qeegashulimson100% (1)
- Chapter - 9 - Making InferencesDocument17 pagesChapter - 9 - Making InferencesGaming User100% (1)
- Bloom's Taxonomy: Educational Objectives (Handbook One, Pp. 201-207)Document3 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: Educational Objectives (Handbook One, Pp. 201-207)Md. Main Uddin BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- 04 Key Psychological ProcessesDocument31 pages04 Key Psychological ProcessesAshutosh Sonker100% (1)
- Formal-Mc Test StrategiesDocument5 pagesFormal-Mc Test StrategiesAri Brownstone100% (1)
- Younger and Older LearnersDocument3 pagesYounger and Older LearnersboukonnashNo ratings yet
- Adl Feeding Assignment 2Document11 pagesAdl Feeding Assignment 2api-631747744No ratings yet
- The Neuropsychology of Men: Charles M. Zaroff Rik Carl D'Amato EditorsDocument245 pagesThe Neuropsychology of Men: Charles M. Zaroff Rik Carl D'Amato EditorsFelipe CortesNo ratings yet
- (Psychology of Learning and Motivation Volume 62) Ross, Brian H - (2015, Academic Press) PDFDocument241 pages(Psychology of Learning and Motivation Volume 62) Ross, Brian H - (2015, Academic Press) PDFJuan David SanzNo ratings yet
- Basic Motivation Concepts: Organizational BehaviorDocument23 pagesBasic Motivation Concepts: Organizational BehaviorAditi SoniNo ratings yet
- Causes of Mental IllnessDocument4 pagesCauses of Mental IllnessRima Pigar Goza MeleloaNo ratings yet
- (IGNOU ASM.) Characteristics of Good CommunicatorsDocument2 pages(IGNOU ASM.) Characteristics of Good CommunicatorsTeleTech RKNo ratings yet
- IAH 231C Syllabus FS14Document4 pagesIAH 231C Syllabus FS14Arthur ChenNo ratings yet
- CB Review Videos Operant ConditioningDocument5 pagesCB Review Videos Operant ConditioningJose G. matamorosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Bullets: Psychiatric Nursing I: 14. Echolalia Is Parrotlike Repetition of Another Person's Words or PhrasesDocument2 pagesNursing Bullets: Psychiatric Nursing I: 14. Echolalia Is Parrotlike Repetition of Another Person's Words or PhrasesJagveer ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Models of Consumer BehaviourDocument8 pagesModels of Consumer Behaviourdibyendu_mondal100% (4)
- Ketamine-Assisted Psychotherapy:: A Practical Guide For Medical ProvidersDocument40 pagesKetamine-Assisted Psychotherapy:: A Practical Guide For Medical ProvidersMannu MoguritoNo ratings yet
- 1950 WeitzenhofferDocument3 pages1950 Weitzenhofferla taupeNo ratings yet
- Conduct Disorder: The Seeds of Crime Sarath Sundar, Ma (Psy), Mphil (M&SP) Clinical Psychologist and HypnotherapistDocument2 pagesConduct Disorder: The Seeds of Crime Sarath Sundar, Ma (Psy), Mphil (M&SP) Clinical Psychologist and HypnotherapistSarath S SundarNo ratings yet
- Learners With Learning Disabilities and AdhdDocument18 pagesLearners With Learning Disabilities and AdhdYanna LozanoNo ratings yet
- Acadsoc BookDocument6 pagesAcadsoc Bookmarizon datuNo ratings yet
- 3nu08 MseDocument3 pages3nu08 MseVILLANUEVA ARASELNo ratings yet
- Differentiated Instruction: Interest Learning Profile ReadinessDocument26 pagesDifferentiated Instruction: Interest Learning Profile ReadinessLiza Cabalquinto LorejoNo ratings yet
Book Based Pathophysiology - Hemorrhagic Stroke
Book Based Pathophysiology - Hemorrhagic Stroke
Uploaded by
ZAY EMOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Book Based Pathophysiology - Hemorrhagic Stroke
Book Based Pathophysiology - Hemorrhagic Stroke
Uploaded by
ZAY EMCopyright:
Available Formats
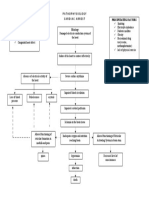
BOOK BASED PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
LEGENDS: DISEASE RISK ETIOLOGY SIGNS AND POTENTIAL DISEASE
MECHANISM FACTORS SYMPTOMS COMPLICATIONS
NON-MODIFIABLE: MODIFIABLE:
Age: 65 y/o and above (old age) High blood pressure
Gender: Female Excessive alcohol intake
Ethnicity: Asian Use of medications (e.g., anticoagulants
Family History of Stroke and amphetamines)
History of Ischemic Stroke Cigarette smoking
Overweight
Cerebral amyloid Hypertension Head Trauma
angiopathy
Vascular Cerebral
malformations atherosclerosis
Compromise integrity of cerebral artery
Weaken the blood vessel wall
Sudden, severe headache Rupture of the cerebral artery
Intraparenchymal blood accumulation
Build-up of pressure
Nausea and vomiting
↓ level of consciousness
Without medical intervention ↑ intracranial pressure Cranial nerve deficit
Pathological posturing
Cushing’s triad
Brain herniation Compression of the brain
Disruption of normal blood flow and O2
Comatose Stupor circulation
↓ cerebral perfusion
DEATH
Cerebral ischemia
Brain cell damage
Alterations in the cerebral component
Right or left hemiparesis Vasospasm
Altered level of consciousness Seizures
Sluggish pupillary reaction Hydrocephalus
Motor and sensory dysfunction Rebleeding
Cranial nerve deficits Hyponatremia
Speech difficulties and visual disturbances
Neck stiffness
(Brunner and Suddarth’s Textbook of Medical-Surgical
(Brunner and Suddarth’s Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing, 14th Edition.) Nursing, 14th Edition.)
HEMORRHAGIC CEREBROVASCULAR ACCIDENT/ STROKE
You might also like
- Rehab Cheat SheetDocument18 pagesRehab Cheat SheetZ A100% (3)
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Pathophysiologynursing concept maps40% (5)
- Neurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IIFrom EverandNeurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeAqeel Al-Mahdaly0% (1)
- Stroke RehabilitationDocument57 pagesStroke RehabilitationWahyu FajarNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology PDFMohd Amir Bin Bashir0% (1)
- Schematic Diagram On The 4 Types of ShockDocument5 pagesSchematic Diagram On The 4 Types of Shockgodgiven25100% (5)
- Pathophysiology Total Anterior Circulation Infarction Left Middle Cerebral Artery (TACILMCA)Document2 pagesPathophysiology Total Anterior Circulation Infarction Left Middle Cerebral Artery (TACILMCA)PATHOSHOPPE100% (1)
- 2 Social Political and Cultural Behavior and PhenomenaDocument4 pages2 Social Political and Cultural Behavior and PhenomenaKeano Christian MacrohonNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Lesson Plan 5Document2 pagesMental Health Lesson Plan 5api-143975079No ratings yet
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument2 pagesSubarachnoid HemorrhageJethro Bacayo Zamora100% (1)
- Pathophysiology ErDocument3 pagesPathophysiology ErAlexa A. AldayNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJet Ray-Ann GaringanNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology StrokeDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology StrokeknazaretaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Disorders of Consciousness and Language I (Coma and Confusional States) LectureDocument119 pages10 - Disorders of Consciousness and Language I (Coma and Confusional States) LectureRanjit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Iskemia Kerusakan Membran Nekrosis Sel Gangguan Sel Ca InflukDocument12 pagesIskemia Kerusakan Membran Nekrosis Sel Gangguan Sel Ca Influkmuhammad_aulia_5No ratings yet
- Stroke Pathophysiology 1Document5 pagesStroke Pathophysiology 1Jeco ValdezNo ratings yet
- Stroke PathoDocument1 pageStroke PathograsyaNo ratings yet
- TBI PathophysioClinicalManifestationsDocument7 pagesTBI PathophysioClinicalManifestationsJan Philippe BelandoNo ratings yet
- Pendukung StrokeDocument202 pagesPendukung StrokeNovita DuffNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: P A R A L Y S I SDocument1 pagePathophysiology: P A R A L Y S I SJordan Garcia AguilarNo ratings yet
- Strokeppt 170720174010Document95 pagesStrokeppt 170720174010Venosha GunasekaranNo ratings yet
- PathophysioDocument2 pagesPathophysioceyieNo ratings yet
- Bab IiDocument13 pagesBab IiNanda SusiloNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Cerebrovascular Accident Hemorrhagic Right Lobe)Document4 pagesPathophysiology (Cerebrovascular Accident Hemorrhagic Right Lobe)jhonkivenNo ratings yet
- 1 - Rehabilitasi Medik Pada Penderita StrokeDocument55 pages1 - Rehabilitasi Medik Pada Penderita StrokeKrisma susantiNo ratings yet
- Definition and Etiology: Back To TopDocument9 pagesDefinition and Etiology: Back To TopMark Earlmafrey SaguiboNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Stroke: The Normal Blood Supply To The Brain Is DisruptedDocument5 pagesIschemic Stroke: The Normal Blood Supply To The Brain Is DisruptedMelchora Lea Castro SorianoNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: Darpen Subhashbhai Mori Group 2, MD 3BDocument13 pagesHemorrhagic Stroke: Darpen Subhashbhai Mori Group 2, MD 3BDarpen MoriNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGYJeroham CoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Stroke - NewDocument4 pagesNursing Care of Stroke - Newninda saputriNo ratings yet
- Stroke Syndromes and Localization 2007Document56 pagesStroke Syndromes and Localization 2007SaintPaul Univ100% (1)
- Geriatric SyndromeDocument49 pagesGeriatric Syndromewita prabawatiNo ratings yet
- Overview of Stroke - Knowledge at AMBOSSDocument19 pagesOverview of Stroke - Knowledge at AMBOSSandimija16No ratings yet
- StrokeDocument28 pagesStrokeBEA RADANo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology MSDocument3 pagesPathophysiology MSLord Allen B. GomezNo ratings yet
- NonmodifiableDocument4 pagesNonmodifiableAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.No ratings yet
- Case Study CvaDocument6 pagesCase Study Cvajing_elizabethNo ratings yet
- Neurology (Cerebrovascular Disease)Document69 pagesNeurology (Cerebrovascular Disease)Mahadhir AkmalNo ratings yet
- KUL 8 Stroke Nursing ManagementDocument45 pagesKUL 8 Stroke Nursing ManagementErina NopiyantiNo ratings yet
- Special Neurology - Second Edition RevisedDocument115 pagesSpecial Neurology - Second Edition RevisedAimee100% (1)
- Special NeurologyDocument115 pagesSpecial NeurologyUbaidillah Romadlon AlfairuziNo ratings yet
- Notes On SyncopeDocument8 pagesNotes On SyncopeViswa Giri100% (1)
- Cva (Npte)Document16 pagesCva (Npte)papermannerNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi Dan Penyimpangan KDM StrokeDocument1 pagePatofisiologi Dan Penyimpangan KDM StrokeNur Fadyla PeluNo ratings yet
- FINALe ISCHEMIC STROKES NEUROSURGDocument13 pagesFINALe ISCHEMIC STROKES NEUROSURGadrian kristopher dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive ICHDocument49 pagesHypertensive ICHmingchuan chuNo ratings yet
- Penilaian Awal Pasien SyokDocument33 pagesPenilaian Awal Pasien SyokatikaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Disease Lipincott 24 10 2012 FinalDocument10 pagesCerebrovascular Disease Lipincott 24 10 2012 Finalرافت العواضيNo ratings yet
- Subdural Woc IchaDocument1 pageSubdural Woc IchaNajla KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Refreshing Shock: Pembimbing: Dr. Fauzi Abdillah Susman, SP - An, MSC Disusun Oleh: Achmad Reza SyamsuladeDocument14 pagesRefreshing Shock: Pembimbing: Dr. Fauzi Abdillah Susman, SP - An, MSC Disusun Oleh: Achmad Reza SyamsuladeSam.No ratings yet
- Seminar On Management of StrokeDocument54 pagesSeminar On Management of Stroke7762n9qsntNo ratings yet
- Stroke PathoDocument15 pagesStroke PathoWiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Pathopyshiology-w-Risk-Factors - DTDocument3 pagesPathopyshiology-w-Risk-Factors - DTDivynne MadeloNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Cva... by Mizzy BaylonDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Cva... by Mizzy BaylonmizzybaylonNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Cardiac ArrestDocument1 pagePathophysiology Cardiac ArrestPATHOSHOPPE100% (2)
- PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPathophysiologyDimple BlancoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - Tia VS CvaDocument6 pagesPathophysiology - Tia VS CvaZeo Zafaralla100% (1)
- Pathways Hypertension On ElderlyDocument1 pagePathways Hypertension On ElderlyFuzna DahliaNo ratings yet
- Compendium on Cardiomyopathies - Basics, Therapeutics, and PerspectivesFrom EverandCompendium on Cardiomyopathies - Basics, Therapeutics, and PerspectivesNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic/Laborator Y Procedures Indication/Purpose S Result Analysis and Interpretation of Results Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDiagnostic/Laborator Y Procedures Indication/Purpose S Result Analysis and Interpretation of Results Nursing ResponsibilitiesZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Area Assessment Description of Findings & Interpretation General Appearance PostureDocument6 pagesArea Assessment Description of Findings & Interpretation General Appearance PostureZAY EMNo ratings yet
- FFFFDocument2 pagesFFFFZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: Is Used To Dissolve (Cholesterol) Gallstones and PDocument9 pagesGeneric Name:: Is Used To Dissolve (Cholesterol) Gallstones and PZAY EMNo ratings yet
- PREECLAMPSIADocument9 pagesPREECLAMPSIAZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Gestational DiabetesDocument6 pagesGestational DiabetesZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument5 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Viral GastroenteritisDocument1 pageViral GastroenteritisZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument2 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Viral GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesViral GastroenteritisZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Gestational DiabetesDocument1 pageGestational DiabetesZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Simplifying Numerical Expressions: Rules For The Order of ExpressionDocument4 pagesSimplifying Numerical Expressions: Rules For The Order of ExpressionZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Florence Nightingale'S Environmental TheoryDocument16 pagesFlorence Nightingale'S Environmental TheoryZAY EMNo ratings yet
- BasketballDocument11 pagesBasketballZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Hildegard Peplau: Interpersonal Relations TheoryDocument4 pagesHildegard Peplau: Interpersonal Relations TheoryZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Hildegard Peplau: Interpersonal Relations TheoryDocument5 pagesHildegard Peplau: Interpersonal Relations TheoryZAY EMNo ratings yet
- InfographicDocument1 pageInfographicZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Speech BullyingDocument1 pageSpeech BullyingZAY EMNo ratings yet
- What Is HallucinogensDocument3 pagesWhat Is HallucinogenskerenNo ratings yet
- Ion Channels PDFDocument7 pagesIon Channels PDFHyunji KimNo ratings yet
- Agggression ScaleDocument4 pagesAgggression ScaleDixha BaggaNo ratings yet
- On Consciousness - Science and Subjectivity - A Q&A With Bernard Baars - Scientific American Blog NetworkDocument16 pagesOn Consciousness - Science and Subjectivity - A Q&A With Bernard Baars - Scientific American Blog NetworkFred MeyerNo ratings yet
- Lab 4: Finger Reaction Time To Visual, Auditory and Combined StimulusDocument7 pagesLab 4: Finger Reaction Time To Visual, Auditory and Combined Stimulusapi-318013724No ratings yet
- Intro To QeegDocument19 pagesIntro To Qeegashulimson100% (1)
- Chapter - 9 - Making InferencesDocument17 pagesChapter - 9 - Making InferencesGaming User100% (1)
- Bloom's Taxonomy: Educational Objectives (Handbook One, Pp. 201-207)Document3 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: Educational Objectives (Handbook One, Pp. 201-207)Md. Main Uddin BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- 04 Key Psychological ProcessesDocument31 pages04 Key Psychological ProcessesAshutosh Sonker100% (1)
- Formal-Mc Test StrategiesDocument5 pagesFormal-Mc Test StrategiesAri Brownstone100% (1)
- Younger and Older LearnersDocument3 pagesYounger and Older LearnersboukonnashNo ratings yet
- Adl Feeding Assignment 2Document11 pagesAdl Feeding Assignment 2api-631747744No ratings yet
- The Neuropsychology of Men: Charles M. Zaroff Rik Carl D'Amato EditorsDocument245 pagesThe Neuropsychology of Men: Charles M. Zaroff Rik Carl D'Amato EditorsFelipe CortesNo ratings yet
- (Psychology of Learning and Motivation Volume 62) Ross, Brian H - (2015, Academic Press) PDFDocument241 pages(Psychology of Learning and Motivation Volume 62) Ross, Brian H - (2015, Academic Press) PDFJuan David SanzNo ratings yet
- Basic Motivation Concepts: Organizational BehaviorDocument23 pagesBasic Motivation Concepts: Organizational BehaviorAditi SoniNo ratings yet
- Causes of Mental IllnessDocument4 pagesCauses of Mental IllnessRima Pigar Goza MeleloaNo ratings yet
- (IGNOU ASM.) Characteristics of Good CommunicatorsDocument2 pages(IGNOU ASM.) Characteristics of Good CommunicatorsTeleTech RKNo ratings yet
- IAH 231C Syllabus FS14Document4 pagesIAH 231C Syllabus FS14Arthur ChenNo ratings yet
- CB Review Videos Operant ConditioningDocument5 pagesCB Review Videos Operant ConditioningJose G. matamorosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Bullets: Psychiatric Nursing I: 14. Echolalia Is Parrotlike Repetition of Another Person's Words or PhrasesDocument2 pagesNursing Bullets: Psychiatric Nursing I: 14. Echolalia Is Parrotlike Repetition of Another Person's Words or PhrasesJagveer ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Models of Consumer BehaviourDocument8 pagesModels of Consumer Behaviourdibyendu_mondal100% (4)
- Ketamine-Assisted Psychotherapy:: A Practical Guide For Medical ProvidersDocument40 pagesKetamine-Assisted Psychotherapy:: A Practical Guide For Medical ProvidersMannu MoguritoNo ratings yet
- 1950 WeitzenhofferDocument3 pages1950 Weitzenhofferla taupeNo ratings yet
- Conduct Disorder: The Seeds of Crime Sarath Sundar, Ma (Psy), Mphil (M&SP) Clinical Psychologist and HypnotherapistDocument2 pagesConduct Disorder: The Seeds of Crime Sarath Sundar, Ma (Psy), Mphil (M&SP) Clinical Psychologist and HypnotherapistSarath S SundarNo ratings yet
- Learners With Learning Disabilities and AdhdDocument18 pagesLearners With Learning Disabilities and AdhdYanna LozanoNo ratings yet
- Acadsoc BookDocument6 pagesAcadsoc Bookmarizon datuNo ratings yet
- 3nu08 MseDocument3 pages3nu08 MseVILLANUEVA ARASELNo ratings yet
- Differentiated Instruction: Interest Learning Profile ReadinessDocument26 pagesDifferentiated Instruction: Interest Learning Profile ReadinessLiza Cabalquinto LorejoNo ratings yet