Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Female and Male Reproductive Organs
Female and Male Reproductive Organs
Uploaded by
Pink Eaint0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
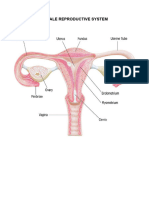
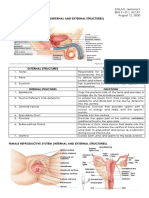
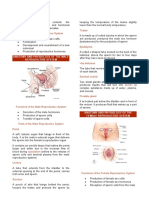
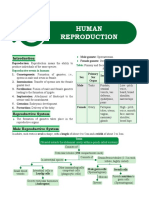
30 views2 pagesThe male reproductive organs include the testes, which produce sperm and hormones; the scrotum, which holds the testes; and the penis, which carries urine, semen, and allows for erection and ejaculation. The female reproductive organs include the ovaries, which produce eggs and hormones; the fallopian tubes, where fertilization occurs; the uterus, which nourishes a fetus; the vagina, which receives sperm; and the cervix, which allows sperm entry into the uterus.
Original Description:
By Aureline
Original Title
Female and male reproductive organs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe male reproductive organs include the testes, which produce sperm and hormones; the scrotum, which holds the testes; and the penis, which carries urine, semen, and allows for erection and ejaculation. The female reproductive organs include the ovaries, which produce eggs and hormones; the fallopian tubes, where fertilization occurs; the uterus, which nourishes a fetus; the vagina, which receives sperm; and the cervix, which allows sperm entry into the uterus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views2 pagesFemale and Male Reproductive Organs
Female and Male Reproductive Organs
Uploaded by
Pink EaintThe male reproductive organs include the testes, which produce sperm and hormones; the scrotum, which holds the testes; and the penis, which carries urine, semen, and allows for erection and ejaculation. The female reproductive organs include the ovaries, which produce eggs and hormones; the fallopian tubes, where fertilization occurs; the uterus, which nourishes a fetus; the vagina, which receives sperm; and the cervix, which allows sperm entry into the uterus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
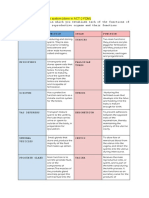
Male reproductive organ Structures Functions
Testes (testis) Two oval shape covered by Produce
scrotum. Each testis is hormones(testosterones
covered by tunica(tough, and androgens) and
fibrous layer) sperm
Scrotum Skin layer covered the Holds the testes and
testes that looks like a sac keeps the temperature
of the testes two degree
below the body
temperature
Penis Made of spongy tissue Carries both urine and
which can be filled with semen ,causes urination,
blood erection and ejaculation
Erectile tissue Located in corpora Capable of erection
cavernosa of the penis
Sperm duct/vas deferen Long, muscular tube that Allow sperm to reach
runs from the epididymis outside
into the pelvis cavity
Epididymis Long, narrow and coiled Carries, stores sperm
tube that rests on each and makes them mature
testis because sperms that
come out of the testes
are immature
Prostate gland Gland located below the Produce the fluid that
bladder and joins sperm nourishes and
duct and urethra transports sperm
Urethra Muscular fibrous structure Allow urine and semen
enclosed by urethral to the outside of the
sphincter that connects the body
exterior of the body
Female reproductive Structures Functions
organ
Ovary Located in dorsal side Produce ovum,
of the abdomen hormones (oestrogen
and progesterone )
Oviduct/Fallopian tube Muscular and elastic Transport follicle from
tube where fertilization ovary to uterus and
occurs allow fertilization
Uterus Hollow, pear-shaped Nourish the fetus for
organ and has three further developments
layers (Endometrium,
myometrium and
perimetrium)
Vagina Muscular, elastic birth Receive penis during
canal with a soft, intercourse and hold
flexible lining the sperm until they
pass uterus; provide the
pathway for child birth
Cervix Circular opening that Allow passage into the
attaches the uterus and uterus and produce
vagina mucus to facilitate
sperm entry
You might also like
- Ana ReproDocument4 pagesAna ReproFIONA DANE MAURERANo ratings yet
- Week 2 Supplementary Activity 1 - Parts and Function Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesWeek 2 Supplementary Activity 1 - Parts and Function Reproductive SystemBernadette Vidon-PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Reproduction NotesDocument2 pagesReproduction NotesNerminNo ratings yet
- MATERNAL-AND-CHILD-NURSING Notes For BoardsDocument10 pagesMATERNAL-AND-CHILD-NURSING Notes For BoardsJill Margarett BongatoNo ratings yet
- Topic 17: ReproductionDocument29 pagesTopic 17: ReproductionEva SidhaniNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument41 pagesHuman ReproductionMmabatho Vilakazi100% (1)
- Y11 Hum - Rep1 20 3 17Document8 pagesY11 Hum - Rep1 20 3 17Rabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction: Male Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesSexual Reproduction: Male Reproductive SystemcyprianNo ratings yet
- Science 5 DLP 1 Human Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesScience 5 DLP 1 Human Reproductive SystemDyaan TrajicoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesReproductive SystemkhakimagdalenaNo ratings yet
- Cmca 1Document5 pagesCmca 1Erika Mae Sta. MariaNo ratings yet
- Third Term s2 BiologyDocument34 pagesThird Term s2 BiologyADEYI KAYODE SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document21 pagesPresentation 2ericasinamagNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System - Bio 2 - 12 Stem - l11Document4 pagesReproductive System - Bio 2 - 12 Stem - l11Lyka Lobido CabeltesNo ratings yet
- Concept Block - NamocoDocument4 pagesConcept Block - NamocoGladys NamocoNo ratings yet
- MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SySTEMDocument10 pagesMALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SySTEMMyca HernandezNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburDocument24 pagesReproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburOKTAVIANI HAPSARINo ratings yet
- Science 10 NOTESDocument23 pagesScience 10 NOTESnamoramica1No ratings yet
- Group3 ReproductivesystemDocument19 pagesGroup3 ReproductivesystemLeonie OngNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesMale Reproductive SystemLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- TWINKL Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesTWINKL Knowledge OrganiserDearbhla HubbardNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageMale Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemEunimae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Biomedical PerpectiveDocument22 pagesBiomedical Perpectiveedmaration 2002No ratings yet
- MCN LEC (Prelims)Document19 pagesMCN LEC (Prelims)BIANCA ANGELICA GERARDONo ratings yet
- Science 5 ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 5 ReviewerAlexandra Pauline DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesReproductive SystemaynNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Reviewer 3RDDocument12 pagesScience 10 Reviewer 3RDaltheaburgas9No ratings yet
- SXSXDocument27 pagesSXSXJoevany E. BigorniaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesReproductive SystemMARYLOUISE SANDIEGONo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System Cut and StickDocument3 pagesHuman Reproductive System Cut and StickLachlan WRIGHTNo ratings yet
- PARTSDocument2 pagesPARTSMary joy DominguezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemHye JinNo ratings yet
- Science 5Document26 pagesScience 5barangay89zone9No ratings yet
- File 0441Document149 pagesFile 0441Kellie ManganNo ratings yet
- Male & Female Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesMale & Female Reproductive SystemCandly SHi100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyanglogaliboNo ratings yet
- Bobiles Edwin Activity No 2Document3 pagesBobiles Edwin Activity No 2Edwin BobilesNo ratings yet
- S10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREDocument35 pagesS10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREREGLOS, Marie Nhelle K.No ratings yet
- Fantiyao Reproductive System Group 2Document4 pagesFantiyao Reproductive System Group 2Jushelle Anne Tigoy PilareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3melanielampera17No ratings yet
- Reproductive System ModuleDocument17 pagesReproductive System ModulePATRICIA KAYE RIONo ratings yet
- Reproductive System ChartDocument2 pagesReproductive System ChartValeria Guadalupe Ramírez MoctezumaNo ratings yet
- Alt 1 Emlan BSN Ii DDocument3 pagesAlt 1 Emlan BSN Ii DJERMINA EMLANNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3RD QuarterDocument13 pagesScience Reviewer 3RD QuarterKurt John DecenaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Sci Ed 204 p2Document29 pagesLesson 7 Sci Ed 204 p2Allysa Marie SilbolNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Systems ReviewerDocument4 pagesReproductive Systems ReviewerAustin LaurenNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 10 ICSEDocument5 pagesPhysics Class 10 ICSEmohammedumar7864521No ratings yet
- 4 Animal Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument26 pages4 Animal Reproduction and DevelopmentEGUIA, MARY SHENIETH M.No ratings yet
- Maternal and ChildDocument20 pagesMaternal and ChildpaderamosNo ratings yet
- PSGUNP279020221123075249578Unit 2 - Lesson 3 - Human Reproductive System - OrgansDocument11 pagesPSGUNP279020221123075249578Unit 2 - Lesson 3 - Human Reproductive System - OrgansAshneel ChakravortyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Introduction To Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesLecture Notes Introduction To Reproductive SystemKirstie Goc-ongNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Power Point AckroydDocument19 pagesReproductive System Power Point AckroydTrung Ngô Lê BảoNo ratings yet
- 07 05 Reproductive SystemDocument6 pages07 05 Reproductive SystemOkoye ClappinNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Old FormatDocument4 pagesReproductive System Old FormatRobie SanaoNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NO 3 - Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesLECTURE NO 3 - Reproductive SystemRebell AeonNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument19 pagesHuman ReproductionSantosh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Gzoo111-Rs-Finals Olfu ReviewerDocument4 pagesGzoo111-Rs-Finals Olfu ReviewerelynpecsonNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Reproduction Education Presentation in Peach Violet Hand Drawn Lightly Textured StyleDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Human Reproduction Education Presentation in Peach Violet Hand Drawn Lightly Textured StylemarcosryanhmaranhaoNo ratings yet
- Ovaries: The Female Gonads, The Ovaries Produce Ova. When One Matures, It Is Released Down Into A Fallopian TubeDocument2 pagesOvaries: The Female Gonads, The Ovaries Produce Ova. When One Matures, It Is Released Down Into A Fallopian TubeCyril AlngogNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q3 W1 Role-of-Hormones Contada Baguio-City FinalDocument15 pagesScience10 Q3 W1 Role-of-Hormones Contada Baguio-City FinalFrancis BordonNo ratings yet
- Topic: Mechanisms of Fertilization:: Presented byDocument16 pagesTopic: Mechanisms of Fertilization:: Presented byMajani RajbonshiNo ratings yet
- Hormones and Related Drugs: Mechanism of ActionDocument21 pagesHormones and Related Drugs: Mechanism of ActionaviraaworldNo ratings yet
- Treatment With Piroxicam Before Embryo Transfer Increases The Pregnancy Rate After in Vitro Fertilization and Embryo TransferDocument5 pagesTreatment With Piroxicam Before Embryo Transfer Increases The Pregnancy Rate After in Vitro Fertilization and Embryo TransferVasantham HospitalNo ratings yet
- MRKH MenopauseDocument3 pagesMRKH Menopausediudiu93No ratings yet
- Individual Activity Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesIndividual Activity Reproductive Systemshiela100% (1)
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument25 pagesHow Do Organisms ReproduceSubrata MallickNo ratings yet
- Histology of Uterus and VaginaDocument22 pagesHistology of Uterus and VaginaMuhammad Touseef TahirNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Physiology "Female Reproductive Anatomy": ResearchDocument18 pagesReproductive Physiology "Female Reproductive Anatomy": ResearchCarol OrequesNo ratings yet
- Detailed EoT Coverage 9 ADVDocument50 pagesDetailed EoT Coverage 9 ADVNKANo ratings yet
- Sind Ovario Poliquistico 2016 - NejmDocument11 pagesSind Ovario Poliquistico 2016 - NejmAntonio MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Elementary Science Grade 5 Lesson Plan PDFDocument348 pagesElementary Science Grade 5 Lesson Plan PDFAruba Ashhar100% (2)
- 1332 (1) D 2019-08-01 PDFDocument17 pages1332 (1) D 2019-08-01 PDFWassim DjennaneNo ratings yet
- Cse Integration Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesCse Integration Lesson PlanCarl Anthony Lague PahuyoNo ratings yet
- Biology Project File On InfertilityDocument13 pagesBiology Project File On InfertilityDhananjay Yadav100% (1)
- Steroids 1Document9 pagesSteroids 1nafkjfnakfaNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER - Gen Bio - 4th QuarterDocument4 pagesREVIEWER - Gen Bio - 4th QuarterJona Rose TecsonNo ratings yet
- Gamete Formation in Animals PDFDocument5 pagesGamete Formation in Animals PDFStarlight 101100% (1)
- Escala de TannerDocument1 pageEscala de TannerEduardo G. AltamiranoNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Teacher NotesDocument3 pagesMale Reproductive Teacher Notespaigebotlon30No ratings yet
- Exercise 4.7Document9 pagesExercise 4.7Norelawati Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- Shukra DhatuDocument29 pagesShukra Dhatushilpa yermeNo ratings yet
- GTU 104.2015 Teaching Timetable and Assessment ScheduleDocument9 pagesGTU 104.2015 Teaching Timetable and Assessment ScheduleJebatAl-KelantaniNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of PcosDocument14 pagesPathogenesis of PcosMitali Narurkar100% (1)
- Tribulus-Terrestris-Protodioscin-In-The-Treatment-Of-Male-Infertility-With-Idiopathic-Oligoasthenoterato-Zoospermia (Biosan)Document4 pagesTribulus-Terrestris-Protodioscin-In-The-Treatment-Of-Male-Infertility-With-Idiopathic-Oligoasthenoterato-Zoospermia (Biosan)Farmasi PHMANo ratings yet
- Ambiguous GenitaliaDocument24 pagesAmbiguous GenitaliaYolanda SamsudinNo ratings yet
- Biology Sample PaperDocument225 pagesBiology Sample PaperSIBINo ratings yet
- Reproduction 8 QP 5090Document10 pagesReproduction 8 QP 5090sunflower rantsNo ratings yet
- Istilah Medis Dan Tindakan Medis Sistem Reproduksi WanitaDocument19 pagesIstilah Medis Dan Tindakan Medis Sistem Reproduksi WanitaJude Had a FarmNo ratings yet
- Follow Up After OrchidopexyDocument5 pagesFollow Up After OrchidopexyMangkubumi PutraNo ratings yet