Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Croprecipitate Guidelines
Croprecipitate Guidelines
Uploaded by
Sahil AroraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Croprecipitate Guidelines
Croprecipitate Guidelines
Uploaded by
Sahil AroraCopyright:
Available Formats
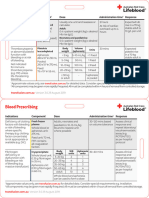
Guidelines for cryoprecipitate transfusion
Table. Characteristics of four frozen plasma products.
Frozen plasma Fresh-frozen plasma Cryoprecipitate plasma Cryosupernatant plasma
(from whole blood collection) (from apheresis collection) (cryo) (cryo-poor plasma)
Whole blood is centrifuged at Whole blood is processed Plasma is frozen for 24 hours, Plasma is frozen for 24 hours,
high speed, allowing separa- through a cell separator to and then thawed at 1°– 6°C and then thawed at 1°– 6°C
tion of plasma, red blood cells obtain plasma. Plasma is until insoluble proteins precip- until insoluble proteins precip-
(RBCs), and the buffy coat frozen within 8 hours of col- itate. The pack is centrifuged itate. The pack is centrifuged
layer (platelets, white blood lection and is designated as to obtain the cryoprecipitate. to obtain the supernatant.
cells, some RBCs and plasma). fresh-frozen plasma (FFP). In The cryoprecipitate is then The supernatant, or cryo-poor
Plasma is frozen within 24 general, 1 unit of FFP from refrozen for storage. plasma, is then refrozen for
hours of collection and is des- apheresis collection is equiva- storage.
ignated as frozen plasma (FP). lent to approximately 2 units Once thawed, the product
It is prepared for use by thaw- of FP from whole blood collec- should be transfused immedi- Once thawed, the product
Preparation
ing at 37°C, a process that can tion. The two products can be ately, with completion of should be transfused immedi-
take up to 30 minutes. used interchangeably. transfusion within 4 hours of ately, with completion of
issuing product. transfusion within 4 hours of
Once thawed, the product Once thawed, the product issuing product.
should be transfused immedi- should be transfused immedi-
ately, with completion of ately, with completion of
transfusion within 4 hours of transfusion within 4 hours of
issuing product. issuing product.
Contains all of the coagulation Contains all of the coagulation Contains FVIII:C, von Is deficient in high molecular
factors, including the labile factors, including the labile Willebrand factor (vWF), fib- weight vWF multimers and
factors (FV and FVIII:C). For factors (FV and FVIII:C). rinogen, FXIII, and fibronectin. FVIII:C.
product prepared within 24 Cryoprecipitate has the fol-
hours of collection, FVIII:C lev- lowing factor activities:
els are less than those found 91 IU of FVIII: C per bag,
in fresh-frozen plasma pre- 113 IU of vWF per bag, and
Factors pared within 8 hours of collec- 150 mg of fibrinogen per bag.
tion, but levels are still at or
above 0.50 IU/mL. FP can be
used for coagulation factor
replacement except for isolat-
ed or severe FVIII deficiency.
Each bag = 1 unit Each bag = 1 unit Each bag = 1 unit (5–15 mL) Each bag = 1 unit (>100 mL)
Volume
(200 – 250 mL) (100 – 600 mL)
Typical adult dose of plasma is Typical adult dose of plasma is Typical adult dose of cryo is Typically 1.0–1.5 times plasma
10–15 mL/kg body weight. 10–15 mL/kg body weight. 1 unit/5 kg body weight, up to volume exchange is
a total dose of 10 units (bags). performed per plasma
The pediatric dose of plasma The pediatric dose of plasma exchange (PLEX) run.
is 10–15 mL/kg body weight. is 10–15 mL/kg body weight. The pediatric dose is
1 unit/5–10 kg body weight or Indicated as replacement fluid
Infusion rate is over 2–3 Infusion rate is over 2–3 5–10 mL/kg. in PLEX for thrombotic throm-
Dose hours, or as required. hours, or as required. bocytopenic purpura.
Will raise fibrinogen by
Will raise factor levels by Will raise factor levels by 0.5 g/L, assuming there is no
25%, assuming there is no 25%, assuming there is no ongoing consumption/loss of
ongoing consumption/loss of ongoing consumption/loss of fibrinogen.
factors. factors.
VOL. 49 NO. 8, OCTOBER 2007 BC MEDICAL JOURNAL 443
You might also like
- PDF Sensory Transduction 2Nd Edition Gordon L Fain Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Sensory Transduction 2Nd Edition Gordon L Fain Ebook Full Chaptermark.sharp847100% (1)
- Atlas of Nerve Conduction Studies and ElectromyographyDocument326 pagesAtlas of Nerve Conduction Studies and ElectromyographySalazar Ángel100% (13)
- Reference: Harmening, D. M. (2012) - Modern Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices (6th Ed.) - Pp. 434Document5 pagesReference: Harmening, D. M. (2012) - Modern Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices (6th Ed.) - Pp. 434Kolin N Jandoc100% (1)
- Plasma Derivatives 2019Document63 pagesPlasma Derivatives 2019IlyasHasan100% (2)
- 2007 JulyAug Plasma TransfusionDocument9 pages2007 JulyAug Plasma TransfusionDR.RAJESWARI SUBRAMANIYANNo ratings yet
- Component & Effective Use of BloodDocument56 pagesComponent & Effective Use of BloodNorlelawati TalibNo ratings yet
- 05 Lanyard Cards - Blood Prescribing Card v3.2 FINALDocument2 pages05 Lanyard Cards - Blood Prescribing Card v3.2 FINALAbdul RaufNo ratings yet
- Cryoprecipitate The Current State of KnowledgeDocument12 pagesCryoprecipitate The Current State of KnowledgeAngel Bernardo GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Blood Component TherapyDocument82 pagesBlood Component TherapyVivek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Therapy HypoalbuminemiaDocument10 pagesTherapy HypoalbuminemiaFeny GoenNo ratings yet
- Blood DisordersDocument75 pagesBlood DisordersmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- OHSS Case Presentation Discussion - Jindal IVF CHDDocument41 pagesOHSS Case Presentation Discussion - Jindal IVF CHDJindal IVF ChandigarhNo ratings yet
- Blood Components and StorageDocument55 pagesBlood Components and Storagesamsonraju07No ratings yet
- Exchange TransfusionDocument13 pagesExchange TransfusionSaba WaheedNo ratings yet
- Blood Products 17-10-122Document40 pagesBlood Products 17-10-122Noorul AlamNo ratings yet
- Blood and Blood ProductsDocument52 pagesBlood and Blood Productswellawalalasith100% (1)
- D 8 Rate of Infusion For Blood Products V3Document2 pagesD 8 Rate of Infusion For Blood Products V3Abu HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Local Media5289763584533511516Document8 pagesLocal Media5289763584533511516Haniya KhanNo ratings yet
- Breeding in FishesDocument25 pagesBreeding in FishesAditya Rudra50% (2)
- PW Lab 4Document22 pagesPW Lab 4Diana CentaurusNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Exchange Transfusion (Neonatal)Document8 pagesNeonatal Exchange Transfusion (Neonatal)Muhammad ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Massive Transfusion SummaryDocument1 pageMassive Transfusion Summarypaul00040No ratings yet
- Exchange Transfusion Guidelines 2019Document8 pagesExchange Transfusion Guidelines 2019Dr AhmedNo ratings yet
- Indications For Plasma Products and CryoprecipitateDocument4 pagesIndications For Plasma Products and Cryoprecipitateraul sinatoNo ratings yet
- FRACP Transfusion Medicine Quiz: Anthea Greenway Clinical Haematology Clinical HaematologyDocument49 pagesFRACP Transfusion Medicine Quiz: Anthea Greenway Clinical Haematology Clinical HaematologyAhmed Abedo0% (1)
- Blood and Blood ProductsDocument16 pagesBlood and Blood ProductsMukhtar KhanNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument18 pagesBlood TransfusionRheimon Jay Abuan BalcitaNo ratings yet
- Blood Components-Practical: Written By: Presented To DateDocument5 pagesBlood Components-Practical: Written By: Presented To Datefayzah alshammariNo ratings yet
- l4. Component-PreparationDocument3 pagesl4. Component-Preparationjmdimasacat9No ratings yet
- Pharmacology Viva For The Anaesthesia PostgraduateDocument91 pagesPharmacology Viva For The Anaesthesia PostgraduateBaha MirzaeifarNo ratings yet
- Blood Components Ni AngelyDocument6 pagesBlood Components Ni AngelyMaxine AraralNo ratings yet
- Shaz 2014Document7 pagesShaz 2014putria aisyahNo ratings yet
- Study of Fertilization in Fish Through Induced Spawning Under Laboratory Conditions. Induced Spawning in FishDocument6 pagesStudy of Fertilization in Fish Through Induced Spawning Under Laboratory Conditions. Induced Spawning in FishMoaz FiazNo ratings yet
- Blood and Blood Product TransfusionDocument75 pagesBlood and Blood Product TransfusionHaileyesus NatnaelNo ratings yet
- AUBF Lec LESSON 1 - Pregnancy TestDocument12 pagesAUBF Lec LESSON 1 - Pregnancy TestnkbmanaliliNo ratings yet
- AEMV 2009 Conference Full ProceedingsDocument66 pagesAEMV 2009 Conference Full Proceedingscristina_gomhNo ratings yet
- Overview of Blood ComponentsDocument42 pagesOverview of Blood Componentsnashwaelsayedq2020No ratings yet
- Manual of Microbiological Culture Media - 14Document1 pageManual of Microbiological Culture Media - 14Amin TaleghaniNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument52 pagesBlood TransfusionAnonymous GC8uMx375% (4)
- West Midlands Regional Training Package For Safe Blood Transfusion PracticeDocument20 pagesWest Midlands Regional Training Package For Safe Blood Transfusion PracticeekramsNo ratings yet
- Embryo Transfer TechnologyDocument49 pagesEmbryo Transfer TechnologyshubhNo ratings yet
- Sperm Freezing Protocol PDFDocument2 pagesSperm Freezing Protocol PDFminh3010No ratings yet
- Blood ComponentDocument33 pagesBlood Componentmatrixtrinity100% (1)
- Blood Transfusion - Megha SoniDocument29 pagesBlood Transfusion - Megha SoniMegha VadanereNo ratings yet
- Blood Componant Therapy (Autosaved)Document47 pagesBlood Componant Therapy (Autosaved)drkapiltNo ratings yet
- Freezing CellsDocument1 pageFreezing CellsFarzana HossainNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 8 Embryo TransferDocument36 pagesLecture # 8 Embryo TransferPirin Pin PinNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion and Conservation During SurgeryDocument86 pagesBlood Transfusion and Conservation During SurgeryajefolakemijohnNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Apheresis - Use of Human Serum Albumin, Fresh Frozen Plasma and Cryosupernatant Plasma in Therapeutic Plasma ExchangeDocument11 pagesTherapeutic Apheresis - Use of Human Serum Albumin, Fresh Frozen Plasma and Cryosupernatant Plasma in Therapeutic Plasma ExchangePritha BhuwapaksophonNo ratings yet
- OB Care Plan - PP Hemorrhage - A.HadadDocument2 pagesOB Care Plan - PP Hemorrhage - A.HadadaudreyhadadNo ratings yet
- Ivm Protocol Medicult 1Document2 pagesIvm Protocol Medicult 1nilesh suvagiyaNo ratings yet
- Blood Banking ProceduresDocument5 pagesBlood Banking ProceduresTalon General Hospital Laboratory DepartmentNo ratings yet
- BLOOD,CELLULAR COMPONENTS AND PLASMA PRODUCTS AND THEIR USESDocument31 pagesBLOOD,CELLULAR COMPONENTS AND PLASMA PRODUCTS AND THEIR USESBenedict AnimNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument37 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationhipoclaudioNo ratings yet
- 551 PDFDocument5 pages551 PDFMouaadh SassiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-Prepa - Storage and Clin IndicationDocument35 pagesChapter 9-Prepa - Storage and Clin Indicationlewionline3No ratings yet
- Embryo Transfer: Paula Curtin Paula - Curtin@mtu - IeDocument12 pagesEmbryo Transfer: Paula Curtin Paula - Curtin@mtu - IePaula SteeleNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument37 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationMuhammad Adeeb100% (1)
- FolateDocument15 pagesFolatecarineNo ratings yet
- Canine Blood Component TableDocument1 pageCanine Blood Component TableTrifan PatriciaNo ratings yet
- Blood Banking - Component PreparationDocument34 pagesBlood Banking - Component PreparationLentoOt EksDiiNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Medical Sciences PDFDocument114 pagesFaculty of Medical Sciences PDFAriey MaQueenNo ratings yet
- Approach To Hematologic DisordersDocument8 pagesApproach To Hematologic DisorderstyasNo ratings yet
- 1ST Sem - Course Outline - BiologyDocument3 pages1ST Sem - Course Outline - BiologyMarielle AlystraNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Pathophysiology 6th Edition Banasik Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Pathophysiology 6th Edition Banasik Test Bank PDFkerolabeaudv100% (15)
- EnzymologyDocument13 pagesEnzymologyRane MandapatNo ratings yet
- 1607613832Document646 pages1607613832Andrei-Dorin BicaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy SGD (Posterior Forearm)Document2 pagesAnatomy SGD (Posterior Forearm)staezyevans0% (1)
- Encyclopedia of Cardiovascular Research and Medicine 1St Edition Douglas B Sawyer Full ChapterDocument67 pagesEncyclopedia of Cardiovascular Research and Medicine 1St Edition Douglas B Sawyer Full Chapterstephanie.stewart777100% (6)
- Case Presentation Intestinal Lymphangiectasia Group 4Document54 pagesCase Presentation Intestinal Lymphangiectasia Group 4Ponciana PasanaNo ratings yet
- Speaking Activity 27 DraftDocument6 pagesSpeaking Activity 27 DraftAishah FarihaNo ratings yet
- b4 Organisation in Animals Exam QsDocument30 pagesb4 Organisation in Animals Exam QsDarius “FlawlessStreak” OpreaNo ratings yet
- AP08 Cardio HeartDocument19 pagesAP08 Cardio HeartAmore BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Tishk International University: ApixabanDocument4 pagesTishk International University: ApixabanDyar MzafarNo ratings yet
- Immunodeficiency DiseasesDocument19 pagesImmunodeficiency DiseasesZaheer Abbas ChannaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 - SUBCELLULAR ORGANELLES. PART 2pdfDocument27 pagesLESSON 2 - SUBCELLULAR ORGANELLES. PART 2pdfVillanueva, Liv Harlet A.No ratings yet
- Antisence TechnologyDocument4 pagesAntisence TechnologyAlishan BangashNo ratings yet
- Basic Nail DesignDocument16 pagesBasic Nail DesignLudivina GalinganNo ratings yet
- Answer Key (Test-7) Zoology - UpdateDocument3 pagesAnswer Key (Test-7) Zoology - Update123No ratings yet
- Glufosinate-Ammonium: A Review of The Current State of KnowledgeDocument58 pagesGlufosinate-Ammonium: A Review of The Current State of KnowledgeYudhaNo ratings yet
- Complete Reflexology For Live (Inglés) Autor Barbara y Kevin Kunz-332-345Document14 pagesComplete Reflexology For Live (Inglés) Autor Barbara y Kevin Kunz-332-345Hombres Alto ValorNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Mock QuizDocument6 pagesGen Bio Mock QuizJarvis RazonNo ratings yet
- Advances in Laparoscopy of The Abdominal Wall HerniaDocument215 pagesAdvances in Laparoscopy of The Abdominal Wall HerniaErlan SantosNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument48 pagesReproductionaufaaNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. Biotech Syllabus MDUDocument51 pagesB. Tech. Biotech Syllabus MDUVineet50% (4)
- Biolympiads Training Camps Brochure - 2023Document15 pagesBiolympiads Training Camps Brochure - 2023martyynyyteNo ratings yet
- Direct Cardiac Reprogramming: Basics and Future Challenges: Andrianto Andrianto Eka Prasetya Budi Mulia Kevin LukeDocument7 pagesDirect Cardiac Reprogramming: Basics and Future Challenges: Andrianto Andrianto Eka Prasetya Budi Mulia Kevin Lukefita triastuti /ananda syifa ahmad syamilNo ratings yet
- WHLP Gen Bio 3 2nd QuarterDocument6 pagesWHLP Gen Bio 3 2nd QuarterSir JoshNo ratings yet
- Dural Opening/Removal For Combined Petrosal Approach: Technical NoteDocument5 pagesDural Opening/Removal For Combined Petrosal Approach: Technical NoteWilson Quispe AlanocaNo ratings yet