Professional Documents
Culture Documents
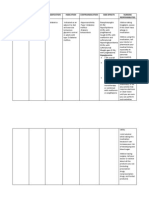
Dosage / Frequency Classification Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibilitites
Dosage / Frequency Classification Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibilitites
Uploaded by
Emm Estipona HaoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dosage / Frequency Classification Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibilitites
Dosage / Frequency Classification Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibilitites
Uploaded by
Emm Estipona HaoCopyright:
Available Formats
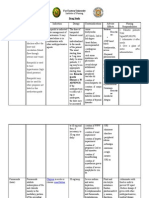
Generic / Trade Name
Dosage / Frequency
Classification
Indication
Contraindicatio n Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug and those with anuria.
Side Effects
Nursing Responsibilitites Alert: Monitor weight, blood pressure, and puls rate routinely with long term use.
Furosemide Acute Pulmonary Edema: Adults: 40 mg IV injected slowly over 1 to 2 minutes; then 80 mg IV in 60 to 90 minutes if needed.
Loop Diuretic
Acute Pulmonary Edema
Edema
CNS: vertigo, headache, dizziness, paresthesia, weakness, restlessness, fever.
Hypertension
Edema: Adults: 20 to 80 mg PO daily in the morning. If response in inadequate give a second dose and each succeeding dose every 6 to 8 hours. Carefully increase dose in 20 to 40 mg increments up too 600 mg
EENT: orthostatic hypotension, thrombophlebitis , with IV administration.
If Oliguria or Azotemia develops or increases, drug may be stopped.
GI: Abdominal discomfort and pain, diarrhea, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, constipation, pancreatitis.
Monitor fluid intake and output and electrolyte, BUN, and carbon dioxidelevels frequently.
Watch for signs of hypokalemia, such as muscle weakness and cramps.
GU:
daily. Once effective dose in attained, may give once or twice daily. Or 20 to 40 mg IV or IM., increased by 20 mg every 2 hours until desired effect achieved.
Azotemia, nocturia, polyuria, frequent urination, oliguria.
Consult prescriber or dietitian about a high-potassium diet or potassium supplements. Foods rich in potassium include citrus fruits, tomatoes, bananas, dates and apricots.
Infants and Children: 2mg/kg PO daily, increased by 1 to 2 mg/kg in 6 to 8 hours if needed; carefully adjusted up to 6mg/kg daily if needed.
Monitor glucose level in diabetic patients.
Hypertension: Adults: 40 mg PO bid. Dosage adjusted based on response. May be used as
Drug may not be well absorbed orally in patient with severe heart failure. Drug may need to be given IV even if patient is taking other oral drugs.
Monitor uric acid level, especially in patients with a
adjunct to other antihypertensiv e if needed.
history of gout.
Children: 0.5 to 2 mg/kg PO once or twice daily. Increase dose as needed up to 6mg /kg daily.
Monitor elderly patients, who are especially susceptible to excessive diuretics because circulatory collapse and thromboembolic complications are possible.
PATIENT TEACHING: Advise patient to take drug with food to prevent GI upset, and to take drug in morning to urinate at night.
Advise patient to immediately report ringing in ears, severe
abdominal pain, or sore throat or fever; these symptoms may indicate toxicity.
You might also like
- Key Questions in Thoracic SurgeryDocument2 pagesKey Questions in Thoracic SurgeryJamal Essam100% (1)
- AIDET Training Presentation1Document29 pagesAIDET Training Presentation1ahmad nurdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NewDocument4 pagesDrug Study NewJehannah Dayanara Berdan HayudiniNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: ActionDocument22 pagesGeneric Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: Actionp_dawg100% (14)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Brand Name Generic Name Classification: PerindoprilDocument3 pagesBrand Name Generic Name Classification: PerindoprilPoinsithia OrlandaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyEzshkha OngueNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Mims EngDocument17 pagesFurosemide Mims EngNur Ilmi SofiahNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Propranolol HydrochlorideDocument8 pagesPropranolol HydrochlorideKrima PatelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Cimetidine (Tagamet)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Cimetidine (Tagamet)mikErlh100% (3)
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument4 pagesFurosemideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Mata Drug Study FurosemideDocument14 pagesMata Drug Study FurosemideNicole Keesha MataNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Lasix Classification: Loop DiureticsDocument5 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Lasix Classification: Loop DiureticsKat ZNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Furosemide (Lasix)Document2 pagesDrug Study - Furosemide (Lasix)mikErlh80% (5)
- Therapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL ClassificationsDocument5 pagesTherapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL ClassificationsAbby MontealegreNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyjackSNMMCNo ratings yet
- Pravastatin SodiumDocument3 pagesPravastatin Sodiumapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJoan RabeNo ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument35 pagesDrugs StudyMark CapillanesNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationDocument6 pagesLisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- Enalapril: Indications and DosageDocument18 pagesEnalapril: Indications and Dosageshahera rosdiNo ratings yet
- Metformin Hydrochloride PDFDocument4 pagesMetformin Hydrochloride PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- Lovastatin PDFDocument3 pagesLovastatin PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- ER Drug StudyDocument13 pagesER Drug StudyJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- AMLODIPINEDocument3 pagesAMLODIPINEDianpratiwi22No ratings yet
- Icu Drug StudyDocument7 pagesIcu Drug StudyHazel Palomares100% (1)
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol Indication & DosageDocument18 pagesHaloperidol Indication & DosageRon Java FantillanNo ratings yet
- Drugs AufDocument6 pagesDrugs AufBrian OballoNo ratings yet
- w15 - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesw15 - Drug StudyGeneva LatorreNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril PDFDocument3 pagesLisinopril PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Medication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Document43 pagesMedication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Kath Rubio0% (1)
- FebuxostatDocument2 pagesFebuxostatJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- Warfarin SodiumDocument3 pagesWarfarin SodiumAndrea Huecas TriaNo ratings yet
- Availability: Verapamil HydrochlorideDocument21 pagesAvailability: Verapamil Hydrochloridesteffy sojanNo ratings yet
- Perindopril ErbumineDocument8 pagesPerindopril ErbumineYanna Habib-MangotaraNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Document13 pagesEmergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Marichu BajadoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- RamiprilDocument3 pagesRamiprilapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Medication FlashcardsDocument10 pagesMedication FlashcardsSilvio PerezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal Diseases: Clinical Pharmacist Hasan BayashotDocument117 pagesGastrointestinal Diseases: Clinical Pharmacist Hasan BayashotRawabi SalehNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ERDocument10 pagesDrug Study - ERbabiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyFides LandichoNo ratings yet
- AtorvastatinDocument7 pagesAtorvastatinKrima PatelNo ratings yet
- DATE ORDERED: August 15, 2009 ORDERED DOSE: 50 Ig IVTT Q 8 Hours GENERIC NAME: Ranitidine Brand Name/SDocument4 pagesDATE ORDERED: August 15, 2009 ORDERED DOSE: 50 Ig IVTT Q 8 Hours GENERIC NAME: Ranitidine Brand Name/SConn_Casipe_8158No ratings yet
- Drug Study ObDocument13 pagesDrug Study ObJash Michael BarbajoNo ratings yet
- Metformin: Dosing & UsesDocument8 pagesMetformin: Dosing & UsesMaria Alejandra Siachoque JaraNo ratings yet
- Drus Study AaaaaaDocument6 pagesDrus Study AaaaaamarkharoldNo ratings yet
- Ranitidine Is Contraindicated in Patients With Known Hypersensitivity To The DrugDocument4 pagesRanitidine Is Contraindicated in Patients With Known Hypersensitivity To The DrugMohd HarizNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOmeprazole Drug StudyFeliza Therese A. DeloriaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudySharwen_R_Rome_5572No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudyJhann0% (1)
- Drug Analysis Table FormDocument3 pagesDrug Analysis Table FormadjnglakaNo ratings yet
- Cimetidine (Drug Study)Document2 pagesCimetidine (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency Common in Pregnant WomenDocument3 pagesChronic Venous Insufficiency Common in Pregnant WomenHerick Rangel do NascimentoNo ratings yet
- To Chronic Musculoskeletal InjuriesDocument2 pagesTo Chronic Musculoskeletal InjuriesMary Jane DumalaganNo ratings yet
- Head Lice Treatment and Prevention GuideDocument2 pagesHead Lice Treatment and Prevention GuideFuture Tech Corp.No ratings yet
- Vit ADocument9 pagesVit AmalathiNo ratings yet
- Lect 18 - Saponin Glycosides (Compatibility Mode)Document16 pagesLect 18 - Saponin Glycosides (Compatibility Mode)ahsanonweb1983No ratings yet
- Evaluation ToolDocument4 pagesEvaluation ToolCarlos TorresNo ratings yet
- Cto 13 06 PDFDocument30 pagesCto 13 06 PDFDr.HarshNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Guide Vancuver ParalympicDocument146 pagesPharmacy Guide Vancuver ParalympicVsevolod BentsianovNo ratings yet
- Sleep Disorders: PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesSleep Disorders: PathophysiologyRodrigo Ehécatl Torres NevárezNo ratings yet
- Guaifenesin Elixir PACKAGE INSERTDocument5 pagesGuaifenesin Elixir PACKAGE INSERTEllie Marie RoyalesNo ratings yet
- Cervical ErosionDocument8 pagesCervical ErosionPipaticoNo ratings yet
- Varma Therapy and Comparison of Varmam Points With Urdhva Jatrugata MarmaDocument3 pagesVarma Therapy and Comparison of Varmam Points With Urdhva Jatrugata MarmaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Disease of Teething Retension Dystopia Retension of 3rd Molar Methods of Surgical InterventionDocument4 pagesDisease of Teething Retension Dystopia Retension of 3rd Molar Methods of Surgical InterventionKandiwapaNo ratings yet
- Superficial and Cutaneous MycosesDocument36 pagesSuperficial and Cutaneous MycosesMich BagamanoNo ratings yet
- Thrombolytic TherapyDocument37 pagesThrombolytic TherapySani sunilNo ratings yet
- Tips and Practical Plasma Applications.FDocument45 pagesTips and Practical Plasma Applications.FSorin RotaruNo ratings yet
- Oral Chondroprotective Agents - Part IDocument7 pagesOral Chondroprotective Agents - Part Itaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Feb 16Document9 pagesDrug Study - Feb 16ciela00034No ratings yet
- Obstructive Uropathy 2Document10 pagesObstructive Uropathy 2jollyannealonzoNo ratings yet
- Rosenberg SelfDocument5 pagesRosenberg SelfHanaeeyemanNo ratings yet
- RH Negative Blood and PregnancyDocument2 pagesRH Negative Blood and PregnancyAnabia TasnimNo ratings yet
- Mastopexia en MultiplanosDocument9 pagesMastopexia en Multiplanossicemiv761No ratings yet
- Tabel PengadaaanDocument63 pagesTabel PengadaaanRahmad Ramadhan RitongaNo ratings yet
- AuriculoterapiaDocument40 pagesAuriculoterapiaCelia SteimanNo ratings yet
- Topical Olopatadine Hydrochloride Versus Ketotifen Fumarate For Allergic ConjunctivitisDocument5 pagesTopical Olopatadine Hydrochloride Versus Ketotifen Fumarate For Allergic ConjunctivitishillarykNo ratings yet
- The Peptide-Hormone Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Activates cAMP and Inhibits Growth of Breast Cancer CellsDocument13 pagesThe Peptide-Hormone Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Activates cAMP and Inhibits Growth of Breast Cancer CellsRidha Surya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- 6504 EapDocument4 pages6504 Eapapi-233075365No ratings yet
- Drug Study On AnestheticsDocument9 pagesDrug Study On AnestheticsKalvinArtRazalanCelebradosNo ratings yet