Professional Documents
Culture Documents
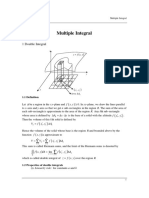
Updated Multiple Integration 3
Updated Multiple Integration 3
Uploaded by
Amna M . Nasr EldinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Updated Multiple Integration 3
Updated Multiple Integration 3
Uploaded by
Amna M . Nasr EldinCopyright:
Available Formats
Intermediate Calculus
Multiple Integration
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Iterated Integrals
Example:
Given that f x ( x, y) 2 xy , evaluate f ( x, y) f x ( x, y) dx
Integrate w.r.t one variable while you are considering the
second one as a constant.
Apply the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus to evaluate
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Iterated Integrals
Integrate w.r.t one variable while you
are considering the second one as a
constant.
h2 ( y )
h2 ( y )
f x ( x, y ) dx f ( x, y ) h1 ( y )
f (h2 ( y ), y ) f ( h1 ( y ), y )
h1 ( y )
g2 ( x)
g2 ( x)
f y ( x, y ) dy f ( x, y ) g1 ( x )
f ( x, g 2 ( x)) f ( x, g1 ( x))
g1 ( x )
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Examples:
Evaluate the following integrals:
x
1) 2x2 y 2
2 y dy
1
2 x
2) 2x2 y 2
2 y dy dx
1 1
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Examples:
Evaluate the iterated integrals:
1 x
1) 1 x 2 dy dx
0 0
2 2y
2) 10 2 x 2 2 y 2 dx dy
0 y
1/ x
3) y dy dx
1 0
3
x2
4) 2
dy dx
0 0
1 y
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Area of a Region in the Plane:
If R is defined by a x b and g1(x) y g2(x) are
continuous on [a,b], then the area of R is given
b g2 ( x)
A dy dx
a g1 ( x )
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
If R is defined by c y d and h1(y) x h2(y) are
continuous on [c,d], then the area of R is given
d h2 ( y )
A dx dy
c h1 ( y )
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Examples:
Use an iterated integral to find to find the area of the
region bounded by the graphs of f(x) = sin x and
g(x) = cos x between x= /4 and x = 5 /4.
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Find the area of the region R that lies below the
parabola y 4 x x 2 above the x-axis, and above the
line y= -3x +6.
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Use an iterated integral to find to find the area of the
region bounded by the graphs of the following
equations. x y 2, x 0, y 0
Evaluate the following integrals
1 1 y2
1) dx dy
0 1 y2
2 2
2) x 1 y3 dy dx
0 x
1 1
3) sin x 2 dx dy
0 y
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Double Integrals and Volume:
If f is defined on a closed, bounded region R in the
xy-plane, the the double integral of f over R is given
by
n
f ( x, y ) dA Lim f ( xi , y j ) A
0
R i 1
provided the limit exists. If the limit exists, then f is
integrable over R.
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Volume of a Solid Region:
If f is integrable over a plane region R and
f(x,y) 0 for all (x,y) in R, then the volume of
the solid region that lies above R and below the
graph f is defined as
V f ( x, y) dA
R
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Properties of double Integrals
Let f and g be continuous over a closed, bounded plane region R,
and let c be a constant.
1. c f ( x, y ) dA c f ( x, y ) dA
R R
2. [ f ( x, y ) g ( x, y )] dA f ( x, y ) dA g ( x, y ) dA
R R R
3. f ( x, y ) dA 0, if f ( x, y ) 0
R
4. f ( x, y ) dA g ( x, y ) dA , if f ( x, y ) g ( x, y ).
R R
5. f ( x, y ) dA f ( x, y ) dA f ( x, y ) dA
R R1 R2
where R is the union of two nonoverlapping subregions R1 and R2
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Examples:
Find the volume of the solid region bounded by the
plane z=2-x-2y and the three coordinates planes
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Find the volume of the solid region R bounded by the
surface f ( x, y) e x and the planes y=0, y=x, and
2
x=1.
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Fubini’s Theorem
Let f be continuous on a plane region R.
If R is defined by a x b and g1(x) y g2(x) are continuous
on [a,b], then
b g2 ( x)
f ( x, y ) d A f ( x, y ) dy dx
R a g1 ( x )
If R is defined by c y d and h1(y) x h2(y) are continuous
on [c,d], then
d h2 ( y )
f ( x, y ) d A dx dy
R c h1 ( y )
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Change of Variables to Polar Form
Let R be a plane region consisting of all points
(x,y) = (r cos , r sin ) satisfying the conditions
0 g1( ) r g2( ),
, where 0 ( - ) 2
If g1 and g2 are continuous on [ , ] and f is
continuous on R, then
g2 ( )
f ( x, y ) d A f ( r cos , r sin ) r dr d
R g1 ( )
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Examples:
Let R be an annular region lying between two circles
x 2 y 2 1 and x 2 y 2 5 . Evaluate the integral x 2 y dA
R
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Use polar coordinates to find the volume of the solid
region bounded above by the hemisphere z 16 x 2 y 2
2 2
and below by the circular region R given by x y 4
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Find the volume of the solid that lies under the
paraboloid 𝑧 = 𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 above the xy-plane, and
inside the cylinder 𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 = 2𝑥.
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
#Absence
Definition of Mass of a Planar Lamina of Variable Density
If is a continuous density function on the lamina
corresponding to a plane region R, then the mass of the lamina
is given by
m ( x, y) d A
R
For a planar lamina, the density is mass per unit area
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Examples:
Find the mass of the triangular lamina with vertices
(0,0), (0,3), and (2,3), given that the density at (x,y)
is (x,y)=2x + y.
Find the mass of the lamina corresponding to the
first- quadrant portion of the circle x 2 y 2 4
where the density at the point (x,y) is proportional to
the distance between the point and the origin.
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Surface Area
If f and its first partial derivatives are continuous on
the closed region R in the xy-plane, then the area of
the surface S given by z = f(x,y) over R is given by
Surface area ds
R
2
1 f x ( x, y ) [ f y ( x, y )]2 dA
R
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Example:
Find the surface area of the part of the plane
3x + 2y +z=6 that lies in the first octant.
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Examples:
Find the surface area of the paraboloid z 1 x 2 y 2
that lies above the unit circle.
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Find the surface area S of the portion of a
hemisphere z 25 x 2 y 2 that lies above the
portion R bounded by the circle x 2 y 2 9
QUIZ#3 Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Triple Integrals
If f is continuous over a bounded solid region Q,
then the triple integral of f over Q is defined as
n
f ( x, y, z ) dV Lim f ( xi , yi , zi ) Vi
0
Q i 1
Provided the limit exists. The volume of the solid
region Q is given by
Volume of Q dV
Q
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Properties of Triple Integrals
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Evaluation by iterated integrals
Let f be continuous on a solid region Q defined
by a x b, h1(x) y h2(x) and g1(x,y) z g2(x,y)
Where h1 , h2 , g1 and g2 are continuous functions. Then,
b h2 ( x ) g 2 ( x , y )
f ( x, y, z ) dV f ( x, y, z ) dz dy dx
Q a h1 ( x ) g1 ( x , y )
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Example:
2 x dV
Evaluate Q
where Q is the region under the
plane 3x + 2y +z=6 that lies in the first octant.
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Examples:
2 x x y
Evaluate the triple iterated integral e x ( y 2 z ) dz dy dx
0 0 0
Find the volume of the solid Q under the plane z=x+y
and above the region bounded by the lines y= 2x, x=0,
and y=2 in xy-plane.
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Mass of a Solid Region
Consider a solid region Q whose density at )(x,y,z) is
given by the density function
Mass of the solid = m
= ( x, y, z ) dV
Q
Example:
Find the mass of the unit cube coincide with the
coordinate planes in the first octant, given that the
density at the point (x,y,z) is proportional to the
square of its distance from origin.
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Triple Integrals In Cylindrical Coordinates
x = r cos
y = r sin
z=z
dV= r dz dr d
2 g 2 ( ) h1 ( r cos , r sin )
f ( x, y, z ) dV f (r cos , r sin , z ) r dz dr d
Q 1 g1 ( ) h1 ( r cos , r sin )
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Examples:
2
Find the volume inside both the sphere x y2 z2 2
2 2
and the cylinder x y 1
Find the volume of the solid region Q cut from the
sphere x2 y 2 z 2 4 by
the cylinder r=2 sin
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Triple Integrals In Spherical Coordinates
0
dV =
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Examples:
Find the volume of the solid region Q bounded below
by the upper portion of the cone z x y and
2 2 2
above by the sphere x 2 y 2 z 2 9
2
y2 z 2 )3 / 2
Evaluate Q
e( x dV
where Q is the unit ball:
Q x, y, z : x 2 y2 z2 1
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Change of variables: Jacobians
Definition of Jacobian
If x= g(u,v) and y = h(u,v), then the Jacobian of x and y
with respect to u and v, denoted by (x,y)/ (u,v), is
x x
( x, y ) u v x y y x
(u, v) y y u v u v
u v
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Change of Variables for Double Integrals
Let R and S be regions in the xy-plane and uv-plane
that are related by the equations x=g(u,v) and
y=h(u,v) such that each point in R is the image of a
unique point in S. If f is continuous on R, g and h
have continuous partial derivatives on S, and
(x,y)/ (u,v) is nonzero on S, then
( x, y)
f ( x, y ) dx dy f ( g (u, v, h(u, v)) du dv
R S
(u, v)
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
Examples:
Let R be the region bounded by the lines
x-2y=0, x-2y=-4, x+y=4,and x+y=1
Evaluate the double integral R 3x y dA
Dr. Sahar Hussein
Intermediate Calculus
e( x
dA y ) /( x y )
Evaluate the integral R , where R is the
trapezoidal region with vertices (1,0), (2,0), (0,-2),
and (0,-1).
Dr. Sahar Hussein
You might also like
- SOLUTIONS MANUAL For Graphs & Digraphs 6th Edition Chartrand Lesniak Zhang 2015Document256 pagesSOLUTIONS MANUAL For Graphs & Digraphs 6th Edition Chartrand Lesniak Zhang 2015Filip Płatek100% (2)
- SOF Level 2 IMO Class 11Document5 pagesSOF Level 2 IMO Class 11Archana JhaNo ratings yet
- Course Materials For Multiple Integrals: Lakshmi Kanta DeyDocument16 pagesCourse Materials For Multiple Integrals: Lakshmi Kanta DeyKANCHAN KUMAR GOSWAMINo ratings yet
- Presented by : Vaishali G. Mohadikar Vinita G. PatelDocument31 pagesPresented by : Vaishali G. Mohadikar Vinita G. PatelUmair MazharNo ratings yet
- Presented by : Vaishali G. Mohadikar Vinita G. PatelDocument31 pagesPresented by : Vaishali G. Mohadikar Vinita G. PatelUmair MazharNo ratings yet
- Week 9 NewDocument12 pagesWeek 9 NewShavin ChandNo ratings yet
- Multiple IntegralsDocument30 pagesMultiple IntegralsMacky GarciaNo ratings yet
- Definite IntegralsDocument5 pagesDefinite Integralsfieldmarshal2011896No ratings yet
- AMA2104 Probability and Engineering Statistics 3 Joint DistributionDocument25 pagesAMA2104 Probability and Engineering Statistics 3 Joint DistributionYH CHENGNo ratings yet
- Double Integrals 2012Document17 pagesDouble Integrals 2012DIey ChokiEyNo ratings yet
- Multiple IntegralsDocument25 pagesMultiple IntegralsRàhuł MathiasNo ratings yet
- Multiple Integrals of Multivariable FunctionsDocument26 pagesMultiple Integrals of Multivariable FunctionsPrateek SInghNo ratings yet
- UNIT-6 Multivariable Calculus (DOC FILE)Document15 pagesUNIT-6 Multivariable Calculus (DOC FILE)chinoerageorge0No ratings yet
- 15 Multiple Integrals 15.1 Double Integrals Double Integrals Over RectanglesDocument4 pages15 Multiple Integrals 15.1 Double Integrals Double Integrals Over RectanglesPraviin JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Multiple IntegralsDocument29 pagesMultiple IntegralsPancham AlvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 MultipleIntegral Part1Document31 pagesChapter3 MultipleIntegral Part1ming01No ratings yet
- BMAT101L Module 4-1Document36 pagesBMAT101L Module 4-1Anurag JoshiNo ratings yet
- 2E02 Multiple IntegralsDocument37 pages2E02 Multiple IntegralsuqashaNo ratings yet
- Chap15 Multiple IntegralsDocument21 pagesChap15 Multiple IntegralsAryan TalwarNo ratings yet
- Lectures 20Document82 pagesLectures 20sudhansh kumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Worksheet 5Document3 pagesTutorial Worksheet 5nicomathias74No ratings yet
- 14 2+lecDocument3 pages14 2+lec고혜인No ratings yet
- Lecture 19Document6 pagesLecture 19angelzengwe8No ratings yet
- Double IntegralsDocument25 pagesDouble IntegralsChalla SaiNo ratings yet
- M3 Unit-3Document63 pagesM3 Unit-3Sathvik WorkspaceNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives - 01 - Class Notes - Math 01Document37 pagesApplications of Derivatives - 01 - Class Notes - Math 01Mohit SuaradkarNo ratings yet
- Applied Maths II Chap 4Document24 pagesApplied Maths II Chap 4qashtikiyya65No ratings yet
- Ma 111 Tutorial 1Document2 pagesMa 111 Tutorial 1pahnhnykNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 2.1 Double Integral)Document9 pagesLecture Notes (Chapter 2.1 Double Integral)Hafzal GaniNo ratings yet
- 5-Multiple Integrals and Their Applications PDFDocument63 pages5-Multiple Integrals and Their Applications PDFLoo Javier Mamani Quea100% (1)
- Vector Calculus Independent Study Unit 6: Double and Triple IntegralsDocument3 pagesVector Calculus Independent Study Unit 6: Double and Triple IntegralsAdil ShafiqNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 Multiple Integrals and Their ApplicationsDocument63 pagesUNIT-4 Multiple Integrals and Their ApplicationsTharun konda100% (1)
- 1-Double IntegralDocument8 pages1-Double Integralأحمد تركي كحيوشNo ratings yet
- 5-Multiple Integrals and Their Applications-Edited PDFDocument63 pages5-Multiple Integrals and Their Applications-Edited PDFSk Abdul ShakeerNo ratings yet
- Integration Final ReviewDocument3 pagesIntegration Final ReviewRajesh KNo ratings yet
- Lecture Week14Document4 pagesLecture Week14Tahzeeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- 22ma2bsmme MCVQBDocument6 pages22ma2bsmme MCVQBchikku0211No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Multiple IntegralsDocument66 pagesUnit 1 Multiple Integralsfshjmij61100% (1)
- Algebraic: (I.T. Leong) Math 200 in 2010 2010 C 10 7 F 1 / 24Document28 pagesAlgebraic: (I.T. Leong) Math 200 in 2010 2010 C 10 7 F 1 / 24eouahiauNo ratings yet
- Double IntegralsDocument178 pagesDouble IntegralsKaushik ReddyNo ratings yet
- 15.1 Double Integrals Over RectanglesDocument16 pages15.1 Double Integrals Over RectanglesHebatallah Mujahed Mohmoud KanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Multivariable FunctionsDocument48 pagesChapter 4 Multivariable Functionssofea anuarNo ratings yet
- Volume Under SurfacesEXP - 3BDocument4 pagesVolume Under SurfacesEXP - 3BvishwadeepNo ratings yet
- Ch2 - Multiple Integral EditDocument12 pagesCh2 - Multiple Integral Edit44. Pol SovanrothanaNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 IMAT101P LO VL2023240106444 2023-10-11 Reference-Material-IDocument4 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 IMAT101P LO VL2023240106444 2023-10-11 Reference-Material-Ijakeklent262No ratings yet
- Updated Vector AnalysisDocument53 pagesUpdated Vector AnalysisAmna M . Nasr EldinNo ratings yet
- Lecture07 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture07 PDFss_nainamohammedNo ratings yet
- Area Between Curves, Average Value of A Function - Gary TaylorDocument4 pagesArea Between Curves, Average Value of A Function - Gary Taylorgauss202No ratings yet
- MA111 Lec6 D3D4Document14 pagesMA111 Lec6 D3D4pahnhnykNo ratings yet
- IntegralesDocument92 pagesIntegralesAbel LopezNo ratings yet
- Paper: Iit-Jam 2005: B A C ADocument4 pagesPaper: Iit-Jam 2005: B A C AMr MNo ratings yet
- Calculus Questions2019Document5 pagesCalculus Questions2019Martin NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chap15 Multiple IntegralsDocument18 pagesChap15 Multiple Integralsf20230485No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Multivariable FunctionsDocument48 pagesChapter 4 Multivariable FunctionsAnonymous hJMbZT7UCsNo ratings yet
- Multiple IntegralsDocument25 pagesMultiple IntegralsAnshulNo ratings yet
- Partial Derivatives: Chapter 2: Function of Several VariablesDocument26 pagesPartial Derivatives: Chapter 2: Function of Several VariablesKhairunnisa ZakiriNo ratings yet
- Double Integrals 1Document22 pagesDouble Integrals 1Aztec MayanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Calculus of Multi Variables 2011Document22 pagesLecture 2 Calculus of Multi Variables 2011Yiauw ShenqNo ratings yet
- Triple IntegralDocument5 pagesTriple IntegralNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Maxima and MinimaDocument35 pagesMaxima and Minimacreativemath0309No ratings yet
- Hyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandHyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsNo ratings yet
- (MAT) Boards SQP Class 12Document12 pages(MAT) Boards SQP Class 1212B 25 Ribhav SethiNo ratings yet
- Physics Letters B: Shin'ichi Nojiri, Sergei D. OdintsovDocument7 pagesPhysics Letters B: Shin'ichi Nojiri, Sergei D. OdintsovAdrian MorenoNo ratings yet
- Mimo PDFDocument40 pagesMimo PDFCool NameNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Polynomial Root Finding TechniquesDocument99 pagesComparative Analysis of Polynomial Root Finding TechniquesChanttle CondeNo ratings yet
- 2 Scale HomogenizationDocument82 pages2 Scale HomogenizationSamNo ratings yet
- HOMEWORK Algebra and Pre-CalculusDocument9 pagesHOMEWORK Algebra and Pre-CalculusAdriel Garcia MatiasNo ratings yet
- Statistical and Mathematical Methods For Data AnalysisDocument39 pagesStatistical and Mathematical Methods For Data AnalysisDrive 02No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Manipulation of Simple PolynomialsDocument24 pagesChapter 10 Manipulation of Simple Polynomialsmxalg5463No ratings yet
- TG2 - Topic 1 - InequalitiesDocument5 pagesTG2 - Topic 1 - InequalitiesJuhari DirumponganNo ratings yet
- Jordan's Proof of The Jordan Curve TheoremDocument16 pagesJordan's Proof of The Jordan Curve TheoremMahmoud NaguibNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Measure of Centeral TendencyDocument20 pagesCHAPTER 3 Measure of Centeral TendencyyonasNo ratings yet
- CombineliketermsactivitiesDocument6 pagesCombineliketermsactivitiesapi-213793181No ratings yet
- MATH3U Binomials QsDocument4 pagesMATH3U Binomials QsAli HaidarNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal Learner - S Packet Q1 Week 7Document6 pagesPre Cal Learner - S Packet Q1 Week 7Gladys Angela ValdemoroNo ratings yet
- Ap22 FRQ Calculus AbDocument11 pagesAp22 FRQ Calculus Ab9338No ratings yet
- On Two Step Lax-Wendroff Methods in Several DimensionsDocument6 pagesOn Two Step Lax-Wendroff Methods in Several Dimensionsadi63No ratings yet
- Final New Conduction in 2dDocument8 pagesFinal New Conduction in 2dBharath SaiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Mathematical Tripos Part II Course GuideDocument17 pagesCambridge Mathematical Tripos Part II Course Guideharry100% (1)
- ViewingDocument49 pagesViewingnishasaiyed2304No ratings yet
- BMTC 131Document4 pagesBMTC 131vaghasiyarita452No ratings yet
- 04 ES Random VariablesDocument17 pages04 ES Random VariablesMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5b Difference EquationDocument15 pagesChapter 5b Difference Equationfarina ilyanaNo ratings yet
- Core Mathematics C1: Pearson Edexcel GCEDocument15 pagesCore Mathematics C1: Pearson Edexcel GCEDylan GakizaNo ratings yet
- Descartes Rule of SignsDocument4 pagesDescartes Rule of SignsMark GalangNo ratings yet
- Techniques For Aircraft Configuration OptimizationDocument11 pagesTechniques For Aircraft Configuration OptimizationallanepNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Math Deep Learning 2018 PDFDocument103 pagesTutorial Math Deep Learning 2018 PDFElnur ƏhmədzadəNo ratings yet
- Types of KrigingDocument9 pagesTypes of KrigingFeduz L Near100% (1)