Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Reading Essentials Structures & Organelles
Bio Reading Essentials Structures & Organelles
Uploaded by
Valerie FallerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Reading Essentials Structures & Organelles
Bio Reading Essentials Structures & Organelles
Uploaded by
Valerie FallerCopyright:
Available Formats
chapter
7 Cellular Structure and Function
section ●
3 Structures and Organelles
Before You Read -!).�� )DEA
The eukaryotic cell contains
For cells to function correctly, each part must do its job. organelles.
Members of families have jobs or chores that help the whole
What You’ll Learn
family. On the lines below, list your family members and their differences in the structures of
jobs. plant and animal cells
Mom - Provision of food, shelter and money for the family. Nurturing and raising the children,
teaching the children morals and values.
Dad - Preparing food and keeping the house in order. Making important decision.
Me & Siblings - Assisting in performing household chores, Living up to family expectations, Obeying
parents.
Read to Learn
Identify the Parts Highlight
Cytoplasm and Cytoskeleton each cell structure as you read
The environment inside the plasma membrane is a about it. Underline the function
semifluid material called cytoplasm. Scientists once thought of each part.
the organelles of eukaryotic cells floated freely in the cell’s
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
cytoplasm. As technology improved, scientists discovered
more about cell structures. They discovered a structure within
the cytoplasm called the cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton is a
network of long, thin protein fibers that provide an anchor
for organelles inside the cell. The cell’s shape and movement
depend on the cytoskeleton.
Two types of protein fibers make up the cytoskeleton.
Microtubules are long, hollow protein cylinders that form a
firm skeleton for the cell. They assist in moving substances
within the cell. Microfilaments are thin protein threads that
help give the cell shape and enable the entire cell or parts of
the cell to move. 1. Name one cell function
that takes place in
organelles.
Cell Structures Chemical Processes of
All chemical processes of a typical eukaryotic cell take place a typical Eukaryotic Cell
in the organelles, which move around in the cell’s cytoplasm.
Proteins are produced, food is transformed into energy, and
wastes are processed in the organelles. Each organelle has a
unique structure and function.
Reading Essentials Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 75
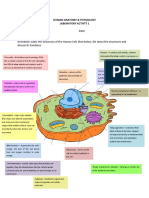
How are plant and animal cells different?
The figure below shows a typical plant cell and a typical
animal cell. Note how many organelles are found in both types
of cells. Also, note a few differences, such as the chloroplast
that appears only in the plant cell. Observe that the vacuole
in the plant cell is much larger than the vacuole in the animal
cell.
Picture This 0LANT�#ELL
2. Highlight the names of .UCLEUS
#ELL�WALL
structures found in both .UCLEAR�PORE -ITOCHONDRION
6ACUOLE
plant cells and animal
#HLOROPLAST
cells. Circle the names of .UCLEOLUS
structures that are found -ICROTUBULE
only in plant cells. Underline
2OUGH
the names of structures that ENDOPLASMIC
are found only in animal RETICULUM
cells. 3MOOTH
ENDOPLASMIC
RETICULUM
2IBOSOME
0LASMA�
MEMBRANE
#YTOPLASM
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
'OLGI�APPARATUS
!NIMAL�#ELL
.UCLEUS
.UCLEOLUS
-ICROTUBULE
.UCLEAR�PORE
2OUGH -ITOCHONDRION
ENDOPLASMIC
RETICULUM 6ACUOLE
#YTOPLASM
6ESICLE
#ENTRIOLE
,YSOSOME 'OLGI�APPARATUS
0LASMA
2IBOSOMES MEMBRANE
3MOOTH
ENDOPLASMIC
RETICULUM
76 Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function Reading Essentials
What structure manages cell processes?
The nucleus is the cell’s managing structure. Most of the
cell’s genetic material (DNA) is in the nucleus. DNA defines
the cell and controls protein production. A nuclear envelope
surrounds the nucleus. Substances pass through the nuclear
envelope to move in and out of the nucleus.
Which organelle produces proteins? 3. Explain What is the role
Ribosomes produce proteins and are made of two of DNA?
components—RNA and protein. Ribosomes are produced in It defines the cell and
the nucleolus, a structure located inside the nucleus. Some controls protein
ribosomes float freely in the cytoplasm. They produce proteins production
that will be used by other cells. Other ribosomes attach to an
organelle called the endoplasmic reticulum.
What attaches to rough endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum, (en duh PLAZ mihk •
rih TIHK yuh lum) also called ER, is a membrane system of
folded sacs and channels to which ribosomes are attached.
There are two types of ER. The first type is called rough
endoplasmic reticulum. This is the area where ribosomes
attach to the ER’s surface. The ribosomes appear to create
bumps or rough places on the membrane. The second type,
smooth endoplasmic reticulum, has no ribosomes attached.
Smooth ER produces complex carbohydrates and lipids.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
What is the purpose of the Golgi apparatus?
Once proteins are created, they move to another organelle,
the Golgi (GAWL jee) apparatus. The Golgi apparatus
modifies, sorts, and packs the proteins into sacs called vesicles.
The vesicles fuse with the cell’s plasma membrane. There the
vesicles release the proteins, which move through the plasma
membrane to the environment outside the cell.
What is stored in vacuoles?
Cells have vesicles called vacuoles that act as temporary
storage for materials in the cytoplasm. Vacuoles can store
food and other material needed by a cell. They can also store
wastes. Plant cells normally have one large vacuole. Animal
cells might or might not have a few small vacuoles.
What are lysosomes?
Lysosomes are vesicles that contain substances that digest
excess or worn-out organelles and food particles. Lysosomes
also digest bacteria and viruses that enter the cell.
Reading Essentials Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 77
What makes up a centriole?
Centrioles are organelles made of microtubules that
function during cell division. They usually are found near the
nucleus of the cell. Plant cells do not contain centrioles.
Which organelle produces energy?
Cells need energy to survive. The organelles that convert
fuel particles such as sugars into usable energy are called
mitochondria (mi tuh KAHN dree uh). A mitochondrion has
an outer membrane and an inner membrane with many folds,
as shown in the figure below. The membrane provides a large
surface area for breaking the bonds of sugar molecules. Energy is
produced when the bonds are broken.
Picture This -ITOCHONDRION
4. Explain why the inner
membrane has many folds.
The membrane provides
a large surface area where
chemical reactions can
take place for breaking the
)NNER� /UTER�
bonds of sugar molecules. MEMBRANE MEMBRANE
How do plant and animal cells differ?
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
In addition to mitochondria, plant cells contain chloroplasts.
Chloroplasts are organelles that capture light energy and
convert it to chemical energy through a process called
photosynthesis. Plants can use light energy from any light
source—usually the Sun. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts
and cannot use solar energy as fuel for cell processes.
Plants also have cell walls. The cell wall is a mesh of
fibers that surrounds the plasma membrane. It protects and
supports the cell. Plant cell walls are made of a carbohydrate
known as cellulose.
What are cilia and flagella?
Some animal cell surfaces have cilia or flagella that extend
beyond the plasma membrane. Cilia are short projections
5. Recall What is another that look like hairs. They move back and forth, similar to
function of microtubules?
the motion of the oars of a rowboat. Flagella are longer,
They assist in moving whiplike projections that propel cells. Both cilia and flagella
substances within the are composed of microtubules. They move cells through their
cell. watery environments. Cilia also move substances along the
surface of the cell.
78 Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function Reading Essentials
Comparing Cells
The table below summarizes the structures of eukaryotic
plant and animal cells. The function of each structure is Picture This
described. Note that prokaryotic cells lack most of the 6. Highlight the organelle
organelles found in eukaryotic cells. to which ribosomes attach.
Present in
Cell Structure Function
Plant/Animal Cells
Cell wall protects and supports plant cells plant cells only
Centriole important in cell division animal cells only
Chloroplast site where photosynthesis occurs plant cells only
Cilia aids in moving the cell and moving substances along the some animal cells
surface of the cell
Cytoskeleton a framework for the cell within the cytoplasm both
Endoplasmic site of protein synthesis; where ribosomes attach both
reticulum (ER)
Flagellum aids in moving and feeding the cell some animal cells
Golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins for distribution outside the cell both
Lysosome contains digestive enzymes for substance break down animal cells only
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Mitochondrion supplies energy to the rest of the cell both
Nucleus directs the production of proteins and cell division both
Plasma membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell both
Ribosome produces proteins both
Vacuole stores materials temporarily plant cell—one
large; animal
cell—a few small
Organelles at Work
The structures in the cell work together to perform cell
functions. The synthesis of proteins is a major cell function,
which begins in the nucleus. Protein synthesis continues with
the ribosomes on the rough ER and the ribosomes that float
freely in the cytoplasm. Most proteins made on the rough ER 7. Identify a major cell
are sent to the Golgi apparatus. There they are packaged in function.
vesicles and sent to other organelles or out of the cell. Like each The synthesis of protein
member of a soccer team, each cell structure has a specific task which begins in the nucleus.
to do to make the cell function properly.
Reading Essentials Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 79
You might also like
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind MapPramod Jaiswal81% (21)
- Grade 8 QUARTER 4 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TOSDocument4 pagesGrade 8 QUARTER 4 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TOSzerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- The Human CellDocument1 pageThe Human CellAira Viloria Orbillo100% (1)
- The Human CellDocument3 pagesThe Human CellA HNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure 2Document5 pagesCell Structure 2slombez 150% (1)
- 4 Structures and OrganellesDocument5 pages4 Structures and Organellessalmasadiq2008No ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsChristine Suizo SebucaoNo ratings yet
- Ivy Jean MartinezDocument11 pagesIvy Jean MartinezmarjmarjNo ratings yet
- Material For Genbio Week 1Document6 pagesMaterial For Genbio Week 1John Ferri PatunganNo ratings yet
- Las #6 AttachmentDocument4 pagesLas #6 AttachmentShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- 1794853-P2. - Cell Structure and DivisionDocument8 pages1794853-P2. - Cell Structure and DivisionCrisNo ratings yet
- B.S 8.1 Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesB.S 8.1 Lesson PlanNiranjan UniqueNo ratings yet
- Nathanael Kean Dimasacat - Worksheet - Cells StructureDocument4 pagesNathanael Kean Dimasacat - Worksheet - Cells StructureNathanael Kean DimasacatNo ratings yet
- The Biology of Agricultural Crops: Nature and Composition of PlantsDocument18 pagesThe Biology of Agricultural Crops: Nature and Composition of PlantsDanica DayananNo ratings yet
- Learning Packet in Level 1-Anatomy and Physiology: College of Nursing School Year 2021-2022Document18 pagesLearning Packet in Level 1-Anatomy and Physiology: College of Nursing School Year 2021-2022Zyke NovenoNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Reinforcement: Key ConceptDocument1 page3.2 Reinforcement: Key ConceptEyad TalaatNo ratings yet
- Cell Grade 7Document65 pagesCell Grade 7SUDARAT THONGPHAYONGNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure, Function and OrganizationDocument1 pageCell - Structure, Function and Organization- adlina -100% (1)
- Cell Structure and Cell Division: Learning Outcomes Laboratory SuppliesDocument6 pagesCell Structure and Cell Division: Learning Outcomes Laboratory SuppliespedroNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell StrucDocument27 pagesEukaryotic Cell StrucHari. ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function ActivityDocument19 pagesCell Structure and Function ActivityrhaineNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell Lesson PlanGilda Genive AriolaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure ASDocument40 pagesCell Structure ASYasmine HadiastrianiNo ratings yet
- CelsszDocument6 pagesCelsszHITANSH NIJHAWANNo ratings yet
- Cell AnalogyDocument11 pagesCell AnalogyMikaella Jayne CatanaoanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument64 pagesChapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationNurul Fatihah Binti MamatNo ratings yet
- M2 Pre-TaskDocument2 pagesM2 Pre-TaskELIZA NICOLE ATANo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument15 pagesBiologyChit su su zawNo ratings yet
- L1 Cells and OrganisationDocument27 pagesL1 Cells and OrganisationGaurav RathiNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures & Functions: Cells Have Many Different Functions and Come in Many Shapes and SizesDocument3 pagesCell Structures & Functions: Cells Have Many Different Functions and Come in Many Shapes and SizesFrank Mecel Arzaga DimalantaNo ratings yet
- Cellstructure PDFDocument3 pagesCellstructure PDFGohar imranNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument1 pageCell Structurekivepe9583No ratings yet
- Cell, Basic Structure of All Living Creatures: Life Science, Human BiologyDocument11 pagesCell, Basic Structure of All Living Creatures: Life Science, Human BiologyAshleigh Jenson WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 2Document13 pages02 Handout 2Janna AngelesNo ratings yet
- Week 2: September 20-25: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 2: September 20-25: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- 5 Grade Science: "Life Science: Living Things"Document11 pages5 Grade Science: "Life Science: Living Things"AAAAANo ratings yet
- Cell Structure AND Cell OrganisationDocument54 pagesCell Structure AND Cell OrganisationAngel Cascayan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- VPHYS 3 200 General Physiology 1 Sem 2021-2022 Laboratory Exercise Written ReportDocument4 pagesVPHYS 3 200 General Physiology 1 Sem 2021-2022 Laboratory Exercise Written ReportRated SPGNo ratings yet
- PRELIMS BIOLOGY - Yrielleeeee: Biology - Organelles - Cell OrganelleDocument8 pagesPRELIMS BIOLOGY - Yrielleeeee: Biology - Organelles - Cell OrganelleYhazmin Iris IlustrisimoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and Organization: Structur e FunctionDocument14 pages2.1 Cell Structure and Organization: Structur e Functionwafa eliasNo ratings yet
- 4 - Cell Structure Gizmo AnswersDocument5 pages4 - Cell Structure Gizmo AnswersCathyNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure AND Cell OrganisationDocument48 pagesCell Structure AND Cell OrganisationBabasChongNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument18 pagesCells현성JacobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 1 Cell Structure and OrganizationDocument15 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 1 Cell Structure and Organizationmotarekthebest320No ratings yet
- Cells To SystemsDocument10 pagesCells To SystemsRoaa HasanNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 1 NotesDocument6 pagesBiology Chapter 1 Notesmohan.shenoy52No ratings yet
- Samillao Gen Bio Week 2 Q1Document11 pagesSamillao Gen Bio Week 2 Q1Gem Kyla Mae SamillanoNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument6 pagesCell StructureZen Kenneth A. PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure CH 1 CH 2 Ver 2Document22 pagesCell Structure CH 1 CH 2 Ver 2FaizNo ratings yet
- L2 - Cell Component RecapDocument15 pagesL2 - Cell Component Recap.No ratings yet
- Zárate CellsDocument9 pagesZárate CellsCAROLINA ELIZABETH ZARATE CHECANo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument76 pagesCell Structure & FunctionMilka RahmanNo ratings yet
- Student Handout 01 - Cell StructureDocument6 pagesStudent Handout 01 - Cell StructureJoslynn SlaytonNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2Document4 pagesGen Bio 2Melrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organisation 2021Document17 pagesLevels of Organisation 2021ronalNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organisation 2021Document17 pagesLevels of Organisation 2021ronalNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organisation L4 Specialised Cells PowerPointDocument24 pagesCells and Organisation L4 Specialised Cells PowerPointJhyvril GulacNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in SCIENCE 7-WPS OfficeDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in SCIENCE 7-WPS OfficeBhea GasparNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureDocument8 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell StructureMishaNo ratings yet
- BEST - BCL - 1 - 2 - Response - Job Ads Cell Structures WantedDocument4 pagesBEST - BCL - 1 - 2 - Response - Job Ads Cell Structures WantedmtauhidNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- FA16Document22 pagesFA16Jay ZNo ratings yet
- SL Paper 2: Do Not Accept Energy StorageDocument73 pagesSL Paper 2: Do Not Accept Energy StoragemanrajNo ratings yet
- Skin 2020Document60 pagesSkin 2020Yousef KhallafNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Glucose HomeostasisDocument39 pagesLesson 7 Glucose Homeostasissaja MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Insect Physiology and ToxicologyDocument22 pagesInsect Physiology and ToxicologywilfredcampadoNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Culture of Unculturable' BacteriaDocument7 pagesStrategies For Culture of Unculturable' BacteriaAbhishek SahuNo ratings yet
- EDU 30 Topic 1 - CHILD AND ADOLESCENCEDocument36 pagesEDU 30 Topic 1 - CHILD AND ADOLESCENCEjessapascual315No ratings yet
- Rivera-Laboratory Exercise No. 2-AnaphyDocument3 pagesRivera-Laboratory Exercise No. 2-AnaphyRivera, Trishia PilonNo ratings yet
- Gendent - jf19 - de Oliveira S IDocument5 pagesGendent - jf19 - de Oliveira S IAndreea RoxanaNo ratings yet
- M223 Ancestral Journey Eng PublDocument28 pagesM223 Ancestral Journey Eng PublGábor BaloghNo ratings yet
- Rev&pat&gen&rai&gup&7th PDFDocument708 pagesRev&pat&gen&rai&gup&7th PDFBkash Shah100% (3)
- Urine Screening For Metabolic Disorders PDFDocument5 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic Disorders PDFJustine Nicole Clavel LachicaNo ratings yet
- The Kingdom Protoctista: Short Question and AnswersDocument5 pagesThe Kingdom Protoctista: Short Question and AnswersNadeem ArainNo ratings yet
- Microbial PhotosynthesisDocument26 pagesMicrobial PhotosynthesisHay PeeNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Structure of DNA & RNADocument3 pages2.6 Structure of DNA & RNATeena Tutor100% (1)
- SAS For Biochemistry BIO 024 Module 6 1Document33 pagesSAS For Biochemistry BIO 024 Module 6 1vovoka449No ratings yet
- DU Anthropology SyllabusDocument111 pagesDU Anthropology SyllabusSolomonNo ratings yet
- Q4 Written Works 2 in Gen Bio 2Document5 pagesQ4 Written Works 2 in Gen Bio 2Miraflor RandingNo ratings yet
- L-Type Calcium Channels: Structure and FunctionsDocument22 pagesL-Type Calcium Channels: Structure and FunctionsrezqNo ratings yet
- Hematology ReviewerDocument10 pagesHematology ReviewerAldren BeliberNo ratings yet
- Sequecing - Khan AcademyDocument16 pagesSequecing - Khan AcademyMaryem SafdarNo ratings yet
- Statistical Methods For Bioinformatics Lecture 3Document33 pagesStatistical Methods For Bioinformatics Lecture 3javabe7544No ratings yet
- 3.2 Reinforcement: Key ConceptDocument1 page3.2 Reinforcement: Key ConceptEyad TalaatNo ratings yet
- BM3251 Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesBM3251 Important QuestionsAmen MuhammedNo ratings yet
- DHSHSJDocument8 pagesDHSHSJsarthakt74No ratings yet
- 12th STD Bio-Botany Lesson-5 EM Book Back Answers-1Document3 pages12th STD Bio-Botany Lesson-5 EM Book Back Answers-1D Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- GENETIC COUNSELLING (FARHEEN KHAN MSC 1st Year)Document8 pagesGENETIC COUNSELLING (FARHEEN KHAN MSC 1st Year)Farheen khanNo ratings yet
- (2018) Sex and Gender Differences Research Design For Basic, Clinical, and Population Studies - Essentials For InvestigatorsDocument16 pages(2018) Sex and Gender Differences Research Design For Basic, Clinical, and Population Studies - Essentials For InvestigatorsXavierNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Diagnostic TestDocument13 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Diagnostic TestDearest NotesNo ratings yet