Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Suggested Answers To Exercise and Reading To Learn: CH 18 Homeostasis
Suggested Answers To Exercise and Reading To Learn: CH 18 Homeostasis
Uploaded by
ya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesOriginal Title
bk2_ch18_sug ans_e
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesSuggested Answers To Exercise and Reading To Learn: CH 18 Homeostasis
Suggested Answers To Exercise and Reading To Learn: CH 18 Homeostasis
Uploaded by
yaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Chapter 18
Suggested answers to Exercise and Reading to learn p.1/3
Suggested answers to Exercise and Reading to
learn
(Note: The overseas examination boards bear no responsibility for the suggested answers
contained in this publication. Answers for HKCEE and HKALE questions are not available due
to copyright restrictions.)
Ch 18 Homeostasis
Exercise
Multiple-choice questions (p. 18-14)
1 C
2 B
Short questions (p. 18-14)
3 a negative feedback 1m
b opposite 1m
c restore 1m
d lowers 1m
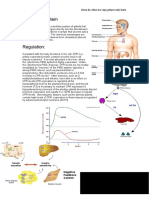
4 On graph:
Mark ‘X’ between 1 hour and 2 hour 1m
Mark ‘Y’ between 0.25 hour and 1 hour 1m
Structured questions (p. 18-14)
5 a Any three from: 1m x 3
Blood glucose level of both man rise in the first half hour.
Blood glucose level of diabetic men shows a greater / faster increase in first half hour.
Between 30 to 60 minutes, blood glucose level of non-diabetic men decreases while
blood glucose level of diabetic men increases.
After one hour the blood glucose level of non-diabetic men is lower than original
while the blood glucose level of diabetic men is higher than original.
b i Insulin causes a fall in blood glucose level. 1m
Blood glucose level does not decrease in diabetic men / decrease only seen in
non-diabetic men. 1m
Oxford University Press 2009
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Chapter 18
Suggested answers to Exercise and Reading to learn p.2/3
ii Any two from: 1m x 2
Body cells need glucose for respiration, which is obtained from the blood.
Too high concentration in blood lowers the water potential of blood,
osmosis occurs which causes water to leave the cells.
Water from the cells enters the blood by osmosis, causing a change in blood
pressure / pH
which would cause coma / death / fainting / nausea / kidney damage.
c Any three from: 1m x 3
Low blood glucose level detected by the pancreas.
Glucagon secreted
by pancreas
which stimulates the liver cells to convert more glycogen to glucose.
More glucose released into the blood / from the liver.
6 HKCEE Human Biology 2001 I Q2b
Essay (p. 18-15)
7 Principle of negative feedback: Any two from: 1m x 2
Negative feedback mechanism maintains constant internal conditions in the body.
A change from the normal level / set point is detected.
A corrective mechanism is switched on / activated.
When condition returns to its normal level / set point, the corrective mechanism will be
switched off.
Maintenance of blood glucose levels: Any six from: 1m x 6
The change in blood glucose / sugar level is detected by the pancreas.
If the blood glucose / sugar level increases, more insulin is secreted.
Insulin increases uptake of glucose by the body cells.
Liver converts more glucose to glycogen / more glucose is converted to glycogen and
stored in liver.
until the blood glucose / sugar level returns to normal / set point.
If blood glucose / sugar level decreases, more glucagon is secreted.
Glucagon increases the conversion of glycogen to glucose.
Glucose is then released into blood
until the blood glucose / sugar level returns to normal / set point.
Oxford University Press 2009
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Chapter 18
Suggested answers to Exercise and Reading to learn p.3/3
Reading to learn (p. 18-16)
1 Bernard discovered that the liver acts as a reserve of carbohydrates for the body by
converting glucose to glycogen or vice versa. 1m
From this, he recognized the role of the liver in regulating blood glucose level which led
him to further investigate homeostasis.
His ideas were also further developed by other scientists. 1m
2 ‘Homeostasis’ means ‘to stay the same’ in Greek. 1m
This word does not accurately describe the condition of the internal environment because
the internal environment is kept within narrow ranges instead of staying the same. 1m
3 Water content / oxygen content / carbon dioxide content in blood / body temperature
(or other correct answer) 1m
Oxford University Press 2009
You might also like
- Minutes of The Homeroom MeetingDocument1 pageMinutes of The Homeroom MeetingRichard Tan Alagos100% (16)
- Andrew's Exercise Solutions - Coursera Coursera Introduction To Physiology - Week 1 - Homeostasis and Endocrine System ExamDocument3 pagesAndrew's Exercise Solutions - Coursera Coursera Introduction To Physiology - Week 1 - Homeostasis and Endocrine System ExamRS123No ratings yet
- Compendium of Logistics Policies Volume III PDFDocument219 pagesCompendium of Logistics Policies Volume III PDFDon-Juan Casanova92% (12)
- Narayana HrudayalayaDocument6 pagesNarayana HrudayalayaPriyanka Bharadwaj100% (1)
- Question Bank - New Questions: Chapter 18 HomeostasisDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank - New Questions: Chapter 18 HomeostasisAnders HuiNo ratings yet
- Y13 Homeostasis BookletDocument62 pagesY13 Homeostasis Booklethummy18No ratings yet
- 5.1 Hormonal Communication QPDocument19 pages5.1 Hormonal Communication QPmaddieNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis Questions Test Mark SchemeDocument7 pagesHomeostasis Questions Test Mark SchemeJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument9 pagesHomeostasisShahriar OntherunNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument31 pagesHomeostasisGEETA MOHAN80% (5)
- PP18. HomeostasisDocument80 pagesPP18. Homeostasislesleymohlala7No ratings yet
- Homeostasis Questions Test Mark SchemeDocument8 pagesHomeostasis Questions Test Mark SchemeJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Control and Regulation: Physiological HomeostasisDocument16 pagesUnit 3: Control and Regulation: Physiological HomeostasisaclumutNo ratings yet
- Homeostatis Principles and Regulation of Glucose in BloodDocument13 pagesHomeostatis Principles and Regulation of Glucose in Bloodk75544863No ratings yet
- 1a She Would Suck Up The Lime Water If She Breathed Through Tube X. B C DDocument4 pages1a She Would Suck Up The Lime Water If She Breathed Through Tube X. B C D李安逸No ratings yet
- Homeostasis QuestionsDocument10 pagesHomeostasis QuestionsJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Hormones: Test Yourself 15.1 (Page 287)Document3 pagesHormones: Test Yourself 15.1 (Page 287)leeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet ANSWER KEY Chapter 7 BIO-CLASSDocument13 pagesWorksheet ANSWER KEY Chapter 7 BIO-CLASSUCL SportsNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Homeostasis (Parts 1 and 2)Document19 pagesIGCSE Homeostasis (Parts 1 and 2)buhNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Antidiabetic Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Hyperglycaemic RatsDocument6 pagesResearch Article: Antidiabetic Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Hyperglycaemic RatsUmmu Ghodah ZurrahmiNo ratings yet
- Case ReportDocument5 pagesCase ReportkevserNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System and Feedback MechanismsDocument8 pagesThe Endocrine System and Feedback MechanismsJame SmithNo ratings yet
- FULL Homeostasis Notes PDFDocument9 pagesFULL Homeostasis Notes PDFTess GallianoNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes - PaediatricsDocument52 pagesFluids and Electrolytes - PaediatricsZweNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and Negative FeedbackDocument23 pagesHomeostasis and Negative Feedbackapi-200177496No ratings yet
- Syaidatul Annisha Sarum - LAB 2 - INSULIN REGULATION OF BLOOD GLUCOSEDocument4 pagesSyaidatul Annisha Sarum - LAB 2 - INSULIN REGULATION OF BLOOD GLUCOSESyaidatulNo ratings yet
- PDF文档Document17 pagesPDF文档Kevin JacksonNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 POSTER Homeostasis Animal Coordination and ControlDocument1 pageTopic 7 POSTER Homeostasis Animal Coordination and Controlaminaha4444No ratings yet
- Emergency Pediatric AidsDocument29 pagesEmergency Pediatric AidsRana SalemNo ratings yet
- Jpfarmasigg 160035Document6 pagesJpfarmasigg 160035nikomang ayuNo ratings yet
- HOMEOSTASISDocument8 pagesHOMEOSTASISlekgotlaclaudiaNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Exercise: Chapter 1 Regulation of Water ContentDocument3 pagesSuggested Answers To Exercise: Chapter 1 Regulation of Water ContentAnnaa WongNo ratings yet
- pb12n Mo8 FwsDocument6 pagespb12n Mo8 FwsIsabella RomeroNo ratings yet
- L9 - The Endocrine System and The Control of Blood SugarDocument18 pagesL9 - The Endocrine System and The Control of Blood SugarNasimNo ratings yet
- 28 Control of Blood Sugar Levels-SDocument5 pages28 Control of Blood Sugar Levels-SAaliya Nagori100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine System23aniNo ratings yet
- BIOchem - Glucose - Tolerance - Report - ) TOMDocument20 pagesBIOchem - Glucose - Tolerance - Report - ) TOMmujuni emanuelNo ratings yet
- Hormones NotesDocument14 pagesHormones NotesTeena SheikhNo ratings yet
- Blood SugarDocument11 pagesBlood SugarYuka TakahashiNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam PhysiologyDocument150 pagesMock Exam Physiologyvnair112100% (1)
- Modeling Glucose Regulation v21Document2 pagesModeling Glucose Regulation v21Jonas WelliverNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Notes Life Sciences Reproduction and Endocrine System and HomeostasisDocument34 pagesGrade 12 Notes Life Sciences Reproduction and Endocrine System and HomeostasisAbonalla,Rycha Gaile Marie GarciaNo ratings yet
- King Saud University College of Pharmacy Department of Clinical Pharmacy Clinical Pharmacokinetics - PHCL 462Document26 pagesKing Saud University College of Pharmacy Department of Clinical Pharmacy Clinical Pharmacokinetics - PHCL 462Altaf AhmedNo ratings yet
- 10th Grade Chapter 14 Part 2 (Sugar and Water Regulation)Document10 pages10th Grade Chapter 14 Part 2 (Sugar and Water Regulation)baselfawadlehNo ratings yet
- Case Study Scenario # 1 Congestive Heart Failure (Mojica)Document10 pagesCase Study Scenario # 1 Congestive Heart Failure (Mojica)Noah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Rev Notes ch18 eDocument3 pagesRev Notes ch18 eEdgar LeungNo ratings yet
- UACE BIOLOGY PAPER 2 2011 UNEB Marking GuideDocument12 pagesUACE BIOLOGY PAPER 2 2011 UNEB Marking GuideArthurNo ratings yet
- Physiology of HomeostasisDocument17 pagesPhysiology of HomeostasisRamadan PhysiologyNo ratings yet
- InsulinDocument5 pagesInsulinEnni Mutiati Al-MaduryNo ratings yet
- Antidiabetic and Long-Term Effects of Elaeocarpus GrandiflorusDocument12 pagesAntidiabetic and Long-Term Effects of Elaeocarpus GrandiflorusAgus FakhrudinNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic Training Packet For PharmacistsDocument24 pagesPharmacokinetic Training Packet For PharmacistsGlory Claudia KarundengNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument10 pagesDiabetes MellitusKyla Francine BandeNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument14 pagesDiabetes MellitusWeeaboo Franz VlogsNo ratings yet
- HSB Week 17Document16 pagesHSB Week 17edhanassarNo ratings yet
- Notes Intensive care fundamentals-Key concepts in Intensive Care MedicineDocument12 pagesNotes Intensive care fundamentals-Key concepts in Intensive Care MedicineNinyNo ratings yet
- Biology, Physics, ChemistryDocument13 pagesBiology, Physics, ChemistryEka Haris PrastiwiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chem NotesDocument3 pagesClinical Chem NotesJenny HaydarNo ratings yet
- HermanYeung DSE Bio CH 3E Temp NoteDocument5 pagesHermanYeung DSE Bio CH 3E Temp NoteliNo ratings yet
- A&P - 7. Physiological Response To Stress (5p)Document5 pagesA&P - 7. Physiological Response To Stress (5p)Sreejith Jagal KishoreNo ratings yet
- Hormones, The Endocrine System and HomeostasisDocument5 pagesHormones, The Endocrine System and Homeostasischiusavi77No ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing: Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument28 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing: Fluids and ElectrolytesDhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- New ThummaDocument5 pagesNew ThummaSabharish KoruturuNo ratings yet
- MONITOR LCD Philips 192E1SB Chassis Meridian 5Document88 pagesMONITOR LCD Philips 192E1SB Chassis Meridian 5Ronan-PUC NolascoNo ratings yet
- Eviction Information Requirements Rev0819 en FilDocument2 pagesEviction Information Requirements Rev0819 en FilLittle TownNo ratings yet
- LAZUDAN ZEKRELLAH I. BSMT 2 BD WATCH 1 Semi Final Exam 1Document8 pagesLAZUDAN ZEKRELLAH I. BSMT 2 BD WATCH 1 Semi Final Exam 1Macxie Baldonado QuibuyenNo ratings yet
- History G4 Report FinalDocument14 pagesHistory G4 Report FinalElvira MirajulNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test Micro Past Papers 2020Document11 pagesPre-Test Micro Past Papers 2020Thanatchawan Janwaro100% (1)
- RPT Internal Scheme ReportDocument16 pagesRPT Internal Scheme ReportChaitanya GunturuNo ratings yet
- Ch04 6e Slutions HoyleDocument44 pagesCh04 6e Slutions HoyleJackie PerezNo ratings yet
- Los Angeles Police OrganizationDocument9 pagesLos Angeles Police OrganizationRylie MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Bed and Bathroom Linen - 29.12.2020Document2 pagesBed and Bathroom Linen - 29.12.2020Eden Led LightingNo ratings yet
- Comp RecDocument60 pagesComp RecMichael WellsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ProblemsDocument4 pagesChapter 4 ProblemsSteve DiazNo ratings yet
- Good Homes - June 2015 IN PDFDocument90 pagesGood Homes - June 2015 IN PDFElena ElenaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Visit ReportDocument3 pagesIndustrial Visit ReportBarzeen Mehr AfareenNo ratings yet
- ELMS Project ReportDocument42 pagesELMS Project ReportLuckinsi Samuel100% (1)
- 1 5 4 Diabetes Mellitus - PDF 2Document6 pages1 5 4 Diabetes Mellitus - PDF 2Maica LectanaNo ratings yet
- CSRDocument16 pagesCSRAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- Notes On The Marsh-BellDocument11 pagesNotes On The Marsh-BellTimóteo ThoberNo ratings yet
- Electrical Resistance Lecture 2Document5 pagesElectrical Resistance Lecture 2bigbang0% (1)
- RMS Titanic Was A British Passenger: Olympic - Class Ocean LinersDocument1 pageRMS Titanic Was A British Passenger: Olympic - Class Ocean Linersandreea uNo ratings yet
- Cost C. Test EM Question 03.03.2023 VI-1, VDI-1Document2 pagesCost C. Test EM Question 03.03.2023 VI-1, VDI-1harish jangidNo ratings yet
- Road Safety FundamentalsDocument122 pagesRoad Safety Fundamentalssmanoj354100% (3)
- Banco de Oro Savings and Mortgage Bank vs. Equitable Banking CorporationDocument15 pagesBanco de Oro Savings and Mortgage Bank vs. Equitable Banking CorporationFD Balita0% (1)
- Q2-COT-LP-Health7 - Wk4 (Malnutrition and Micronutrients Deficiency)Document4 pagesQ2-COT-LP-Health7 - Wk4 (Malnutrition and Micronutrients Deficiency)ivonneNo ratings yet
- Beg Unit5 RevisionDocument2 pagesBeg Unit5 RevisionSimina EnăchescuNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document5 pagesModule 7marleteNo ratings yet
- Lead Free DFM Guidelines From SMTCDocument18 pagesLead Free DFM Guidelines From SMTCsmtdrkd100% (4)