Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circulatory System Notes
Circulatory System Notes
Uploaded by
hannah peloniaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circulatory System Notes
Circulatory System Notes
Uploaded by
hannah peloniaCopyright:
Available Formats
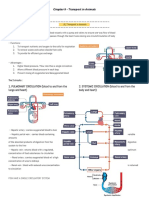
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Blood
It is the medium of how we transport glucose and gases throughout the body.
It maintains certain pH, temperature, osmotic pressure => important for
homeostasis
It transports hormones, nutrients and gases.
Four types of blood : A, B, AB, O
Components of Blood
1. Platelets – cellular fragments
– helping blood clot
2. Cells – cellular components
– Red blood cells: transporting gases; has
hemoglobin => it is where the red coloring of
blood come from
– White blood cells: can fight infections
3. Plasma – liquid portion
– contains water, proteins, salts, lipids
Heart
It is divided into two distinct and
separated partitions – deoxygenated
or low-oxygen partition and
oxygenated partition.
It is a pump and a muscular organ
about size of your fist.
located slightly left center in the chest
Arteries Veins
Carries blood away from the Carries blood to the heart.
heart. typically oxygen-poor
typically oxygen- rich
Capillaries
small blood vessel and it is where oxygen is delivered to organs and tissues
and also it is where carbon dioxide will be picked up to travel back to the
lungs.
Four chambers of the heart
Atria Ventricle
top of the heart bottom of the heart
have thinner walls have thicker walls
Valves Aorta
one-way structure that help major artery that carries
separate chambers oxygenated blood throughout
prevents backflow of the blood the body
Four types of valve: tricuspid valve,
pulmonary valve, bicuspid valve, aortic
valve => works like gates on a fence,
open only one way and only when
pushed; each valve opens and closes
once per heartbeat
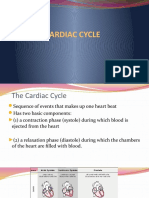
A beating heart contracts and relaxes.
Systole – contraction; ventricles Diastole – relaxing; ventricles relax
contract forcing blood into vessels to and filled with blood from upper
lungs and body chambers
Pathway of Circulatory System
Inferior vena cava => Right atrium => Tricuspid valve => Right
ventricle => Pulmonary valve => Pulmonary artery => Lungs =>
Pulmonary vein => Left atrium => Bicuspid valve => Left ventricle
=> Aortic valve => Aorta
Coronary artery
heart can receive blood supply through it
blockage of it could lead to heart attack
it branch off the aorta and delivers blood into capillaries wherein it delivers
oxygen and glucose to the heart
Electrical impulses
electrical wiring which keeps heart beating
begins in right atrium and travels to specialized pathways to ventricles
delivering the signal to pump
Coronary veins
it takes the deoxygenated blood to the right atrium where the blood will
eventually travel the pathway to become oxygenated.
Human heart beat: 5 quarts of blood per minute, 100, 000 beats per day, 35
million beats per year
Atrial Septal Defect
a heart condition wherein the
pathway flow of blood has changed.
it could mean an opening and
oxygen-rich blood could mix with
oxygen-poor blood.
it can cause abnormal heartbeats,
stroke or heart failure => could be treated with medications or surgery
You might also like
- Autopsy of Pazuzu AlgaradDocument7 pagesAutopsy of Pazuzu AlgaradFOX8No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument44 pagesCirculatory SystemAdonai Jireh Dionne BaliteNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: Ronmar T. Riňo Abegail Bersamin Maila C. TamondongDocument30 pagesThe Circulatory System: Ronmar T. Riňo Abegail Bersamin Maila C. TamondongKelly Troy Alano100% (13)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Transportation 1 PDFDocument9 pagesTransportation 1 PDFNakshatra PaliwalNo ratings yet
- SystemDocument63 pagesSystemBeth Rubin RelatorNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascularsystem 090820055728 Phpapp02Document75 pagesCardiovascularsystem 090820055728 Phpapp02muhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesCirculatory SystemMaria Theresa DemeterioNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory SystemCookies AndcreamNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument34 pagesCirculatory SystemMHAR CHRISTOPHER MAMASIGNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesMammalian Circulatory SystemAudreyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesCardiovascular Systemyousaf Murad khurramNo ratings yet
- f3 Chapter 3Document25 pagesf3 Chapter 3aniszainuddin77No ratings yet
- Transport in HumansDocument6 pagesTransport in HumansJason Ng100% (5)
- Cardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As ADocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As AMalaquias VallejosNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Sci 6Document26 pagesCirculatory System Sci 6Regin BaguioNo ratings yet
- Function of The Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesFunction of The Circulatory SystemChristine SegundoNo ratings yet
- Vascular SystemDocument20 pagesVascular SystemHama HamidNo ratings yet
- 024-Premedical Circulatory SystemDocument31 pages024-Premedical Circulatory Systemchealzea asuncsionNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System in Finfish and ShellfishDocument27 pagesCirculatory System in Finfish and ShellfishDr. Abir IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Cardiovascular System: Inquiry Into Life, Thirteenth EditionDocument3 pagesChapter 12: Cardiovascular System: Inquiry Into Life, Thirteenth Edition117320No ratings yet
- القلبDocument11 pagesالقلبNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument30 pagesCirculatory SystemIra Lavigne De VillaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory Systemsyrine mendozaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument31 pagesCirculatory SystemKalev MaricqNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument66 pagesThe Circulatory Systemcuetodustin01No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory SystemNaiomiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System PPT FeDocument26 pagesCardiovascular System PPT FeAngel Grace GaliasNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemGennelle GabrielNo ratings yet
- 6th Lecture Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pages6th Lecture Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDwnya S HasanNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument7 pagesTransport in Animalstmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument12 pagesTransport in AnimalsJedidiah DickNo ratings yet
- Science 9 1.3 LessonDocument31 pagesScience 9 1.3 LessonHdisbdbd NfjdnbdncNo ratings yet
- Notes Grade: 9 Subject: Biology Chapter No: 9 Chapter Name: Transport in Animals ObjectivesDocument36 pagesNotes Grade: 9 Subject: Biology Chapter No: 9 Chapter Name: Transport in Animals Objectivespraneeth satishNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Transport in HumansDocument11 pages5.2 Transport in Humans박찬우No ratings yet
- Functions of The Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesFunctions of The Circulatory SystemJulliane OrtizNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Unit 1: Module 1Document29 pagesCirculatory System: Unit 1: Module 1Michael Escriba100% (1)
- Transport in AnimalsDocument10 pagesTransport in Animalswarona letangNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Cardiovascular SytemDocument37 pagesGroup 3 Cardiovascular Sytemsophiapelayo326No ratings yet
- BookDocument8 pagesBookmohamed aweys abuukarNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemHimanshu JindalNo ratings yet
- Presidium Indirapuram Students Handout-3 Grade X (Biology) Chapter: Life Processes Topic: TransportationDocument8 pagesPresidium Indirapuram Students Handout-3 Grade X (Biology) Chapter: Life Processes Topic: TransportationSaniya nebNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemSaadNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORTATIONDocument9 pagesTRANSPORTATIONAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory Systemvedansh duttNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportDocument39 pagesScience Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportNadzirah RedzuanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesCirculatory SystemAhmad S AlkarmyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory SystemJheyrick Casipe BaliguatNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument33 pagesCirculatory SystemMarco DadoNo ratings yet
- NOTES- TRANSPORTATION IN HUMANSDocument6 pagesNOTES- TRANSPORTATION IN HUMANScomputer8gbNo ratings yet
- Circ UlaDocument4 pagesCirc UlaShanice BedecirNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document22 pagesWeek 2Jesseryl MargalloNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesBlood Circulatory SystemstephanietoppoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 by Jaskirat KaurDocument18 pagesLecture 3 by Jaskirat KaurmparineetNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: Karan Arora Ix-B byDocument33 pagesThe Circulatory System: Karan Arora Ix-B bykaranarorarafaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System ReviewerDocument4 pagesThe Circulatory System ReviewerKaten KyoukotsuNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATORYDocument20 pagesCIRCULATORYDannica Trisha CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Transports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsDocument46 pagesTransports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsElla LlamasNo ratings yet
- Quarter1 Week2 Lesson2Blood and Gas ExchangeDocument24 pagesQuarter1 Week2 Lesson2Blood and Gas ExchangeRicky RickyNo ratings yet
- Types of Circulatory SystemsDocument8 pagesTypes of Circulatory SystemsJanis Micaela EsmasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System NotesDocument3 pagesRespiratory System Noteshannah peloniaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Skull Vertebral Column/spinal Cord Thoracic CageDocument7 pagesSkeletal System: Skull Vertebral Column/spinal Cord Thoracic Cagehannah peloniaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument6 pagesEndocrine System Noteshannah pelonia100% (1)
- Digestive System: 9m 20 Specialized Cell TypesDocument4 pagesDigestive System: 9m 20 Specialized Cell Typeshannah peloniaNo ratings yet
- Lab - Urinary SystemDocument29 pagesLab - Urinary Systemapi-3698357No ratings yet
- Pre - Lab # 4 - Circulatory System: Label The Diagrams of Anterior, Posterior and Coronal View of The HeartDocument23 pagesPre - Lab # 4 - Circulatory System: Label The Diagrams of Anterior, Posterior and Coronal View of The Heartmpetrov_2No ratings yet
- Punjab Group of Colleges: 1 Quarter Test (Chapter 15, 16, 17)Document2 pagesPunjab Group of Colleges: 1 Quarter Test (Chapter 15, 16, 17)Qadir RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka Skripsi Daun CiplukanDocument4 pagesDaftar Pustaka Skripsi Daun CiplukanshonsakarisaNo ratings yet
- FINAL QUIZ 1 - Attempt ReviewDocument5 pagesFINAL QUIZ 1 - Attempt ReviewAshnesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests - CP - Pharmd 4th YearDocument62 pagesLiver Function Tests - CP - Pharmd 4th Yearsri deepika sri deepikaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 Q1-WK 1-2.b FOR STUDENTDocument16 pagesSCIENCE 9 Q1-WK 1-2.b FOR STUDENTErra PeñafloridaNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter Release and ProcessDocument14 pagesNeurotransmitter Release and ProcessRain TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Ebook Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology PDF Full Chapter PDFlloyd.odell127100% (37)
- Tabalba Lab - 1-Y1-2 Lab Exercise 3Document10 pagesTabalba Lab - 1-Y1-2 Lab Exercise 3Shane V. TabalbaNo ratings yet
- Female Physiology Before Pregnancy and The Female HormonesDocument3 pagesFemale Physiology Before Pregnancy and The Female HormonesspringdingNo ratings yet
- Lymph NodesDocument6 pagesLymph NodesIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Im - Chronic Kidney Disease - Dr. Lorna Wong - March 20 2021Document107 pagesIm - Chronic Kidney Disease - Dr. Lorna Wong - March 20 2021Christine MendozaNo ratings yet
- Quantec ReviewDocument64 pagesQuantec Reviewapi-279520503No ratings yet
- Thyroid CancerDocument22 pagesThyroid CancerHidayah JaiNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 35-2 and 35-3 Divisions of The Nervous SystemDocument21 pagesBiology Chapter 35-2 and 35-3 Divisions of The Nervous Systemapi-239353579No ratings yet
- Chapter 128 - Thyroid and Adrenal Disorders: Episode OverviewDocument15 pagesChapter 128 - Thyroid and Adrenal Disorders: Episode OverviewIkenna EzeiloNo ratings yet
- AdrenokortikoidmcDocument15 pagesAdrenokortikoidmcMeilia AndiniNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology Unit 2 Circulatory SystemDocument20 pagesCape Biology Unit 2 Circulatory SystemKemoy Francis100% (1)
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Body SystemsDocument40 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Body Systemsdonibung 007No ratings yet
- Dumping Syndrome - Background, Pathophysiology, EtiologyDocument6 pagesDumping Syndrome - Background, Pathophysiology, EtiologyW CnNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and Circulation (1) MMMDocument52 pagesBody Fluids and Circulation (1) MMMRjNo ratings yet
- Kode DiagnosaDocument158 pagesKode DiagnosaTAUFIK SIREGARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Transport in AnimalsDocument6 pagesChapter 9 - Transport in AnimalsLeann LeeNo ratings yet
- Approach To JaundiceDocument16 pagesApproach To JaundiceMuvenn KannanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 6 - Special SensesDocument8 pagesLaboratory Activity 6 - Special SensesPaulynne PaulynneNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Psy 2480Document3 pagesNeuroanatomy Psy 2480Anonymous eQhd0QUNo ratings yet
- Digestive ExamDocument13 pagesDigestive Examapi-294622133No ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesThe Respiratory SystemIftikharNo ratings yet