Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ADA Medication Profiles and Side Effects
ADA Medication Profiles and Side Effects
Uploaded by
HillariOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ADA Medication Profiles and Side Effects
ADA Medication Profiles and Side Effects
Uploaded by
HillariCopyright:
Available Formats
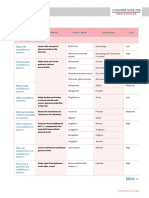
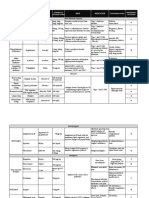
Medication Profiles of Antihyperglycemic Medications
Sodium Glucose Secretagogues
Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Thiazolidinediones
SU GLN
Metformin Receptor Agonists (GLP1 RAs) (SGLT2is) Inhibitors (DPP4is) (TZDs)* Insulin
Moderate /
Hypoglycemia Neutral Neutral Neutral Neutral Neutral Mild Moderate to severe
severe
Loss
Weight Slight loss Semaglutide > liraglutide > dulaglutide > Loss Neutral Gain Gain Gain
exenatide > lixisenatide
Exenatide not indicated if CrCl Not indicated for eGFR <45 Dose adj necessary
Contraindicated if eGFR <30 mL/min Genital mycotic infections (except linagliptin)
Renal / GU Neutral More hypoglycemia risk More hypoglycemia risk
<30 Possible benefit of Effective in reducing
Possible benefit of liraglutide albuminuria
empagliflozin
GI AEs Moderate Moderate Neutral Neutral Neutral Neutral Neutral
Possible benefit of Possible risk for
Cardiac—CHF Neutral Moderate More CHF risk More CHF risk
empagliflozin saxagliptin and alogliptin
Neutral
May reduce stroke
Cardiac—ASCVD Possible benefit of LA GLP1 RA Possible CV benefit Neutral Possible ASCVD risk Neutral
risk
Moderate fracture
Bone Neutral Neutral Canagliflozin warning Neutral Neutral Neutral
risk
Ketoacidosis Neutral Neutral Neutral Neutral Neutral Neutral Neutral
Efficacy High High Intermediate Intermediate (target PPG) High High
Administration Oral Injectable Oral Oral Oral Oral Injectable
Cost Variable High High High Low Low
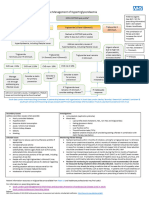
HbA1c above target: Preferred initial • Consider early introduction if:
pharmacologic agent plus − evidence of ongoing catabolism
comprehensive lifestyle − hyperglycemia symptoms
(weight management and − A1C levels (>10%) or BG levels
physical activity) ≥300 mg/dL
• Consider dual therapy in newly
diagnosed T2DM with an A1C ≥1.5%
above their glycemic target
If A1C remains above target despite recommended AND NO ASCVD OR CKD
first-line treatment
PLUS ESTABLISHED ASCVD or CKD
and ASCVD PREDOMINATES → GLP1 RA with proven CV benefit SGLT2 inhibitor with proven CV
(Liraglutide > semaglutide > benefit, if eGFR adequate
dulaglutide) (empagliflozin > canagliflozin >
dapagliflozin)
and HF or CKD PREDOMINATES → AND SGLT2 inhibitor is not tolerated, SGLT2 inhibitor with proven CV
is contraindicated, or eGFR is less benefit, if eGFR adequate
than adequate, add a GLP1 RA with (empagliflozin > canagliflozin)
proven CV benefit (Liraglutide >
semaglutide > dulaglutide)
ASCVD = atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; CHF = congestive heart failure; CrCl = creatinine clearance; DKA = diabetic ketoacidosis; DPP4is = Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors; eGFR = estimated glomerular filtration rate; GLN = glinide (meglitinides);
GLP1 RAs = Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists; GU = Genitourinary; Met = Metformin; SGLT2 = sodium glucose cotransporter 2; SU = sulfonylurea; T2D = type 2 diabetes; TZDs = Thiazolidinediones
Few adverse events or possible benefits Use with caution Likelihood of adverse effects ? Uncertain effect
American Diabetes Association. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes—2021. Dia Care. 2021;44(Supplement 1):S111-S124. doi:10.2337/dc21-S009
Garber AJ, Handelsman Y, Grunberger G, et al. Consensus statement by the american association of clinical endocrinologists and american college of endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management
algorithm – 2020 executive summary. Endo Pract. 2020;26(1):107-139. doi:10.4158/CS-2019-0472
You might also like
- Cpje Secrets Preview 2021Document12 pagesCpje Secrets Preview 2021Diana Pham100% (3)
- P66 B1 M5 Lufthansa PDFDocument196 pagesP66 B1 M5 Lufthansa PDFDAVID FAJARDO PUERTO100% (1)
- Compendium of Logistics Policies Volume III PDFDocument219 pagesCompendium of Logistics Policies Volume III PDFDon-Juan Casanova92% (12)
- 10-11 - Anti-Hyperlipidemic Drugs (Summary SAQ and MCQS)Document6 pages10-11 - Anti-Hyperlipidemic Drugs (Summary SAQ and MCQS)Purvak Mahajan100% (1)
- Diabetes Topic DiscussionDocument9 pagesDiabetes Topic DiscussionSamNo ratings yet
- Coagulation DrugsDocument1 pageCoagulation Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Antihyperglycemic Agents Comparison Chart PDFDocument9 pagesAntihyperglycemic Agents Comparison Chart PDFconcoz100% (1)
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) Adult Treatment PathwayDocument2 pagesType 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) Adult Treatment PathwayFaidil Akbar100% (1)
- Quick Reference Guide - Management of Diabetes 1 2022 Version FINALDocument20 pagesQuick Reference Guide - Management of Diabetes 1 2022 Version FINALHigh Class Education (H.C.Education)No ratings yet
- DM TYPE 2 by THEADocument29 pagesDM TYPE 2 by THEAThea SelinaNo ratings yet
- DM TTTDocument2 pagesDM TTTBell GatesNo ratings yet
- Mono Dual Triple Therapy DiabetesDocument1 pageMono Dual Triple Therapy DiabetesbharatNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Type 2 Treatment AlgorithmDocument25 pagesDiabetes Type 2 Treatment AlgorithmJ Wong100% (1)
- Table 173-3 - Agents Used For Treatment of Type 1 or Type 2 DiDocument2 pagesTable 173-3 - Agents Used For Treatment of Type 1 or Type 2 DiKiran ShelkeNo ratings yet
- Table 1. Antihyperglycemic Agents For Use in Type 2 DiabetesDocument5 pagesTable 1. Antihyperglycemic Agents For Use in Type 2 DiabeteszeiarraNo ratings yet
- Approach 2024Document25 pagesApproach 2024light tweenNo ratings yet
- Sylfonylurea: Class Generic Trade Store NotesDocument4 pagesSylfonylurea: Class Generic Trade Store NotesMohammadSAL-RawashdehNo ratings yet
- CPG T2DM 6th Edition 2020 13042021Document4 pagesCPG T2DM 6th Edition 2020 13042021harisa yasmanNo ratings yet
- Non Insulin Management of DM - PPTX 2Document33 pagesNon Insulin Management of DM - PPTX 2Meno AliNo ratings yet
- 43 The Importance of Diabetes ManagementDocument33 pages43 The Importance of Diabetes ManagementHarli AMNo ratings yet
- Therapeutics Diabetes DrugchartDocument4 pagesTherapeutics Diabetes DrugchartSharan SahotaNo ratings yet
- ADA 2023.-154-159 - OrganizedDocument6 pagesADA 2023.-154-159 - OrganizedEfren BalsecaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Endocrino Unidad 2 Diabetes Cont.Document33 pagesEndocrino Unidad 2 Diabetes Cont.GenesisGissellPlazaQuesadaNo ratings yet
- Manajemen DM Tipe 2 - HBD Idi LabuselDocument40 pagesManajemen DM Tipe 2 - HBD Idi LabuselJunni EdyNo ratings yet
- More : Drug Class How It Works Generic Name Brand Name Cost Type 2 Oral Medications BiguanideDocument4 pagesMore : Drug Class How It Works Generic Name Brand Name Cost Type 2 Oral Medications BiguanideJoshua LewisNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyGiselle TutorNo ratings yet
- Topiramate: May Decrease Glyburide Levels Colesevelam:decreases The Absorption of SulfonylureasDocument3 pagesTopiramate: May Decrease Glyburide Levels Colesevelam:decreases The Absorption of SulfonylureaserinNo ratings yet
- Non-Insulin Management of Diabetes MellitusDocument15 pagesNon-Insulin Management of Diabetes MellitusrogeracasusoNo ratings yet
- 23-5-2022 Presentation JentadeutoDocument52 pages23-5-2022 Presentation JentadeutofsvtqsNo ratings yet
- DiabetesDocument40 pagesDiabetesA RNo ratings yet
- NENC Regional SGLT2 Top Tips v1.2 NTAG Approved March 2023Document5 pagesNENC Regional SGLT2 Top Tips v1.2 NTAG Approved March 2023Nehal ElnagarNo ratings yet
- Summary Drugs Table - GERR BlockDocument2 pagesSummary Drugs Table - GERR BlockRiley WestwoodNo ratings yet
- Five Steps in Management of DMDocument62 pagesFive Steps in Management of DMarti tyagitaNo ratings yet
- New Dyslipidemia 2021 Naplex QuickDocument2 pagesNew Dyslipidemia 2021 Naplex Quickkaylakmills_1013586883% (6)
- Visual Summary Full Version Choosing Medicines For Firstline and Further Treatment PDF 10956472093Document5 pagesVisual Summary Full Version Choosing Medicines For Firstline and Further Treatment PDF 10956472093BiancaPancuNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MedicationDocument3 pagesDiabetes MedicationRuben Gutierrez-ArizacaNo ratings yet
- SGLT 2Document21 pagesSGLT 2Genix PharmaNo ratings yet
- DPP 4Document20 pagesDPP 4Genix PharmaNo ratings yet
- Step 3 - PharmacologyDocument10 pagesStep 3 - PharmacologyLauren LevyNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Drug Reference SheetDocument12 pagesCritical Care Drug Reference SheetYanina CoxNo ratings yet
- Dyslipidemia SummaryDocument6 pagesDyslipidemia SummaryJan Angela BaylonNo ratings yet
- Class Generic Brand MOA Indication: GetrylDocument6 pagesClass Generic Brand MOA Indication: GetrylDr. Sadaf khanNo ratings yet
- Diabetes DrugsDocument1 pageDiabetes Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Diabetes and Its Management: Rohit ThanageDocument10 pagesDiabetes and Its Management: Rohit ThanageRohit ThanageNo ratings yet
- The Metabolic Syndrome From Insulin Resistance To Obesity and DiabetesDocument44 pagesThe Metabolic Syndrome From Insulin Resistance To Obesity and DiabetesDwiPutriArlinaNo ratings yet
- Acs Review - Student VersionDocument3 pagesAcs Review - Student Versionapi-549451092No ratings yet
- Diabetes Treatment: PancreatitisDocument2 pagesDiabetes Treatment: PancreatitisSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- SGLT2 IDocument24 pagesSGLT2 IFiErCeNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular KBKDocument7 pagesCardiovascular KBKDavid SantosoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes in CKDDocument20 pagesDiabetes in CKDdr_iswahyudhiNo ratings yet
- Updates On Metformin JDM2019 DTDocument37 pagesUpdates On Metformin JDM2019 DTLaurentius JohanNo ratings yet
- Dyslipdiemia 2022Document75 pagesDyslipdiemia 2022LeeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Therapeutics: Case 1Document17 pagesClinical Therapeutics: Case 1NoreenNo ratings yet
- Crash Course 1 StudentDocument1 pageCrash Course 1 Studentapi-648595816No ratings yet
- Oral Antidiabetic DrugsDocument46 pagesOral Antidiabetic Drugscarms100% (1)
- 2020 - Diabetes PharmacotherapyDocument68 pages2020 - Diabetes PharmacotherapyAmal HijaziNo ratings yet
- Diabetes ManagementDocument2 pagesDiabetes ManagementronaldNo ratings yet
- نسخة abdullah alhajri final check 25Document16 pagesنسخة abdullah alhajri final check 25abdulrahman AlrashedNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS Guidance For The Management of Hypertriglyceridaemia July 2018Document2 pagesLIPIDS Guidance For The Management of Hypertriglyceridaemia July 2018siti munajaliahNo ratings yet
- Mounjaro MonographDocument13 pagesMounjaro Monographlu161513No ratings yet
- Communication Aids and Strategies Using Tools of TechnologyDocument14 pagesCommunication Aids and Strategies Using Tools of TechnologyJussel CataloNo ratings yet
- Vibration LectureDocument49 pagesVibration LectureMark Oliver BernardoNo ratings yet
- TITLE: Distillation and Hardness of Water AbstractDocument4 pagesTITLE: Distillation and Hardness of Water AbstractnotmeNo ratings yet
- FullereneDocument12 pagesFullereneapi-249970885No ratings yet
- Currency Detection For Blind PeopleDocument19 pagesCurrency Detection For Blind Peoplehaffah1245No ratings yet
- KPI FormulaDocument3 pagesKPI FormulaSrikant GuptaNo ratings yet
- Business Math AssignmentDocument4 pagesBusiness Math AssignmentiamshowrovNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection Valves: Effective March 18, 2013 - Supercedes FPP-0312 of March 26, 2012Document8 pagesFire Protection Valves: Effective March 18, 2013 - Supercedes FPP-0312 of March 26, 2012Jorge Alberto Martinez OrtizNo ratings yet
- Multi Evaporator System With Single Compressor and Individual Expansion ValveDocument4 pagesMulti Evaporator System With Single Compressor and Individual Expansion ValveALL THE GOOD STUFFNo ratings yet
- Assignment Management System: Project Report OnDocument68 pagesAssignment Management System: Project Report OnAnuj Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Timothy StainbrookDocument1 pageTimothy Stainbrookapi-548131304No ratings yet
- Fruits and Veg SCMDocument11 pagesFruits and Veg SCMamoldhawanNo ratings yet
- Adult PSG Guidelines 2014Document49 pagesAdult PSG Guidelines 2014mohanNo ratings yet
- Coralia AntenasDocument3 pagesCoralia AntenasALEX_125No ratings yet
- Cleanroom Design GOODDocument135 pagesCleanroom Design GOODtony manyookNo ratings yet
- BGBA Membership ProcedureDocument2 pagesBGBA Membership ProceduremizanacmaNo ratings yet
- Procedures For Reimbursement of Expenses Relating To Official TravelsDocument14 pagesProcedures For Reimbursement of Expenses Relating To Official TravelsNeringa Gudelevičiūtė - PolitienėNo ratings yet
- KaksbsjsusnsklsDocument244 pagesKaksbsjsusnsklskevin0% (1)
- Colors and Effects - PSG Pigment Preparations PolyolefinsDocument24 pagesColors and Effects - PSG Pigment Preparations PolyolefinsBoonyarit LurdgrienggraiyingNo ratings yet
- AbanDocument12 pagesAbanIsmar MorenoNo ratings yet
- XdealSkin Vitamins Tiktok ProposalDocument4 pagesXdealSkin Vitamins Tiktok ProposalElixia KiteNo ratings yet
- List of Organisations Covered by Regional Office-Kolar (As On 30.09.2014) (F-Register)Document284 pagesList of Organisations Covered by Regional Office-Kolar (As On 30.09.2014) (F-Register)mutton moonswamiNo ratings yet
- Berklee Drum Notation FinaleDocument25 pagesBerklee Drum Notation Finalenbelane100% (2)
- Astm D 4258Document2 pagesAstm D 4258anthonybarnard100% (1)
- City Builder 10 - Governmental PlacesDocument30 pagesCity Builder 10 - Governmental Placesskypalae86% (7)
- Invaders Around The World in 2018Document18 pagesInvaders Around The World in 2018RVLEBNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Media PPT FinalDocument50 pagesEvolution of Media PPT FinalRoxette SantillanNo ratings yet
- Q2-COT-LP-Health7 - Wk4 (Malnutrition and Micronutrients Deficiency)Document4 pagesQ2-COT-LP-Health7 - Wk4 (Malnutrition and Micronutrients Deficiency)ivonneNo ratings yet