Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Frontal Lobe Plays in Daily Functions Include: Speech and Language Production: Broca's
Frontal Lobe Plays in Daily Functions Include: Speech and Language Production: Broca's
Uploaded by
Marygold SalesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Frontal Lobe Plays in Daily Functions Include: Speech and Language Production: Broca's
Frontal Lobe Plays in Daily Functions Include: Speech and Language Production: Broca's
Uploaded by
Marygold SalesCopyright:
Available Formats
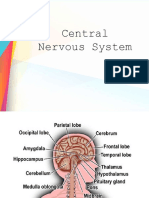
The precentral gyrus is called the somato-motor cortex because it controls volitional
movements of the contralateral side of the body.
The central sulcus ( of Rolando) is a very important landmark in both anatomical and
functional neuroanatomy. The central sulcus separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe,
and more specifically separates the primary motor cortex anteriorly from the primary
somatosensory cortex posteriorly 1.
The Postcentral gyrus is a prominent gyrus in the lateral parietal lobe of the human brain. It
is the location of the primary somatosensory cortex, the main sensory receptive area for the
sense of touch. Like other sensory areas, there is a map of sensory space in this location,
called the sensory homunculus.
The Parietal lobe also plays a role in functions such as navigation and controlling the body,
as well as understanding spatial orientation and direction. A person’s dominant hand will
often determine which side of the parietal lobe is more active. A person who is right-handed
may have a more active left hemisphere parietal lobe.
Frontal lobe plays in daily functions include: Speech and language production: Broca’s
area, a region in the frontal lobe, helps put thoughts into words. Damage to this area can
undermine the ability to speak, to understand language, or to produce speech that makes
sense.
The function of the Occipital lobe is related to the perception and processing of visual
information, as well as the organization of complex processes of visual perception.
The Temporal lobes sit behind the ears and are the second largest lobe. They are most
commonly associated with processing auditory information and with the encoding of
memory. The temporal lobes are also believed to play an important role in processing
affect/emotions, language, and certain aspects of visual perception.
The Sylvian fissure divides the top of the brain from the bottom. In the front portion of the
brain, the Sylvian fissure divides the frontal lobe — which controls decision-making,
problem-solving, and emotion — from the temporal lobe — which regulates memory,
language, and learning functions.
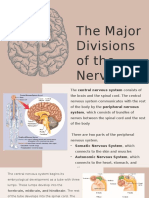
The brainstem regulates vital cardiac and respiratory functions and acts as a vehicle for
sensory information.
The Spinal cord is a long, fragile tubelike structure that begins at the end of the brain stem
and continues down almost to the bottom of the spine. The spinal cord consists of nerves that
carry incoming and outgoing messages between the brain and the rest of the body.
the Cerebellum helps in the coordination of the motor skills such as driving, walking,
running, dancing or even as simple as cutting a sheet of paper with a pair of scissors. The
cerebellum also helps with balance and muscle tone
You might also like
- Cook, Claire Kehrwald - The MLA's Line by Line, How To Edit Your Own Writing (1985)Document243 pagesCook, Claire Kehrwald - The MLA's Line by Line, How To Edit Your Own Writing (1985)Ting Guo100% (13)
- Community Helpers Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesCommunity Helpers Lesson Planapi-250797681No ratings yet
- Communication Style of The Honorable Lee Kuan YewDocument5 pagesCommunication Style of The Honorable Lee Kuan Yewhashish83No ratings yet
- PPP PsychDocument36 pagesPPP Psychbadass bitxch50% (2)
- 4 Lobes FunctionDocument4 pages4 Lobes FunctionAcharya PradeepNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument77 pagesNervous SystemPeter Jay CorrosNo ratings yet
- Brain Parts and FunctionDocument6 pagesBrain Parts and FunctionChabbigillNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument13 pagesHuman BrainAaniya AsadNo ratings yet
- Major Structures of The Brain and The Influence They Have On Cognition and Learning Name CollegeDocument4 pagesMajor Structures of The Brain and The Influence They Have On Cognition and Learning Name CollegeKioko NziokaNo ratings yet
- CNS PNS Physiol NotesDocument11 pagesCNS PNS Physiol NotesVivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Brain Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesBrain Structure and Functionmademoiselle in transitNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 LobesDocument35 pagesLec 3 Lobesmishal.sarosh75No ratings yet
- Science ReportDocument3 pagesScience ReportAna Miadel Mojica MartalNo ratings yet
- General Structure and Function of BrainDocument3 pagesGeneral Structure and Function of BrainFajarrNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and FunctionDocument3 pagesAnatomy and FunctionKalebNo ratings yet
- Brain InfoDocument3 pagesBrain InfoRona May EsperanzateNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Nueroscience - NotesDocument8 pagesCognitive Nueroscience - NotesEirrah AcenasNo ratings yet
- HumanasdhDocument4 pagesHumanasdhPatricia Camille FermoNo ratings yet
- CognitiveDocument6 pagesCognitivesanika kadamNo ratings yet
- 1.7 What Does The Brain DoDocument3 pages1.7 What Does The Brain DoStella StaryNo ratings yet
- HNP - Predisposing FDocument42 pagesHNP - Predisposing FLady Jean Milan ColataNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOLINGUISTISDocument16 pagesPSYCHOLINGUISTISAmigos VideoNo ratings yet
- Temporal LobesDocument5 pagesTemporal LobesGreyed OutNo ratings yet
- What Is The Brain?: CerebrumDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Brain?: CerebrumAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Document 6Document16 pagesDocument 6Vaneeza AliNo ratings yet
- Functional Areas of BrainDocument8 pagesFunctional Areas of BrainirfanzukriNo ratings yet
- Brain Regions: The Cerebral CortexDocument4 pagesBrain Regions: The Cerebral Cortexmohitnet1327No ratings yet
- Anatomy of StrokeDocument4 pagesAnatomy of StrokeMarvin Manuel RamosNo ratings yet
- Gen Psyc by Caserial. WdocDocument4 pagesGen Psyc by Caserial. WdoccassandraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of TH Brain: BrainstemDocument2 pagesAnatomy of TH Brain: BrainstemHanna RamosNo ratings yet
- SubjectDocument11 pagesSubjectRoshni GuptaNo ratings yet
- Brain Structure and Function: Embryologically Derived From 3 Primary Brain VesiclesDocument17 pagesBrain Structure and Function: Embryologically Derived From 3 Primary Brain VesiclesMukesh YadavNo ratings yet
- The BrainDocument28 pagesThe BrainAnania EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 (A) Brain Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesUnit 1 (A) Brain Structure and FunctionAvni SinghNo ratings yet
- Areas de BrodmannDocument9 pagesAreas de BrodmannJosé TouzettNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document8 pagesAssignment 4Favour NwaforNo ratings yet
- Discuss Action Potential of The Axon and Nerve ImpulseDocument3 pagesDiscuss Action Potential of The Axon and Nerve ImpulsePink PastaNo ratings yet
- Personal-Development-2 (3RD Quarter)Document5 pagesPersonal-Development-2 (3RD Quarter)karilesbackupaccNo ratings yet
- Transcript Public SpeakingDocument2 pagesTranscript Public SpeakingPivvkyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Brain BrainDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Brain BrainSherena NicolasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Brain BrainDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Brain BrainSherena NicolasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BrainDocument3 pagesIntroduction To BrainrgdevikaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrum: Frontal LobeDocument2 pagesCerebrum: Frontal LobeCJParisEbasNo ratings yet
- PSY106 2011 Brain StructuresDocument9 pagesPSY106 2011 Brain StructuresAnisia VillamejorNo ratings yet
- PSYC 21 2022 Brain Structures - Short Edited - ForebrainDocument3 pagesPSYC 21 2022 Brain Structures - Short Edited - ForebrainsdahjdhasjkdhaskdNo ratings yet
- PL PT CogpsyDocument3 pagesPL PT CogpsyArsela MaeNo ratings yet
- Brain System: Parts and FunctionsDocument9 pagesBrain System: Parts and FunctionsChristhoper John Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- The Brain and The Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesThe Brain and The Nervous SystemElena-Andreea MutNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyMaquirang Cris JaisonNo ratings yet
- Brain and Its PartsDocument26 pagesBrain and Its PartsYoucef KhanNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesCentral Nervous SystemMeg ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- PERDEV Group 4 Power of MindDocument28 pagesPERDEV Group 4 Power of MindAhron SanchezNo ratings yet
- The Major Divisions of The Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesThe Major Divisions of The Nervous SystemLiana BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Functions: A. The Neuron 1.cellbody: Transmit A Neurotransmitter From One Neuron To AnotherDocument4 pagesFunctions: A. The Neuron 1.cellbody: Transmit A Neurotransmitter From One Neuron To AnotherKurt Lubim Alaiza-Anggoto Meltrelez-LibertadNo ratings yet
- Major Parts of The Brain and What They DoDocument3 pagesMajor Parts of The Brain and What They DoJeff CallantaNo ratings yet
- Brain and StructuteDocument10 pagesBrain and Structutedhatreyi.g.gubbalaNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy (Reading Topic 1)Document6 pagesNeuroanatomy (Reading Topic 1)Fernanda LópezNo ratings yet
- Brain and MindDocument5 pagesBrain and MindMubashir AminNo ratings yet
- Nervous System SGDocument4 pagesNervous System SGNammywhammyNo ratings yet
- Factors That Affect Brain Development: 3eredityDocument6 pagesFactors That Affect Brain Development: 3eredityAlphie BersabalNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument9 pagesResearch Paperapi-282381441No ratings yet
- PsychologyDocument6 pagesPsychologymahbinaalone7No ratings yet
- The Cerebrum Is Divided Into Two Major PartsDocument4 pagesThe Cerebrum Is Divided Into Two Major PartslisaNo ratings yet
- B2 Phrasal Verbs PV010: WWW - English-Practice - atDocument2 pagesB2 Phrasal Verbs PV010: WWW - English-Practice - atchoon lee minNo ratings yet
- Słowotwórstwo - Tworzenie Rzeczowników: Prefixes - Przedrostki Suffixes - PrzyrostkiDocument3 pagesSłowotwórstwo - Tworzenie Rzeczowników: Prefixes - Przedrostki Suffixes - PrzyrostkiAgata KNo ratings yet
- Lbs 400 Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesLbs 400 Lesson Planapi-281124194No ratings yet
- Assessment's AssessmentDocument4 pagesAssessment's Assessmentkitai123No ratings yet
- The Explanation Text: Subject: English Class: Xi Ipa 3 Day/Date: Wednesay, April 8thDocument11 pagesThe Explanation Text: Subject: English Class: Xi Ipa 3 Day/Date: Wednesay, April 8thoyo keunNo ratings yet
- 18 Safia AkhtarDocument13 pages18 Safia AkhtarNimra Rafique100% (1)
- Sociology Lecture 1Document26 pagesSociology Lecture 1Jamielee PacumioNo ratings yet
- Module - 3 Written CommunicationDocument21 pagesModule - 3 Written CommunicationHarsha MathadNo ratings yet
- Mike's Life: Activity TypeDocument3 pagesMike's Life: Activity TypeКсения СкрыльNo ratings yet
- المدرسة الجزائرية - رهانات و تحدياتDocument17 pagesالمدرسة الجزائرية - رهانات و تحدياتsaadNo ratings yet
- Indian Evidence Act in MarathiDocument92 pagesIndian Evidence Act in MarathiLokpal MahajanNo ratings yet
- Amazing Adjectives LessonDocument3 pagesAmazing Adjectives LessonJosé Alfonso Pérez CristianiNo ratings yet
- Onject Oriented ProgrammingDocument16 pagesOnject Oriented ProgrammingDeepak MalusareNo ratings yet
- Adding-Ed-Powerpoint Ver 2Document20 pagesAdding-Ed-Powerpoint Ver 2eriko.sakurabaNo ratings yet
- Adverbial Clauses BüyükDocument24 pagesAdverbial Clauses BüyükşerifeNo ratings yet
- Using The Dictionary Guide Words: (Noun) (Noun)Document1 pageUsing The Dictionary Guide Words: (Noun) (Noun)Louise YongcoNo ratings yet
- Topic: Civilian Letter : Parts of A Civilian Letter Types of Civilian LettersDocument36 pagesTopic: Civilian Letter : Parts of A Civilian Letter Types of Civilian LettersJOLLYBEI JEAN C SEROT100% (2)
- Present Perfect Simple Vs Present Perfect ContinuousDocument14 pagesPresent Perfect Simple Vs Present Perfect ContinuousnubiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Part 3 & Part 4: Formal Emails: I. Sample QuestionsDocument10 pagesLesson 9 - Part 3 & Part 4: Formal Emails: I. Sample QuestionsPhương Thanh VũNo ratings yet
- American Modernist PoetryDocument36 pagesAmerican Modernist Poetrysnezhko100% (2)
- Wipro WILP Placement Papers With Answers Set 1Document87 pagesWipro WILP Placement Papers With Answers Set 1Arjun SinghNo ratings yet
- Ngữ pháp thực hành 1 - Bài tậpDocument33 pagesNgữ pháp thực hành 1 - Bài tậpUyen LuuNo ratings yet
- 프로그램 CEESOK 2023 BudapestDocument4 pages프로그램 CEESOK 2023 Budapest이해성No ratings yet
- 8 Book ReviewsDocument16 pages8 Book Reviewsapi-257580746No ratings yet
- Listening Advantage 1 5Document4 pagesListening Advantage 1 5Tâm anh TrầnNo ratings yet
- Airport Check in Lesson Plan Final 0 PDFDocument2 pagesAirport Check in Lesson Plan Final 0 PDFSiti KusumadewiNo ratings yet