Professional Documents
Culture Documents
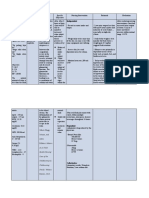
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term Goal
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term Goal
Uploaded by
Ace FabrigasCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 818507-M ELITE Service and Parts ManualDocument374 pages818507-M ELITE Service and Parts Manualotrupon melli100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument11 pagesNursing Diagnosis Diabetic Ketoacidosismonisha50% (4)
- NCP 3rd YearDocument6 pagesNCP 3rd YearTotoro AblogNo ratings yet
- NCP AgeDocument1 pageNCP AgecaressmeNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENTDocument3 pagesASSESSMENTMariane Joy ReolalasNo ratings yet
- NCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- 1ST NCPDocument2 pages1ST NCPGerrico TrumataNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Ni KevinDocument5 pagesPneumonia Ni Kevinjacobprince0016No ratings yet
- Excess Fluid Volume Related To Compromised Renal Regulatory Mechanisms As Evidenced by Glomerular Filtration RateDocument4 pagesExcess Fluid Volume Related To Compromised Renal Regulatory Mechanisms As Evidenced by Glomerular Filtration RateSHININo ratings yet
- NCP DHFDocument8 pagesNCP DHFChareigna Ramac MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Fvd2Document2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Fvd2ghellersNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium ChlorideDocument4 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium ChloridehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Date Assessed: December 11, 2017 Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Objective Nursing Intervention Scientific Explanation EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Date Assessed: December 11, 2017 Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Objective Nursing Intervention Scientific Explanation EvaluationCelyn Nicole Fernandez RollanNo ratings yet
- NCP UTI (Artillo)Document3 pagesNCP UTI (Artillo)Al TheóNo ratings yet
- NCP SGH DianaDocument2 pagesNCP SGH Dianadaniloabautista44No ratings yet
- NCP of Fever and HypertensionDocument2 pagesNCP of Fever and HypertensionDayan CabrigaNo ratings yet
- SAJAA (V27) p126-130 2691 FCA SupplementDocument5 pagesSAJAA (V27) p126-130 2691 FCA SupplementVivek PatangeNo ratings yet
- Data Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesData Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationmarielfmerlanNo ratings yet
- DM ncp2Document1 pageDM ncp2Mark PabalanNo ratings yet
- CC2 - Electrolytes and Inorganic IonsDocument4 pagesCC2 - Electrolytes and Inorganic Ionsjohnjoseph.ermitanoNo ratings yet
- Marcos Er NCPDocument1 pageMarcos Er NCPAssasination ClassroomNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPDocument5 pagesAcute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPMyrvic Ortiz La OrdenNo ratings yet
- Activity On Pituitary Disorders and Diabetes MellitusDocument8 pagesActivity On Pituitary Disorders and Diabetes MellitusSherlyn Miranda GarcesNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic ExamDocument2 pagesDiagnostic ExamGLYDEL CORDERONo ratings yet
- Cu 7Document6 pagesCu 7VALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- HAES-steril 6 %-Solution For InfusionDocument2 pagesHAES-steril 6 %-Solution For InfusionASDASDDD2No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Nov 13 2023Document4 pagesAdobe Scan Nov 13 2023api-741551545No ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Management of Paediatric Neurosurgical Patients at Risk of Diabetes Insipidus Di Syndrome of Inappropriate Anti Diuretic Hormone Siadh and Cerebral Salt Wasting CSW Apr 23Document18 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Management of Paediatric Neurosurgical Patients at Risk of Diabetes Insipidus Di Syndrome of Inappropriate Anti Diuretic Hormone Siadh and Cerebral Salt Wasting CSW Apr 23Caity YoungNo ratings yet
- Nabic HyponatremiaDocument2 pagesNabic HyponatremiaAin RahmaniaNo ratings yet
- HYPO and HYPERNATREMIA IN NEONATESDocument10 pagesHYPO and HYPERNATREMIA IN NEONATESraghava mbbsNo ratings yet
- NCP For DengueDocument6 pagesNCP For DengueSoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- DS PNSSDocument2 pagesDS PNSSCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationEverly Escobar-SastrilloNo ratings yet
- NCP SGHDocument2 pagesNCP SGHdaniloabautista44No ratings yet
- Hyper Vole MiaDocument7 pagesHyper Vole MiaMICHELLE BIANCA PATRICE CRUZNo ratings yet
- Caro NCPDocument17 pagesCaro NCPAbegail PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Department: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Department: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Interventions Rationale EvaluationNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP ApalisokDocument3 pagesNCP ApalisokApalisok GerardNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationer balotNo ratings yet
- NCP For HYPERTHERMIADocument3 pagesNCP For HYPERTHERMIAGil Ganiban0% (1)
- NCP JagDocument10 pagesNCP JagArvinjohn GacutanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPSteffi MurielNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia Review. Clinician's Brief: January 2010Document6 pagesHyponatremia Review. Clinician's Brief: January 2010david alonsoNo ratings yet
- Ngo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPDocument7 pagesNgo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPAMIEL SIMON NGONo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentGina PrancelisoNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis For FNCPDocument6 pagesCase Analysis For FNCPOfficially RandomNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementatio N Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Indipendent Short TermDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementatio N Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Indipendent Short TermKenneth PoncialNo ratings yet
- Keterolac Digoxin ClonidineDocument2 pagesKeterolac Digoxin ClonidineDays AniarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationPam RomeroNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument19 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FeverChristian James MataNo ratings yet
- CDK DMDocument3 pagesCDK DMK-Ann EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- PBL Compilation 2ndDocument21 pagesPBL Compilation 2ndMichael GemenianoNo ratings yet
- NCP For HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP For HyperthermiaNikael Patun-ogNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac Output NCPMae Denn LabordoNo ratings yet
- Nurses Pocket Guide by Doenges, Moorhouse, Murr 11 Edition Pg. 327-330 Pediatric Nursing by Potts and Mandleco ThomsonDocument3 pagesNurses Pocket Guide by Doenges, Moorhouse, Murr 11 Edition Pg. 327-330 Pediatric Nursing by Potts and Mandleco ThomsonMikaela Angeles NazarNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Decreased CO 1 PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For Decreased CO 1 PDFdubsNo ratings yet
- 03 - Special Clinical SituationsDocument32 pages03 - Special Clinical SituationsClaudia KosztelnikNo ratings yet
- NCP-hepatitis-MATA (Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume)Document7 pagesNCP-hepatitis-MATA (Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume)Nicole Keesha MataNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Agn - NCPDocument3 pagesAgn - NCPRap De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Volunteer ConsentDocument1 pageVolunteer ConsentAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- NCM 118acase Analysis IV B2Document26 pagesNCM 118acase Analysis IV B2Ace FabrigasNo ratings yet
- FDAR Eclarinal 4 B5Document4 pagesFDAR Eclarinal 4 B5Ace FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Tetanus and MeningicoccalDocument9 pagesTetanus and MeningicoccalAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Inp LasDocument3 pagesInp LasAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Epi ReportDocument5 pagesEpi ReportAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Onco, Endocrine, Gastrointestinal, Hepatobiliary, Immunologic DisordersDocument2 pagesOnco, Endocrine, Gastrointestinal, Hepatobiliary, Immunologic DisordersAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis & DiptheriaDocument20 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis & DiptheriaAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Diseases Causative Agent Signs and Symptoms (3) Mode of Transmission Incubation Period Nursing Intervention With Rationale (2) Preventive MeasuresDocument5 pagesDiseases Causative Agent Signs and Symptoms (3) Mode of Transmission Incubation Period Nursing Intervention With Rationale (2) Preventive MeasuresAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Table 2. Nurses' Preparedness For Disaster N % Organizations Considered Most Involved in Disastrous SituationsDocument6 pagesTable 2. Nurses' Preparedness For Disaster N % Organizations Considered Most Involved in Disastrous SituationsAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
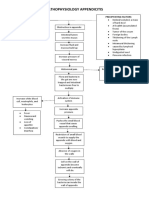
- Pathophysiology Appendicitis: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Appendicitis: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study For Ob WardDocument7 pagesNCP and Drug Study For Ob WardAce Fabrigas100% (1)
- Endocrine: (Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus) : A1C TestDocument8 pagesEndocrine: (Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus) : A1C TestAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing.Document32 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing.Ace FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Risk Control: Proposed Control Measure Due Date/ StatusDocument2 pagesRisk Control: Proposed Control Measure Due Date/ StatusAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ParacetamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study ParacetamolAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- By Dr. B. Williams, Media SpecialistDocument27 pagesBy Dr. B. Williams, Media SpecialistAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Task 1. Active Learning Template: Assessment Teamwork and CollaborationDocument2 pagesTask 1. Active Learning Template: Assessment Teamwork and CollaborationAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (Hiv) : Republic of The Philippines Tarlac State UniversityDocument13 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (Hiv) : Republic of The Philippines Tarlac State UniversityAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Basic Theories As Frameworks in EthicsDocument28 pagesBasic Theories As Frameworks in EthicsAce Fabrigas100% (1)
- NCM 117 Module 1 - Nilo, KlarenzDocument5 pagesNCM 117 Module 1 - Nilo, KlarenzAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Template ACMP Standard Change Impact AnalysisDocument5 pagesTemplate ACMP Standard Change Impact Analysismnabil77No ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet Presentation DENTALDocument10 pagesSafety Data Sheet Presentation DENTALkhuloodNo ratings yet
- ROBINSON Et Al - 2017 - Relashionship Between Poor Quality of Life and Hasten DeathDocument7 pagesROBINSON Et Al - 2017 - Relashionship Between Poor Quality of Life and Hasten DeathLuísa MartoNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev Reviewer MidtermDocument10 pagesEcon Dev Reviewer MidtermjonNo ratings yet
- New Therapies in Heart Failure Management: Nagendra S ChouhanDocument87 pagesNew Therapies in Heart Failure Management: Nagendra S ChouhanNagendra ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Siddha Therapeutic Index - 18-Article Text-133-1-10-20210308Document7 pagesSiddha Therapeutic Index - 18-Article Text-133-1-10-20210308Dr.kali.vijay kumkarNo ratings yet
- Nurs FPX 4010 Assessment 1 Collaboration and Leadership Reflection VideoDocument5 pagesNurs FPX 4010 Assessment 1 Collaboration and Leadership Reflection Videofarwaamjad771No ratings yet
- Reading-Comprehension-Exercises Kamila CruzDocument2 pagesReading-Comprehension-Exercises Kamila CruzRodrigo CruzNo ratings yet
- Classroom Instructional Delivery Alignment Map For JHS: (Based On AMT/RBT Classification)Document4 pagesClassroom Instructional Delivery Alignment Map For JHS: (Based On AMT/RBT Classification)Queenie GamboaNo ratings yet
- Pylorus Preserving PancreaticoduodenectomyDocument22 pagesPylorus Preserving PancreaticoduodenectomypaingmyintNo ratings yet
- Tugas SL Using A Nebulizer Kel3 - Miranda Putri Dan Muthianisa RamadhaniDocument3 pagesTugas SL Using A Nebulizer Kel3 - Miranda Putri Dan Muthianisa RamadhaniMiranda Putri 2111112825No ratings yet
- Educ 223 M2Document7 pagesEduc 223 M2Celon Jr. GultimoNo ratings yet
- Trauma and EndoDocument49 pagesTrauma and EndoKekelwa MutumwenuNo ratings yet
- Rothgerber Hank 2015. Can You Have Your Meat and Eat It Too Conscientious Omnivores Vegetarians and ..Document8 pagesRothgerber Hank 2015. Can You Have Your Meat and Eat It Too Conscientious Omnivores Vegetarians and ..Camille ManuelNo ratings yet
- Health 3Document11 pagesHealth 3Ha LinhNo ratings yet
- Progress Testing For Medical Students at The University of Auckland R.PDF - 6065Document6 pagesProgress Testing For Medical Students at The University of Auckland R.PDF - 6065Data AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Ielts Speaking Question 2Document15 pagesIelts Speaking Question 2Dunca Ana-MariaNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy For ElderlyDocument14 pagesDrugstudy For ElderlyJenniferP.BarrosoNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Substance Abuse TreatmentDocument8 pagesLiterature Review Substance Abuse Treatmentafdtorpqk100% (1)
- Assessment of Learning 2 Module 2Document15 pagesAssessment of Learning 2 Module 2jen arcelle moscaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - E-Waste - Grade 12Document3 pagesLesson Plan - E-Waste - Grade 12api-279605653No ratings yet
- Bibliografija Gestalt Resource and ReferencesDocument196 pagesBibliografija Gestalt Resource and ReferencesDusanka MilosavljevicNo ratings yet
- Endotracheal Tube IntubationDocument5 pagesEndotracheal Tube IntubationKim Kristine D. GuillenNo ratings yet
- Study of Dental Plaque in Orthodontic PatientsDocument6 pagesStudy of Dental Plaque in Orthodontic PatientsYeimyHernándezNo ratings yet
- Final of Final Harari HSTP-II Document For PrintDocument161 pagesFinal of Final Harari HSTP-II Document For PrintMohammed MuhidinNo ratings yet
- RRL Mental Health Adjustment and Perceived Academic Performance of Senior Highschool StudentsDocument19 pagesRRL Mental Health Adjustment and Perceived Academic Performance of Senior Highschool StudentsNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Project Key Project Campaign Name Organiza Tion Descripti OnDocument450 pagesProject Key Project Campaign Name Organiza Tion Descripti OnPriskilla Celine KurniajayaNo ratings yet
- Blue Modern Technology Business PresentationDocument1 pageBlue Modern Technology Business PresentationMahreen MalikNo ratings yet
- EQB74 Eng - Legal Metrology and International TradeDocument29 pagesEQB74 Eng - Legal Metrology and International TradejuanNo ratings yet
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term Goal
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term Goal
Uploaded by
Ace FabrigasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term Goal
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term Goal
Uploaded by
Ace FabrigasCopyright:
Available Formats
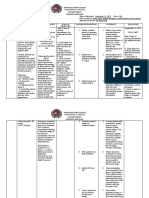
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
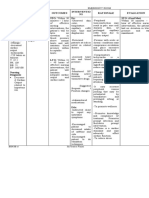
Subjective Data: Risk for electrolyte Short Term Goal: -Establish rapport -To gain patients Short Term
No verbalization imbalance (excess After 4 hours of trust Goal:
from the patient fluid volume) nursing intervention Goal not met the
related to the the patient will -Monitor Na+ (Sodium ion) level, -In presence of a patient has
Objective Data: compromised increase in output to weight and notify health care syndrome of expired
Temperature 39.4 regulatory 30ml/hr. provider in case of significant inappropriate
mechanism with an findings. ADH secretion Long Term
Heart rate 91 bpm increase in Anti- Long Term Goal: (SIADH), the Goal:
diuretic hormone After 8 hours of Patient has Goal not met the
Respiratory rate (ADH) as nursing intervention inappropriate patient has
connected to evidenced by the patient’s urine urinary expired
mechanical decrease in urine specific gravity will concentration
ventilator specific gravity be at 1.010-1.030 causes excessive
water retention.
Blood pressure If the Na+ level
130/80 mmHg reaches below
118 mEq/L there
02 saturation 97% may be seizure
activity.
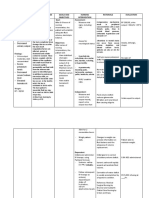
-Fluid intake may be restricted to
500ml-1000ml per 24 hrs. -Fluid restriction
helps to achieve
homeostasis.
-Free use of Na+(Sodium
ion) may be advised. -It normalizes
Na+ levels.
-Elevate the head of the bed to 10-
20 degrees, in case of
hypervolemia is present. -It promotes
venous return and
reduces ADH
release.
-The regular specimen should be
sent for evaluating electrolytes
levels especially Na+. -To check the
improvement in
Na+ level due to
- Administer electrolyte-binding treatment.
medications
-Medications,
such as
Kayexalate for
hyperkalemia, as
- Administer IV fluids prescribed.
-To promote renal
excretion of
excess electrolyte
levels, as
- Educate the patient and family prescribed.
members about dietary choices
corresponding to the specific
electrolyte imbalance. - Provide
information about
monitoring for
potential
electrolyte
imbalances at
home resulting
from their
medications.
You might also like
- 818507-M ELITE Service and Parts ManualDocument374 pages818507-M ELITE Service and Parts Manualotrupon melli100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument11 pagesNursing Diagnosis Diabetic Ketoacidosismonisha50% (4)
- NCP 3rd YearDocument6 pagesNCP 3rd YearTotoro AblogNo ratings yet
- NCP AgeDocument1 pageNCP AgecaressmeNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENTDocument3 pagesASSESSMENTMariane Joy ReolalasNo ratings yet
- NCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- 1ST NCPDocument2 pages1ST NCPGerrico TrumataNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Ni KevinDocument5 pagesPneumonia Ni Kevinjacobprince0016No ratings yet
- Excess Fluid Volume Related To Compromised Renal Regulatory Mechanisms As Evidenced by Glomerular Filtration RateDocument4 pagesExcess Fluid Volume Related To Compromised Renal Regulatory Mechanisms As Evidenced by Glomerular Filtration RateSHININo ratings yet
- NCP DHFDocument8 pagesNCP DHFChareigna Ramac MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Fvd2Document2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Fvd2ghellersNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium ChlorideDocument4 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium ChloridehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Date Assessed: December 11, 2017 Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Objective Nursing Intervention Scientific Explanation EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Date Assessed: December 11, 2017 Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Objective Nursing Intervention Scientific Explanation EvaluationCelyn Nicole Fernandez RollanNo ratings yet
- NCP UTI (Artillo)Document3 pagesNCP UTI (Artillo)Al TheóNo ratings yet
- NCP SGH DianaDocument2 pagesNCP SGH Dianadaniloabautista44No ratings yet
- NCP of Fever and HypertensionDocument2 pagesNCP of Fever and HypertensionDayan CabrigaNo ratings yet
- SAJAA (V27) p126-130 2691 FCA SupplementDocument5 pagesSAJAA (V27) p126-130 2691 FCA SupplementVivek PatangeNo ratings yet
- Data Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesData Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationmarielfmerlanNo ratings yet
- DM ncp2Document1 pageDM ncp2Mark PabalanNo ratings yet
- CC2 - Electrolytes and Inorganic IonsDocument4 pagesCC2 - Electrolytes and Inorganic Ionsjohnjoseph.ermitanoNo ratings yet
- Marcos Er NCPDocument1 pageMarcos Er NCPAssasination ClassroomNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPDocument5 pagesAcute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPMyrvic Ortiz La OrdenNo ratings yet
- Activity On Pituitary Disorders and Diabetes MellitusDocument8 pagesActivity On Pituitary Disorders and Diabetes MellitusSherlyn Miranda GarcesNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic ExamDocument2 pagesDiagnostic ExamGLYDEL CORDERONo ratings yet
- Cu 7Document6 pagesCu 7VALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- HAES-steril 6 %-Solution For InfusionDocument2 pagesHAES-steril 6 %-Solution For InfusionASDASDDD2No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Nov 13 2023Document4 pagesAdobe Scan Nov 13 2023api-741551545No ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Management of Paediatric Neurosurgical Patients at Risk of Diabetes Insipidus Di Syndrome of Inappropriate Anti Diuretic Hormone Siadh and Cerebral Salt Wasting CSW Apr 23Document18 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Management of Paediatric Neurosurgical Patients at Risk of Diabetes Insipidus Di Syndrome of Inappropriate Anti Diuretic Hormone Siadh and Cerebral Salt Wasting CSW Apr 23Caity YoungNo ratings yet
- Nabic HyponatremiaDocument2 pagesNabic HyponatremiaAin RahmaniaNo ratings yet
- HYPO and HYPERNATREMIA IN NEONATESDocument10 pagesHYPO and HYPERNATREMIA IN NEONATESraghava mbbsNo ratings yet
- NCP For DengueDocument6 pagesNCP For DengueSoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- DS PNSSDocument2 pagesDS PNSSCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationEverly Escobar-SastrilloNo ratings yet
- NCP SGHDocument2 pagesNCP SGHdaniloabautista44No ratings yet
- Hyper Vole MiaDocument7 pagesHyper Vole MiaMICHELLE BIANCA PATRICE CRUZNo ratings yet
- Caro NCPDocument17 pagesCaro NCPAbegail PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Department: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Department: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Interventions Rationale EvaluationNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP ApalisokDocument3 pagesNCP ApalisokApalisok GerardNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationer balotNo ratings yet
- NCP For HYPERTHERMIADocument3 pagesNCP For HYPERTHERMIAGil Ganiban0% (1)
- NCP JagDocument10 pagesNCP JagArvinjohn GacutanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPSteffi MurielNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia Review. Clinician's Brief: January 2010Document6 pagesHyponatremia Review. Clinician's Brief: January 2010david alonsoNo ratings yet
- Ngo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPDocument7 pagesNgo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPAMIEL SIMON NGONo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentGina PrancelisoNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis For FNCPDocument6 pagesCase Analysis For FNCPOfficially RandomNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementatio N Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Indipendent Short TermDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementatio N Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Indipendent Short TermKenneth PoncialNo ratings yet
- Keterolac Digoxin ClonidineDocument2 pagesKeterolac Digoxin ClonidineDays AniarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationPam RomeroNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument19 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FeverChristian James MataNo ratings yet
- CDK DMDocument3 pagesCDK DMK-Ann EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- PBL Compilation 2ndDocument21 pagesPBL Compilation 2ndMichael GemenianoNo ratings yet
- NCP For HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP For HyperthermiaNikael Patun-ogNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac Output NCPMae Denn LabordoNo ratings yet
- Nurses Pocket Guide by Doenges, Moorhouse, Murr 11 Edition Pg. 327-330 Pediatric Nursing by Potts and Mandleco ThomsonDocument3 pagesNurses Pocket Guide by Doenges, Moorhouse, Murr 11 Edition Pg. 327-330 Pediatric Nursing by Potts and Mandleco ThomsonMikaela Angeles NazarNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Decreased CO 1 PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For Decreased CO 1 PDFdubsNo ratings yet
- 03 - Special Clinical SituationsDocument32 pages03 - Special Clinical SituationsClaudia KosztelnikNo ratings yet
- NCP-hepatitis-MATA (Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume)Document7 pagesNCP-hepatitis-MATA (Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume)Nicole Keesha MataNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Agn - NCPDocument3 pagesAgn - NCPRap De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Volunteer ConsentDocument1 pageVolunteer ConsentAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- NCM 118acase Analysis IV B2Document26 pagesNCM 118acase Analysis IV B2Ace FabrigasNo ratings yet
- FDAR Eclarinal 4 B5Document4 pagesFDAR Eclarinal 4 B5Ace FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Tetanus and MeningicoccalDocument9 pagesTetanus and MeningicoccalAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Inp LasDocument3 pagesInp LasAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Epi ReportDocument5 pagesEpi ReportAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Onco, Endocrine, Gastrointestinal, Hepatobiliary, Immunologic DisordersDocument2 pagesOnco, Endocrine, Gastrointestinal, Hepatobiliary, Immunologic DisordersAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis & DiptheriaDocument20 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis & DiptheriaAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Diseases Causative Agent Signs and Symptoms (3) Mode of Transmission Incubation Period Nursing Intervention With Rationale (2) Preventive MeasuresDocument5 pagesDiseases Causative Agent Signs and Symptoms (3) Mode of Transmission Incubation Period Nursing Intervention With Rationale (2) Preventive MeasuresAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Table 2. Nurses' Preparedness For Disaster N % Organizations Considered Most Involved in Disastrous SituationsDocument6 pagesTable 2. Nurses' Preparedness For Disaster N % Organizations Considered Most Involved in Disastrous SituationsAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Appendicitis: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Appendicitis: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study For Ob WardDocument7 pagesNCP and Drug Study For Ob WardAce Fabrigas100% (1)
- Endocrine: (Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus) : A1C TestDocument8 pagesEndocrine: (Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus) : A1C TestAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing.Document32 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing.Ace FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Risk Control: Proposed Control Measure Due Date/ StatusDocument2 pagesRisk Control: Proposed Control Measure Due Date/ StatusAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ParacetamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study ParacetamolAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- By Dr. B. Williams, Media SpecialistDocument27 pagesBy Dr. B. Williams, Media SpecialistAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Task 1. Active Learning Template: Assessment Teamwork and CollaborationDocument2 pagesTask 1. Active Learning Template: Assessment Teamwork and CollaborationAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (Hiv) : Republic of The Philippines Tarlac State UniversityDocument13 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (Hiv) : Republic of The Philippines Tarlac State UniversityAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Basic Theories As Frameworks in EthicsDocument28 pagesBasic Theories As Frameworks in EthicsAce Fabrigas100% (1)
- NCM 117 Module 1 - Nilo, KlarenzDocument5 pagesNCM 117 Module 1 - Nilo, KlarenzAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Template ACMP Standard Change Impact AnalysisDocument5 pagesTemplate ACMP Standard Change Impact Analysismnabil77No ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet Presentation DENTALDocument10 pagesSafety Data Sheet Presentation DENTALkhuloodNo ratings yet
- ROBINSON Et Al - 2017 - Relashionship Between Poor Quality of Life and Hasten DeathDocument7 pagesROBINSON Et Al - 2017 - Relashionship Between Poor Quality of Life and Hasten DeathLuísa MartoNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev Reviewer MidtermDocument10 pagesEcon Dev Reviewer MidtermjonNo ratings yet
- New Therapies in Heart Failure Management: Nagendra S ChouhanDocument87 pagesNew Therapies in Heart Failure Management: Nagendra S ChouhanNagendra ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Siddha Therapeutic Index - 18-Article Text-133-1-10-20210308Document7 pagesSiddha Therapeutic Index - 18-Article Text-133-1-10-20210308Dr.kali.vijay kumkarNo ratings yet
- Nurs FPX 4010 Assessment 1 Collaboration and Leadership Reflection VideoDocument5 pagesNurs FPX 4010 Assessment 1 Collaboration and Leadership Reflection Videofarwaamjad771No ratings yet
- Reading-Comprehension-Exercises Kamila CruzDocument2 pagesReading-Comprehension-Exercises Kamila CruzRodrigo CruzNo ratings yet
- Classroom Instructional Delivery Alignment Map For JHS: (Based On AMT/RBT Classification)Document4 pagesClassroom Instructional Delivery Alignment Map For JHS: (Based On AMT/RBT Classification)Queenie GamboaNo ratings yet
- Pylorus Preserving PancreaticoduodenectomyDocument22 pagesPylorus Preserving PancreaticoduodenectomypaingmyintNo ratings yet
- Tugas SL Using A Nebulizer Kel3 - Miranda Putri Dan Muthianisa RamadhaniDocument3 pagesTugas SL Using A Nebulizer Kel3 - Miranda Putri Dan Muthianisa RamadhaniMiranda Putri 2111112825No ratings yet
- Educ 223 M2Document7 pagesEduc 223 M2Celon Jr. GultimoNo ratings yet
- Trauma and EndoDocument49 pagesTrauma and EndoKekelwa MutumwenuNo ratings yet
- Rothgerber Hank 2015. Can You Have Your Meat and Eat It Too Conscientious Omnivores Vegetarians and ..Document8 pagesRothgerber Hank 2015. Can You Have Your Meat and Eat It Too Conscientious Omnivores Vegetarians and ..Camille ManuelNo ratings yet
- Health 3Document11 pagesHealth 3Ha LinhNo ratings yet
- Progress Testing For Medical Students at The University of Auckland R.PDF - 6065Document6 pagesProgress Testing For Medical Students at The University of Auckland R.PDF - 6065Data AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Ielts Speaking Question 2Document15 pagesIelts Speaking Question 2Dunca Ana-MariaNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy For ElderlyDocument14 pagesDrugstudy For ElderlyJenniferP.BarrosoNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Substance Abuse TreatmentDocument8 pagesLiterature Review Substance Abuse Treatmentafdtorpqk100% (1)
- Assessment of Learning 2 Module 2Document15 pagesAssessment of Learning 2 Module 2jen arcelle moscaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - E-Waste - Grade 12Document3 pagesLesson Plan - E-Waste - Grade 12api-279605653No ratings yet
- Bibliografija Gestalt Resource and ReferencesDocument196 pagesBibliografija Gestalt Resource and ReferencesDusanka MilosavljevicNo ratings yet
- Endotracheal Tube IntubationDocument5 pagesEndotracheal Tube IntubationKim Kristine D. GuillenNo ratings yet
- Study of Dental Plaque in Orthodontic PatientsDocument6 pagesStudy of Dental Plaque in Orthodontic PatientsYeimyHernándezNo ratings yet
- Final of Final Harari HSTP-II Document For PrintDocument161 pagesFinal of Final Harari HSTP-II Document For PrintMohammed MuhidinNo ratings yet
- RRL Mental Health Adjustment and Perceived Academic Performance of Senior Highschool StudentsDocument19 pagesRRL Mental Health Adjustment and Perceived Academic Performance of Senior Highschool StudentsNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Project Key Project Campaign Name Organiza Tion Descripti OnDocument450 pagesProject Key Project Campaign Name Organiza Tion Descripti OnPriskilla Celine KurniajayaNo ratings yet
- Blue Modern Technology Business PresentationDocument1 pageBlue Modern Technology Business PresentationMahreen MalikNo ratings yet
- EQB74 Eng - Legal Metrology and International TradeDocument29 pagesEQB74 Eng - Legal Metrology and International TradejuanNo ratings yet