Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SM PC 60-6
SM PC 60-6
Uploaded by
Fris Ainur100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
66 views440 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
66 views440 pagesSM PC 60-6
SM PC 60-6
Uploaded by
Fris AinurCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 440
SEBM02010607
SOW"
IMTAINIUZA\ Io
KOMATSU
PC60-6
PC6OL-6
PC90-1
MACHINE MODEL SERIAL No.
PC60-6 28001 and up
PC6OL-6 8001 and up
PCg90-1 1001 and up
© This shop manual may contain attachments and optional equipment that are not available
in your area. Please consult your local Komatsu distributor for those items you may
require Materials and specifications are subject to change without notice.
‘* PC6O, GOL and PC80 mount the 4D9SL-1 engine
For details of the engine, see the 95 series engine Shop Manual.
@
CONTENTS
10 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 00... 0000 ton
20 TESTING AND ADJUSTING ........... seiseweveun@4
30 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Si
40 MAINTENANCE STANDARD ........c00. ssecessseess 404
020106
020106
The affected pages are indicated by the use of the
following marks. t is requested that necessary actions Indication Action required
be taken to tase pages according to the table below.
ial 7 Page to be newty added
age tobe reolaced
‘Page to be doloted
Pages having no marks are those previously revised!
‘or made additions,
LIST OF REVISED PAGES
Wen oe Mipset|wen toe Rie |wemn roe Seagh|ven tom Rinse wer] Ravan
ware page MeNBCC Tomar rage ROMEO] wae Page “ex Pom Revber]min rege Sevton]wam rece Savhah|wan rome Rava" rae Memerl aan page Rewer
oor gg 1021 © 10-53 | 1082 ® 2010 @
02 2 1022 @ 10-54 1088 ® 20-11 ®
© 021 F 10-23 10-55 1087 © 2042 OD
© 0022 oO 1024 ® 10-56 1088 20-13 @
00.3 1025 @ 1057 @ 1088 20-131 @
00-4 10-251 6 10571 @ 1090 @ 2014 @
00.8 10.252 © 10572 © | 1091 ® 2015
00-6 10.28 @ 10873 6 | 1092 20-15 @
00.7 10.27 @ 10574 @ 1093 © | © 217 @
00-8 | 1028 @ 1058 @ | 1094 20-18 O
00-9 10-29 ® 10-59 | 1095 @ 20-19 @
00.10 | 10.291 © 10-60 1098 ® 2020
00-12 10-292 © 10-61 1097 © 2021 ®
© 0013 @ | 1030 1081-1 @ | 1098 20.211
00-14 | toa 10612 6 1099 20-22 ®
| 10-32 10813 @ 10.100 © 20-23 ®
tor @ | 10.33 tose @ | 0101 © 20-24 @
10-2 | 10.38 10-62 @) 20-25 @
03 o 10.35 1062 @ 201 © 2028 @
04 10-36 10-64 © 22 © 2027 @
05 «© | 10.37 jos © 8 3 OD 20.28 ®
106 =O 10871 © 1066 © «© 24 20:29 @
107 OD 10.372 © 1087 @ e205 Oo 20:30 @
108 6 O 10:38 10-68 206 20:31 @
09 O 10-39 1070 @ 0 27 20-32 @
to10 © 10-40 1071 208 © 20:33 ®
O11 1041 ® 073 © | 29 ® 20-38 ®
1012 10.42 1074 «© 2091 © 20:35
tors 3 | toes 1% | 2082 @ | os @
1014 @ 10-44. ° 107% @ 2033 © 20:37 ®
1015 OD 10451 © | ¢ 1077 @ 2094 @ 20.38 @
1017 © | 10452 © | @ 107 @ © 2095 @ 20:39 ®
ore © 1048 som @ |e wes 9] we 6
wis @ | 1047 © 108 2097 ® 20-41 ®
ro-191 @ | 10.48 2 1081 G @ 2038 & 20-42 ®
so1s-2 © | 10-49 108-1 @ 209.8 © 20-44 @
> 1018.3 @ 10.50 1081-2 @ , 208-10 © 2045 ®
1019-4 © , 10-81 10-82 @ | © 20911 @ 20.46 @
1020 © | 1062 108 «| @ 20912 @ 20.47 ®
00-2-1
Mark Poye REVEION storm Page REVECT| trash Page Rewser| tart Page Parent Poge Rewcion
20-48 20.105 soe & 30.602 © 404
2049 @) 20198 3081 20603 € 40.5
2050 4) 20-107 309 2 30-804 46
2091 20.108 x10 30-50.5 407
2051 @ 20-109 3011 8 30-50.8 40-8
2053 @ 20.110 3012 > 30-50-7 408
2053.1 @ 20111 @ | 3043 | 508 @ | 40-10
20.54 20-112 7 2014 509 8 4019
20.55 | 20113 @ 3015 2 30-50.10 © 40-12
20.58 20114 @ , 316 @ 20.60.11 & a0.18
20.87 2015 @ | 3017 ® 40.15
20.68 20.116 & gaia g & 40-16
20.58 2017 @ | 3019 6 4017
208) 20-118 } 3020 ® ® | 4018
20.82 20.119 9 | 90-21 @ |e 4019 %
© 2063 7 20120 % | 3022 2 40191 &
2064 20121 @ | 9023 2 4020 6
2065 & 20122 2 | 3024 2 40-21
2066 4 20.123 4 3025 3 > 40.21-1 &
2067 4 20-124 4 30.28 > | « D 40.212 6
2068 20.128 30:27 3 | 4022 8
2070 4 | 20128 & 3028 | © 2 | 40-23
27 6g | (20827 @ 3028 >| 40231 ®
2072 20-128 3030 a 40232 @
© 20% 20429 a | 3091 2 1024 ©
20:75 20130 4 2032 © @ Z| 40.26
en) 20131 4 | 30321 @ | @ % | 40-261 §
©2077 o 20432 4 | 30322 © 30631 7 10.25.2
20-78 @ 20133 | 3032.3 & 3063.2 7 | 4025.3 #
2079 go134 6 | 30924 & 30633 y | 40.254 &
2080 «@ 20135 @ 30325 30034 7 | 40255 8
2081 @ 20136 9 | 30326 % 30-66 | 40-25-6
2082 20-137 «@ | 30927 % ges 2 | 4026 &
2083 a 20138 20328 © 3085 > | 4027
2084 20.139 4 20:32 3087 2 aoa) &
zoe? a | 2011 3038 7 3069 > 4028 8)
20.88 4) 20142 5038 > | @ 3070 > 40.29 ®
2089 aw 20183 2037 30-71 g 40-29-13
20:80 @ 20144 so38 6g | 3072 & 40.292
2081 20445 6 3039 2 | O73 dD 40293 7
282 & 20146 goao | 078 10.294
© 2092 2 20147 soar og | 9075 8 0-30 gh
2094 20148 3042 | 3076 40.31 @
2095 4 3043 2 3077 5 40.22
2098 @ | @ 301 304a 30-78 3 40330
2087 @ | © 302 @ 3045 30-739 3 40-34
2098 @ | 3030 2 2046 & 3080 > 40-35
20-100 g | 304 oD 3047 | 3081 8
20101 @ | 305g 3048 5
20-102 308 2 30493 | @ aor
20-103 3081 8 3050 40.2
20.108 4 307 30801 # 404
00-2-2
020106
Ay IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
Proper service and repair is extremely important for the safe operation of your machine.
‘The service and repair techniques recommended by Komatsu and described in this
manual are both effective and safe methods of operation. Some of these operations re-
quire the use of tools specially designed by Komatsu for the purpose
To prevent injury to workers, the symbols QM and “A are used to mark safety pre-
cautions in this manual, The cautions accompanying these symbols should always be
followed carefully. if any dangerous situstion arises or may possibly arise, first consider
safety, and take the necessary actions to deal with the
ation.
A SAFETY
GENERAL PRECAUTIONS
Mistakes in operation ate extremely dangerous.
Read the Operation and Maintenance Manual
carefully BEFORE operating the machine.
1.Before carrying out any greasing or repairs,
read oll the precautions given on the
decals which are fixed to the machine.
2.When carrying out any operation, always
wear safety shoes and helmet Do not wear
loose work clothes, or clothes with buttons
missing
* Always wear safety glasses when hitting
parts with a hammer.
«Always wear safety glasses when
grinding parts with a grinder, etc
3.1 welding repairs are needed. always have a
trained, experienced welder carry out the
work When carrying out welding work,
always weer welding gloves, apran, glasses,
cap and other clothes suited for welding
work
4.When carrying out any operation with two
‘or more workers, alweys agree on the op-
erating procedure before starting. Always
inform your fellow workers before starting
‘any step of the operation. Before starting
work, hang UNDER REPAIR signs on the
controls in the operator's compartment.
5.Keep all tools in good condition and learn
the correct way to use them.
6 Decide a place in the repair workshop to
keap tools and removed parts Always keep
the tools and parts in their correct places,
Always keep the work area clean and make
sure that there 1s no ditt or oil on the floor
Smoke only in the areas provided for
smoking. Never smoke while working
PREPARATIONS FOR WORK
7. Before adding oil or making any repairs,
park the machine on hard, level ground, and
block the wheels or tracks to prevent the
machine from moving.
8.Before starting work. lower blade, ripper,
bucket or any other work equipment to the
Ground. If this is not possible, insert the
safety pin or use blocks to prevent the work,
equipment from falling. In advition, be sure
to lock all the control levers and hang
warning signs on them.
9.When disassembling or assembling. sup-
port the machine with blocks, jacks or
stands before starting work.
10. Remove all mud and oi! from the steps or
other places used to get on and off the
machine. Always use the handrails, ladders
or steps when geting on or off the
machine Never jump on or off the machine.
If it is impossible to use the handrails,
ladders or steps, use a stand to provide safe
footing
00-3
PRECAUTIONS DURING WORK
11 When removing the off filer eap, drain plug
ue hydrauhe pressure measuring plugs,
sen them slowly to prevent the oil trom
urting out
Setore discoaneeting oF removing compo:
nents of the oll, water or air circults, first
remove the pr jetely from the
ure comp
circu.
42 The water and oil in the circuits are hot
when the engine 1s sieaped, so be caretul
not to get burned
Wait for the oi! ond water to cool betore car
ying out
oneuits,
ry work on the oll C€ weter
starting work, remave the leads from
the battery Always ramove the lead trom
the negative (—) terminal firs
14 When ‘aising heavy components. use a
horst or crane
Check that the wire rope, chains and hooks
ae free from damage
Always use lifting equipment which has
ample capacity
fastal the lifting equipment at the correct
places. Use a hoist or crane and operate
slowly to prevent the component fram hit
ting any other part. Do net work with ai
part still raised by the hoist or crane
15 When removing covers which are under i=
ternal pressure or under pressure from a
spring, always eave two bolts in position on
opposite sides, Slowly release the pressure,
then slowly loosen the bolts to remove.
16 When removing components, be caratul not
to break or Gamage the wiring Damaged
wining may cause electrical fires.
17 When removing piping, stop the fuel or oil
from spilling out. If any fue! or ail dps cn to
the floor, wipe it up immediately, Fuel ar oil
fon the floor can cause you to slip, oF car
even start fires
18.As a general rule, da not use gasoline to
wash parts. In particular, use only the mai
rum of gasoline whon washing electrical
parts
00-4
18.Be sure to assemble all parts again in their
orginal places
Replace any damaged parts with new parts
© When installing hoses and wares, be
sure that they will not be damaged by
contact with other parts when the ma-
chine is being operated
20 When installing bigh pressure hoses. make
twisted, Damaged
tubes are dangerous, $0 be extremely cate:
ful when installing tubes for high pressure
Cicuits Also, check that connecting paris
are correctly installed
sure that they are
21 When assembling or i
Salling parts, always
use the specified tightening torques. When
Installing protective parts such as guards.
parts which vibrate violently or rotate at
high speed, be particularly caretul to check
thot they are installed correctly,
22. When aligning two holes, never insert your
fingers or hand Be careful not to get your
fingers caught in a hole.
23 When messuring hydraulic pressure, check
that the measuring taal 's correctly assem
bled before taking any measurements.
24 Take care when semoving oF installing the
tracks of track: type machines
When removing the track, the track sepa-
sajes suddenly, so never let anyone stand at
either end of the track.
FOREWORD
This shop manual has been prepared as an aid to improve the quality of repairs by giving the
serviceman an gccurate understanding of the product and by showing him the correct way to perform
repairs and make judgements. Make sure you understand the contents of this manual and use it to full
effect at every opportunity.
‘This shop manual mainly contains the necessary technical information for eperations performed in
a service workshop
For ease of undersianding, the menual is divided into chapters for each main group of
components, these chapters are further divided into the following sections
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
This section explains the structure and function of each component. It serves not only to give
an understanding of the structure, but also setves as reference material for troubleshooting,
TESTING AND ADJUSTING
This section explains checks to be made before end aft
adjustments to be made
‘Troubleshooting charts correlating “Problems” to “Causes
performing repairs, as well ay
¢ completion of the checks and repairs,
ar@ also nolucied in this section.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
This section explains the order to be followed when removing, installing, disassembling or
assembling each component, as weil as precautions to be taken for these operations.
MAINTENANCE STANDARD
This section gives the judgement standards whon inspecting disassembled parts.
NOTICE
The specifications coatained in this shop manual sre subject to change at any
time and without any advance notice. Contact your KOMATSU distributor for the
latest information.
00-5
HOW TO READ THE SHOP MANUAL
HOW TO READ THE SHOP MANUAL
VOLUMES:
Shop manuals are issued as a guide to carry:
ing out repairs. They are dividect as follows
Chassis volume: Issued for every machine
motiel
Engine volume: Issueu for aach engine series
| Each issued as
ane volume to
cover ail models
Etectrical volume |
Attachments volume : |
These various volumes are designed 10 avoid
Guplicating the seme information Therefore to
deal with all repairs fer any model, at is neces-
sary that chassis, engine, electrical and attach-
ment volumes are ready
DISTRIBUTION AND UPDATING
Any additions, amendments or other
changes will be sent to KOMATSU distributers.
Get the most up-to-date information before
you start any work
FILING METHOD.
1 See the page number on the bottom of the
page File the pages in correct orser
2. Following exemples shows how to read the
page number
Example + (Chassis volume):
— item number
and Furetion!
L__ Consecutive page number tue
each item
10. Structure
Example 2 (Engine volume)
12-410
- Unit number (1. Engine)
Item number {2 Testing and
Adjusting]
Group No. (4. Fue! system!
Consecutive page No. [Page
10 of Group 4)
3. Additional pages Additional pages are in-
aicated by a hyphen |-) and number after the
page number, File as in the example.
Example
teed 12-208
te ce 12-203-1
16-4. bAdded pages {7 5 3°593 9
10-5 12-204
00-6
REVISED EDITION MARK [260 1)
When @ menual is revised, an edition mark is
recorded on the bottom outside corner of the
pages
REVISIONS
Revised pages are shown at the LIST OF
REVISED PAGES on the between the title page
and SAFETY page.
symeos
So thet the shop manual can be of ample
orectical use, important places for safety and
quality ara marked with the following aymbols.
ier Remarks
Special salery precautions are
necessary when performing the
work
anf Safety
Extra special sefety precautions
ace necessary when performing
the work becouse its under
| Spacial weednical precautions or
{otter precautions for
proserving stanuaeds are
necessary when performing the
wou
“{ Weight af pacts or syst
Caution necessary when
Waight
selecting hoistna wire, ar when
working nostureis important
ete
* “- Cautio
=
hgnten- a
ng Uer. | attention tor the tghterung
More eo rgue during as sembly
ae
| coat
Places to be costed with
adhesives and lubricants ete
Places where oi, water oF fuel
Oi, water |must be added and the
| capacity.
ad Places where oil or water muse
(Brain [ibe drained, and cuaat ty 10 be
| drained
HOISTING INSTRUCTIONS
HOISTING INSTRUCTIONS
AA Heovy parts (25 kg or more) must be
lifted with 2 hoist etc. In the Disassembly
and Assembly section, every part weigh=
ing 25 kg or more is indicated clearly with
the symbol ~ yy
1. If @ part cannot be smoothly removed from
the machine by hoisting, the following
checks should be made
# Check for removal of all bolts fastening
the part to the relative parts.
+ Check for existence of another part
causing interference with the part to be
removed.
2. Wire ropes
1)Use adequete ropes depending on the
weight of parts to be hossted, referring to
the table below
Wire sopes
(Standard "2" or “S” twist ropes.
without galvanizing)
Rope diameter (mm) | Allowable load (tons)
14 22
16 28
18 36
20 a4
22.4 | 58
30 t 10.9
ao 180
50 28.0
60 \ 40.0
a
The allowable load value \s estimated to
be one-sixth or one-seventh of the
breaking strength of the rope used
2) Sling wire ropas from the middle portion
of the hook.
Slinging near the edge of the hook may
cause the rope to slip off the hook during
hoisting, and a serious accident can result
Hooks have maximum strength at the
middle portion,
3)Do not sling a heavy load with one rope
alone, but sling with two or more ropes
symmetrically wound on to the load
A. Binsing with one rope moy cause
turning of the load during hoisting,
untwisting of the rope, or slipping of
the rope from its original winding
position on the foad, which can result
ina dangerous accident
4)Do not sling a heavy load with ropes
forming a wide hanging engle from the
hook
When hoisting a load with two or more
ropes, the force subjected to each rope
will increase with the hanging angles. The
table below shows the vanation of
allowable load (kg) when hoisting is made
with two ropes, each of which is allowed
to sling up to 1000 kg vertically. at various
hanging angles.
When two ropes sling a load vertically, up
to 2000 kg of total weight can be
suspended. This waight becomes 1000 kg
when two ropes make a 120° hanging
angle. On the other hand, two ropes are
Subjected to an excessive force as large as
4000 kg if they sling @ 2000 kg load at «
lifting angle of 150°,
Lifting angie 5
STANDARD TIGHTENING TORQUE
STANDARD TIGHTENING TORQUE
1, STANDARD TIGHTENING TORQUE OF BOLTS AND NUTS
The following charts give the standard tightening torques of bolts and nuts. Exceptians are given in
sections of “Disassembly and Assembly”
Thread diameter width
‘of bolt actoss flat J
(am) (mm) Xs 5 a
kom |
6 10 135-015
8 13 32203
2 v7 67207
12 19 115-10
14 2 180%20
16 28523 |
iB 39 |
20 56:6
22 768
24 94.510
a a 138218 13204140
30 46 175-20 1720-190
33 50 22525 2210240
36 685 280-30 27504290
39 60 335435 3280 #:340
—
This torque table does not apply to the bolts with which nylon packings or other non
ferrous metal washers ate to be used, or whic recuire tghtening to othorwise spacified
torque.
* Nm [newton meter):
Nm & 0.1 kam
2. TIGHTENING TORQUE OF SPLIT FLANGE BOLTS
Use these tarques for split flanga bolts
Thread diameter Width Tightening torque
‘of bolt across flats - -
lin immi kgm Nm
ae
10 14 6.7407 eo 7+68
12 v7 1641 112=9.8
16 22 28562 279423
00-8
STANDARD TIGHTENING TORQUE
Seaing surtace
a
3. TIGHTENING TORQUE FOR NUTS OF FLARED
Use these torques for nut part of flared —
~ FS00E8
Thread diameter | Wwieth across tars | Tightening torque
of rut pare Dtrmetpere jes .
tnd ime) | tom twa
14 19 25605 2a 5249
” 18 24 522 492196
22 2 | ge2 7852196
2a 2 | 1as3 13732294
30 38 tars 17652294
33 4 2025 | 196.1249
35 46 2545 245.2249
az 85 g0%8 294249
COATING MATERIALS
Nomerctsture Komatsu code “Applications.
Used to appv cutber pace, rubber gaskals, and cork plugs
Used to voeiy resin fubber, metalic and
pon-metalle ports whens fest sword seal y reeded.
Agheswes Preventing bolts, nutsand plugs from loosening and leaking a)
Frodtes an aiid, slgctricay meuating
Spd tor atau surtaces
said coar plugs Ipire shaped bow shapedl are halen ana
mating portion of shalt
Used with gaskets an
packings to increase nealing effect
“Teal eater gbaketTorBiecombasTan ohabes
Used by sfelt on minting eurtacee on the Waal arve and anemic
cneee (Thyeknets after tgntening 0.07 — 9.08 mm
by sell 10 se ai grease fittings, ‘epeved scraw rings and tapered
ydeaule cucuite-o¢ tees than 80 shen in oarmater
Sealent goake'
Sinzon base type weed n combination with LG-1 ond LG-4.
“Ward master carag wae fan (C6, and caver
to.pe01 of
“Kniiiciion compound
(atest inelucing
moiynderum diculfcieh
Grease Gu ‘Tpaued te bean ngs shaing parts and ol seal Yor lubrication, ast
iin tease) levennion and faciitavonot assembling work
‘ing ang to
ae ‘Applic to beutings and taper shatis to faci tate pre
prevent sticking, Burning or ‘usting
Veseline [scatter retectina tater eloctoda termina om comasion
“LT-2 ts alsceated LOCTITE in tha shoo manuals.
00-9
ELECTRIC WIRE CODE
ELECTRIC
lo the wiring diagrams, various colors and symbols are employed to indicate the thickness of wires
This wire cose table wil help you understand WIRING DIAGRAMS,
Example
CLASSIFICATION BY THICKNESS
ELECTRIC WIRE CODE
SWE indicates a cable having 9 nominal number § and white coating with black stripe
Norner
stands
Copper wre
‘i of strane] Crags seahon
tab oo.
il
sang, signal et
Changing ava signa
CLASSIFICATION BY COLOR AND CODE
1
He hese | ons fiona |} vane |] nature | sign omar
4
Ww a @ ® t ¥ c t
: wie | aaa Bee | eon fae
we | aw a aw
wo ey ve , a wn
* Tce | Color] Waite # Back oc 4 Yelow Yalow iach | Gwen’ fed | Given Moa
wary Cone vei cy Ve wd wv
S| reef 2 aC a
00-10
WEIGHT TABLE
a
This weight table is a guide for use when transporting or handling companents
_ 7 Unit:_kg
Machine Mode! | PC806 PC6OL 6 Pcs.
Serial Numbers | 2001 andup | 8001andup | 1001 andup
310 | 310 310
Engine assembly (excluding water and oii)
fa
20
OF and Of cater assembly 27 | 2 a
“TRevane frame - Ty oS a5 oa
Operator's cab oo 7 240 ag
Operator's seat
| 2 22
“Hydraulic tenk ard fuel tank enemy | 2512 30
texcluding oi ard fuel) i
Counterweight 700 | 1,a00.
Hyaraulie pump assemaly - a nr
L.H. 6 spon! contra! valve
RH. 5 spo0) control valve
‘Swing cirele assembly
‘Swing mach inery essembly
‘Swing motor
Center swivel joint
frame assembly
© Track frame
© Idler
© Idler cushion
© Carrier roller
Track roller
Travel motor
Sprocket
718
535x2
36.5 x 2
x2
142%10
915 x2
28x2
x2
ea |
142% 12
182 x2
2x2
6B5x2
S2x2
112
19.3x 12
167 x2
29x2
00-12
020106
020106
Unit: kg
Machine model
PC60-6
PCBOL-6
PC90.1
Serial Numbers
28001 and up
8001 and up
1001 and up
Hh HH
Track shoe assembly
Tripie shoe [450 mm) 800x2 - -
Triple shoe (480 mm) — - 1185 x2
Wide triple-shoe (600 mm) 9702 1,080 x 2 1,616 x2
Wide triple-shoe (700 mm} + 1,200.2 1,790 x2
Flat shoe (480 mm) 1.1402 1,380 x 2
Swamp shoe (700 mm) 980x2 1,090x2 —
Swamp shoe (750 mm) - - 1.585 x2
Rubber shoe (450 mm) 403. x2
Boom assembly 419 419 530
Arm assembly 157 157 213
Link assembly 55 58 55
Bucket assembly 2u 201 236
Blade 360 -
Boom cylinder assembly 109 108 127
Arm cylinder assembly 80 toa
Bucket cylinder assembly 6 61 61
Blade cylinder 48 = 2s
00-13
LIST OF LUBRICANT AND WATER
NDF AMBIENT TENPERATURE CAPACITY if)
RESERVOIR és
FLUID 6% 8 SBE Specie Reta
Engine oil pan
PTO case |
(SAE tow, 80 70
SAE 10W-30 |
mm ome er sore
| ea oa
Swing mac inery case seis 24 24
Final drive case (ezchi pe A poe: ir) Pew
be POsOL.90; 3° | PCOOL|0. 3
a |
siydemiie eyetom PC6D.6OL. 109 | POSO.6OL: 67
tS aa Pcoo: 105 Pee. 7
‘eer (each) [Peso.60L-008 | Peco.s01: 0.05
Poa: | pean
0.120-0.136) 0.120-0.195
“Trike roller (1 place) Jeceneou: 0.08 | ecso,601:; 0.08
pa Poo0
| © 100-0.118 0100-0115
Carrie role (1 ites) | | oor oor
hi i ASTM 0875 No. 2 Pca: 200 |
“ Ls epeseeee micah
CCoeting system water |Add antiteeeze 0 |
ASTM 0075 No.1
NOTE:
ASTM: American Society of Testing and
Material
SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers
API: American Petroleum institute
Specified capacity: Total amount of oi/ including oil tor components and oil in piping,
Refill capacity: Amount of oil needed to refill system during normal inspection and maintenance.
(1) When fuel sulphur content is less than 0.5%,
change oil in the of pan every periodic
tenance hours described in this manual.
Change oil according to the following table
If fuel sulphur content is ebove 0.5%,
Charge avtervat of oi ia
engine ext pen
Fuel sutohur coment |
0.5 101.0% 1/2 of rrguler intevval
Abou
co 1.4 of reguist interval
00-14
(2) When starting the engine in an atmospheric
temperature of lower than O°C, be sure to
use engine vil of SAE1OW, SAE10W-30 and
SAETSW-40 ever’ though an atmospheric
temperature goes up to 10°C more or less in
the day time.
13) Use AP) classification CD as engine oil and
vf API classification CC, reduce the engine
cil change interval to half
02011
10 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
020106
Engine mount and engine related
BOHS ceenpeeecenn en 2
Radiator and oil cooler . 3
PTO 4
Powertrain... 5
Swing circle. 7
Swing machinery « a
Track frame +10: 9
Idler... +1012
Idler cushion 2510-12
Carrier foller ...s.eeeee eee 10-13
ThaekeFAMEr ce scerw ences 10-13
Track shoe 2 10-14
Hydraulic piping . - : 10-17
Hydraulic circuit diagram .. 10-19
Hydrualic tank and fuol tank » 10-19-4
Hydrualic pump ajagaiens 1020
Blade pump... 0.00 10-29-2
LH 6-spool control valve =. +++. 10-30
RH. 6-spool control valve.
Blade control valves. .-+ ++
Swing motor .. 2...
Center swivel joint. .
Travel motor... sseseeeeeeee
Boom safety valve... 2...
Valve control
PPC valve
Solenoid valve assembly .
Safety lock valve
Shuttle valve «6...
Hydrualic cylinder 7
Work equipment .......
Electrical wiring diagrain
Electrical circuit diagram
Engine control. cee
Total contral system...
EMMAC (Electronic Monitor and
Control Console}... 6.0 .e ee
10-1
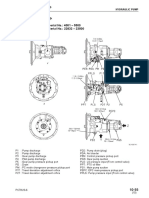
ENGINE MOUNT AND ENGINE RELATED PARTS.
5
2
Je
a
; a
1 4
§ ’ 8
ae Ee al
201F06007
2. Front engine mount 6 Rubber pads:
10-2
020108
020106
RADIATOR AND OIL COOLER
Nomson-
Drain vaive
Sub tank
Oil cooler
Radiator
Fan guard
Radiator inlet hose
Radiator outlet nose
201F 06008
SPECIFICATIONS
Radiator’ PC60 Serial No. 2800131195
PC6OL Serial No. 8001-8047
PC90 Serial No. 1001-1232
cD-3
PC6O Serial No. 31196 and up
PC6OL Seria! No. 8048 and up
PC90 Serial No. 1233 and up
cCWX.3
Oil cooler: SACS
10-3
P.T.O.
Section A~ A
1 Coupling
2 Sati
3. Breather and lubricating plug
4 Case
8 Oil level plug
201F 08010
920106
020108
POWER TRAIN
PC60, GOL-6
1 2 a 4 5 &
\
ea
eae 1
i
| ta:
: yh
f '
10 3
W Ww
:
20108011
1. idler 7. Hydraulic pump.
2. Center swivel joint B Engine
3. AH. 5-spool control valve 9. LH. 6-spool control valve
4. Swing brake solenaid valve 10. Swing motor
5. Travel speed solenoid valve 11. Swing machinery
6. Travel motor and final drive 12. Swing circle
PCgo-1
1 taer
2. Centar swivel joint
3.R.H.5 spool control valve
4. 2-stage reliel solenoid valve
©. Swing brake solenoid valve
6. Travel speed solenoid valve
7. Travel| motor and final drive
10-6
201 F080! 2
8. Hydraulic pump
9 Engine
10 LH. -spool control valve
11, Swing metor
12. Swng machinery
13 Swing circle
020106
020106
SWING CIRCLE
‘Swing circle outer race
Ball bearing
‘Swing circle inner race (80 teeth)
Inner race soft zone “s”
Quter race soft zone“s”
a's
Section A— A
201F06013
SPECIFICATIONS
80 _
Reduction ratio: 82 = 6.154
Grease volume: 5 { (grease G2-L1]
10-7
SWING MACHINERY
Section A
Swing pinion (13 teeth)
Cage
Planet carrier
Ring gear (77 toath)
Bearing holder
Drive gear (22 teeth} [18 teeth]
‘Swing motor
Cover
9. Driven gear (73 teeth) [77 teeth]
and sun gear (16 teeth)
10. Planet gear (30 teeth)
11. Oil level gauge
12. Drain plug
£1 Pcg0.1
evenaurss
10-8
A
é
2o1FO601a
SPECIFICATIONS
PC6O, 60L-6
Reduction rao: 23x 1+ 72 |= 49.286
2 16
PC90-1
24.865
Reduction ratios 22x 1+
18
20106
020106
TRACK FRAME
Pce0.6
1
1. Idler
2. Track frame
3. Carrier roller
4. Travel motor
exos
201F06015
Sprocket
Track shoe
Idler cushion
Track roller
10-9
PCEOL-6
1 tales
2 Track frame
3. Carrier roller
4. Travel motor
10-10
1
201F06016
Sprocket
Track shoe
later cushion
Track roller
020106
020106
PC90-1
Idler
Track frame
Carrier roller
Travel motor
evox
20106017
Sprocket
Track shoe
Idler cushion
Track roller
10-17
1
IDLER
® The drawing shows PC60,80L 6
Idle
Floating seat
3. Support
4. Idler shatt
5 Bushing
1
201FOBO1E
IDLER CUSHION * The drawing shows PC60,60L-6
Yoke
Rod
Front support (eylinder)
Recoil spring
Wear ring
Packing
Rear support
Lubrivator
Drain plug
1
2
woues
1 2 9 4 § § 7 B SPECIFICATIONS
a Grease volume.
160ce (PCEO, GOL}
Grease volume,
180ce (PC3O)
G2.u1
201F06019
10-12
1
020106
CARRIER ROLLER
Lubricating plug
Carriar rotier
Bushing
Floating seal
Collar
Shaft
eoserna
201F06115
020106
TRACK ROLLER 4% The drawing shows PC90-1
1. Floating seal
Track roller
Shatt
Bushing
Collar
DLR
9202033028
10-13
4
TRACK SHOE
Regular bushing
Regular pin
Regular dust seal
Master bushing
Master pin
Master dust sea
Shoe
Shoe bolt
Link
eoryensons
10-14
4
+ The drawing shows PC90-1
202F 05018
SPECIFICATIONS (Standard shoe)
PC6O
450mm triple-shoe
Link Pitch: 154mm
Number of shae, 74
Pcé6oL,
600mm tripie-shoe
Link pitch: 154mm
Number of shoe, 82
cao
480mm triple-shoe
Link pitch 175mm
Number of shoe. 76
020106
SELECTION OF TRACK SHOE
- Select the most suitable track shoe from the folloiwng table.
PC6O-6 PCBOL-6 PC90.4
Specifications oe Specitications | Ge Specifications | a
450 mm triple shoe A 600 mm triple shoe B 480 mm triple shoe | A
600 mm triple shoe |B a 7900 mm wipleshoe BTS
~ = | = |timetoeae | 6 |iionspsae Te
700 mm swamp shoe | € | 700mmswampshoe | C | 760mmawempanos |G
480 mm flat shoe | D = ~ 480 mm flat shoe dD
+ Category
oe Use | Precautions when using
020106
A | Rocky ground, normal river | + Travel in Lo when traveling on rough ground with obstacles
soi such 8s lerge boulders and fallen trees,
+ Cannot be used on rough ground where there are large
obstacles such as boulders and falien trees,
B | Normal soil, soft lend + Travel in Hi spaed only on flat ground, and when itis,
impossible to avoid traveling over obstacles, lower the
travel speed to approx, half of Lo speed.
+ Use only for ground where “A"' and “B" sink and are
possible to use.
Extremely soft ground Cannot be used on rough ground where there are large
c obstacles such as boulders and felien trees
(Swampy ground) + Travel in Hi spead only on flat ground, and when it is
impossible to evoid traveling over obstactes, lower the
‘ravei speed 10 approx. half of Lo speed,
D Paved surface + The shoes are flat, so they have low gradeability,
% Categories "BY and "C” are wide shoes, so When selecting the shoe width, select the
There are restrictions on thei use. There- narrowest shoe possible within the range
fore, botore using, check the restrictions and thet will give no problem with flotation and
consider carefully the conditions of use ground pressure
before recommending a suitable shoe width. fa wider shoe than necessary is used, there
If necessary, give the customer guidance in will be a large load on the shoe, and this
their use may lead to bending of the shoe. cracking
of the links, breakage of the pins, loosening
of the shoe bolts, or other problems.
10-15
1
HYDRAULIC PIPING
1017
‘s
HYDRAUUC CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
020108
HYDRAULIC TANK AND FUEL TANK
Section A--A Section B—- B.
20106026
1, Dram Plug (Hydraulic tank) SPECIFICATIONS
2. Filler cap (Hydraulic tank} Hydraulic tank
3. Pressure valve © Tank capacity. 954
4. Fuel tank © Oil amount, 674
5. Filler cap (Hydraulic tank) © Pressure valve
6. Strainer Relief set pressure 0390.15 kg/em?
7, Fuel ievel sensor Suction sei pressure Q- 0.046 kg/cm?
8, Hydraulic tank + Bypass valve set pressure, 1,080.20 kg-em?
9. Return oil filter (Hydraulic tank)
10. Bypass valve Fue! tank
11. Sight gauge (Fuel tank) * Tank capacity 160¢ (PC60, 6OL)
12. Sight gauge (Hydrauhe tank) © Tank capacity 2001 (PCO)
13 Straner
14 Drain valve (Fuel tank)
10-19-4
&
HYDRAULIC PUMP
PC6O, 60L-6, PC90-1
020108
201F06027
a. Power set signal pressure PmF port
b. Power set signal pressure Pm port
Front main pump
Front servo valve
Rear servo valve
Rear main pump
Charging relief vaive
Charging pump
onawne
10-20
3
PC60-6 (WITH BLADE)
020106
201 Fo8A 12
Power set signal pressure Pme port
Blade sencing pressure Par port
Power set signal pressure Pma port
Blade sencing pressure Per port
Front main pump
Front servo valve
Rear servo valve
Rear main pump.
Charging relief valve
Charging pump
OOAeno
10-21
5
1. FRONT MAIN PUMP AND REAR MAIN PUMP (HPV035+035)
020108
20106028
Rear main pump discharge Paz por: m. Front main pump discharge Pav port
Front main pump disenarge Pat port 1 Servo valve output pressure PSv2a port
a Front main pump disenerge PAt port fh Charging pump pressure Psvt port
b. Rear main pump discharge PA2 port i. Servo valve output pressure PSV1A port
Suction PS port i. Servo vaive output pressure PSV2A port
4 Drain port k. Charging pump pressure P8v2 port
©. Servo vaive output pressure PSv18 port | Rear main pump discharge Pa2 port
'
4
10-22
1
020106
MoOonons
3d $e6 7 8 8 wn 13a is 16 17 18
Air bleeding plug
Drain plug
Front drive shaft
Front cradle
Front pump case
Front rocker cam
Front piston
Section ~ B
8 Front cylinder
9 Front vaive plate
10. End cap
11. Couphiag
12. Rear valve seat
13. Rear cylinder
14 Rear piston
201F06029
18. Rear rocker cam
16. Rear pump case
17. Rear cradle
18 Rear drive shatt
19. Servo piston
10-23
2. SERVO VALVE
PC6O. 6OL-6, PCSOL-1
% The drawing shows the servo valve for the front main pump.
appeal dL
& ‘ible, he
a
920108
Soction DD Section EE Section FF SectionG—G Section H —H
ia) es
GectionJ—J Section K — K Section — L
10-24
wg
020106
201FO6030
Power set signal pressure Pm port
Front main pump discharge inlet Pat port
Rear main pump discharge iniet Pa2 port
Servo valve output pressure Psv1a port
Charging pump pressure inlet Psv1 port
Servo valve output pressure Psvia port
Section A — A
1. Screw
2 Plug
3 Sleave
4, Guide spool
5. Spring
6. Plug
7, Serew
8. Body
9. Rod
10. Spring
11, Seat
201F06031
12. Spring
13 Seat
14. Pin
15. Arm
16. Control piston
17. Sleeve
18. Piston
19. Sleeve
20 Piston
21 Piston
22. Sleeve
10-25
@
PC60-6 (WITH BLADE)
4 The drawing shows the servo valve for the front main pump.
020106
10-25-1
6
s
$
a
b
¢
4.
e.
f
8
Section A—A
Power set signal pressure Pat port 1
Blade sencing pressure Par port 2
Front main pump discharge inlet Pat port 3
Rear main pump discharge inlet Paz port 4
Servo valve output pressure Psvia port 5
Charging pump pressure iniet Psv1 port 6
Servo valve cutput pressure Psvve port 7
8
9.
10
W
12.
Screw
Plug
Sleeve
Guide spoo!
Spring
Plug
Serow
Body
Rod
Spring
Seat
Spring
13,
14.
15,
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
24
22.
23
24
201 FUG4IS
201Fo8a14
Seat
Pin
Arm
Control piston
Sleeve
Piston
Sleeve
Piston
Piston
Steeve
Piston
Sleeve
OPERATION
1) S mode {for normal operation), No load on moin pump
* When the power set switched is pressed to
select S mode, signal pressure Perc from the
power set solenoid valve does not enter port
f of the servo valve
* Tho charging pump output pressure Poa
enters ports b of spool (4)
When there is no load on the pump port by
and port ¢ are connected, so the pressurized
oil from the charging pump enters chamber
A of servs piston (23) and pushes serve piston.
(23) to the right in the direction of the arrow
When this happens, the pump delivery
amount is maximum
Pump discharge volume (‘enn
10-25-2
®
Power sat
g solenoid valve
ower Set sivitch
tS mode)
F20106004
8 made
L mode’
Pump discharge pressure {kg/em@)
(g.1)
20106005
020106
020106
10-26
2) S mode, Load on main pump (front pump)
* When the load on the frent main pump
increases and the delivery pressure becomes
farger, delivery pressure PA1 of the front main
pump enters port d and pushes piston (18)
to the left in the direction of the arrow.
As a result, piston (16) is pushed to the lett
in the direction of the arrow and arm (15)
uses servo piston (23) as a fulerum to push
spool (4) to the left in the direction of the
arrow When this happens, port b and port
a of spogl (4) are connected, and the pres.
surized oil PGA from the charging pump enters
chamber B of serve piston (23), and pushes
sorvo piston (23) to tha left in the direction
of the arrow
Power set
soleneid valve
Pon ae nich |
ek
a
zt
tt |
Controiter
20106008
© Arm (15) uses pin (14) as a fulcrum and
rotates clockwise to move guide spool (4) to
the right. Servo piston (23) stops at a position
where the connection between porta and port
bis cut.
© In this way, the discharge volume from the
front main pump is reduced according to the
discharge pressure, and ts controlled as
shown in the graph for the S mode in Fig
1
3) L mode, (for light load operations)
Power set
solenoid valve
al |
© When the power set switch set to L mode
The power set solenoid valve is switched, and
signal pressure Prec enters port f and pushes
piston (21) to the left in the direction of the
arrow.
As a result, piston (16} is pushed to the left
in the direction of the arrow. and arm (15)
uses servo piston (23) as a fulerum to push
spool (4) to the left in the direction of the
arrow.
When spool (4) is pushed to the left, port b
and port a are connected, and pressurized oil
Pga from the charging pump enters chamber
B of servo piston (23), and pushes servo piston
(28) to the ‘eft in the direction of the arraw
20106007
Arm (15) uses pin (14) as a fulcrum and
rotates clockwise 19 move guide spool (4) to
the right: Servo piston (23) stops at a position
where the connection between porta and port
bis cut
In this way, springs (70) and (12) are
comprassed, and become greater than the set
pressure, so the main pump is controlled as
shown in the graph for the L mode in Fig
1
026106
10-28
1
920108
4) When blade is operated (for machines with blade specifications)
egatrot
* For machines equipped with blade, the
absorption torque of the main pump is
reduced in accordance with the foad on the
blade pump to prevent the engine from
stalling when the blade is used
* Toachieve this, the discharge pressure of the
blade pump goes to the pilot port of the servo
vaive, and the load an the blade pumps taken
by piston (23), By pushing control piston (16)
to the left in accordance with the load, the
absorption torque of the main pump is
reduced.
* When there is no load on the blade pump,
the pump absorption torque is near the
digging mode curve (light mode curve for light
mode) in the diagram on the right, and as
the load rises, it is reduced and moved
towards the blade mode cutve So when the
blade pump is at maximum load. the
Working mode
solenoid valve
va
Working mooe |
“To tiade
Pump discharge volume
—=
Iconieaier
ul
201 FOE 1S
Pump discharge pressure feg/ern®)
20) FoSa16
ee ee eee ee eae
10-29
3. CHARGING PUMP (BARO20) AND RELIEF VALVE
=
PSN | easuetion
biseharge
8
g
\ 8
=
©
Section A A
201F06036
1. Body SPECIFICATIONS
2. Driven gear Type: BARO20
3. Cover Theoretical detivery: 20.9 ce/rev
4. Drive gear Set pressure: 30 kg/em*
5 Relief valve
6. Filter
10-29-1
®
BLADE PUMP
PC60-6 (WITH BLADE)
Discharge
020108
Bracket
Drive gear
Housing
Cover
Driven gear
geens
20106617
SPECIFICATIONS
Type: SBL21
Theoretical delivery 21.0 cc/rey
Set pressure 210 kg/em?
L.H. 6-SPOOL CONTROL VALVE
PC6O, B0L-6
ze-sance
10-29-2
5
h 9
Pa3 port {irom LH. PPC valve)
Pas port (from LH. PPC valve)
P1 port (from tear main pump)
Aa port {T- svsing motor MA port]
As por: (To arm cylinder bottom side}
As por (To LH. travel motor A port)
P2 port (From straight travel vaive)
Ts port (To tank}
ge
ave
20\FO6O37
Bs port |To arm cylinder head side)
83 port (To swing motor MB port)
Bz port ITo boom cylinder battom side)
Paz port (From HH. HPC valve)
P83 port (From {H. PPC valve}
Pea port (From swing brake solenoid valve)
Pas port (From LH. PPC valve}
T port (To tank)
020106
'
BO POP 1G RF. EVEL INGhOn Ss pers
10-30
020106
1, Main relief valve
2. Spool (service)
3. Spool (boom-Hi)
4. Spoal (swing)
5. Spool {arm-Lo}
6 Spool {L_H travel)
Section C
Section HH
201F06038
7. Spool return spring
8 Check valve
9. Check vaive spring
10. Safety-suction valve
11. Spool (swing priority}
Pe9o-t
one
ec
PR port (From 2-stage relief solenoid valve)
Pao port (Fram LH. PPC valve}
Pas port (From L1H. PPC valve)
P1 port (From rear main pump}
A3 part [Ta swing motor MA port}
As port [To arm cylinder bottom side)
AG port (To LH. travel motor A port)
P2 port (From straight-travel valve)
soneange
evesg-77
Mey
OMe ma,
Mt aye ng h aag
ws
bo
vire
pa
2o1ro8039
Bé port (To LH. 1ravel motor B port)
Bs port (To arm cylinder head side)
B3 port (To swing motor MB port)
82 port (To boom cylinder bottom side}
Paz port (From RH. PPC valve)
Pp3 port (From L.H. PPC valve)
Pad port (From swing brake solenoid valve}
Pes port (To LH. PPC valve}
10-317
020106
HS por ho taney
10-32
920108
Main relies valve
Spool (service)
Spool (boom-Hi)
Spool (swing)
Li
PARES
Se SER ee
STH
WU
Section — 0
Section 8
Section H—H.
Section — C
201F06040
7. Spoo! return spring
8 Check valve
9. Check vaive spring
10. Safety-suction valve
11, Spool! {swing priority)
ER ERE Ae See ere
10-33
SWING PRIORITY VALVE
FUNCTION
© When operating the swing and arm at the
same ume, most of the oll flows to the arm,
which has less load. The flow of ol to the
swing circuit is reduced so the arm speed is
faster than ihe swing speed. This makes
combined operations difficult
© To prevent this, the swing priority vaive is
switched by the pilot pressure from the swing
holding brake solenoid valve to restrict the
flow of pressure oil to the arm-Lo control
vaiue This restricts the arm speed and makes
2 easier to operate the arm and swing at the
same ume.
GREBATION Beisfeawe_|
When swing at neutral
* When ihe swing is at neutral, no pitot
pressure oil flows from the solenoid valve
The swing priority valve 18 not actuated, 96 sg, GE
the pressurized oi! from the front main pump —satersidvoivel
passes through gort P1 and flows to the arm. gf! uN
Le control valve
20108
When swing is operated
© When the swing is operated, spool (11) af she
swing priority valve 1s pushed to the right by
the pilot pressure from the solenoid vaive,
Because of tus, the pressunzed oll flowing
front main pump to the arm Le central
valve 1s throttled by the swing priority valve
and the arm speed |s controlled so the
simultaneous operation pertd
ance is.
improved
201FO6042
10-34
3
020106
MAIN RELIFE VALVE (PC90-1)
201F06049
FUNCTION
© The main relief valve is in the circuit between
the pump and the contro! vatve. This valve
acts to protect the pump from damage from
any abnormal oi! pressure. When abnormal
pressure is produced or when the hydraulic
cylinder reaches the end of its stroke during
operations, the oi! sent from the pump is
telievad through the main relief valve
(It sets the maximum high pressure in the
cireuit during operations.)
OPERATION
‘© Chamber A forms a pump circuit and chamber
€ forms @ tank drain circuit, The oil flows
into chamber B through the main vaive (1)
orifice to keep the chamber tilled
Poppet vaive (3) is set in the sleeve (5).
© If the pressure in chamber B reaches the pilot
valve spring force (set pressure), the poppet
valve {3) moves, allowing the oil in chamber
B to fiow into chamber C through orifice. in
addition, the oll flows from chamber & to B
through orifices.
If the oil flows through the orifice of main
valve (1), @ differential pressure occurs
between the chambers A and B, moving main
valve (1) to the right. This allows the oil in
chamber A to flow into chamber ©
+ When the travel is operated, the 2-stage relief
solenoid valve is actuated, so oil is shut to
chamber E, and pushes piston (6) to the left,
The set pressure is raised by compressing
arenes: ehsiree HES.
Main valve
Main valve spring
Poppet valve
Poppet valve spring
Sleove
Piston
Adjustment sleeve
Adjustment plug
PNOMEEN=
Set pressure
When work equipment and swing oper:
ated: 325 ka/em? (at 27 L/min)
When traveling operated: 355 kg/cm? (at 24
/min)
5
7 From 2-stage ‘lie!
solenoid valve
201F 6050
From 2-stage reliet
\ solenoid valve
201 F06051
§ rom 2
\ { From 2-stage raiet
{sotonoie valve
a ee ee
201F 06082
10-35
R.H. 5-SPOOL CONTROL VALVE
PC60, 60L-6
8
zl rol aed 8
oo€ & 8 fy w® 4
b
ua ‘ . . 201F 08043,
Pa port (From staight-travel valve)
a PBS port (From RH. PPC valve)
As port (To arm cylinder bottom side}
bh Pa4 port (From RH PPC valve} m
© Pas port (From LH. PPC valve} 6. Aaport (Ta boom cylinder head side)
«Pt port From front main pump) 2, Aa port (To bucket cylinder bottom side}
Bi port (To RH, travel motor A port) 9, A2 port (From rear main pump)
f Ba port {To LH. travel control valve) 21 Pe port (Te arm Hi control valve)
g: B3 por (To bucket cylinder head side) 1 At port (To RH. travel motor B port}
Ba port (To boom cylinder bottom side ) s, Paz port (From straight travel solenoid valve|
Bs port (To arm cylinder head side} 1 Paa ort (From RH, PPC valve)
Ts port {To tans) Pa port (From RH PPE valve)
TAS POC IT TOET LAY. Eke WANES
kT port (To tank)
10.36
020106
Section C ~ Section H—
Jo1Fosoaa
1. Main relief valve 6. Spool (arm-Hi)
2. Spool return spring 7. Check vaive
3. Spool (RH travel) 8. Check valve spring
4 Spool (bucket) 9. Satety-suction vaive
5. Spool (boom-Lo} 10. Spool! (straight-travel)
PC60-6 (WITH BLADE}
Pas port (From R.H. PPC valve)
Pea port (From R.H. PPC valve)
Pas port (From LH. PPC valve}
1 port (From front main pump}
B1 port (To R.H. travel motor A port)
Bz port {To LH. travel control valve)
Bo port (To bucket cylinder head side)
Be port (To boom cylinder bottom side)
Bs port (To arm cylinder head side)
10-37
cal
020106
2orFo6s1a)
Ps port (From straight-travel valve)
. As port (To arm cylinder head side)
As port {To boom cylinder heed side)
As port (To bucekt cylinder bottom side}
‘Az port (From rear main pump}
P2 port (To eem-Hi control valve)
At port (To RH travel motor 8 port)
Paz port (From straight-travel selencid valve)
Pas port (From 8.H. PPC valve)
He ey oe geet
*
k
ae ee
T port (To tank)
10-37-1
6
020106
vy Pas port (From LH. PPC valve}
SectionH—H_ Section JJ
Section ¢~C
2o1F 05419
1. Main relief valve 6. Spool (arm-Hi}
2 Spool return spring 7. Check valve
3. Spool (R.H. travel) 8. Check valve spring
4. Spool (bucket) 9. Satety-suction valve
5, Spool boom: Lo) 10. Spool (straight-travel)
PC90-1
Pa port (From 2-stage relief solenoid valve}
Pas port (From RH. PPC valve)
Psa port (From RH PPC valve)
Pas port (From LH. PPC valve}
P1 port (From front main pump)
B1 port {To R.H. travel motor A port)
B2 port (To LH. travel control valve)
Bs port (To bucket cylinder head side)
Bs port (To boom oylinder bottom side}
Bs port (To arm cylinder head side}
Ts port (To tank)
» 201FO6048
3 port (From straight-travel valve)
As port (To arm cylinder bottom side}
‘Aa port (To boom cylinder head side)
3 port (To bucket cylinder bottom side)
‘A2 port (From rear main pump)
P2 port (To arm-Hi control valve}
At port (To RH. travel motor B port}
Paz port
(From straight-travel solenoid valve}
Pa3 port (From R.H. PPC valve}
Pad port (From RH. PPC valve)
10-37-2
6
020106
T part (To tank) w. Pas port (From L.H. PPC valve)
10-38
020106
Section CC
Section HH.
20106045
1 Main relief valve 6. Spool (arm-Hip
2. Spool return spring 7 Check valve
3. Spool (P.H. travel) 8 Check valve spring
4. Spool (bucket)
9. Safety-suction valve
5. Spoo! (boom-Lo}
19, Spool (straight-travel)
STRAIGHT TRAVEL VALVE
FUNCTION
© While operating the swing, boom, arm, oF
bucket when traveling, the pressure oil
flowing to the RH, and LH. travel circuits
branches into the swing, boom, arm, or bucket
circuit,
Since the supply of pressure oil in a branched
travel circuit is less than that in the circuit
before the branch, the motor naturally slows
down, resulting in a turn
© When the straight-travel valve is switched
‘over to establish continuity between the RH
and L.H. travel circuits, this undesired turning
is prevented by equalizing the supply of
pressure oil to the RH. and LH. travel motors
$0 that they rotate at the same speed.
OPERATION
‘When traveling only:
* Since ro pilot hydraulic o1l flows trom
solenoid valve, the travel-straight vaive is not
operated
© Therefore, the circuit between port PR (RH
travel circuit) and port PL {LH. travel circuit)
remains closed and both circuits remain
independent.
During simultaneous operation
‘+ When operating the work equipment or swing
while traveling, spoot (10) is pushed to the
Fight in the direction of the arrow by the pilot
pressure from the straight-travel solenoid
vatve.
© Because of this, port PR and port PL then
become connected to each other and an equal
amount of pressure oi! is supplied ta the RH.
and L.H. travel motors, allowing both motors
to rotate at the same speed
The machine travels thus in a straight line
my
Eline wie!
110
Bucher
aint
Bucket
Boom vo
2o1Fo8047
|
FE On tawet
10-39
020106
ES
10-40
BLADE CONTROL VALVE
PC60-6 (WITH BLADE)
020106
Section 8-8
201F08420
a, B1 port (To blade cylinder haad side) 1. Spool (Blade)
b, Ar port {To blade cylinder bottom side) 2. Main relief vaive
¢. T port (To tank) 3. Spool return spring
dP port (From bialde pump) 4 Check valve
5. Check valve spring
6 Satety-suction valve
SWING MOTOR
S por
B port (From swing brake solenoid vaiva)
T port (To tank}
MB port (From LH. 6-spool control valve}
MA port (From LH. 6-spoo! control valve)
201706053
SPECIFICATION
Type: KMF40AB.2
Theoretical delivery: 40.2ce/rev
Safety valve set pressure:
236% kg/cm? (PC6O, 60L)
+5
oO
Rated speed: 1.585 rpm (PCO, 60L)
1 80)
21075 kavem# (PCO)
10-41
3
020106
10-42
020106
Re ae
Max. 14 kg/cm?
1, Drive shatt
2. Cover
3. Housing
4. Disk
5. Plate
6. Brake piston
7. Brake spring
8. End cover
9. Piston
201F 06054
10. Cylinder
11, Valve plate
12. Air bleeding plug
13, Center shaft
14, Center spring
18. Safety valve
16. Check vaive
17. Check valve spring
SWING HOLDING BRAKE
OPERATION
1)
2)
When swing brake solenoid valve is
deactivated
When the swing brake solenoid valve is
deactivated, the pressurized oil from the
charging pump is shut off and port B is
connected to the tank circuit
Because of this, brake piston (6) is pushed
down in the direction of the arrow by brake
spring (7), so dise (4) and plate (5) are pushed
together and the brake is applied
When swing brake solenoid valve is excited
When the swing brake solenoid valve is,
excited, the valve is switched and the
pressurized oi! from the charging pump
enters port B and flows to brake chamber
a
The pressurized oll entering chamber a
overcomes the force of brake spring (71, and
brake piston (6] is pushed up in the direction
of the arrow. Because of this, disc (4) and
plate (5) separate, and the brake is releesed
Deactivated
MEPL
Charging eump
wd
10-43
[Swing brake
| solenoid valve
202F08048A,
020106
Swaine broke
solenoid valve
202F0S060A,
CENTER SWIVEL JOINT
opens
10-44
Cover
Body
ipper seal
Oil seal
Shaft
201#06085
A1.From R.H. 5-spool control valve A1 port
A2,To RH. travel motor B port
8), From A.H. 5-spool control valve 81 port
Ba. To RH. travel motor A port
C1, From LH. 6-sp00l control valve As port
2, To LH. travel motor port
©). From LH. 6-spool control valve Bs port
D2, To LH, travel motor B port
E1, From travel speed solenoid valve
£2, To LH. and RH, travel motor D port
020106
10-45-1
5
020106
T2 From LH and RH travel motor © port
PC60-6 (WITH BLADE)
Cover
Body
Slipper seal
Oil seat
Shaft
. From R.H, 5-spool control valve A1 port
. To RH. travel motor B port
From R.H. 5-spool control vatve B1 port
To RH. travel motor A port
From LH. 6-spool control valve As port
ToL.H. travel motar & port
Se eal dl tenn ett lal oes inte
201706421
E1, From blade control valve B1 port
E2 To blade cylinder head side
F 1 From blade control valve A1 port
F2. To blade cylinder bottom side
G1. From travel speed solenid valve
G2.ToL.H. and RH. travel motor D port
D2, To LH. travel motor B port Ta. From LH. and RH. travel moter € port
10-45-2
"
TRAVEL MOTOR
PC60-6
bees
PE
20108056
a. C port (To tank} SPECIFICATIONS
b. A port (From travel contro! valve) Type: GMOSVL-D
c. D port (From travel speed solenoid valve) Hydraulic motor
4. B port (From travel control valve! Theoretical delivery: Lo 37.2 cc/rev
Hi 26.7 cc/rev
Rated pressure. 320 kg/cm*
Reted speed: Lo 1,897 rom
Hi 2.689 1pm
Parking brake releasing pressure: 9 kg/cm?
Hi-Lo switching pressure: 30 kg/cm?
Final drive
Reduction ratio: 48
Rated speed: Lo 39.6
Hi 66.5
020106
10-46
020106
SSeeavanmsans
Check valve spring
Check valve
Safety valve spring
Satoty vaive
Counterbalance valve
Return spring
End cap
Regulator vaive
Spring
Brake piston
Cylinder
12
13.
14
15
16
7
18
19
20
21
22.
{it fi | PE YLAN
330320 0 aD) 8 B25 A922
Piston
Rocker com
Crankshaft
RV gear
RY gear
Cover
Driven gear
Drive gear
Drain plug
Shatt
Coupling
23.
24,
25
26
27.
28.
29.
30.
31
32
33
201F08057
Center shaft
Case
Regulator piston
Spindle
Floating seal
Plate
Disk
Broke spring
Vaive plate
Spring
Chack valve
PCBOL-6
aoge
C port (To tank)
A port (From travel control valve)
D port (From travel speed solenoid valve)
B port (From travel control vaive)
Ia rAL
201F06088
SPECIFICATIONS
Type: GM17VY-E
Hydraulic motor
‘Theoretical delivery: Lo 37.2 cc/tey
Hi 25.7 ce/rev
Rated pressure: $20 kg/emt
Rated speed: Lo 1.897 rom
Hi2,717 rem
Parking brake releasing pressure: 10 kg/cm’
Hi-Lo switching pressure: 30 kg/cm?
Final drive
Reduction ratio: 53.5
Rated speed: Lo 35.6 rpm
Hi 50.9 rpm
10-47
020108
10-48
020106
SSeanonsons
Check valve spring
Check valve
Salety valve spring
Safety valve
Counterbatance valve
Return spring
End cap
Rogulator valve
Spring
Brake piston
Cylinder
12
13
14
15.
16
17.
18.
19.
20,
2
22
Piston
Rocker cam
Crankshaft
RY gear
RY gear
Cover
Driven gear
Drive gear
Drain plug
Shaft
Coupling
a M08
80 0
|
wu bn
LV EV YAY
wm ha hh
201F06059
23. Center shat
24, Case
26 Regulator piston
26 Spindie
2? Floating seal
28 Plate
29 Disk
30 Brake spring
31 Valve plate
32. Spring
33 Cheek valve
PCa0-1
eecs
© port (To tank)
A port [From travel cantrol vaive)
D port {From travel speed solenoid valve)
B port (From travel controt valve}
10-49
020108
201F06060
SPECIFICATIONS
Type GMI7VIL-F
Hydraulic motor
Theoretical delivery: Lo 86.3 cc/rev
Hi 55.3 ce/rev
Rated pressure: 350 kg/cm?
Rated speod: Lo 965 rpm
Hi 1,491 pm.
Parking brake releasing pressure: 10 ka/em*
Hi-Lo switching pressure: 30 kg/cm?
Final drive
Reduction ratio: 29.1
Rated speed: Lo 33.2 rpm
Hi 81.2 rpm
10-50
020106
ZSeevaonawns
Check vaive spring
Check valve
Safety valve spring
Safety valve
Counterbalance valve
Return spring
End cap
Regulator vaive
Spring
Brake soncg
Brake piston
12.
13.
14
15
16.
17
18.
19
20
21
22
1 8 8 19 11 12 13 14 18 16 17 1 49 20
Cylinder
Piston
Rocker cam
Crankshait
RY gear
RV gear
Cover
Driven gear
Drive gear
Drain plug
Center shaft
3110 29 28 27
23
24
25
26
27,
28
29
30
31
1 l |
Bea 2D
20106081
Case
Regulator piston
Spindie
Floating seal
Plate
Disk
Valve plate
Spring
Check valve
MOTOR
OPERATION
1) At Lo speed (motor rocker cam angle at maximum)
| droke vaive
© Tho solenuid vave % deactivated, so the pilet
pressure oil om the charging pump does not
How te port D.
For ths reason, regulator valve (Bt is pushed
fo the dell on the diction of the arrow by
spring (9)
Because of ti ,
rd the mary pressure oil from the contrat
pushes check valve (2
valve ta end cover (7) 16 closed for equator
valve (By
© The pressurized oil in chamber aot requlal
piston (24) at the bottom passes through
orifice bins regulator valve (B) end 1s drained
202FOSO5SA
a rasult, rocker cam (14) moves in the
maximum swash plate angle direction for
main pressure oll in cylinder chamber P, the:
and the
mater capacity becomes maximum
system is set to Lo speed.
10-51
020106
10.52
at minimum)
——
cecal Ay |||
iy! |
i
Brake valve
Travel speed
Travel contol } solenoid vaive
vaive Hi) T
020106
Fs
202FOS0S5A,
# The solenoid vaive is excited, so the pilot
pressure oll from the charging pump flows
Je port D, and pushes regulator valve (8) is
pushed to the right in the direction of the
arrow
* Because of this, the main pressure oil from
the control valve passes through passage ¢
in regulator valve (8}, enters regulator piston
(24) at the bottom, and pushes regulator
piston (24) to the left in the direction of the
arrow
# As a result, rocker cam (14) moves in the
minimum swash plate angie direction, the
motor capacity becomes minimum, and the
system 1s set to Hi speed
PARKING BRAKE
OPERATION
1) When starting to travel
When the travel iever is operated, the
pressurized oi] from the pump actuates
counterbalance valve spoo! 16), the circuit
10 the parking brake is opened, and opened
check valve (31) and the oil flaws into
chamber a of brake piston (11), overcomes
the force of spring (10}, anc pushes pision
(12) 10 the left in the direction of the arrow
When thes happens, the force pushing plato
(27) and cise (28) together is lost, 20 plate
(27) and disc (28) separate and the brake
15 released
2) When stopping travel
When the travel lever is placed in netval
counterbalance valve spool (5) returns te tne
neutral position and the cwreurtto the parking
brake is closed
The pressurized ot! in chamber a of brake
piston (11) is drained to the case from the
orifice of check vaive (31) in the brake pistcm,
and brake piston (11) 15 pushed to the right
in the direction cf the arrow by spring (19).
As a result, plave (27) and dise (28) are
pusted togerher, and the brake is applied
10-53
Wd FB
\ | fe
2o2Fos0s68,
020108
bk
=
2 contol vatve
10-54
020106
BRAKE VALVE
* The brake valve consists of a check valve,
counterbalance vaive, and safety valve in a
circuit as shown in the diagram on the right.
ig.1)
* The function and operation of each compo-
‘nent is as given below.
1) Counterbalance vatve, check valve
Function
‘* When traveling down a slope, the weight
of the machine makes it try to travel faster
than the speed of the motor.
As a result, if the machine travels with
the engine at low speed, the motor will
rotate without jad and will run away,
which is extremely dangerous.
To prevent this, these valves act to make
the machine travel according 10 the
‘engine speed (pump discharge volume).
Operation when pressure is supplied
* When the travel lever is operated, the
pressurized oil from the control valve is
Supplied to port PA. It pushes open check
valve (2a) and flows from motor intet port
MA to motor outlet port MB.
However, the motor outlet port is closed
by check valve (2b) and spool (5), so the
pressure at the Supply side rises. (Fig. 2)
© The pressurized oil at the supply side
flows from orifice Et in spool (5) to
chamber $1, and when the pressure in
chamber $1 goes above the spool switch-
ing pressure, spool (5) is pushed to the
right in the direction of the arrow.
AS a result, port MB and port PB are
connected, the outlet port side of the
motor is opsned, and the motor starts to
rotate. (Fig. 3)
20ZFOS0S78
fi contro! vah
iFig.1) 202F95058
da
(Fig 2) 202FO805S
Operation of brake when traveling downhill
© If the machine (ries to run away when traveling
downhill, the motor will turn under ne load, 50
the pressure at the motor inlet port will drop,
and the pressure in chamber $1 through orifice
Et will also drop
When the pressure in chamber $1 drops below
the spool switching pressure, spool (5) \s
returned to the left in the direction of the arrow
by spring (8), and outlet port MB is throttled
AS @ result, the pressure at the outle} port side
Fises. resistance is generated 10 the rotation of
the motor, and this prevents running away
In other words, tne spool is moved to a position
where the pressure at outlet pert port MB
baiances the pressure at the intet port and the
force generated by the weight of the machine
I throttles the outlet post sircurt and controls
the speed aceordmg to the discharge volume.
of the pump. (Fig. 4)
2} Safety valve
Function
* When travel is stopped (or when traveling
doverhill, the circuit at the inlet and outlet ports
of the motor are closed by the counterbalance
valve, but the motor is rotated by inertia, so the
pressure at the outlet port of the motor will
become abnormally high and damage the motor
oF piping. The safety valve acts to release this
abnormal pressure and sent tto the inlet port
side of the motor to prevent damage to the
equipment
Operation
When stepping travel (or when traveling
downhill), chamber a (or chamber b)in the outlet
port ciréult 1s closed by the check valve of the
counterbalance valve, but the pressure at the
outlet port rises because of inertia (Fig 5)
When the pressure goes above the set pressure,
the pressurized oil in chamber a overcomes the
force of spring (3), pushes spool (4) 1a the right
in the direction of the arrow. so the pressurized
«il flows to chamber b on the opposite side
(When the pressure in chamber @ is high}
(Fig. 8)
When ihe pressure goes above the set pressure
the pressurized oil flows into chamber d through
orifice ¢ in spool (4). It overcomes the force of
spring (@), pushes spool (4) to the right in the
direction of the arrow, so the pressurized oi
flows to chamber a on the opposite side
ig.) 202FO5060
10-55
Lees)
4
” 2e2=08081
eg ” 8
2
2o2r0saes
ESOMEEY SORE POOR ent WC PMrMENeS OP Tee Cage 4 3
(Fra, 7) fg
202-5054
10-56
BOOM SAFETY VALVE
PC60-6 (WITH BLADE)
oom 2
.
|
|
2 ea
3
8
201F06422
a, Cy port (Boom cylinder head circuit) OUTLINE
b. Thort (To tank) © The boom safety valve is in the circuit
between the LH. 5-spo0! contro! vaive
1. Block and boom eylinder head, and is installed
2. Safety-suction valve to the tip of the rovolving frame.
VALVE CONTROL
PC60-6 Serial No.: 28001~34100
PCEOL-6 Serial No.: 80018075
PC90-1 Serial No. 1001-1403
Bucket duine
we
Beam loner
Hydraulic pump
2. LH. 6-spoo! conirol valve
RH. 5-spool control valve
3.
4, Shuttle valve
g
g
8
8
20706008
7. LH, work equipment control lever
8 LH, travel contro! lever
9. RH. travel contral lever
10. R.H. PPC valve
a SED Tae So ee aa eee
6 LH, PPC valve
10-57-1
BS
PC60-6 Serial No.: 34101 and up
PC6OL-6 Serial No.: 8076 and up
PC90-1 Serial No.: 1404 and up
920106
7 20106303
1, Hydraulic pump 7. LH, work equipment control laver
2. LH 6-spool contro! vaive 8. LH. travel control lever
3. A.H. 5-spool control valve 9. RH. travel control lever
See eee
5. Safety tock valve
6. LH. PPC valve
eR ee
11. RH. work equipment control
PC60.6 (WITH BLADE) Serial No.: 28001 ~-34100
io
1 Hydraulic pump
2. LH. 6-spool control valve
3. AH. 5-spool control valve
4 Shuttle valve
eee ee ee
1
8. LH. work equipment control lever
9. LH. travel control lever
10. RH, travel control lever
41. RH, PPC valve
Se ei a gS Acc
lever
10-57-2
5
Fr0106304
020106
work equipment control lever
7H PPC valve
10-57-3
é
PC60-6 (WITH BLADE) Serial No.: 34101 and up
#
Blode lower
Bucket dump
.
020106
1 eormais
Wh
io
f 7
a
8
Fro1083is
1. Hydraulic pump 8 LH. work equipment control lever
2. LH. 6-spool control valve 9. LH. travel contro! lever
3.A.H. 5-spool contro! valve 10. R.H, travel control lever
4. Shunte valve 11, LH PPC valve
5 Blede control valve- 19 Blade cantral lever
6. Safety look valve 13. R.H. work equipment control fever
7. LH PPC valve
10-57-4
%
PPC VALVE
PC60-6 Serial No.: 28001-34100
PC6OL-6 Serial No.: 8001—8075
PC90-1 Serial No.: 1001—1403
g
S
20208086
a. Pport (trom charging pump) FUNCTION
b. Tort {To tank) * The PPC valve supplies pressure oil from the
we. Fe port (LR, arm in/RLH., bun sarse) charging pump to the side face of the spac!
dd) Paport(L KH: RK. swing/R-H. bucket dump) ol each control valve according to the amount
1
10.
20106
Py port (LH. arm out/R.H., boom lower)
Ps port (LH LH. swing/RH. bucket curl)
58
&
Section C ~C
1. Spoot
2, Metering spring
3. Centering spring
4, Damper piston
5. Damper spring
6. Piston
of travel of the control lever This pressure
oll actuates the spool
202F05067
7.Disk
8. Lever
9. Joint
10. Plate
41. Collar
12. Body
10-59
OPERATION
1) Controi fever at neutral
Ports Pt and P2 of the PPC valves in circuits
A and B of the conisol valve are connected
todrain chamber B through fine contro! hole
Fin spool (1). (Fig. 4)
2) Control lever operated
trol)
When piston (8) starts to be pushed by dise
(7), retainer (13) § pushed. Spool (1) 1s also
pushed by spring (2) and moves down aay
When this happens, fine control hale t « Lng contrat vaive
shut off from drain chamber D At almost a
the same time it is conrwsted te pump Fiot 202F08066
pressure chamber Pp, and the pilot pressure
‘of the control valve is sent through fin
control hole f to port Pt, When the pressure
a1 port P1 rises, spool |1) is pushed back
Fine control hole fis shut off from pump.
pressure chamber Pp. A: almost the same
ume its connected 0 drain chamber D, $9
the pressure at port P1 escapes 10 drain
chamber D
Spool (1) moves up and down unt) the force
of metering spring (2| is balanced with the
pressure of port Pt
The relationship of the positions of spoal (1)
and body (12) (fine control hale fis in the
middle between drain hele D and pump
pressure chamber Pp} does not change unul
damper piston (4) conzacts piston (6)
Therefore, metering spring(2) seompressed
‘9 propertian te the travel of the control lever,
9 the pressure at port Pt also rises in
proportion to the travel of the contro! lever
The spool of the contral valve moves to a
position where the pressure of port A (same
a8 pressure at port Pr and ihe force fo the
sein ipin aralilcn, i Gi Leaps norton Addie
020106
(Fig
10-60
020106
2)
3) During fine control (control lever returned}
When dise (7) starts to be returned, spooi
(1) 1s pushed up by the force of cemering
(2) and the pressure at port Pa
Because of this, fine control hole f is
connected t drain chamber D, and the
pressurized oil at port P1 is released
if the pressure at port P1 drops too much,
spool (1) is pushed up by metering spring
(2), 80 tine control hole 4 1s shut off from
drain chamber D. At almost the seme time
it is connected to pump pressure chamber
Pp, so the pressure at port P1 supplies the
pump pressure until the pressure recovers
(0 @ pressure aquivatent to the position of
me lever.
When the contral valve spool returns, oil in
drain chamber D from fine control hole
of the valve on the side that is not moving
folws through pori Pz and goes to chamber
B, so the oil 1s 1s charged. (Fig. 3)
4) At full stroke
Disc (7) pushas down piston (6), but damper
piston (4) also follows this and pushes down
spool (1). Fine contro! hole Fis shut off from
drain chamber D, and is connected to pump
pressure chamber Pp. Therefore, the pilot
pressure oil from the charging pump passes
through fine contral nole f and flows to
chamber A trom port Pt to push the control
valve spool.
The return oil from chamber B passes from
port P2 through fine control hole f* and flows
to drain chamber D
With damper piston |4) that was following
piston (6), the pressurized oil in the spring
chamber flows out from orifice a, and
damper piston (4) and spool |1) are pushed
back by the force of metering spring (2) and
the hydraulic pressure at port Pt
The time lag when the lever 15. suddeniy
operated 1s prevented by damper piston (4)
(During fine control, damper piston (4) does
not follow piston (6), so the fine control
reve | ge
Fig 2 202F05063
202F05070
Control vaive Ee
an +
ig 4)
performance is maintained,| (Fig. 4) AR ne
10-61
PC60-6 Serial No.: 34101 and up
PC6OL-6 Serial No.: 8076 and up
PC90-1 Serial No.: 1404 and up
3
g
8
ll . a
| 5)
4 |
/ f : @
2orFo ‘002
P port (Fram charging pump)
T port (To tank’
P2 port LH: Arm dump/R.H. Boom lower)
Pa cort iL. H = Swing left/R.H.: Bucket curl)
10-61-1
s
901070
4. Piston
5 Disc
OPERATION
1) Atneutral
Ports A and B of the control valve and ports P7
and P2 of the PPC valve are connected to drain
chamber D through fine control hole f in spool
1) (Fig, 1)
2). During fine contro! (neutral fine control)
When piston (4) starts to be pushed by disc |S),
retainer (9) is pushed, spool (1) is also pushed
by metering spring (2), and moves down
When this happens, fine control hole f is shut
off from drain chamber D, and at slmost the same:
ume, it is connected to pump pressure chamber
Pe, so pilot pressure oil from tha charging pump.
passes through fine contro! hole Fand goes from
port Pr te por A
When the pressure at port Pr bacomes tugher
sp00| (1) 1S pushed back and fine control hole
fis shut off from pump oressure chamber Pr
At almost the same time, it is connected to drain
chamber D fo release the pressure at port P1
When this happens, spool {1} moves up or down
0 hat the force of mataring spring (2} is balanced
with the pressure at port Pt. The relationship
‘8 the position of spool (1) and body 10} (tine
gonitol hole Fis at a point micway nerween drain
hole D and pump pressure: chamber P| dees not
change until retaimer (9) contacts spool (1)
Theretore, metering soring (2) 1s compressed
proportionally to the amount of movernent of the:
zon rol lever, sothe pragsure at port Pr alsa rises
in propertion to the traval of the conteat lever.
In this way, the eantrol valve spool moves toa
position where the pressure in chamber A (the
ines:
10, Body
a
2oTFo1D4s
2oTFOoas
8
g
8
CINE | Cine FP EES BE BE EY ES TENE: TE
of the control valve spol return spring are
balanced (Fig. 2)
10-61-3
3
020106
3) During fine controt
{when contro! lever is returned)
When disc (5) starts to be returned, spool (1) is
pushed up by the force of centering spring (3)
‘and the pressure at port Pa
When this happens, fine control hole £ is
connected to drain chamber D and the pressure
oil at port Py is released.
If the pressure at port P1 drops 100 far, spool
(1) is pushed down by metering spring (2), and
fine contrat hole f is shut off from drain chamber
D. At almost the same time, it is connected to
pump pressure chamber Pr, and the pump
Pressure is supplied until the pressure at port
Pt recovers to 4 pressure that corresponds to
the lever position.
When the spool of the control valve returns, oil
in drain chamber D flows in trom tine control
hofe f* in the valve on the side that is not working.
The cif passes through port P2 and aniers
chamber 8 to fill the chamber with oil. (Fig. 3)
4) At full stroke
When disc (5) pushes down piston (4), and
telainar (9) pushes down spool (1), tine contrat
hote fis shut off from drain chamber D, and is,
connected with pump pressure chamber Pp,
Therefore. the pilot pressure ail from thecharging
bump passes through fine control hale and flows
te shomber A from port P1, and pushes the
control valve spool
The oil returning from chamber B passes from
port P2 through fine control hole #” and flows
10 drain chambar D (Fig. 4)
a 20TFO 1085
93)
in
4
a
f
pe
©
mag] Control valve PGB
20TFo108?
(Fig ay
10-61-4
SOLENOID VALVE ASSEMBLY
PC6O, 6OL-6
FOR TRAVEL SPEED, SWING BRAKE, POWER SET AND STRAIGHT-TRAVEL
070106
201606063
T port (To tank} 1. Block
P port (From charging pump) 2. Travel speed sotenoid vaive
Tr port 3, Swing brake solenoid valve
Te port 4, Power set solenoid valve
Ts port 5. Swaight-travel solenoid valve
Ax port (To LH. and RH. travel motor)
Az port (To swing priority valve and swing motor)
Aa port (To front and rear servo valve)
tha port Ifo: etraichttravel vale)
10-62
i
PC90-1
FOR TRAVEL SPEED, SWING BRAKE, POWER SET STRAIGHT-TRAVEL AND 2-STAGE RELIEF
0201068
201F0606a
T port (To tank) 1. Block
P port (From charging pump) 2. Travel speed solenoid valve
T1 port 3. Swing brake solenoid valve
T2 port 4, Power set solenoid valve
‘T3 port 5. Straight-trevel solenoid valve
6
At port (To LH. and R.H. travel mator}
A2 port (To swing priority valve and swing motor)
As port (To tront and rear servo vaive)
Aé port (To straight-travel vatve)
2-stage relief solenoid vaive
-sesepange
— a ne
Cannector
Plunger
Coil
Push pin
Spool
Spring
Block
Neosens
Section A
202FOSO75
OPERATION
Solenoid deactivated
© No signal current flows from the controller,
so solenoid (8) is deactivated.
As @ result, spool (5] is pushed to the left
in the direction of the arrow by spring (6)
Because of this, port A is closed, and the
pressurized oil from the charging aump does
not ilow to the actuator
At the same time, the oil from the actuator
flows from port B to port © and is drained
to the tank
3
a
§
202708076
Solenoid excited
* When the signa! current flows from the
controller to solenoid (3), solenoid (3) is
excited
As a result, Spool (5) is pushed to the left
in the direction of the arrow by push pin (4)
Because of this, the pressurized oil from the
charging pump passes from prot A through
the inside of spool (5), flows to port B and
then flows to the actuator.
At the same time, port C is closed, so the
oil does not flow to the tank
Actuator
|
202F 08077
10-64
020108,
SAFETY LOCK VAVLE
Lever
Body
Seat
Ball
End cap
1
2
3.
4
5
201F 06087
SHUTTLE VALVE
FOR WORK EQUIPMENT OIL PRESSURE SWITCH AND SWING OiL PRESSURE SWITCH
Plug
Bady
Ball
Ps port (LH. swing)
Ps port (F.H. swing)
P? port (Arm in)
Pa port (Arm out)
Pt port (Boom raise)
Pa port (Bucket dump}
P2 port (Boom lower)
|. Ps port (Bucket curl)
Bs port {installed hole of work
equipment oil pressure switch)
B2 port (Installed hale of swing
oil pressure switch)
201F06068
10-65
1
HYDRAULIC CYLINDER
1. BOOM CYLINDER
201F06070
3. BUCKET CYLINDER
020106
10-66
7
020106
4. BLADE CYLINDER (PC60 WITH BLADE)
201F06071
1, Rod side bushing
2. Piston rod
3. Cylinder head
4. Rod packing
5. Buffer ring
6. Wear ring
7. Cylinder
SPECIFICATIONS
8. Head side tube
9. Casting ring
10. Piston ring
11. Wear ring
12, Piston
13. Piston nut
14, Bottom side tube
201F 08826
15, Bottom side bushing
16. Bottom side cushion plunger
17. Ball
18, Collar
19, Head side cushion plunger
Unit: am
= Cyuncer Boom arm ce
Fe60 P80 po80, ao. | p0«0
sae = PC6OL ee PCEOL, pean PcaG WITH BLADE)
Cylincer insice diameter 10 | 110 a0 108 390 130
| |
Piston tod outside dlamener ws | | 60 | 6 % | 70
T
‘Stroke 1,005 1,000 870 910 710 150
Masiniom le pass | 2ase | 2201 | 2207 | 1023 | 600
Mint oath vaso | tas | vast | ager | ain | ao
Piiton fat widen acres Mate nm | | 6 | | o | o
WORK EQUIPMENT
1 Bucket
2. Bucket cylinder
3. Arm
4. Arm cylinder
Smal! swing specification (PC60, 6OL)
* By changing the position of the pin in the
mounting hole at the boom cylinder bottom
on the revolving frame, itis possible to change
to the smali swing specification by raising the
boom higher than normal
* For details of the values, see the Speci-
fication Dimension Drawing
10-67
8
8
8
2orFoBea?
5. Boom
6, Boom cylinder
7. Blade cylinder {PC6O WITH BLADE}
8. Blade |PCGO WITH BLADE)
Sag py im
(Py
Boom eyhnder es
/
Sinall swing Standard swing
position postion
snarcenecea:
10-68
3
ELECTRICAL WIRING DIAGRAM.
COV MpENs
10.
W
12
14,
+5
Monitor panel
Swing lock switch
Horn switch
Starting switch
Fuel control dial
Cigarette lighter
Buzzer
Service meter
Radio
Swing lock prolix ewitoh
System controller
Engine throttle controller
Heater
Glow plug resistor
Jinan bathe
18,
19.
20.
2
22.
23
2a.
26.
26.
2
oR
Detail A
Speaker
Heater Hi relay
Fuse box
Working lamp,
2-stage relief solenoid
valve (PC90- 1 only)
Straight-travel solenoid
valve
Power set solenoid valve
Swing brake
solenoid valve
Travel speed
solenoid valve
Room lamp.
Pispenveert irene:
31
32
33
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39
40
a
ao
0106011
Conant temperature sensor
Swing oil pressure
switch
Work equipment oti
ressure switch
Fusible link
Battery relay
Battery
Alternator
Engine oil pressure
switch
Wiper motor
LH. travel limit switch
RH. travel limit switch
Horn.
020106
16 Wipor retay 29, Glow plug 43, Fuel level sensor
17 Heater Lo relay 30. Starting motor 44, Head |amp
10-70
wort
ENGINE CONTROL
020106
5 View Z
F20106018
1, Starting seritch OUTLINE
2 Fuel comtrel dial * Tho engine can be storted and stopped simply
3. Governor motor by using the starting switch
4. Staring motor © The engine speed can be controlied using @
5 Battary relay dial contro! system for the fuel control
6. Battery * The engine throttle controller also controls
7. Engine throttle controller the engine speed at the same time using
8. Fuel injection pump signals from the system controier.
For detail, see TOTAL CONTROL SYSTEM
10-75
i
GOVERNOR MOTOR LINKAGE
020106
F20100331
1. Governor lever
2. Spring assembly
3. Governor motor
10-76
7
1. OPERATION OF SYSTEM
Starting engine
When the starting switch is turned to the START
position, the start signat fiows to the starting | s
motor, and the starting moter turns to start the EES
engine 7 AL
When this happens, the engine throttle con: '
teoller checks the signal voltage from the fuel
control dial and sets th engine speed to the set
speed,
Fuck contrat diet «2
zoar0B0g?
Engine speed control
The fuel control dial sends 2 signal valtage 10 fuer contri sai fA"
the engine throttle controller according to the a
position of the dial
The engine throttle controller caiculates the
angle of the governor motor according to this
signal valtage, and drives the governor motor
30 that it 18 Set to that position
When this happens, it detects the operating
angie of the governor motor using @ potent!
ometer and observes the governor motor
Engine woe
020106
Stopping engine —
When the engine trate controller detecte that iy
the starting switch is at the STOP position, it
dees the governor mator to set itto the ac Z
injection positon, and stops the engine Se
When this happens. to maintain the electric a
power in the system until the engine sions
completely, the engine throttie controller sel
drives the battery relay. {
2oar0so89
10-77
7
2. COMPONENT EQUIPMENT OF SYSTEM.
1) ENGINE THROTTLE CONTROLLER
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- PC78UU-6 NhoDocument123 pagesPC78UU-6 NhoFris Ainur100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- SH210-6/SH210LC-6: Service ManualDocument68 pagesSH210-6/SH210LC-6: Service ManualFris Ainur100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- PB CS533eDocument201 pagesPB CS533eFris Ainur100% (1)
- GC380F 2Document6 pagesGC380F 2Fris AinurNo ratings yet
- Data Pengeluaran Lain - Lain: No Item Qty Harga / Biaya NotaDocument5 pagesData Pengeluaran Lain - Lain: No Item Qty Harga / Biaya NotaFris AinurNo ratings yet
- Price List Lomos For Sales (13 Jan, 2023) MDocument338 pagesPrice List Lomos For Sales (13 Jan, 2023) MFris AinurNo ratings yet
- Engine Isuzu 4JJ1Document254 pagesEngine Isuzu 4JJ1Fris Ainur100% (2)
- Testing and Adjusting Data: Engine Model S4D95LE-3 Applicable Machine Model PC78US-6, PC78UU-6, PC78MR-6Document1 pageTesting and Adjusting Data: Engine Model S4D95LE-3 Applicable Machine Model PC78US-6, PC78UU-6, PC78MR-6Fris AinurNo ratings yet
- Engine Deutz Service TrainingDocument80 pagesEngine Deutz Service TrainingFris AinurNo ratings yet
- Bobcat 74 SeriesDocument140 pagesBobcat 74 SeriesFris AinurNo ratings yet
- Nissan G18 Engine RM PDFDocument181 pagesNissan G18 Engine RM PDFFris AinurNo ratings yet
- Operator's Manual: QY25D Truck CraneDocument172 pagesOperator's Manual: QY25D Truck CraneFris Ainur100% (1)
- BR-AXBX50-003 Eng 1912 PDFDocument6 pagesBR-AXBX50-003 Eng 1912 PDFYogi PurchasingNo ratings yet