Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
194 viewsNursing Care Plan No. 1 3
Nursing Care Plan No. 1 3
Uploaded by
Kristina ParasThe patient is experiencing disturbed sleep patterns and auditory hallucinations related to cognitive impairment. Within 8 hours of nursing interventions, the goal is for the patient to report an increased sense of well-being and feeling rested. Interventions include assessing the patient's sleep patterns, encouraging a consistent sleep schedule, introducing relaxing pre-bedtime activities, restricting caffeine, and providing nursing aids to promote rest.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Bailey's Othorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck SurgeryDocument3,775 pagesBailey's Othorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck SurgeryDr. Christian Dimitrov92% (12)
- Thenatural RsdmaxDocument52 pagesThenatural RsdmaxSteven Rojas100% (8)
- NCP For HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP For HypertensionChristian Daayata0% (1)
- Occupational Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesOccupational Nursing Care PlanADOLF FRUELAN HIDALGONo ratings yet
- 1 Child Abuse Nursing Care Plan PDFDocument7 pages1 Child Abuse Nursing Care Plan PDFMAHESH KOUJALAGINo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationAndrew James Javier Quidez100% (1)
- Schizophrenia NCPDocument2 pagesSchizophrenia NCPNicole cuencos100% (3)
- 13 Areas of AssessmentDocument13 pages13 Areas of Assessmentrachael95% (21)
- NCP PsychosisDocument3 pagesNCP PsychosisKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-is100% (1)
- NAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen: Subjective: DXDocument5 pagesNAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen: Subjective: DXTyn TynNo ratings yet
- CASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonDocument6 pagesCASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonTiffany GordonNo ratings yet
- Schizphrenia Nursing Car PlanDocument2 pagesSchizphrenia Nursing Car PlanAmjad AliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNNikolai FuncionNo ratings yet
- Nicu Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesNicu Lesson PlanSAYMABANUNo ratings yet
- Process Recording, Suicide Assesment and Psyche-Med ConditionDocument44 pagesProcess Recording, Suicide Assesment and Psyche-Med ConditionShy Dela PuertaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Antibiotics - ViosDocument8 pagesAssignment On Antibiotics - ViosIra Velle ViosNo ratings yet
- A Descriptive Study To Assess The Knowledge Regarding Substance Abuse and Ill Effects Among P.U. Students in The Selected P.U. College of BagalkotDocument3 pagesA Descriptive Study To Assess The Knowledge Regarding Substance Abuse and Ill Effects Among P.U. Students in The Selected P.U. College of BagalkotInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Subjective:: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Nursing Nursing Care Plan: ManiaDocument1 pageSubjective:: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Nursing Nursing Care Plan: ManiaJasmine BaduaNo ratings yet
- Nurse Patient RelationshipDocument29 pagesNurse Patient Relationshipaseel jamalNo ratings yet
- Tonsilitis NCPDocument2 pagesTonsilitis NCPFATIMA MARYAMA USMANNo ratings yet
- Nurse Patient Interaction: I. Background InformationDocument6 pagesNurse Patient Interaction: I. Background InformationLizli LoredoNo ratings yet
- Care of Eye - FOOT AND NAILS NCPDocument12 pagesCare of Eye - FOOT AND NAILS NCPchaitali shankarNo ratings yet
- Pragyan College of Nursing Bhopal, M.P.: Subject - Mental Health Nursing TopicDocument11 pagesPragyan College of Nursing Bhopal, M.P.: Subject - Mental Health Nursing Topicannu100% (1)
- CDNCPDocument2 pagesCDNCPGooph BusterNo ratings yet
- Rle AssDocument5 pagesRle AssMikaCasimiroBalunanNo ratings yet
- F Discharge Plan 2019Document1 pageF Discharge Plan 2019Besael BaccolNo ratings yet
- Febrile Seizures NCPDocument9 pagesFebrile Seizures NCPNurul IrhamnaNo ratings yet
- Case Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomsDocument2 pagesCase Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomskslhfwoiebvNo ratings yet
- Health TeachingDocument4 pagesHealth TeachingChamelli RobinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale Evaluatio N SubjectiveDocument58 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale Evaluatio N SubjectiveJemina Rafanan RacadioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Bobonao, RotchelDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Bobonao, RotchelMika SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching On Neurological AssessmentDocument18 pagesClinical Teaching On Neurological AssessmentFiyas BiNo ratings yet
- NCP OsteomyelitisDocument6 pagesNCP OsteomyelitisRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- MAHILOM NCP Risk For FallDocument2 pagesMAHILOM NCP Risk For Fallkasandra dawn BerisoNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia An OverviewDocument12 pagesSchizophrenia An OverviewEriekafebriayana RNo ratings yet
- NCP of PnuemoniaDocument13 pagesNCP of PnuemoniaFrando kenneth100% (1)
- NCP FinalDocument3 pagesNCP FinalCheska Mae PalicNo ratings yet
- History On TBDocument5 pagesHistory On TBNavpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Case 2Document8 pagesCase 2Kreshnik IdrizajNo ratings yet
- Artillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument5 pagesArtillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Nursing ManagementDocument56 pagesSchizophrenia Nursing ManagementHumphreyNo ratings yet
- Group NCPDocument17 pagesGroup NCPNiña Noreen Torres VallegaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching 2Document2 pagesClinical Teaching 2cha cuteNo ratings yet
- Restraint and Seclusion ppt-2Document22 pagesRestraint and Seclusion ppt-2api-233645719100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Marife: 45 Years Old Assessment Diagnosis Background Study/ Planning Implementation Rationale Expected Outcome/ EvaluationDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan Marife: 45 Years Old Assessment Diagnosis Background Study/ Planning Implementation Rationale Expected Outcome/ EvaluationAngelica Malacay RevilNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Relationship - 2Document45 pagesTherapeutic Relationship - 2Zaraki yami100% (1)
- Family Care PlanDocument9 pagesFamily Care PlanakoismeNo ratings yet
- Application of Orem TheoryDocument17 pagesApplication of Orem TheoryKit LaraNo ratings yet
- CHN 1 Reg 8 HEALTH TEACHING PLAN FORMATDocument2 pagesCHN 1 Reg 8 HEALTH TEACHING PLAN FORMATChristine SaliganNo ratings yet
- NCP Depression1Document1 pageNCP Depression1kyreNo ratings yet
- NCP Knowledge Deficit FINALDocument8 pagesNCP Knowledge Deficit FINALJOSHUA JOSE TERCEnONo ratings yet
- Vital Signs TPRDocument21 pagesVital Signs TPRfloremer guimalanNo ratings yet
- Impaired Social InteractionDocument4 pagesImpaired Social InteractionAaron ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Anticipatory GrievingDocument2 pagesAnticipatory GrievingJamaeka GotisNo ratings yet
- Betty Neuman Final SlidesDocument19 pagesBetty Neuman Final Slidesreymart bolagaoNo ratings yet
- NCP Alzheimers DiseaseDocument2 pagesNCP Alzheimers DiseaseShawn TejanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ON Upper Respiratory Tract Infections: Presented by Saranya.K Lecturer IconDocument26 pagesLesson Plan ON Upper Respiratory Tract Infections: Presented by Saranya.K Lecturer IconKumar BijayNo ratings yet
- CoughDocument2 pagesCoughBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Role - Responsibilities of Psychiatry Health NurseDocument3 pagesRole - Responsibilities of Psychiatry Health NurseDhAiRyA ArOrANo ratings yet
- Drug-Study NCPDocument5 pagesDrug-Study NCPMURILLO, FRANK JOMARI C.No ratings yet
- Hallucinations NCP PDFDocument3 pagesHallucinations NCP PDFANGELA ERES BALINGBING100% (2)
- NCP For CSDocument2 pagesNCP For CSIris Coronel AdamosNo ratings yet
- Altered Sensory and Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument4 pagesAltered Sensory and Disturbed Thought ProcessRosecinie Torrente100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: "Nabalaka Ko Kay First Time Nako Ma-Operahan, Basin Pud Maunsa Si Baby," AsDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: "Nabalaka Ko Kay First Time Nako Ma-Operahan, Basin Pud Maunsa Si Baby," Asunnamed personNo ratings yet
- Recall Intervals and NICE GuidelinesDocument7 pagesRecall Intervals and NICE Guidelinesdruzair007No ratings yet
- Respectful Maternity CareDocument33 pagesRespectful Maternity CareJenelle Melinda TullochNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument35 pagesEndocrine Systemmbok diyirNo ratings yet
- Normal Flora of The Human BodyDocument7 pagesNormal Flora of The Human Bodyshahbaz88% (16)
- Pizza Technique in Site 1 Restoration in Lower Second Molar Tooth: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesPizza Technique in Site 1 Restoration in Lower Second Molar Tooth: A Case ReportKarissa NavitaNo ratings yet
- The Use of Multivariate Statistical Methods For Optimization of The Surface Water Quality Network Monitoring in The Paraopeba River Basin, BrazilDocument17 pagesThe Use of Multivariate Statistical Methods For Optimization of The Surface Water Quality Network Monitoring in The Paraopeba River Basin, BrazilAna Carolina NevesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Epidemiology: Arba Minch University School of Public Health Epidemiology and Biostatistics UnitDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Epidemiology: Arba Minch University School of Public Health Epidemiology and Biostatistics UnitTesfahun TesfuNo ratings yet
- Volunteer OptionsDocument6 pagesVolunteer Optionsapi-287824447No ratings yet
- Luma - Health Insurance Quotation - May Kabyar Oo (3 Options)Document3 pagesLuma - Health Insurance Quotation - May Kabyar Oo (3 Options)Kabyar MayNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Practice Report SampleDocument26 pagesPharmacy Practice Report Samplesaransh misra67% (3)
- UPSC Civil Services Examination SyllabusDocument122 pagesUPSC Civil Services Examination SyllabusnityagpkNo ratings yet
- Sop For Bio-BurdenDocument5 pagesSop For Bio-BurdenMusyoka Urbanus100% (1)
- Group Name 2 English ClubDocument10 pagesGroup Name 2 English ClubWill HensNo ratings yet
- English. 101 Midterm Week 1 3A.Y. 2021 2022 First Sem PDFDocument75 pagesEnglish. 101 Midterm Week 1 3A.Y. 2021 2022 First Sem PDFZarah E. DinoyNo ratings yet
- Family TIES Resource Directory 2020Document218 pagesFamily TIES Resource Directory 2020juanmiguelperez20kNo ratings yet
- JOGNN Guidelines For AuthorsDocument3 pagesJOGNN Guidelines For AuthorsPrathibha Lydia Braggs DsouzaNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Mobil DTE 26 UltraDocument10 pagesMSDS - Mobil DTE 26 UltraYosua SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Eas 749 2010 Brown Sugar SpecificationDocument10 pagesEas 749 2010 Brown Sugar SpecificationFelix MwandukaNo ratings yet
- Health Information Systems - PresentationDocument29 pagesHealth Information Systems - PresentationYusto FoshizoNo ratings yet
- Yokoyama Et Al. C-BED Hikikomori SupportDocument10 pagesYokoyama Et Al. C-BED Hikikomori SupportKayu LowNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness TestDocument15 pagesPhysical Fitness TestKaori Miyazono (Kobe)No ratings yet
- ESP Debate Week 5 - Child PerformersDocument5 pagesESP Debate Week 5 - Child PerformersViệt Anh TạNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan: NAME: CASTILLO, Nina Beleen F. CHN Section: 2nu03Document3 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan: NAME: CASTILLO, Nina Beleen F. CHN Section: 2nu03NinaNo ratings yet
- Global Testing and Certification Programs: Expect More From Csa GroupDocument2 pagesGlobal Testing and Certification Programs: Expect More From Csa GroupKaveh EbadiNo ratings yet
- MSDS Stearic Acid NewDocument6 pagesMSDS Stearic Acid NewMASH TLMOSNo ratings yet
- Open BiteDocument32 pagesOpen BiteMohammed Al-MusawiNo ratings yet
Nursing Care Plan No. 1 3
Nursing Care Plan No. 1 3
Uploaded by
Kristina Paras0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
194 views4 pagesThe patient is experiencing disturbed sleep patterns and auditory hallucinations related to cognitive impairment. Within 8 hours of nursing interventions, the goal is for the patient to report an increased sense of well-being and feeling rested. Interventions include assessing the patient's sleep patterns, encouraging a consistent sleep schedule, introducing relaxing pre-bedtime activities, restricting caffeine, and providing nursing aids to promote rest.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe patient is experiencing disturbed sleep patterns and auditory hallucinations related to cognitive impairment. Within 8 hours of nursing interventions, the goal is for the patient to report an increased sense of well-being and feeling rested. Interventions include assessing the patient's sleep patterns, encouraging a consistent sleep schedule, introducing relaxing pre-bedtime activities, restricting caffeine, and providing nursing aids to promote rest.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
194 views4 pagesNursing Care Plan No. 1 3
Nursing Care Plan No. 1 3
Uploaded by
Kristina ParasThe patient is experiencing disturbed sleep patterns and auditory hallucinations related to cognitive impairment. Within 8 hours of nursing interventions, the goal is for the patient to report an increased sense of well-being and feeling rested. Interventions include assessing the patient's sleep patterns, encouraging a consistent sleep schedule, introducing relaxing pre-bedtime activities, restricting caffeine, and providing nursing aids to promote rest.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
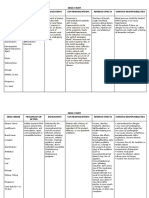
PSYCHOD
NURSING YNAMICS GOAL AND OBJECTIVES NURSING
RATIONALE
ASSESSMENT & THEORY INTERVENTIONS
Disturbed sensory Within 6 hours of proper
perception related to nursing interventions, the - Assess sensory - Information is essential to
psychological stress patient will be able to awareness, client safety. All sensory
as evidenced by demonstrate behaviors and including response systems may be affected
auditory lifestyle changes to compensate to touch, hot/cold, by TBI, loss of or
hallucination. for, or overcome, deficit. dull/sharp, and difference in sensations,
awareness of as well as in the ability to
motion and location perceive and respond
Subjective: of body parts. Note appropriately to stimuli.
problems with
vision and other
senses.
Objective:
- Be alert for signs of - Might herald hallucinatory
increasing fear, activity, which can be
anxiety or agitation. very frightening to client,
Vital signs taken: and client might act upon
T- command hallucinations
RR- (harm self or others).
PR-
BP: - Explore how the - Exploring the
hallucinations are hallucinations and sharing
experienced by the the experience can help
client. give the person a sense of
power that he or she might
be able to manage the
hallucinatory voices.
- Help client to - Helps both nurse and client
identify times that identify situations and
the hallucinations times that might be most
are most prevalent anxiety-producing and
and frightening. threatening to the client.
- Stay with clients - The client can sometimes
when they are learn to push voices aside
starting to when given repeated
hallucinate and instructions. especially
direct them to tell within the framework of a
the “voices they trusting relationship.
hear” to go away.
Repeat often in a
matter-of-fact
manner.
- Decrease the potential for
- Decrease anxiety that might trigger
environmental hallucinations. Helps calm
stimuli when client.
possible (low noise,
minimal activity).
- Promotes consistency and
- Provide structured
reassurance, reducing
therapies, activities,
anxiety
and environment.
associated with the
Provide written
unknown. Promotes sense
schedule for
of control
client/family to
and cognitive retraining.
refer to on a
regular basis.
PSYCHODYNAM GOAL AND
NURSING NURSING
ICS & THEORY OBJECTIVES RATIONALE
ASSESSMENT INTERVENTIONS
Disturbed sleep pattern Within 8 hours of - Assess the patient’s - Sleep pattern may vary
related to cognitive proper nursing sleep patter and take for each individual.
impairment as evidenced interventions, the note for the amount of Evaluating these
by reports of sleep patient will be able to sleep, sleep routine, patterns will provide
disturbance/auditory report increased sense and position general information
hallucination. of well-being and that needs to be
feeling rested. assessed or improved
Subjective:
- Observe for signs of - To attain baseline date.
Objective: sleep-wake problems
- Presence of eye and note for the
bags patient’s hours of sleep
- Restlessness
- Yawning - Encourage the patient - Consistent sleep and
- Lethargic to have a consistent rest schedule may help
- Less than 6 sleep schedule. to regulate and manage
hours of sleep Suggest to drink a cardiac rhythm.
glass of milk. Drinking a glass of
milk has been
correlated with sleep
Vital signs taken: promotion.
T-
RR- - Introduce relaxing - These activities
PR- activities such as calm provide relaxation and
BP: music, reading a book, distraction to prepare
and relaxation mind and body for
exercises before sleep.
bedtime.
- Restrict intake of - Caffeine may delay
caffeine-containing client’s falling asleep
foods and fluids. and interfere with
REM (rapid eye
movement) sleep,
resulting in client not
feeling well rested.
- Provide nursing aids - To promote rest.
(e.g., back rub,
bedtime care, pain
relief, comfortable
position, relaxation
techniques).
You might also like
- Bailey's Othorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck SurgeryDocument3,775 pagesBailey's Othorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck SurgeryDr. Christian Dimitrov92% (12)
- Thenatural RsdmaxDocument52 pagesThenatural RsdmaxSteven Rojas100% (8)
- NCP For HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP For HypertensionChristian Daayata0% (1)
- Occupational Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesOccupational Nursing Care PlanADOLF FRUELAN HIDALGONo ratings yet
- 1 Child Abuse Nursing Care Plan PDFDocument7 pages1 Child Abuse Nursing Care Plan PDFMAHESH KOUJALAGINo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationAndrew James Javier Quidez100% (1)
- Schizophrenia NCPDocument2 pagesSchizophrenia NCPNicole cuencos100% (3)
- 13 Areas of AssessmentDocument13 pages13 Areas of Assessmentrachael95% (21)
- NCP PsychosisDocument3 pagesNCP PsychosisKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-is100% (1)
- NAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen: Subjective: DXDocument5 pagesNAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen: Subjective: DXTyn TynNo ratings yet
- CASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonDocument6 pagesCASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonTiffany GordonNo ratings yet
- Schizphrenia Nursing Car PlanDocument2 pagesSchizphrenia Nursing Car PlanAmjad AliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNNikolai FuncionNo ratings yet
- Nicu Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesNicu Lesson PlanSAYMABANUNo ratings yet
- Process Recording, Suicide Assesment and Psyche-Med ConditionDocument44 pagesProcess Recording, Suicide Assesment and Psyche-Med ConditionShy Dela PuertaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Antibiotics - ViosDocument8 pagesAssignment On Antibiotics - ViosIra Velle ViosNo ratings yet
- A Descriptive Study To Assess The Knowledge Regarding Substance Abuse and Ill Effects Among P.U. Students in The Selected P.U. College of BagalkotDocument3 pagesA Descriptive Study To Assess The Knowledge Regarding Substance Abuse and Ill Effects Among P.U. Students in The Selected P.U. College of BagalkotInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Subjective:: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Nursing Nursing Care Plan: ManiaDocument1 pageSubjective:: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Nursing Nursing Care Plan: ManiaJasmine BaduaNo ratings yet
- Nurse Patient RelationshipDocument29 pagesNurse Patient Relationshipaseel jamalNo ratings yet
- Tonsilitis NCPDocument2 pagesTonsilitis NCPFATIMA MARYAMA USMANNo ratings yet
- Nurse Patient Interaction: I. Background InformationDocument6 pagesNurse Patient Interaction: I. Background InformationLizli LoredoNo ratings yet
- Care of Eye - FOOT AND NAILS NCPDocument12 pagesCare of Eye - FOOT AND NAILS NCPchaitali shankarNo ratings yet
- Pragyan College of Nursing Bhopal, M.P.: Subject - Mental Health Nursing TopicDocument11 pagesPragyan College of Nursing Bhopal, M.P.: Subject - Mental Health Nursing Topicannu100% (1)
- CDNCPDocument2 pagesCDNCPGooph BusterNo ratings yet
- Rle AssDocument5 pagesRle AssMikaCasimiroBalunanNo ratings yet
- F Discharge Plan 2019Document1 pageF Discharge Plan 2019Besael BaccolNo ratings yet
- Febrile Seizures NCPDocument9 pagesFebrile Seizures NCPNurul IrhamnaNo ratings yet
- Case Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomsDocument2 pagesCase Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomskslhfwoiebvNo ratings yet
- Health TeachingDocument4 pagesHealth TeachingChamelli RobinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale Evaluatio N SubjectiveDocument58 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale Evaluatio N SubjectiveJemina Rafanan RacadioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Bobonao, RotchelDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Bobonao, RotchelMika SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching On Neurological AssessmentDocument18 pagesClinical Teaching On Neurological AssessmentFiyas BiNo ratings yet
- NCP OsteomyelitisDocument6 pagesNCP OsteomyelitisRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- MAHILOM NCP Risk For FallDocument2 pagesMAHILOM NCP Risk For Fallkasandra dawn BerisoNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia An OverviewDocument12 pagesSchizophrenia An OverviewEriekafebriayana RNo ratings yet
- NCP of PnuemoniaDocument13 pagesNCP of PnuemoniaFrando kenneth100% (1)
- NCP FinalDocument3 pagesNCP FinalCheska Mae PalicNo ratings yet
- History On TBDocument5 pagesHistory On TBNavpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Case 2Document8 pagesCase 2Kreshnik IdrizajNo ratings yet
- Artillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument5 pagesArtillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Nursing ManagementDocument56 pagesSchizophrenia Nursing ManagementHumphreyNo ratings yet
- Group NCPDocument17 pagesGroup NCPNiña Noreen Torres VallegaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching 2Document2 pagesClinical Teaching 2cha cuteNo ratings yet
- Restraint and Seclusion ppt-2Document22 pagesRestraint and Seclusion ppt-2api-233645719100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Marife: 45 Years Old Assessment Diagnosis Background Study/ Planning Implementation Rationale Expected Outcome/ EvaluationDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan Marife: 45 Years Old Assessment Diagnosis Background Study/ Planning Implementation Rationale Expected Outcome/ EvaluationAngelica Malacay RevilNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Relationship - 2Document45 pagesTherapeutic Relationship - 2Zaraki yami100% (1)
- Family Care PlanDocument9 pagesFamily Care PlanakoismeNo ratings yet
- Application of Orem TheoryDocument17 pagesApplication of Orem TheoryKit LaraNo ratings yet
- CHN 1 Reg 8 HEALTH TEACHING PLAN FORMATDocument2 pagesCHN 1 Reg 8 HEALTH TEACHING PLAN FORMATChristine SaliganNo ratings yet
- NCP Depression1Document1 pageNCP Depression1kyreNo ratings yet
- NCP Knowledge Deficit FINALDocument8 pagesNCP Knowledge Deficit FINALJOSHUA JOSE TERCEnONo ratings yet
- Vital Signs TPRDocument21 pagesVital Signs TPRfloremer guimalanNo ratings yet
- Impaired Social InteractionDocument4 pagesImpaired Social InteractionAaron ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Anticipatory GrievingDocument2 pagesAnticipatory GrievingJamaeka GotisNo ratings yet
- Betty Neuman Final SlidesDocument19 pagesBetty Neuman Final Slidesreymart bolagaoNo ratings yet
- NCP Alzheimers DiseaseDocument2 pagesNCP Alzheimers DiseaseShawn TejanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ON Upper Respiratory Tract Infections: Presented by Saranya.K Lecturer IconDocument26 pagesLesson Plan ON Upper Respiratory Tract Infections: Presented by Saranya.K Lecturer IconKumar BijayNo ratings yet
- CoughDocument2 pagesCoughBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Role - Responsibilities of Psychiatry Health NurseDocument3 pagesRole - Responsibilities of Psychiatry Health NurseDhAiRyA ArOrANo ratings yet
- Drug-Study NCPDocument5 pagesDrug-Study NCPMURILLO, FRANK JOMARI C.No ratings yet
- Hallucinations NCP PDFDocument3 pagesHallucinations NCP PDFANGELA ERES BALINGBING100% (2)
- NCP For CSDocument2 pagesNCP For CSIris Coronel AdamosNo ratings yet
- Altered Sensory and Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument4 pagesAltered Sensory and Disturbed Thought ProcessRosecinie Torrente100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: "Nabalaka Ko Kay First Time Nako Ma-Operahan, Basin Pud Maunsa Si Baby," AsDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: "Nabalaka Ko Kay First Time Nako Ma-Operahan, Basin Pud Maunsa Si Baby," Asunnamed personNo ratings yet
- Recall Intervals and NICE GuidelinesDocument7 pagesRecall Intervals and NICE Guidelinesdruzair007No ratings yet
- Respectful Maternity CareDocument33 pagesRespectful Maternity CareJenelle Melinda TullochNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument35 pagesEndocrine Systemmbok diyirNo ratings yet
- Normal Flora of The Human BodyDocument7 pagesNormal Flora of The Human Bodyshahbaz88% (16)
- Pizza Technique in Site 1 Restoration in Lower Second Molar Tooth: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesPizza Technique in Site 1 Restoration in Lower Second Molar Tooth: A Case ReportKarissa NavitaNo ratings yet
- The Use of Multivariate Statistical Methods For Optimization of The Surface Water Quality Network Monitoring in The Paraopeba River Basin, BrazilDocument17 pagesThe Use of Multivariate Statistical Methods For Optimization of The Surface Water Quality Network Monitoring in The Paraopeba River Basin, BrazilAna Carolina NevesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Epidemiology: Arba Minch University School of Public Health Epidemiology and Biostatistics UnitDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Epidemiology: Arba Minch University School of Public Health Epidemiology and Biostatistics UnitTesfahun TesfuNo ratings yet
- Volunteer OptionsDocument6 pagesVolunteer Optionsapi-287824447No ratings yet
- Luma - Health Insurance Quotation - May Kabyar Oo (3 Options)Document3 pagesLuma - Health Insurance Quotation - May Kabyar Oo (3 Options)Kabyar MayNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Practice Report SampleDocument26 pagesPharmacy Practice Report Samplesaransh misra67% (3)
- UPSC Civil Services Examination SyllabusDocument122 pagesUPSC Civil Services Examination SyllabusnityagpkNo ratings yet
- Sop For Bio-BurdenDocument5 pagesSop For Bio-BurdenMusyoka Urbanus100% (1)
- Group Name 2 English ClubDocument10 pagesGroup Name 2 English ClubWill HensNo ratings yet
- English. 101 Midterm Week 1 3A.Y. 2021 2022 First Sem PDFDocument75 pagesEnglish. 101 Midterm Week 1 3A.Y. 2021 2022 First Sem PDFZarah E. DinoyNo ratings yet
- Family TIES Resource Directory 2020Document218 pagesFamily TIES Resource Directory 2020juanmiguelperez20kNo ratings yet
- JOGNN Guidelines For AuthorsDocument3 pagesJOGNN Guidelines For AuthorsPrathibha Lydia Braggs DsouzaNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Mobil DTE 26 UltraDocument10 pagesMSDS - Mobil DTE 26 UltraYosua SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Eas 749 2010 Brown Sugar SpecificationDocument10 pagesEas 749 2010 Brown Sugar SpecificationFelix MwandukaNo ratings yet
- Health Information Systems - PresentationDocument29 pagesHealth Information Systems - PresentationYusto FoshizoNo ratings yet
- Yokoyama Et Al. C-BED Hikikomori SupportDocument10 pagesYokoyama Et Al. C-BED Hikikomori SupportKayu LowNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness TestDocument15 pagesPhysical Fitness TestKaori Miyazono (Kobe)No ratings yet
- ESP Debate Week 5 - Child PerformersDocument5 pagesESP Debate Week 5 - Child PerformersViệt Anh TạNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan: NAME: CASTILLO, Nina Beleen F. CHN Section: 2nu03Document3 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan: NAME: CASTILLO, Nina Beleen F. CHN Section: 2nu03NinaNo ratings yet
- Global Testing and Certification Programs: Expect More From Csa GroupDocument2 pagesGlobal Testing and Certification Programs: Expect More From Csa GroupKaveh EbadiNo ratings yet
- MSDS Stearic Acid NewDocument6 pagesMSDS Stearic Acid NewMASH TLMOSNo ratings yet
- Open BiteDocument32 pagesOpen BiteMohammed Al-MusawiNo ratings yet